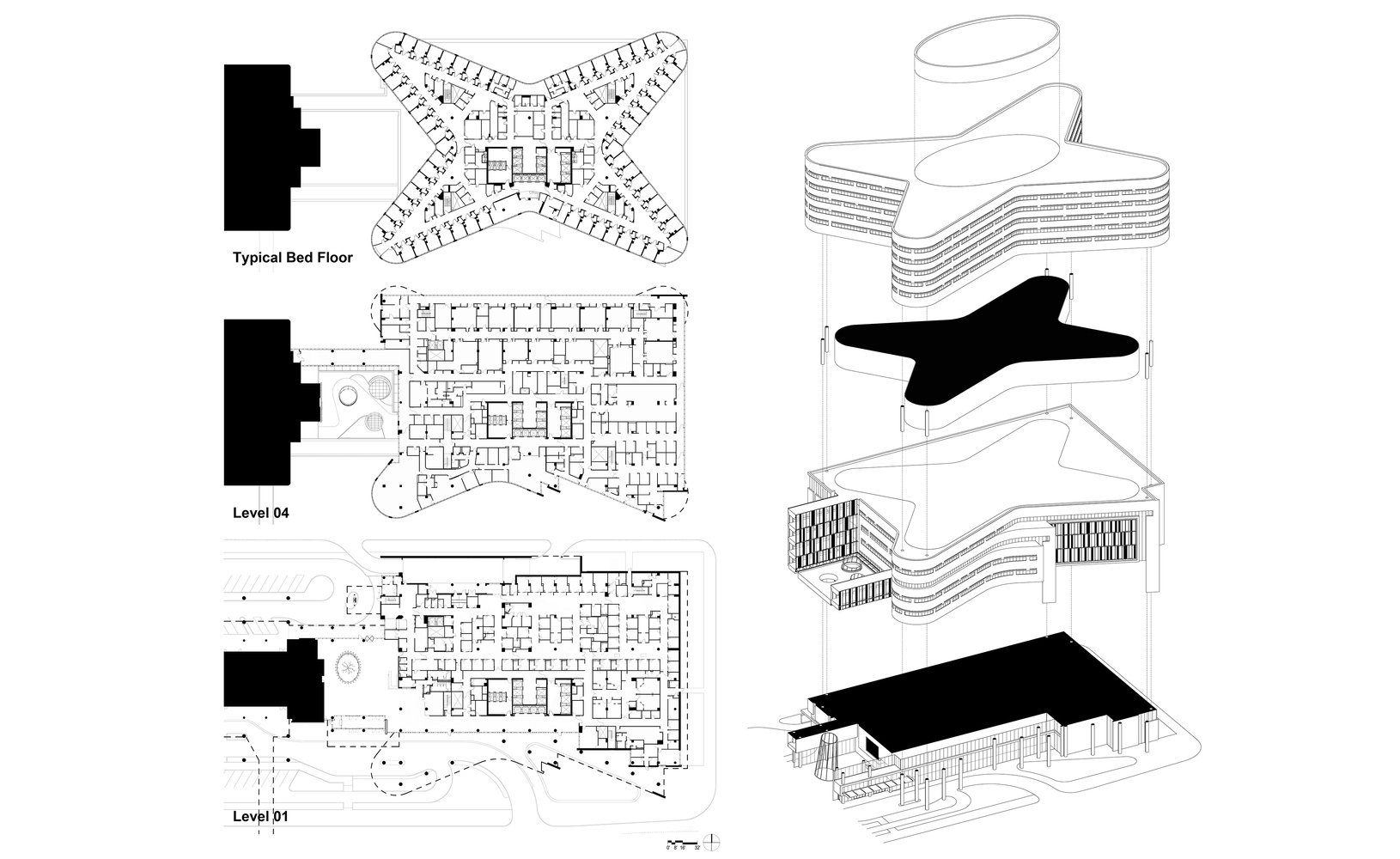
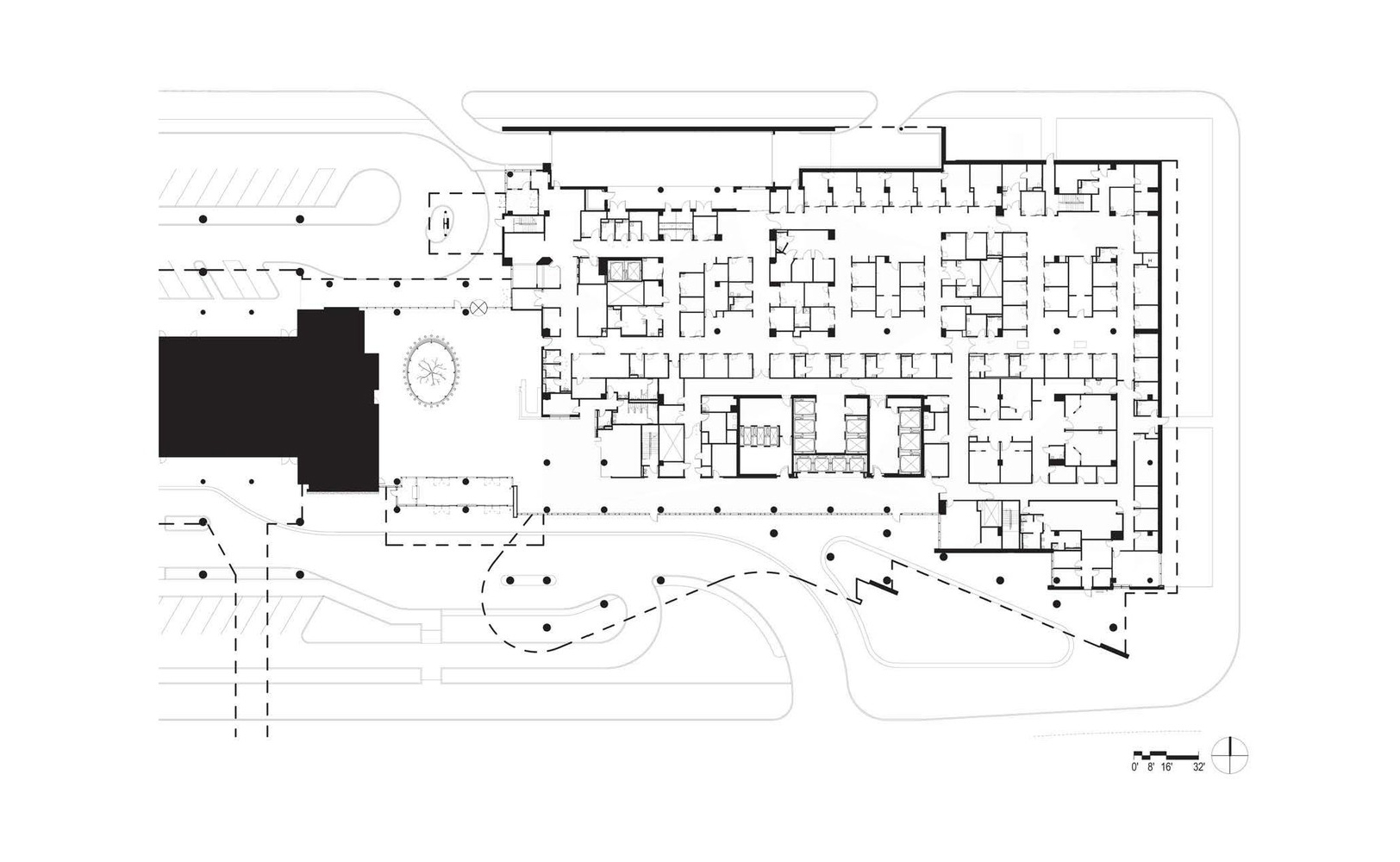
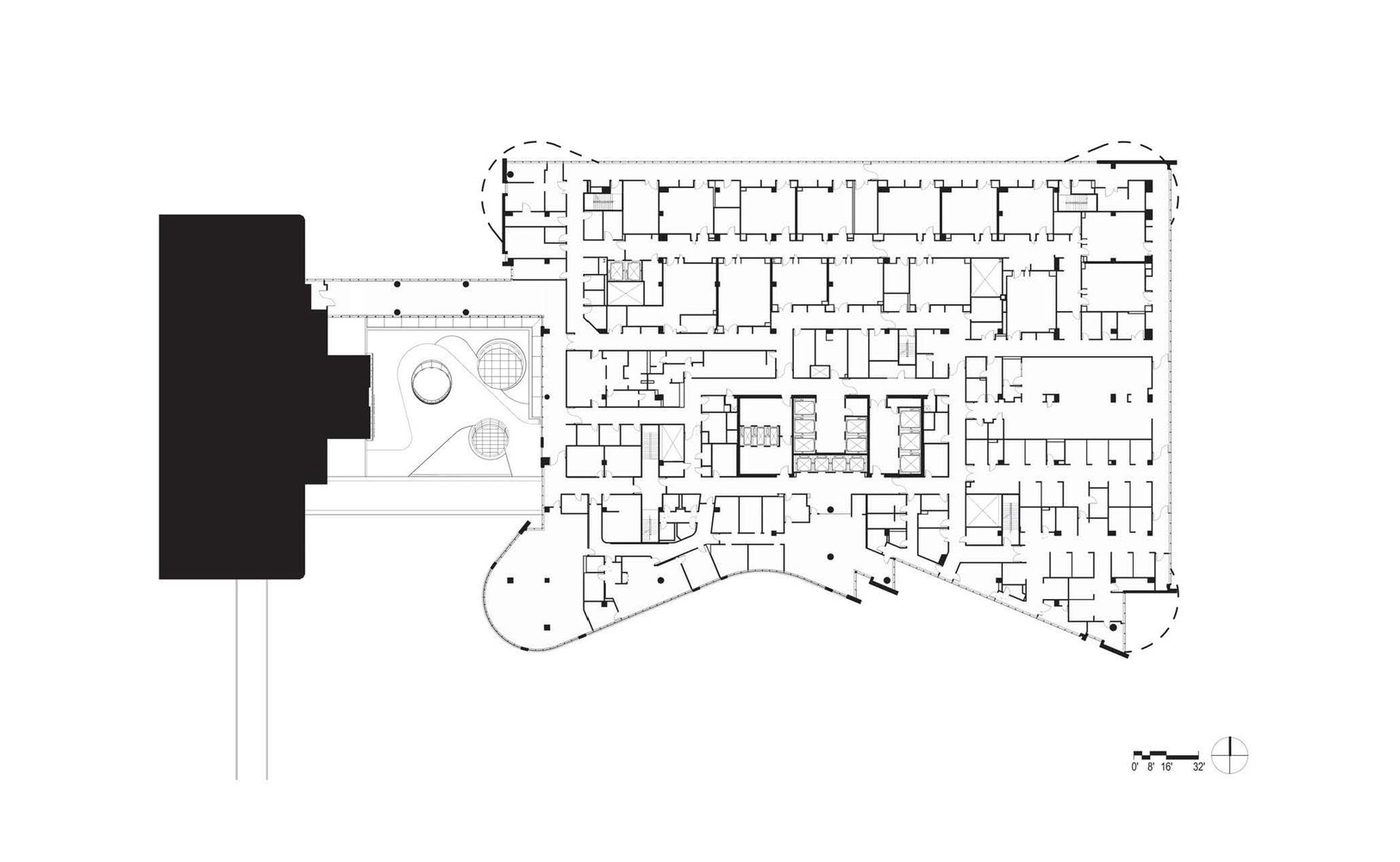
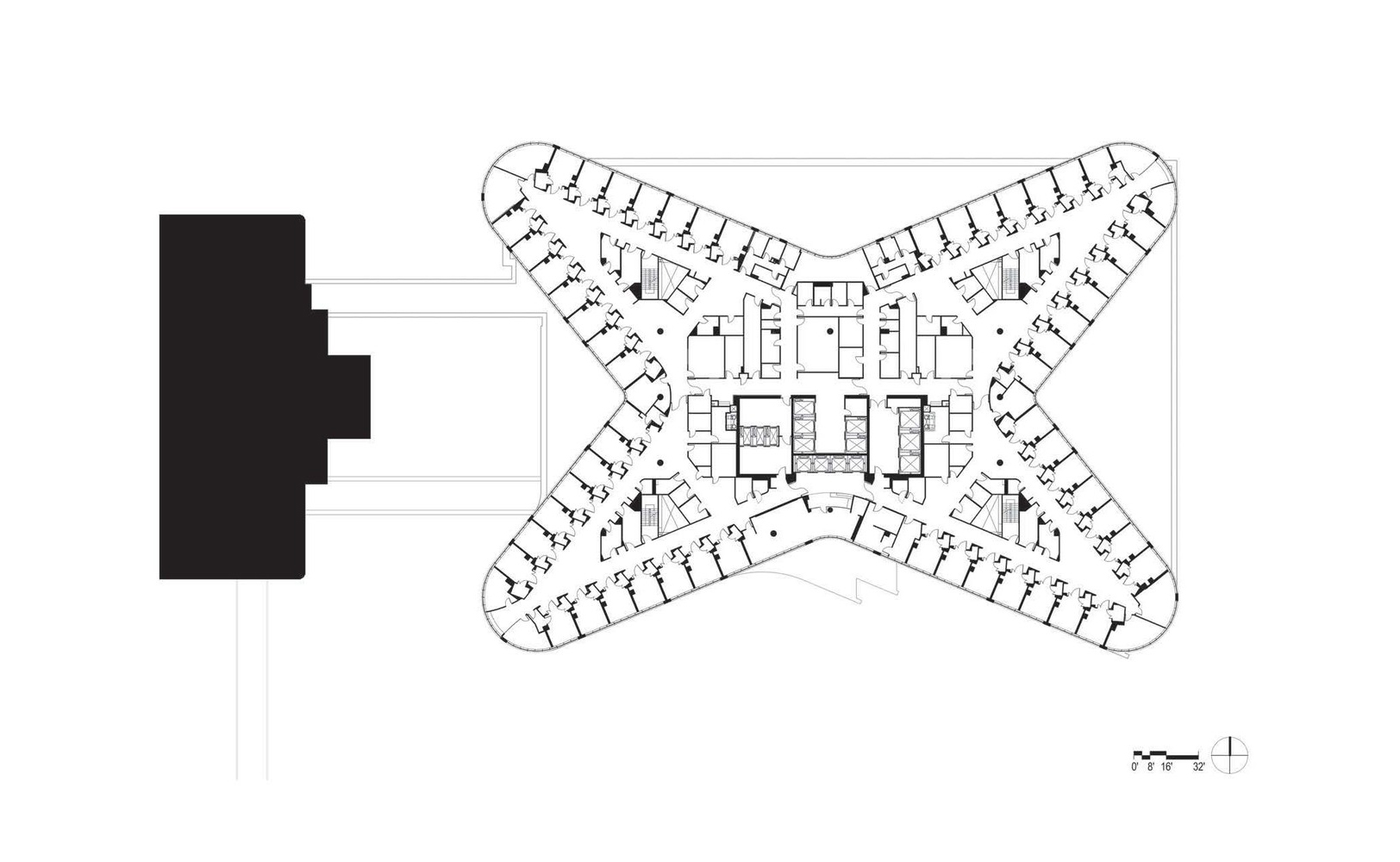
project04:P1
P1
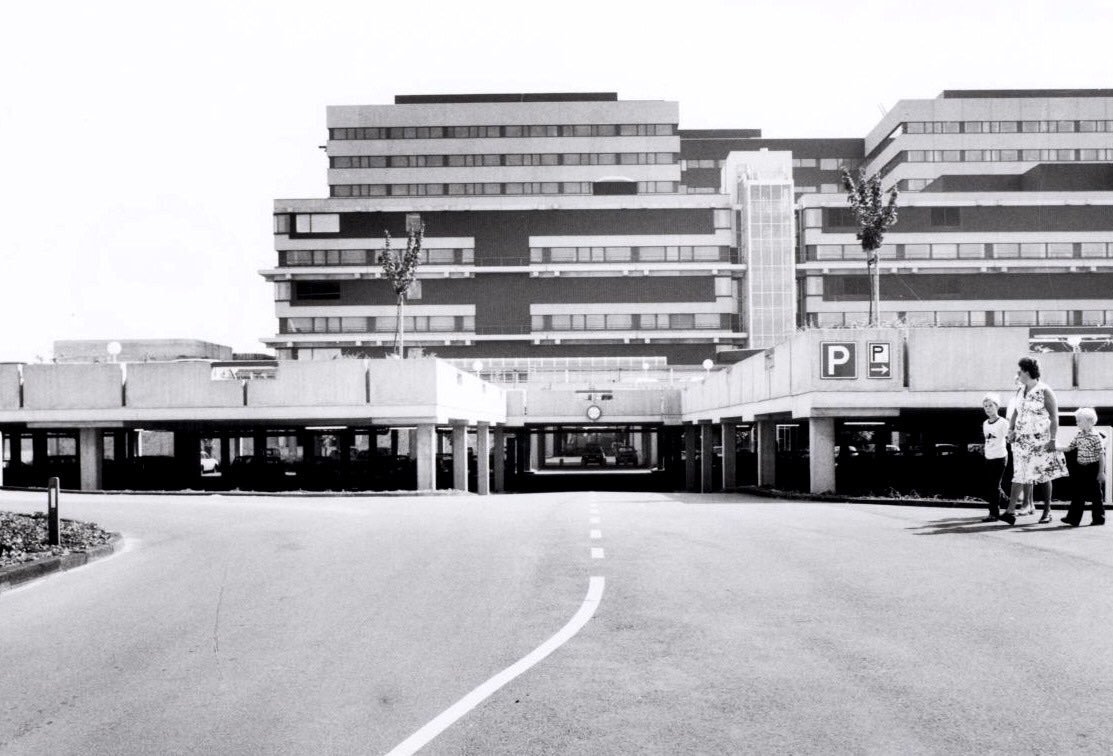
The Academic Medical Center(AMC) is one of the largest hospitals in the Netherlands. The AMC is among the top medical centers in the world. The building dates back to the eighties of the last century. Up until now various architectural interventions have been made but the currently the quality of the building is right on the acceptable level. To maintain an acceptable quality of the building renovation and transformation is required. Therefor the AMC building has to be renewed to face the future. Designing new state of the art medical facilities as for creating a sustainble hospital with a neutral carbon footprint. Within the Architectural Enigineering graduation track this challenge is explored. This is the first presentation in the graduation track presenting my proposal for the new AMC based on Robotic Building principles.
The Academic Medical Center
Key figures
Completed:
Floorspace:
Clinical admissions:
Day care admissions:
Outpatient visits:
Beds:
Employees:
Medical students:
Medical informatics students:
1983.
500.000m2
25.000 per year.
30.000 per year.
356.000 per year.
1.002.
7.000.
2.200.
100.
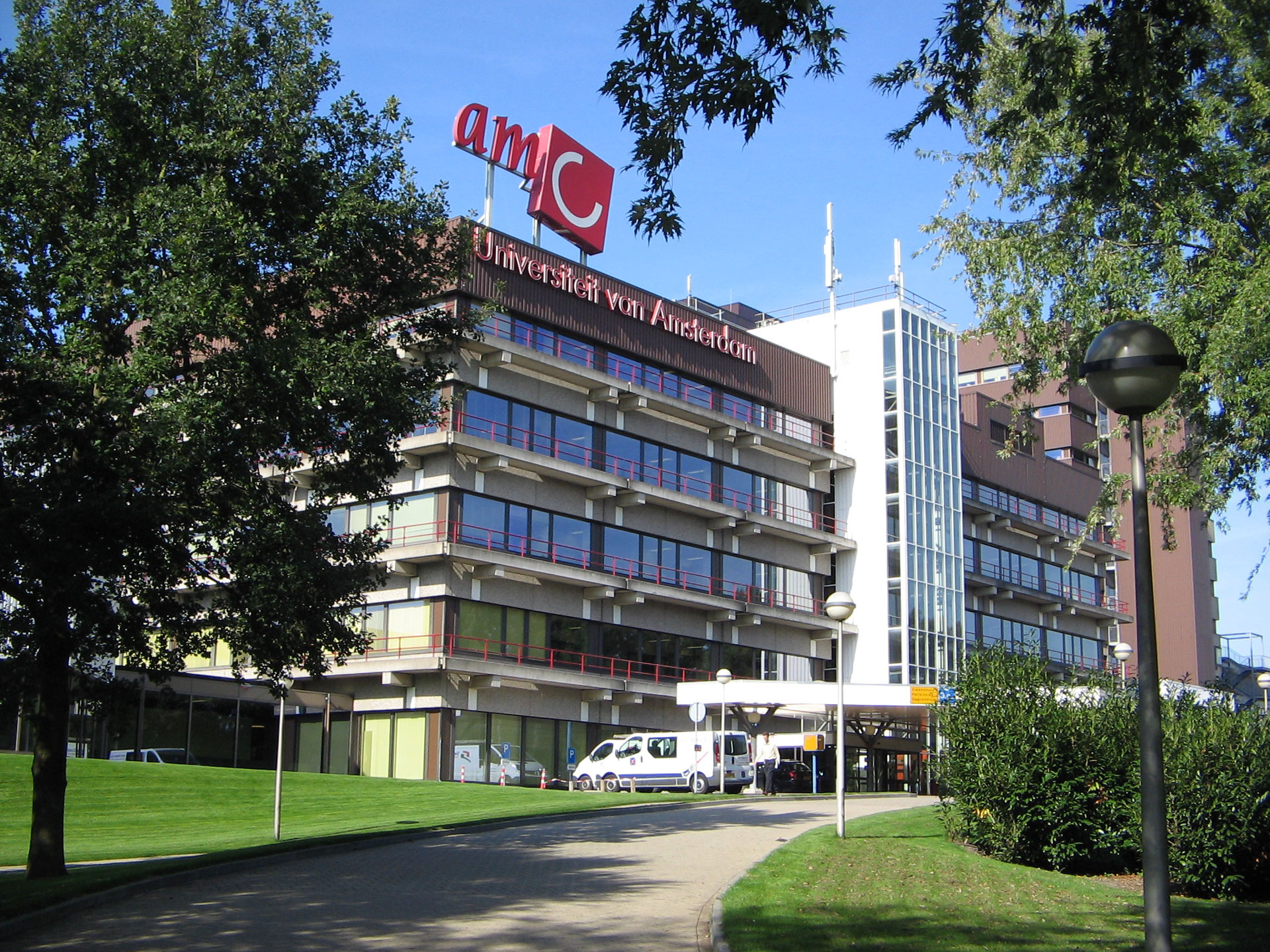
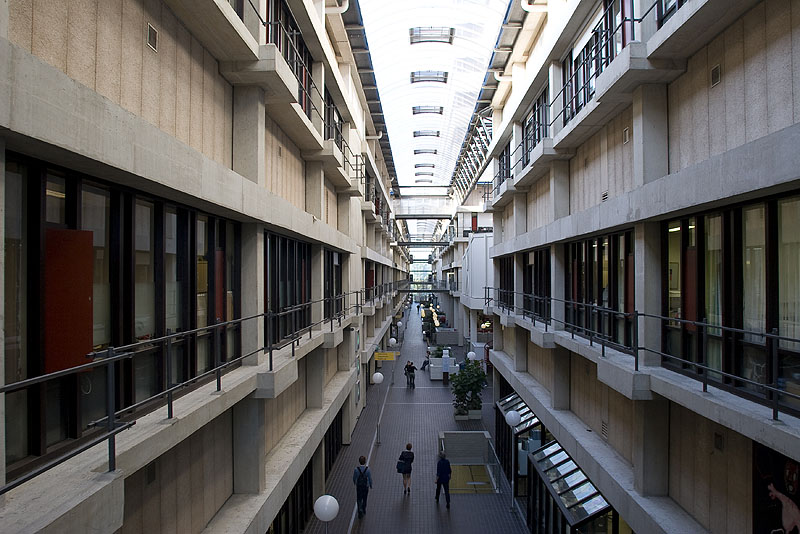
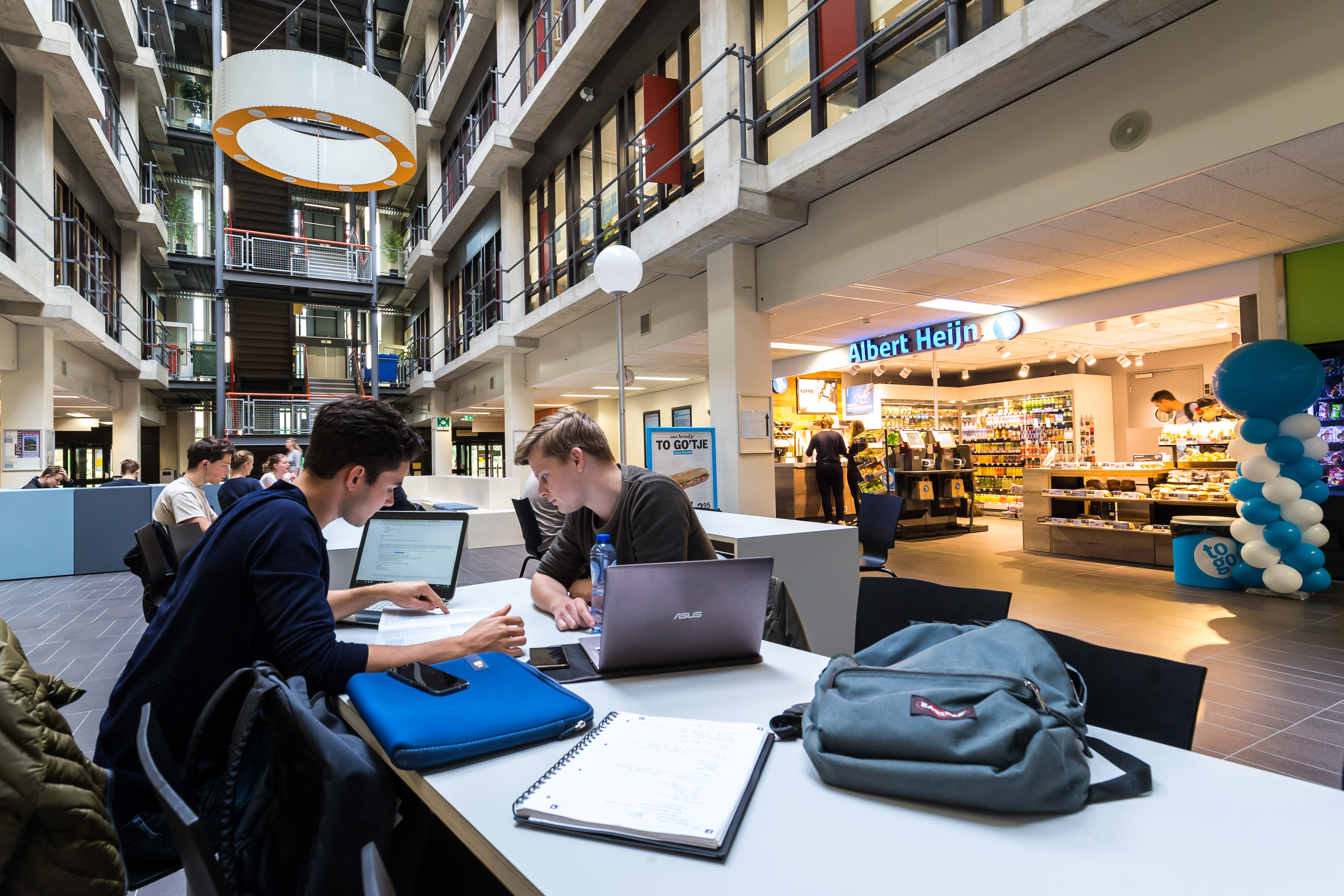
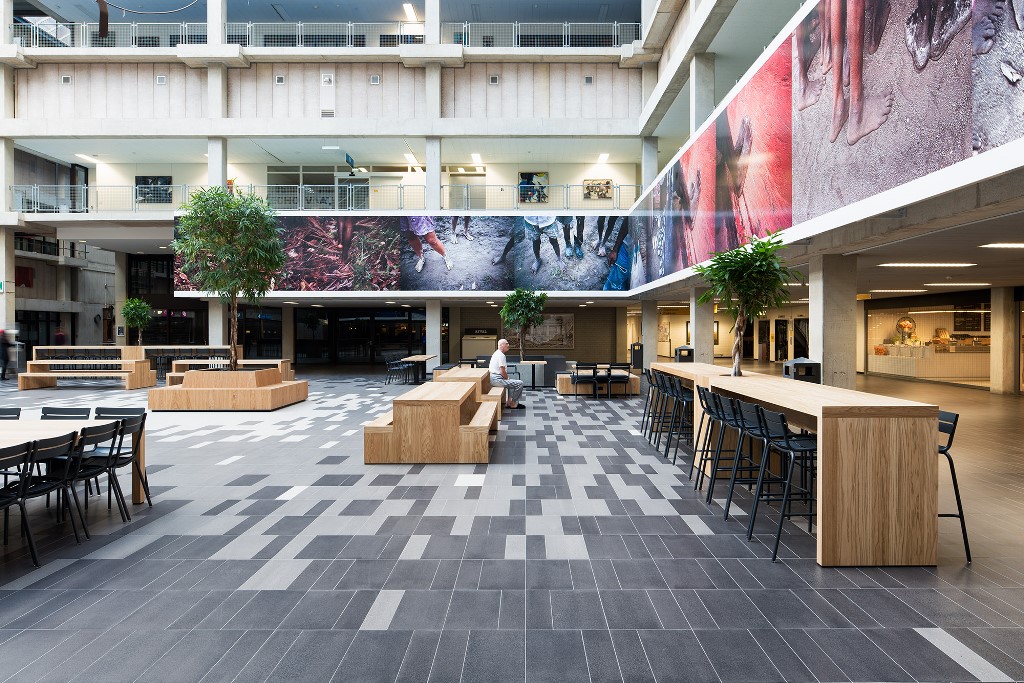
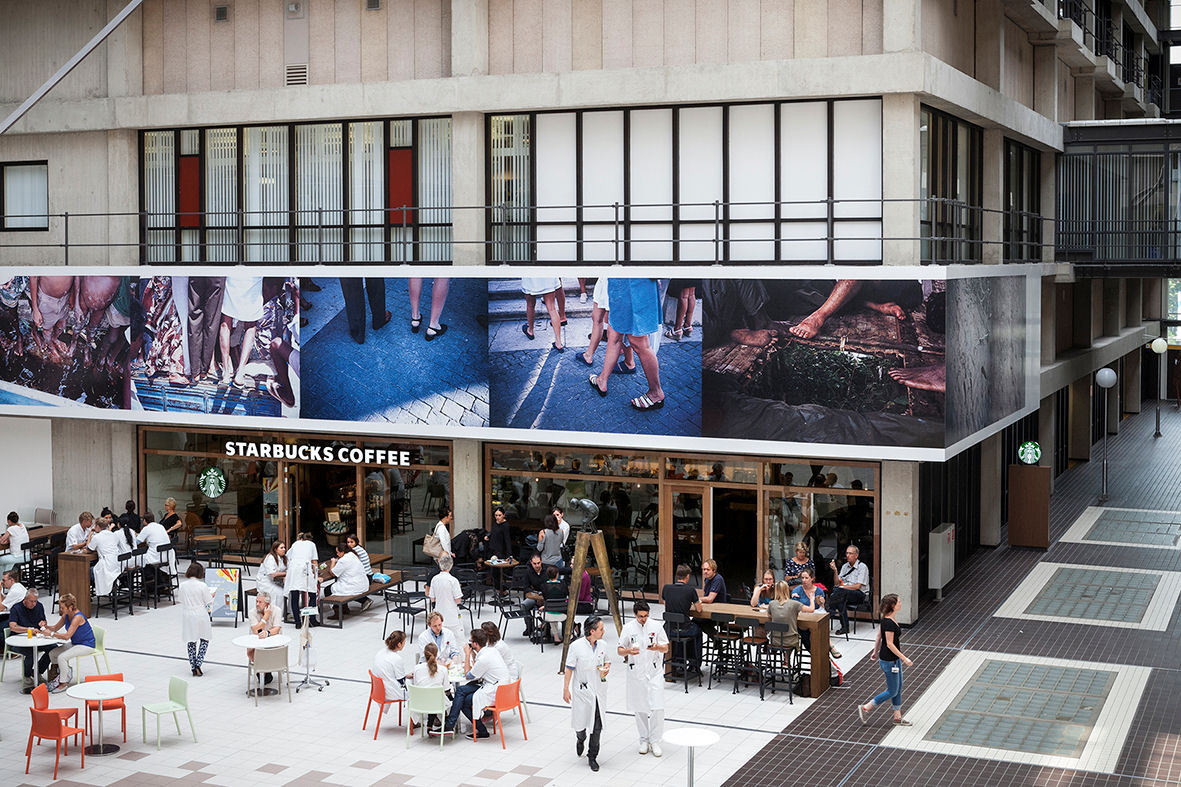
Impression
This slideshow presents images of the AMC. These images show the internal street of the AMC, the building as a whole which is often described as the monolith. Within these images the brutalist architecture is clearly visible as the bare concrete structure.
Various images of the AMC
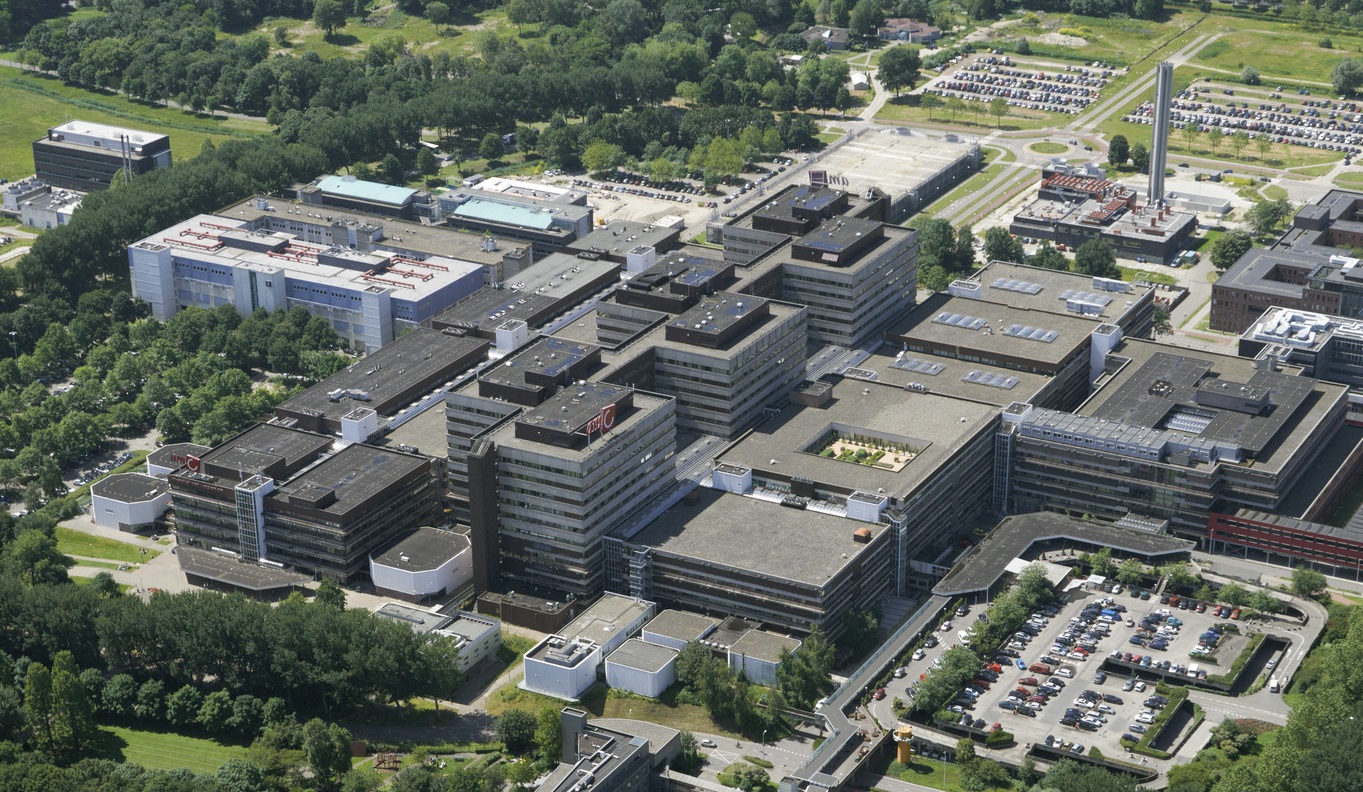
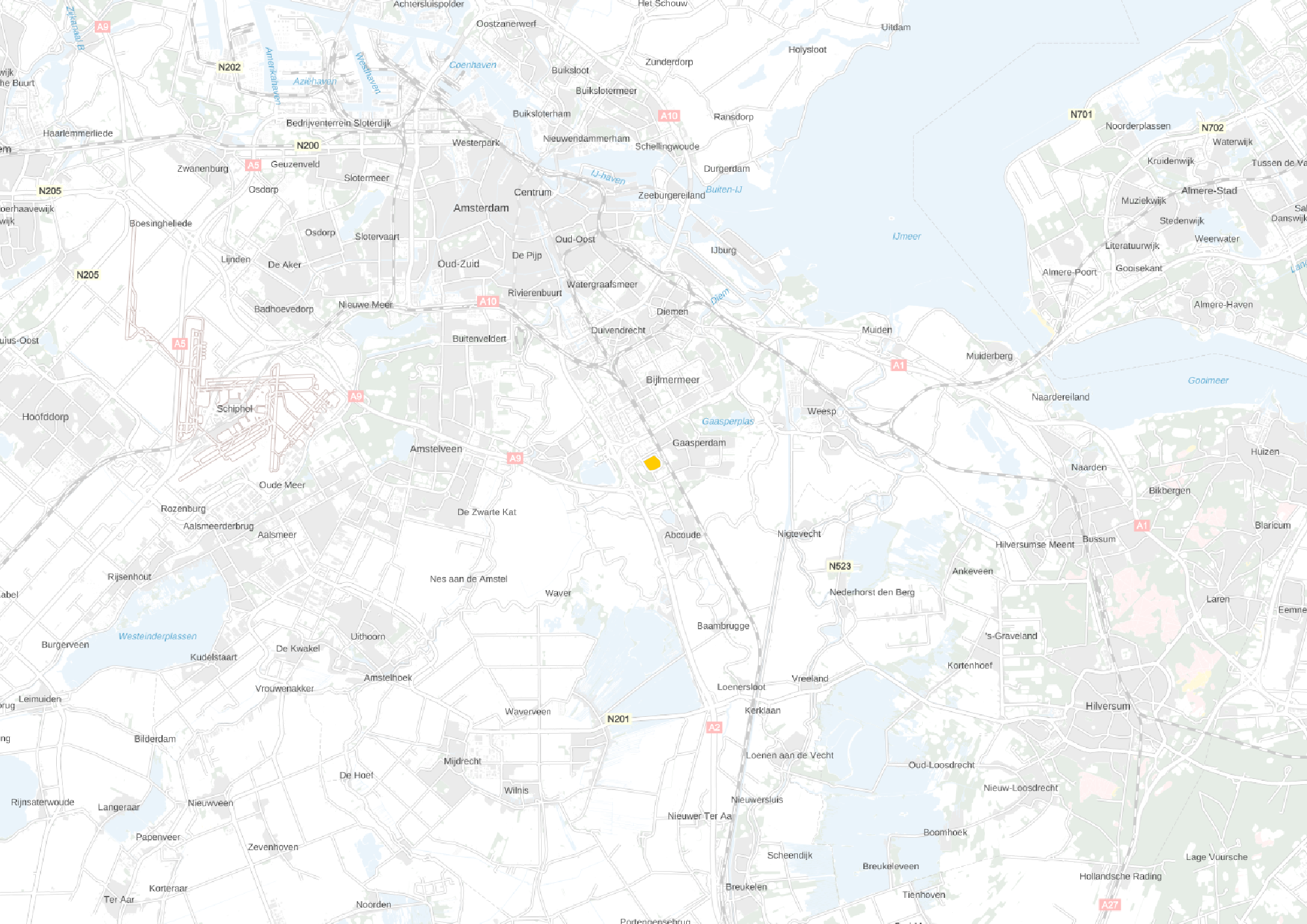
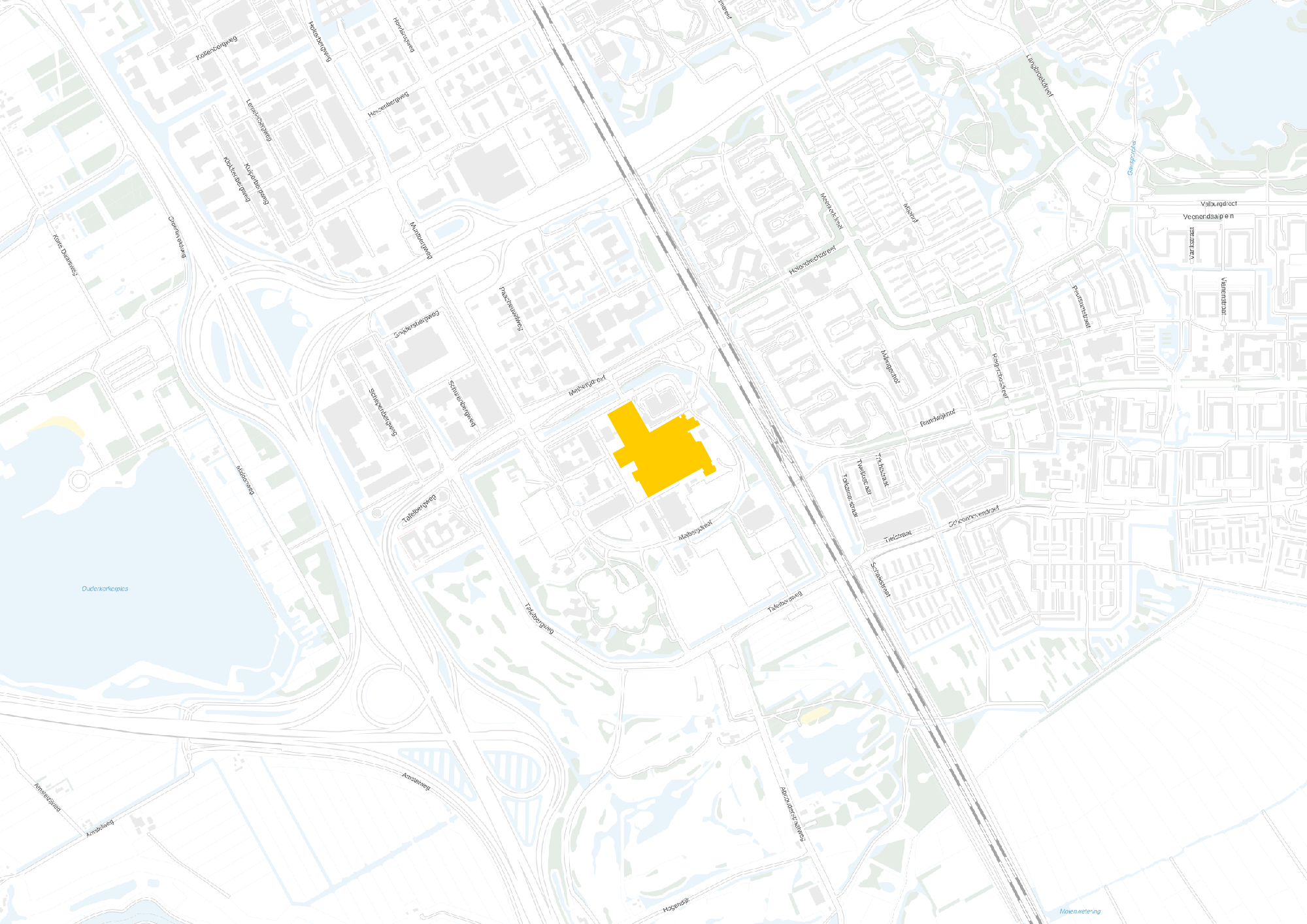
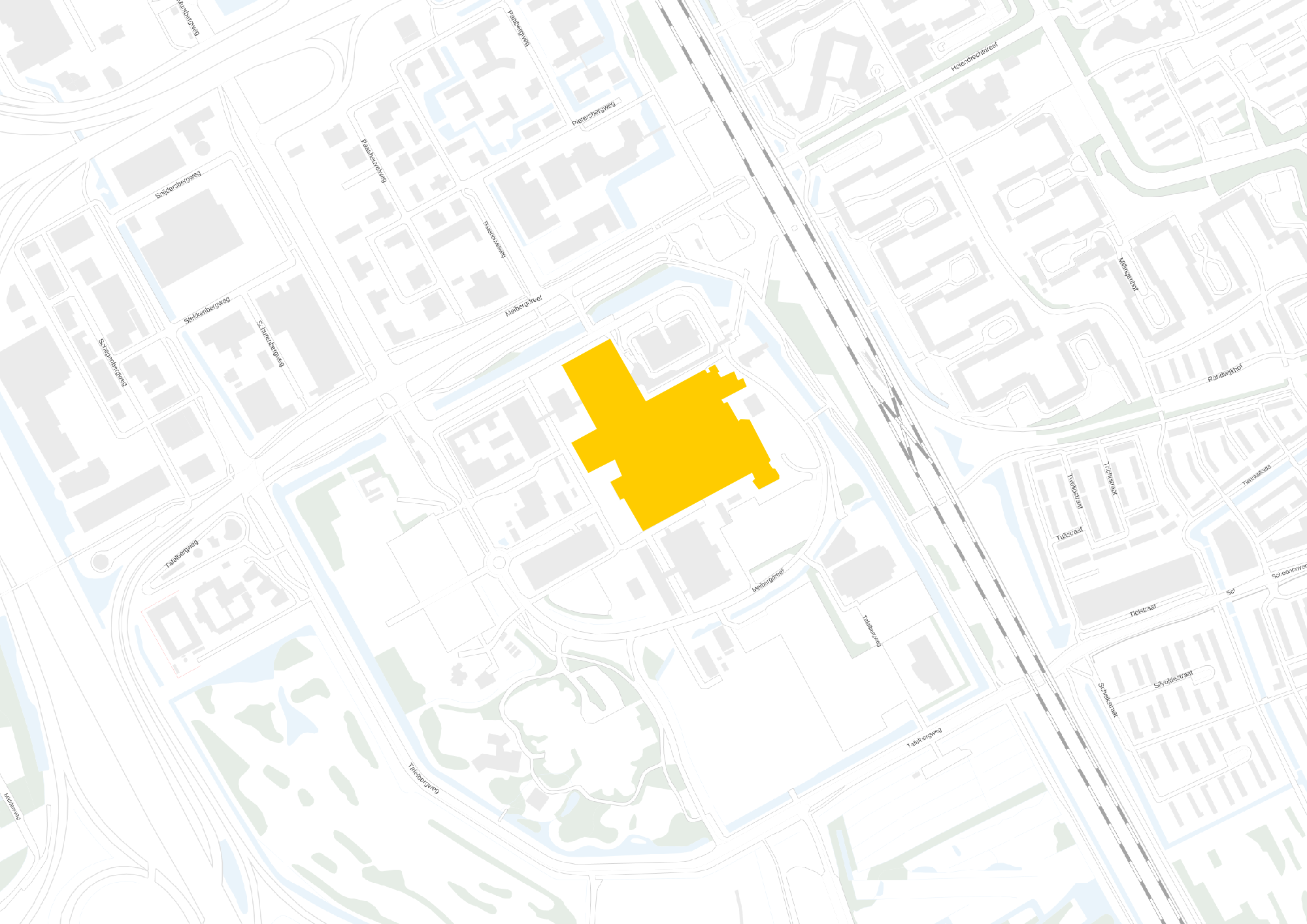
Location
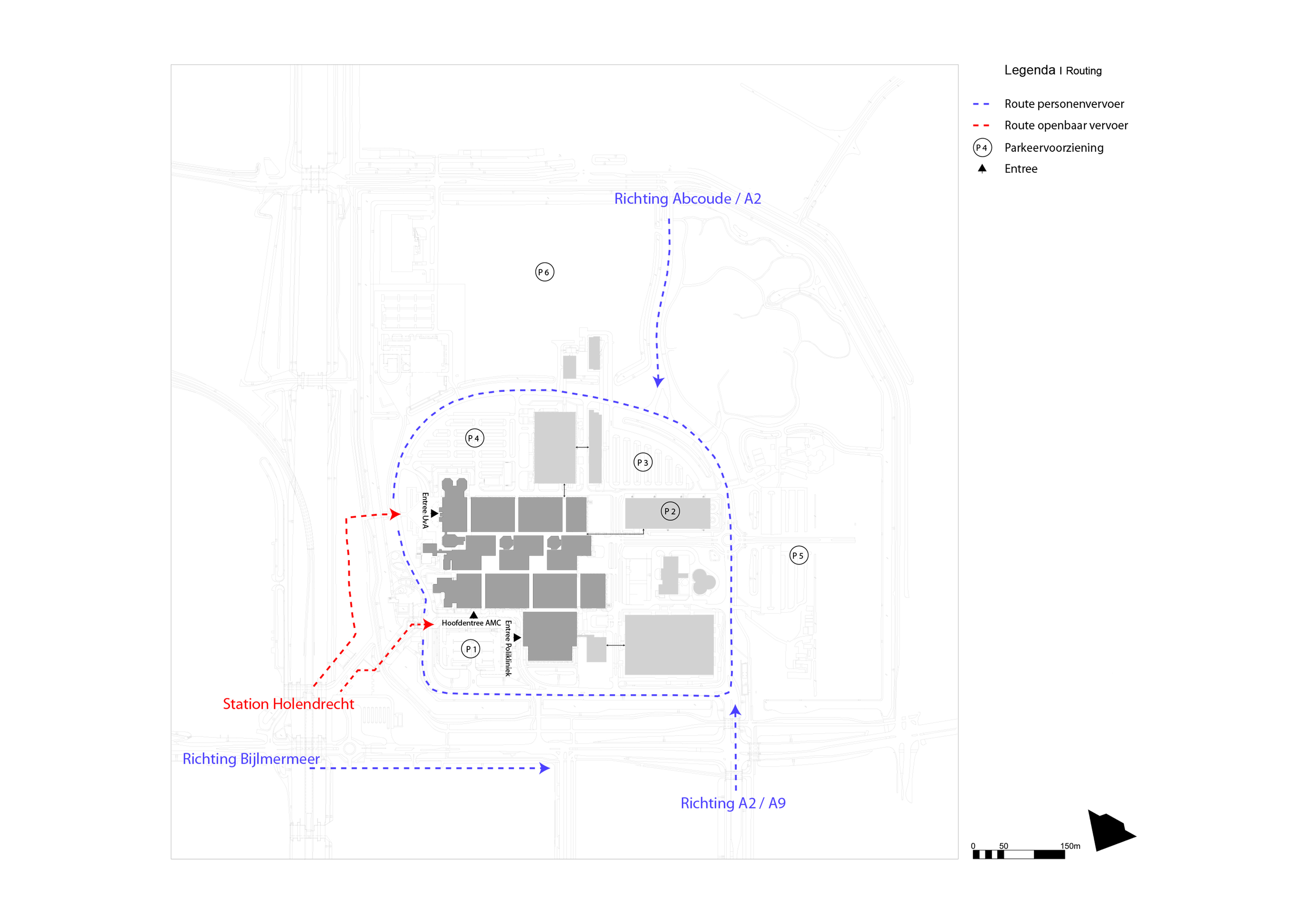
This slideshow presents the location of the AMC. As previously mentioned the AMC is located in the southeast of Amsterdam. There it can be accessed by car from the A2 and A9 highway network and by train, metro and busses via Amsterdam Holendrecht station.
Own images showing the location of the AMC and the access to the building by car and public transport
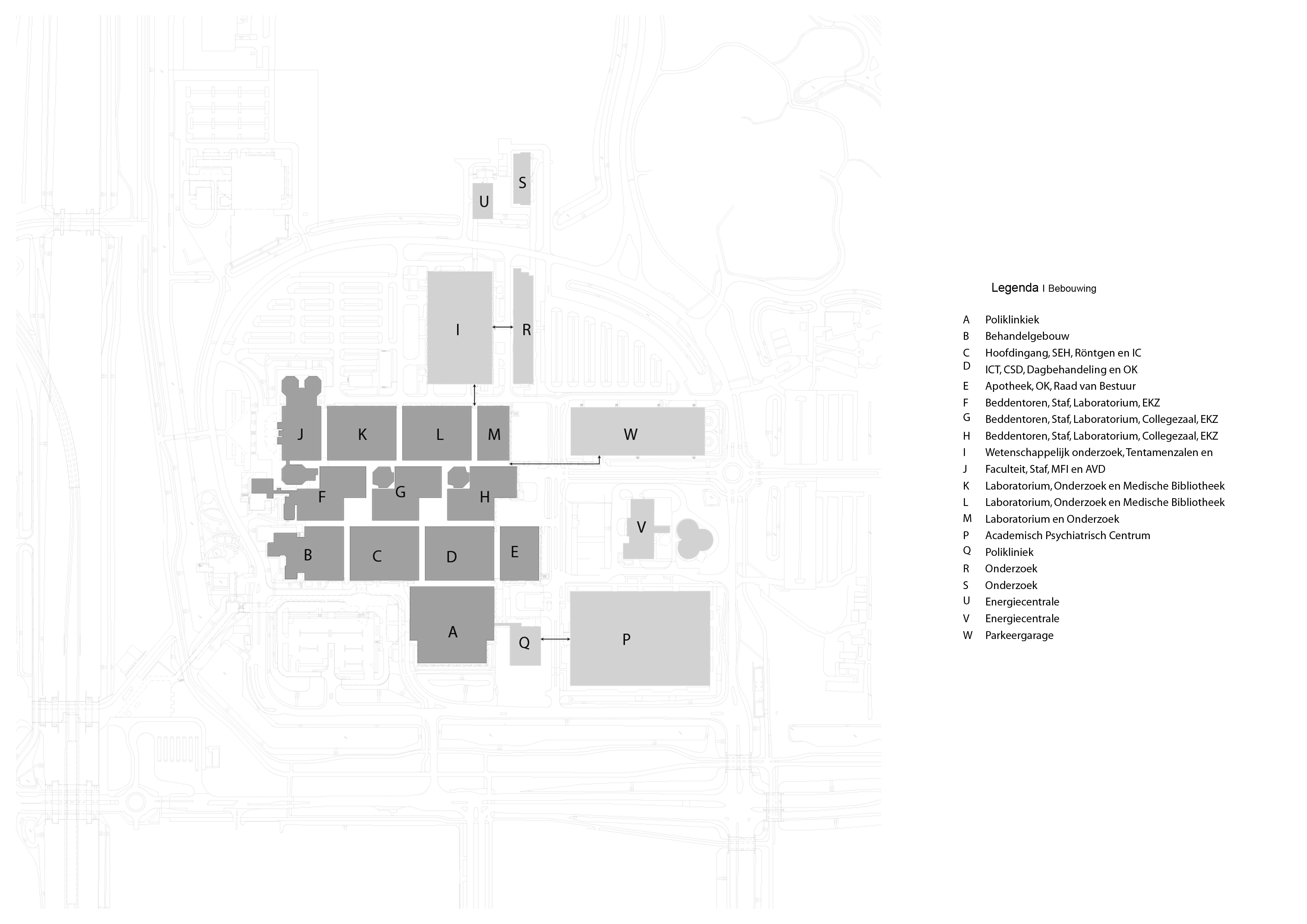
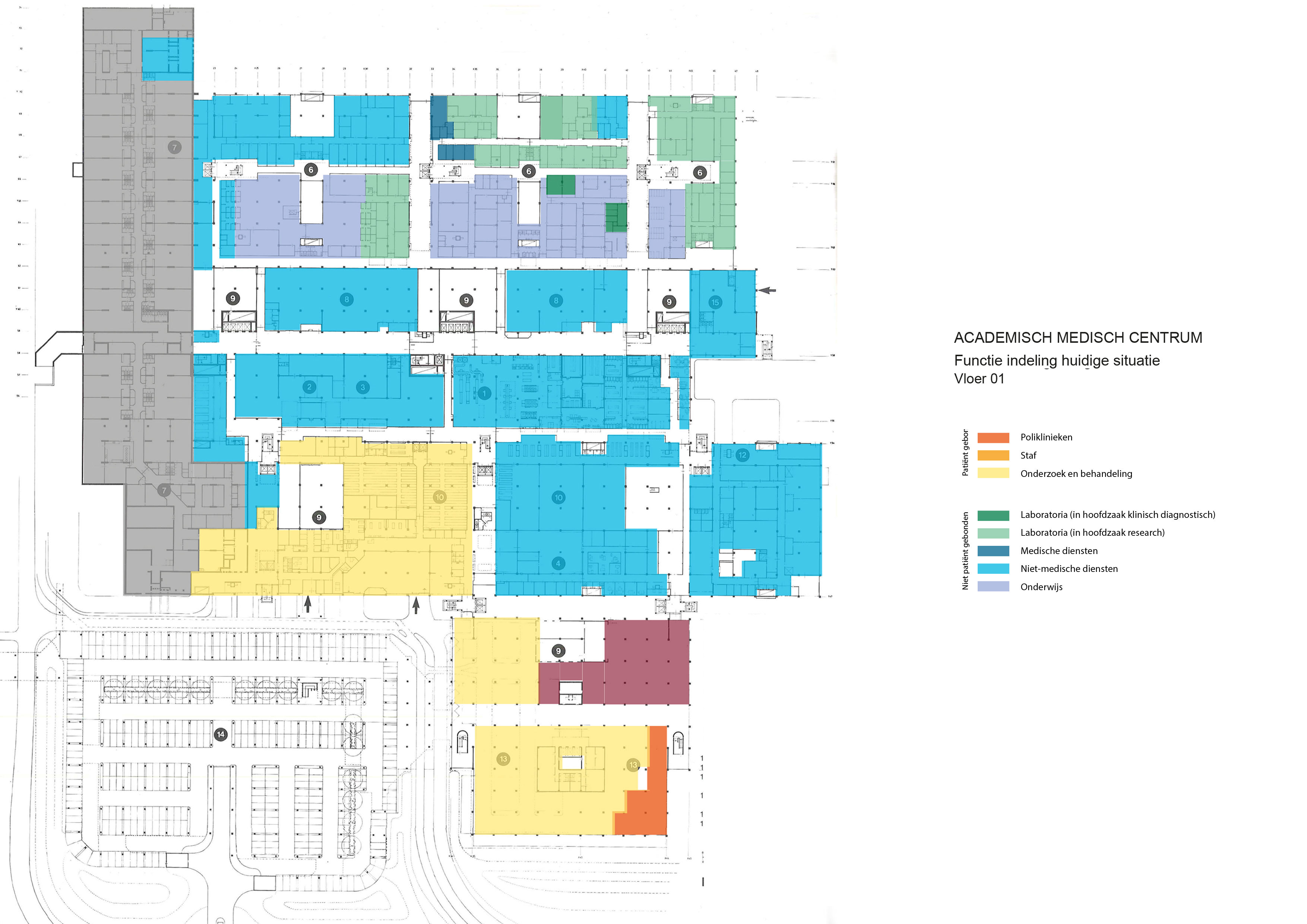
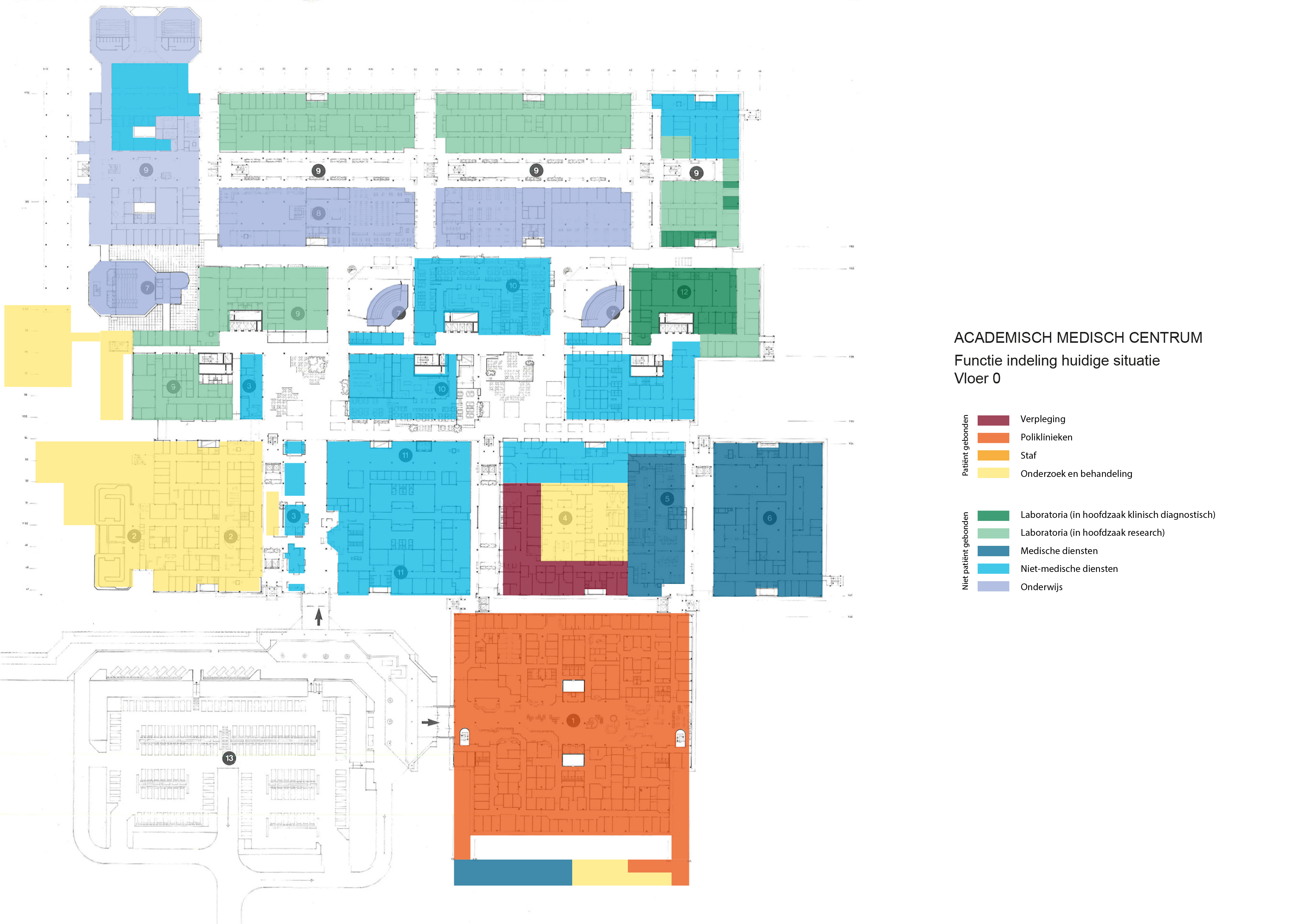
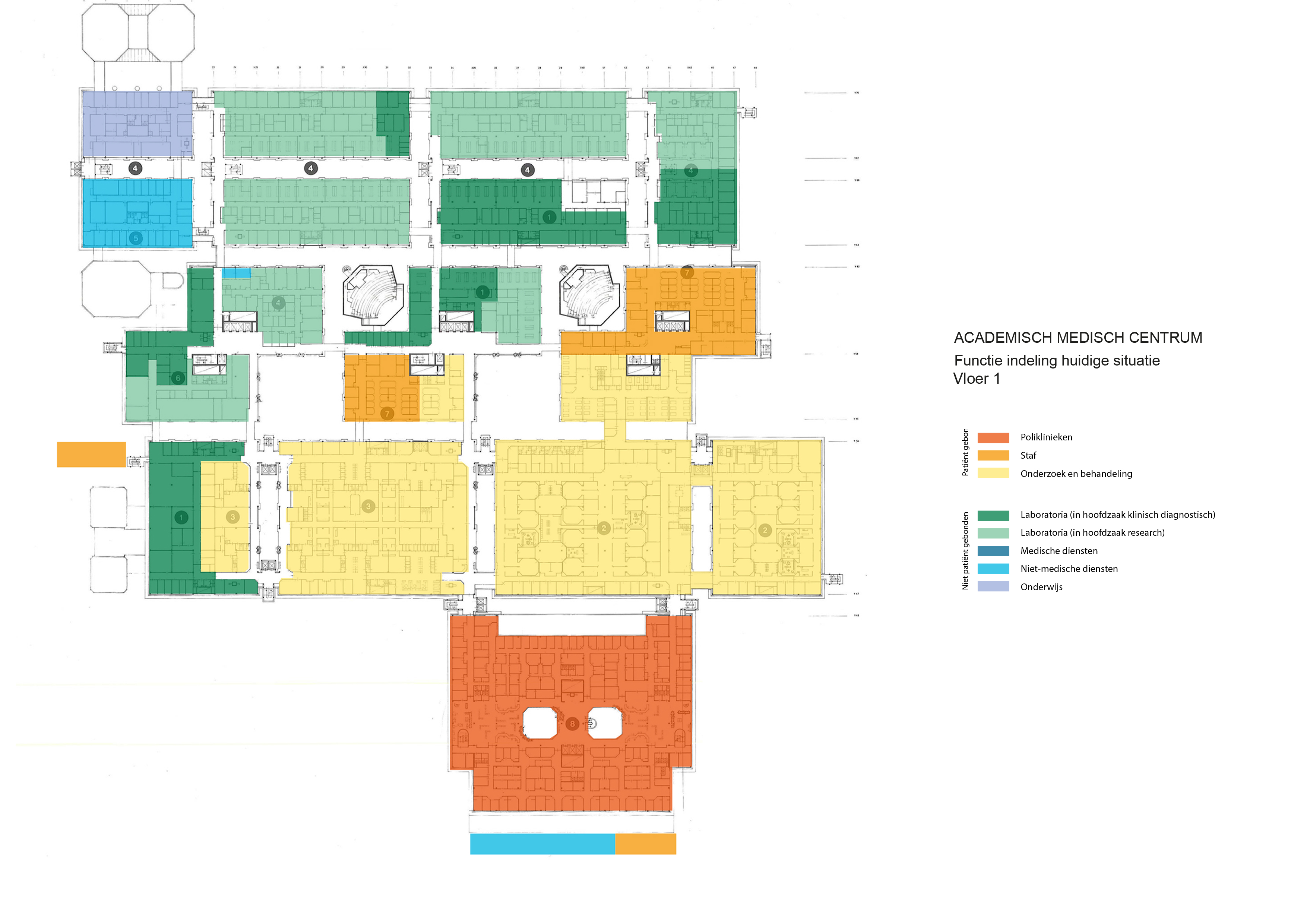
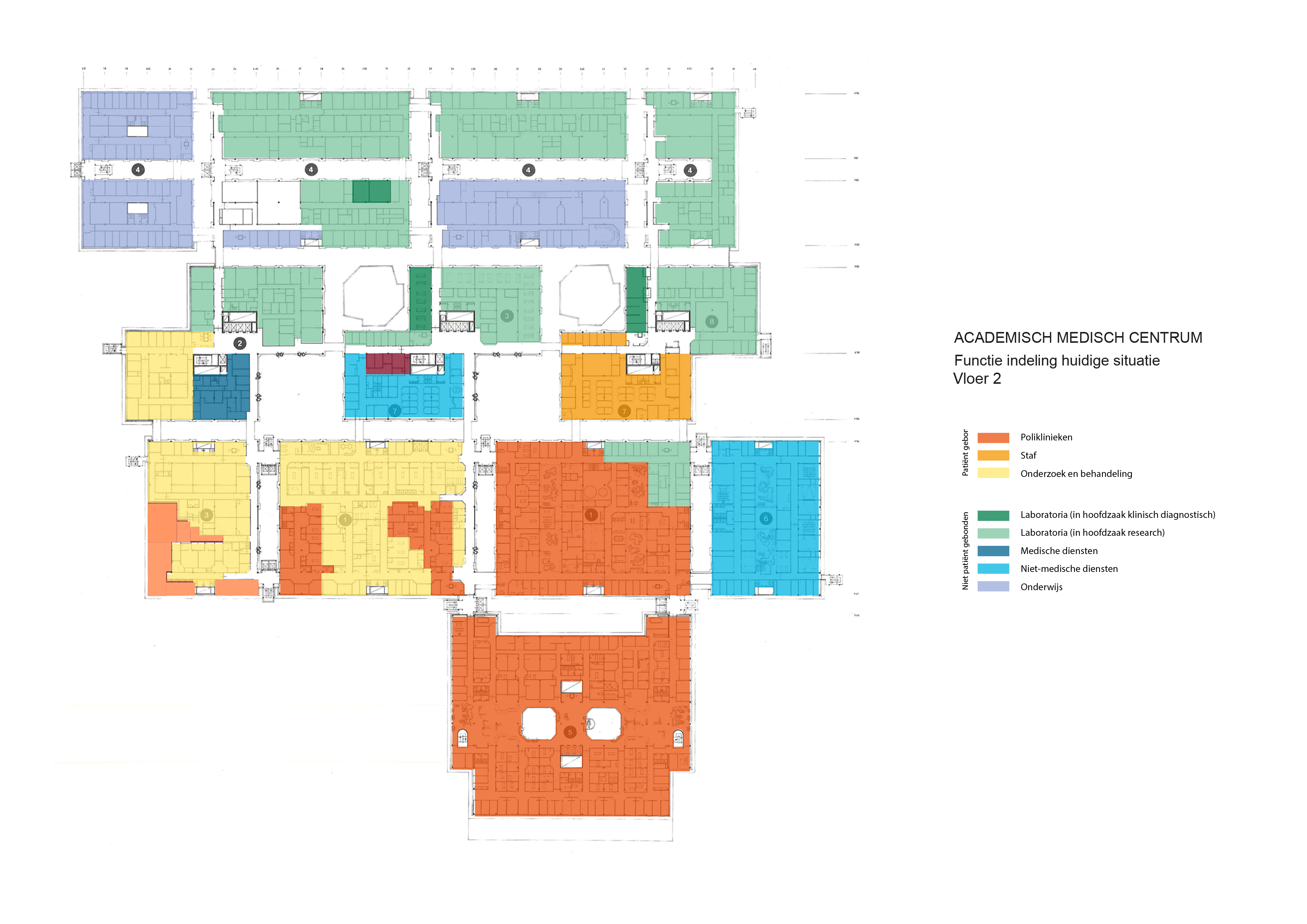
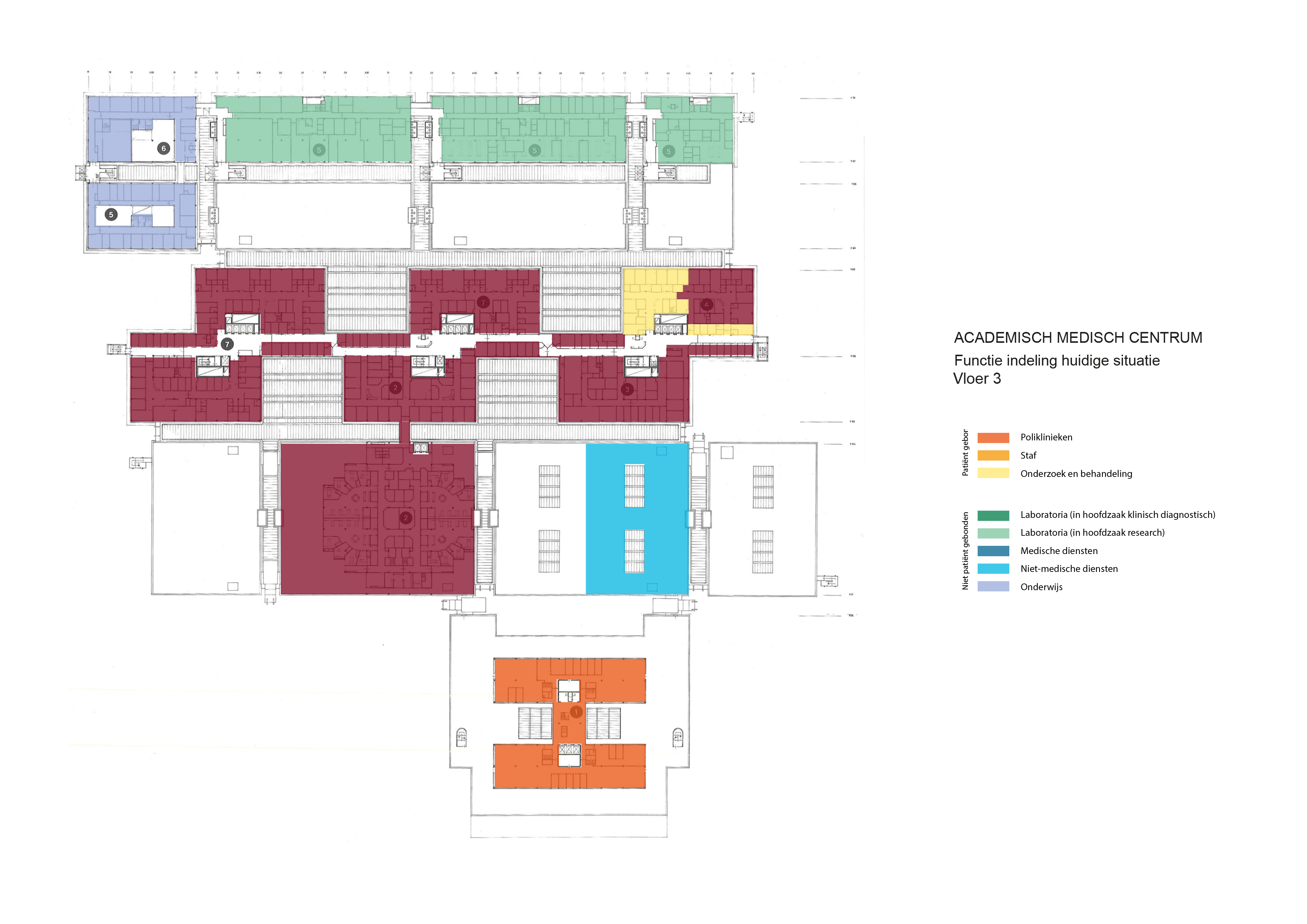
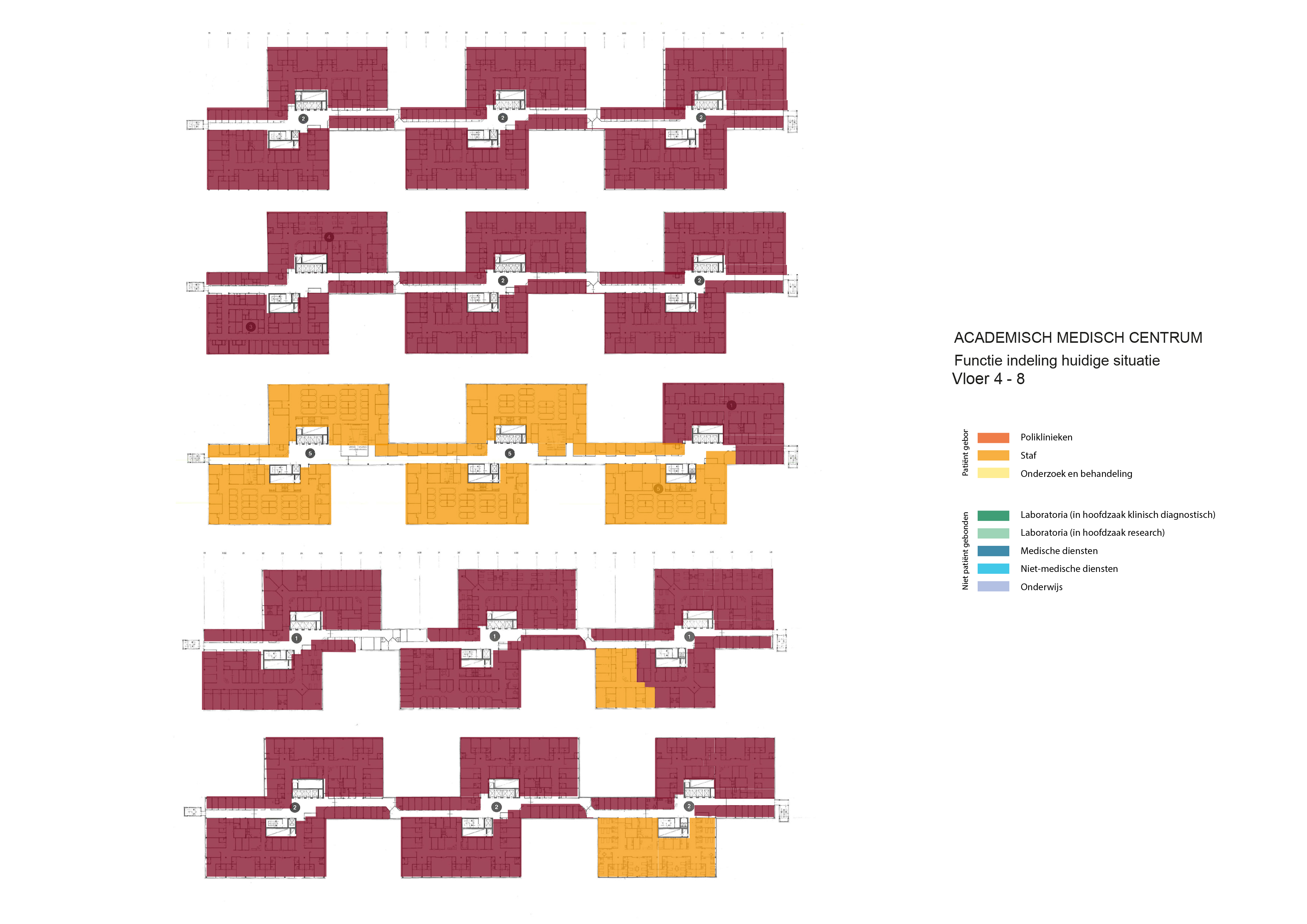
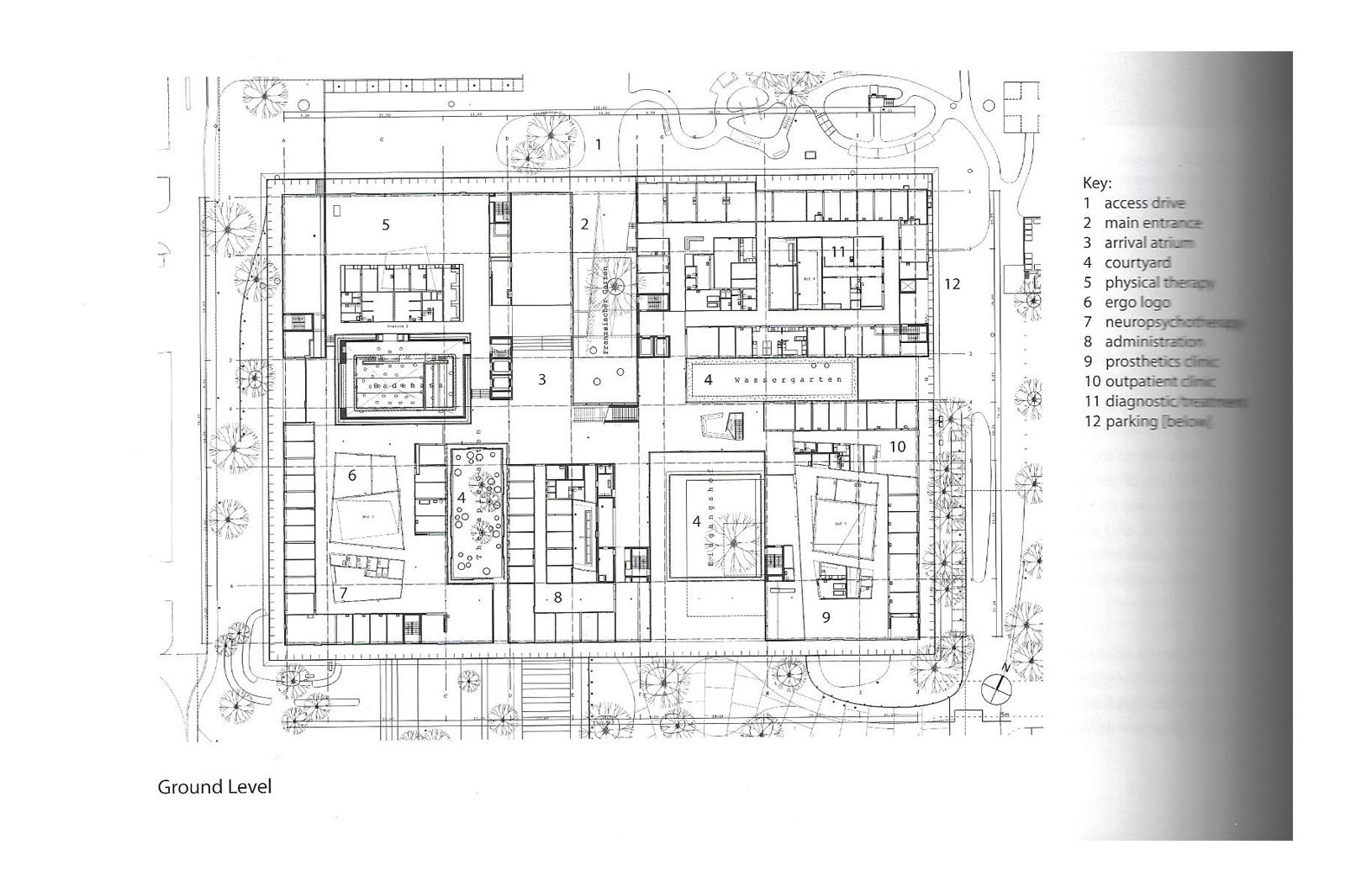
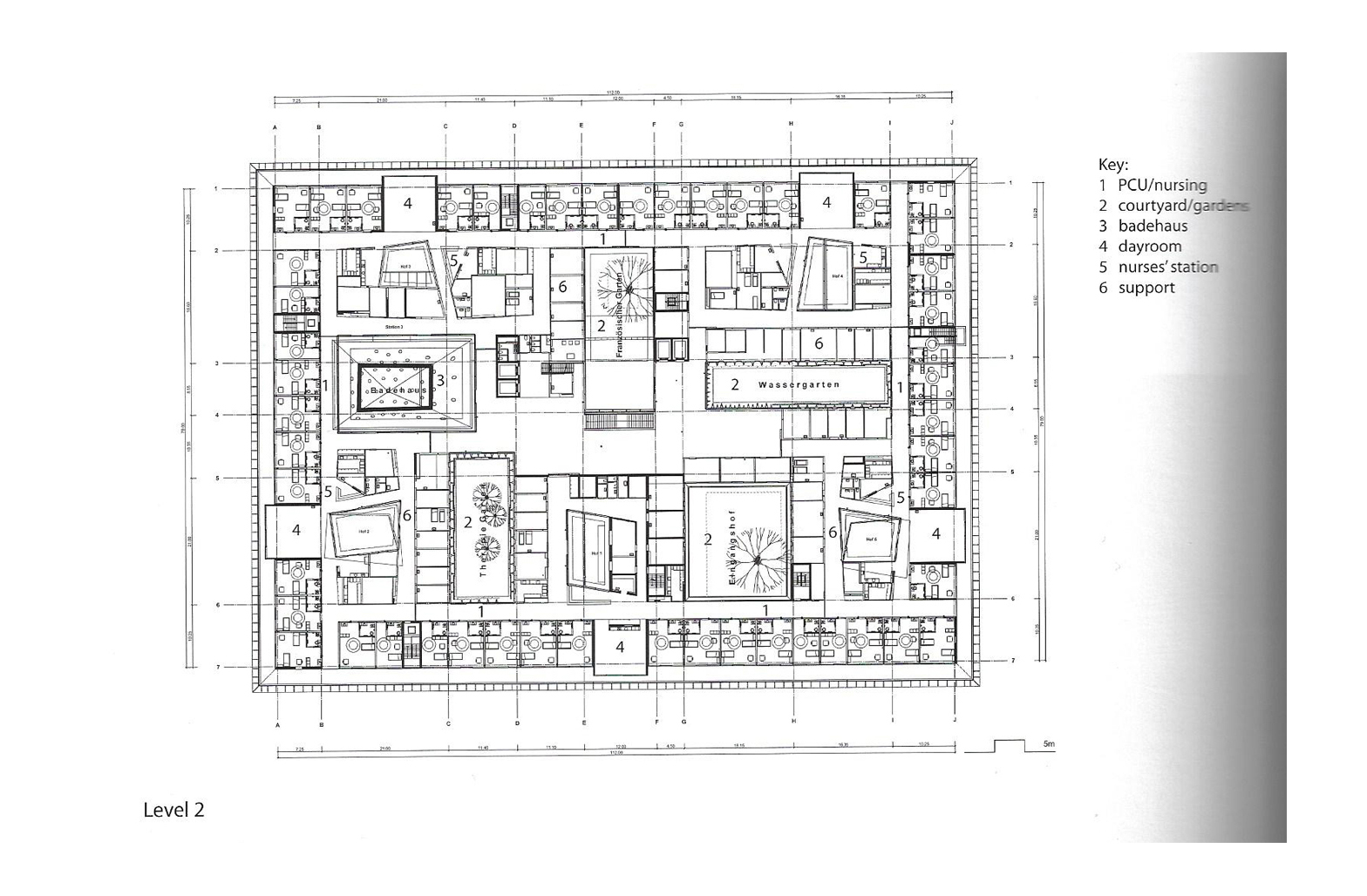
Floorplans
The floorplans of the AMC show that all the different floorplans within the AMC. Besides showing the floorplans it provides an analysis of the plans. It becomes clear that there is a clear division between the northern part and the southern part. The northern part is meant for non patient functions like education and laboratories while the southern part of the floorplans is meant for patient care.
The floorplans of the AMC with function analysis.(AMC, 2016)
Specialism
The AMC has various top-referral specialties. These include cardiovascular diseases, immunology and infectious diseases, diseases of the digestive system (surgery and internal medicine), metabolic diseases, gynecological oncology, specialized care in early pregnancy, prenatal diagnostics, pediatric oncology, pediatric immunology/ hematology, vascular disorders of the brain, severe hearing disorders, schizophrenia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and deep brain stimulation for severe obsessive-compulsive disorders. Besides these specialties the AMC has also been allocated various top clinical functions by the Dutch government. These are functions that provide medical treatments and services in limited number of hospitals, this due to high costs and required expertise. The AMC’s allocated top-clinical functions include kidney dialysis and kidney transplantation, open heart surgery, radiotherapy, neurosurgery, neonatology and nuclear medicine.
The AMC tries to distinguish itself from other hospitals through seven core areas of medical research. These are: cardiovascular diseases, immunity and infections, gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders, neurological and psychiatric disorders, oncology and epidemiology & public health. All of these core areas covers the whole spectrum of medical research: from fundamental biomedical, translational and clinical research to the evaluation of new medical methods and techniques.
Infectious diseases and immunity
In a Dutch and international context, AMC researchers are working on the development of drugs and the evaluation of combination therapies for HIV/AIDS. Another line of research focuses on the development of vaccines, and bacterial research concentrates on pneumonia, meningitis and septicemia. Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are also being studied, with researchers concentrating mainly on the inhibition of proinflammatory proteins by means of an inactivated virus. Phagocytes, dendritic cells and T-cells are the central focus of fundamental immunological research.
Oncology
Most of the research in the core area of oncology concerns the molecular and biochemical backgrounds of cancer. There are four lines of research: gastrointestinal oncology, hematological oncology, pediatric oncology and neuro-oncology. The focus of the research is the hypothesis that only cells of one certain type – called cancer stem cells – cause tumors to grow and spread. The pediatric oncology research covers everything from fundamental research (genetic profiling) to clinical research. Much attention is focused on new drugs, and the later effects of oncology therapy.(AMC, 2009)
cardiovascular diseases
immunity and infections
gastrointestinal diseases
metabolic disorders
neurological and psychiatric disorders
oncology
epidemiology & public health
The seven core areas of medical research, own image.
AMC's development vision and aims
In the spirit of the original principles of the core principles for redevelopment of the AMC are flexibility and standardisation. Within these principles safety and patient-centrality. The different phases of care will be more separated and then accordingly relocated within the hospital network. These phases include diagnostics, treatment, screening, after care, nursing and caring.
Another important aspect of the AMC is the increase in scientific research, in quantity (promotions and publications) as well as quality (research funds and impact scores). It is important for the AMC to remain as one of the top UMC research institutes. Through international cooperation it remains a key player within its core areas as previously mentioned. To increase its international presence valorisation is promoted from start-up companies.
The functional state of the bedroom towers has decreased under an acceptable level for modern medicine. Therefor these towers need to be redeveloped to once again live up to the modern standards. Another problem is that there is hidden vacancy within the towers. Theoretical one full tower could be removed or repurposed.
The research and treatment centre forms the core of the AMC, these function feature high investment costs, complex housing and growth. The functions feature policlinics, research centres e.g. but in the future the policlinic functions need to grow. In order to achieve this sub functions have to be segregated, that would mean that research functions are supposed to be clustered as for the other functions.
AMC functions remarkable well for its age when it comes down on patient care. But the wayfinding, approach and entering of the area and the complex are out dated. The current main entrance and the policlinic entrance are out dated, not representative and don't contribute to the welcome feelings patients and visitor should have.
Flexibility plays a role within the strategy to make more efficient use of the current facilities. This means that employees will have to share their office facilities with employees from other facilities. Therefore reducing 70 offices spots per 100 employees. Another aim is the redevelopment of internal spaces so that they can be used for one main purpose like offices, waiting, research, consultant rooms e.g. and not just for one specific department.(AMC, 2016)
Redevelopment constraints
Since the board of the AMC does not want to demolish the current building it means that the current building has to be transformed. The diffeculty with that is that a running hospital cannot simply be shut down. Appointments, surgercies and threatments are planned far ahead and what to think for the sterile research facilities that have to transported without any external influences on what is being researched. Therefor the AMC has to remain in function and with that come constrains in order to keep the atmosphere of the building as it is. The constraint that are set by the AMC are:
1. During transformation the hospital should remain in function. That would imply that a phased devellopment plan should be develloped.
2. The redevellopment should remain within the current boundries of the building. Excluding the entrences of the building and the renewed landscape plan.
3. The concrete structure should remain in place and should remain visible.
1. Remain active while construction
2. Building boundries
3. Concrete structure
Future developments in healthcare
There is a lot of research and innovation being done in the field of medicine and healthcare. As a species we try to survive as long as possible on this planet. Globally many breakthroughs are being made to improve human health. With innovation not slowing down any time soon it is worth the investigation of what the future developments in healthcare and medicine will be. Below is a video visualising research done by the Economist showing what the future of healthcare and medicine will look like. In my opinion there are seven elements which are very important for healthcare and medicine, these are:
1. Data collection and exchange.
2. Virtual and augmented reality.
3. AI solutions for medication.
4. Nanomachinery.
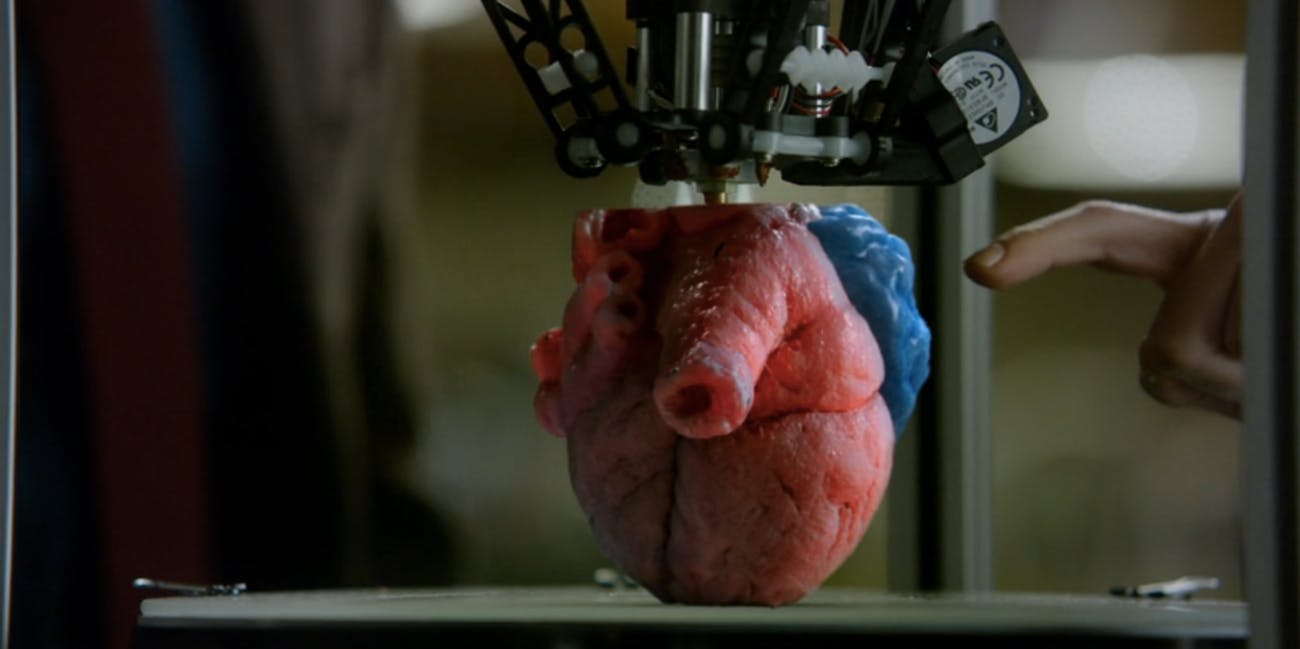
5. 3d printed organs.
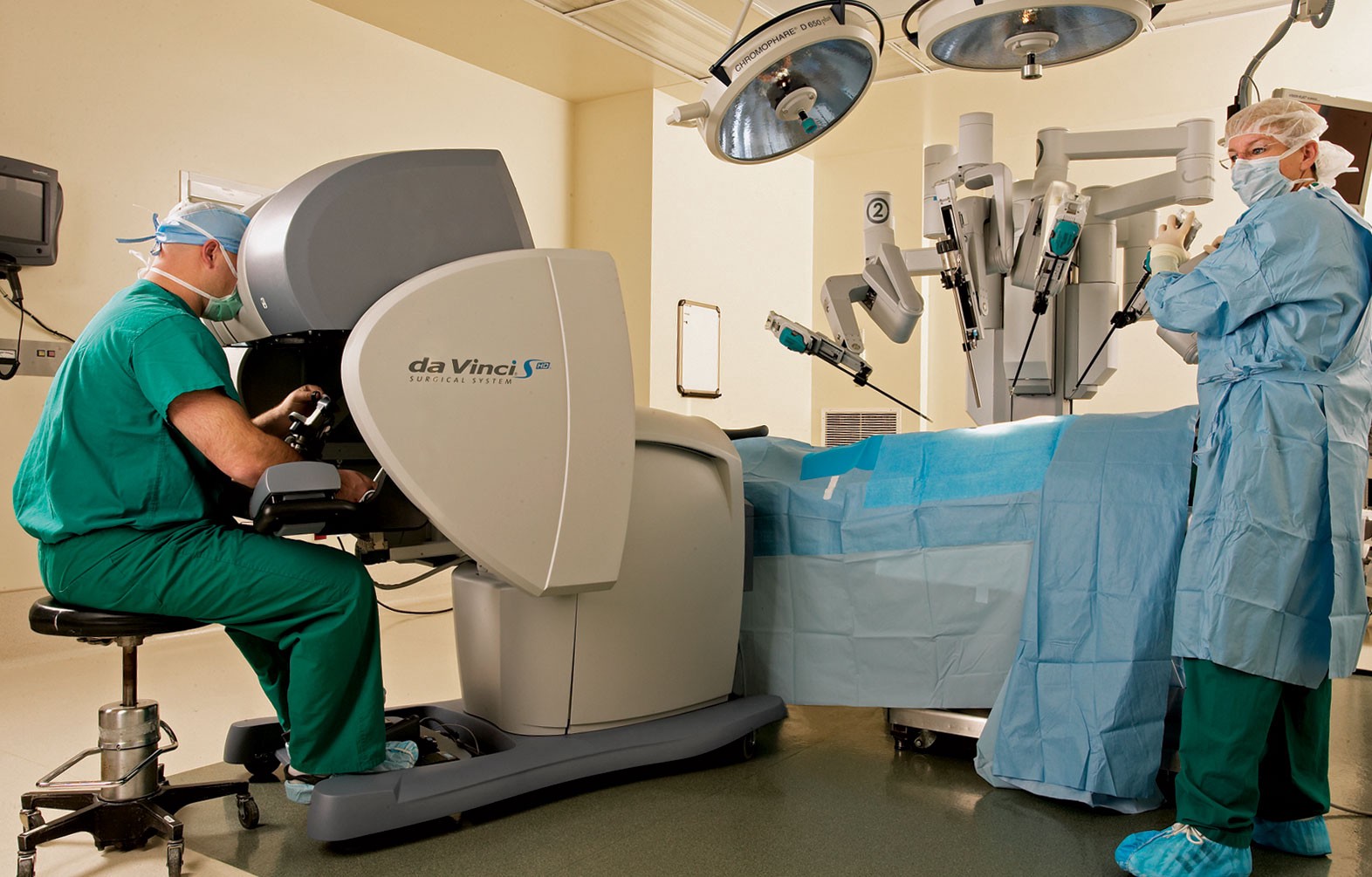
6. Surgery through machinery.
7. Genetical adeption of babies.
A video from the economist portaying the future of healthcare.
A slideshow portaying seven key elements of the future of healthcare.
Design Proposal
As previously mentioned the Academic medical center is due for renovation. When the AMC was build it was build as an city/ island providing healthcare to people visiting. The current function of the hospital is to provide human sustainability in effort to elong human survivalibilty. This concept of the hospital will change. At the moment we are facing various environmental problems, with hospitals as the AMC contributing in a negative way due to their large carbon footprint. To stand the course of time hospitals will have to reevaluate their role within the environment and its context. This will result to hospitals adopting a new purpose by not just providing human but also environmental sustainability.
This implies that the new AMC will be changed drastically to adopt it's new role. That will mean the AMC will get a carbon neutral footprint. This will imply that the AMC will have to reduce its current carbon footprint. This requires an energy transition into renewable energy sources. Currently the energy that is used within the building is produced through unsustainable manners.
A hospital produces large amounts of waste in a wide range of wastestreams. The hospital produces plastic waste, organic waste, toxic waste and among other nuclear waste. To become waste neutral it is important to close the waste cycles within the hospital itself. Therefor it is necessery to reconsider the materials that are used within the building to reduce the usage of materials that are hardly recyclable. In the most ideal situation the AMC will be able to produce the products it uses.
This idea of self-sufficieny reduces the carbon footprint created by the import of goods. To increase the hospitals self-sufficieny local food production should promote within the hospitals boundries. The food can than be fed to the patients within the hospital. In this way the hospital is in control of producing foods with health benefitial properties or health malaptive properties like pesticides.
Besides its role as environmentalist the hospital will provide human sustainability. Within this sustainability the patients- and their family will be central. At the core of our humanity is the need to survive, we prefer to be in control of what we do. Whenever we become ill that control is lost and emotions like doubt, uncertainty and fear are surfacing. When hospitalized these feelings are present even more. It makes us unsure about what will occur next, this can result in isolation, alienation, stress and depression on part of the patient and his or her family. All these feeling are reducing the psychological health of the patient and as a consequence the process of healing is slowed down. The role of a patient- familycentral hospital is to reduce and take away these negative feelings.
These emotions and feelings can partially reduced by the usages of design. When patients are meant to stay in the hospital they spend most of their time at and in the patient care units. These places should therefor provide the means for healing and regeration. It is in this place where the mental state can be improved. To change the state of mind of patients the design should tackle what they fear and what causes stess. As mention before this is often the lack of control. That means the patient should get the feeling to be in control. The patient care unit should provide oppertinuties for the patient to adjust aspects of its room. That could imply that the patient could open and close the windows and blinds, change the temperature and ventilation, adjust the bed settings in order to get more comfortable. But not just that kind of control, it is also the control of knowing about the medical conditions and getting a voice in the medical threatment.
Patient care units should also provide the means for human interaction, not just with other patients, but also with their family. The place should become more relatable to the patients home so he or she can find comfort in the things the patient knows. This would include the ability for the patient to bring attributes from home or offer places for family to sleep.
To further improve a patients well being and psychological state patient care units should offer appropiate visual settings, transmission of natural light to the interior, contact with nature, landscape and vieuwing amenities. All these aspects improve a patients well being.
Another important aspect of healing is the privacy the patient can get within the patient care units. Privacy is an umbrella condition for various different kind of privacies. These are auditory privacy (sound), visual privacy (sight), tactile privacy (touch), spatial privacy (personal space) and olfactory privacy (smell). That means the architecture of the patient care unit should provide ease on all these five different fronts to optimize the regeration proces of the patient.
The previously mentioned aspects do not just apply to the patient care unit itself. The same story goes up for the common rooms, silent areas, laboratories, restaurants, threatment rooms, surgery rooms, entrances, policlinics, waiting rooms, dialysis center. In some these factors apply more than in the others. But the hospital forms a whole, it will be from the first until the last step that the hospital will center around the patient and its family, each and every room they visit.
To transform the hospital into something sustainable it is important to also integrate the previously mentioned ideas established by the AMC. These are the aspects include the of the AMC vision and aims for their hospital. But also the constraints set up by the board to maintain the atmosphere of the amc. And not to forget about the future developments in healthcare.
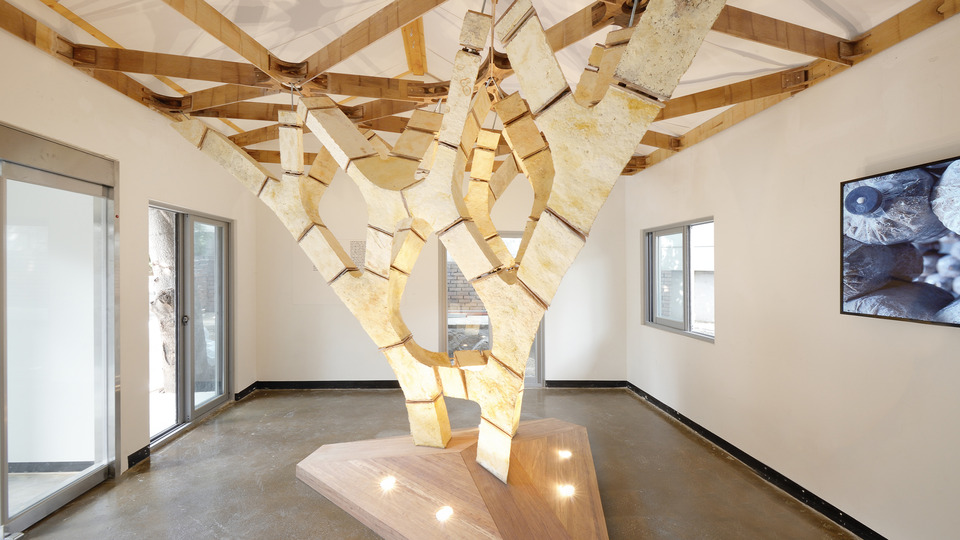
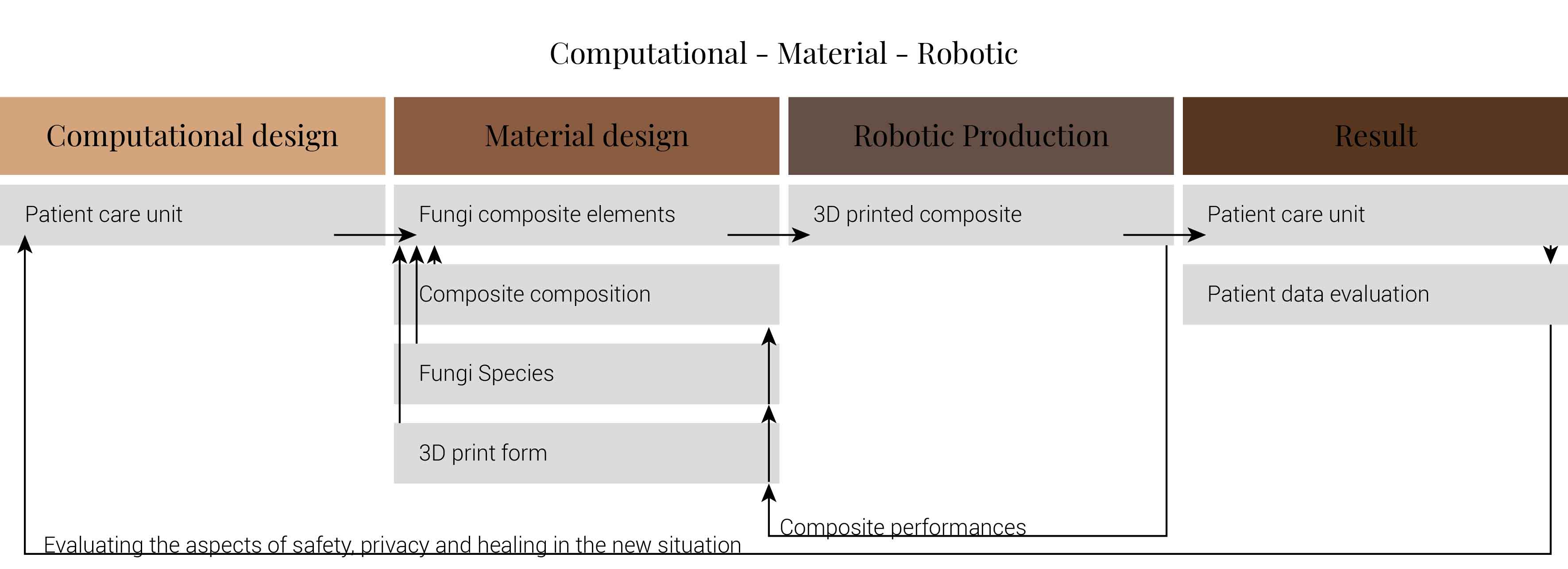
It is these ideas that I would like to implement in the new design for the AMC. To achieve the architectural infill of the AMC I propose the usage of mycelium as a building material. It is this material, which will be discussed later on in further detail, that provides a wide variety of oppertunities. Mycelium is a composite made from fungi and an organic substrate. This composite can be locally produced by the hospital itself. During the production various more benefits for hospitals start to appear, the growing of mushrooms which could function as food, serve as medicine, provide building blocks for antibiotics. These fungi can be grown on waste, they can deconstruct plastics and harmful matter into harmless matter. Therefor it provides an important chain in the zero waste hospital.
A slideshow portaying the design proposal.
Fungi
Introduction
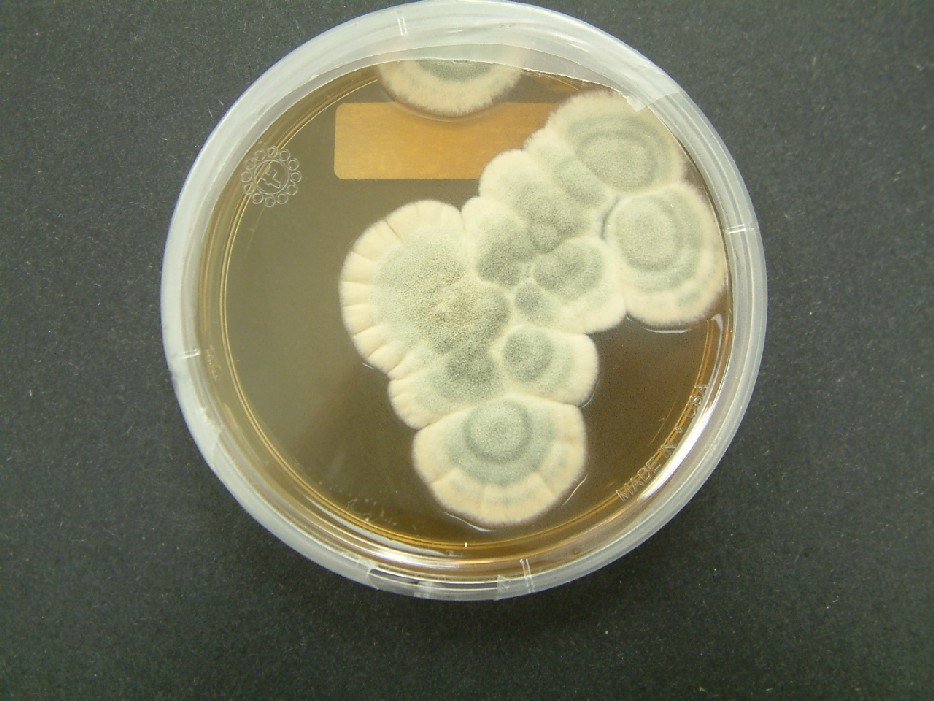
This project revolves around the growing of architecture by application of mycelium. Mycelium is the vegetative part of fungi. This biological tissue/ material is composed from tube-like fibers. These fibers are called hypha and are approximately 1 lm in diameter. Hypha grow by elogation of the apical tip. Which means that the fibers grow faster in the tips than in its branches. On occasion these fibers branch out and merge with other hyphae. As a consequence a random fibernetwork structure is formed; The mycelium (Lull et al., 2005).
The hyphae network
Mycelium can be grown in multiple forms, (pure) mycelium, synthetic mycelium and composite mycelium. The last one will be the main focus of this material study since this is the form that is most used within the product development and the built environment. The composite is a mixture of mycelium mixed with a organic substrate most preferably a lignocellulosic biomass. Mycelium than forms it's network of hyphae on and through the substrate by (partly) consuming the substrate. It then transforms the substrates biomass into chitine (up to 45%), Protein and polysacharides. As a result of this process mycelium and the substrate are bonded into the mycelium composite (Tazelaar, 2017).
Mycelium composite
Pure mycelium
Synthetic mycelium
Lifecycle of fungi
Since fungi is a living organism the species goes through the cycle of life. In order to produce and reproduce mycelium knowledge of it's cycle is required. The image below portaits the lifecycle of the fungi.
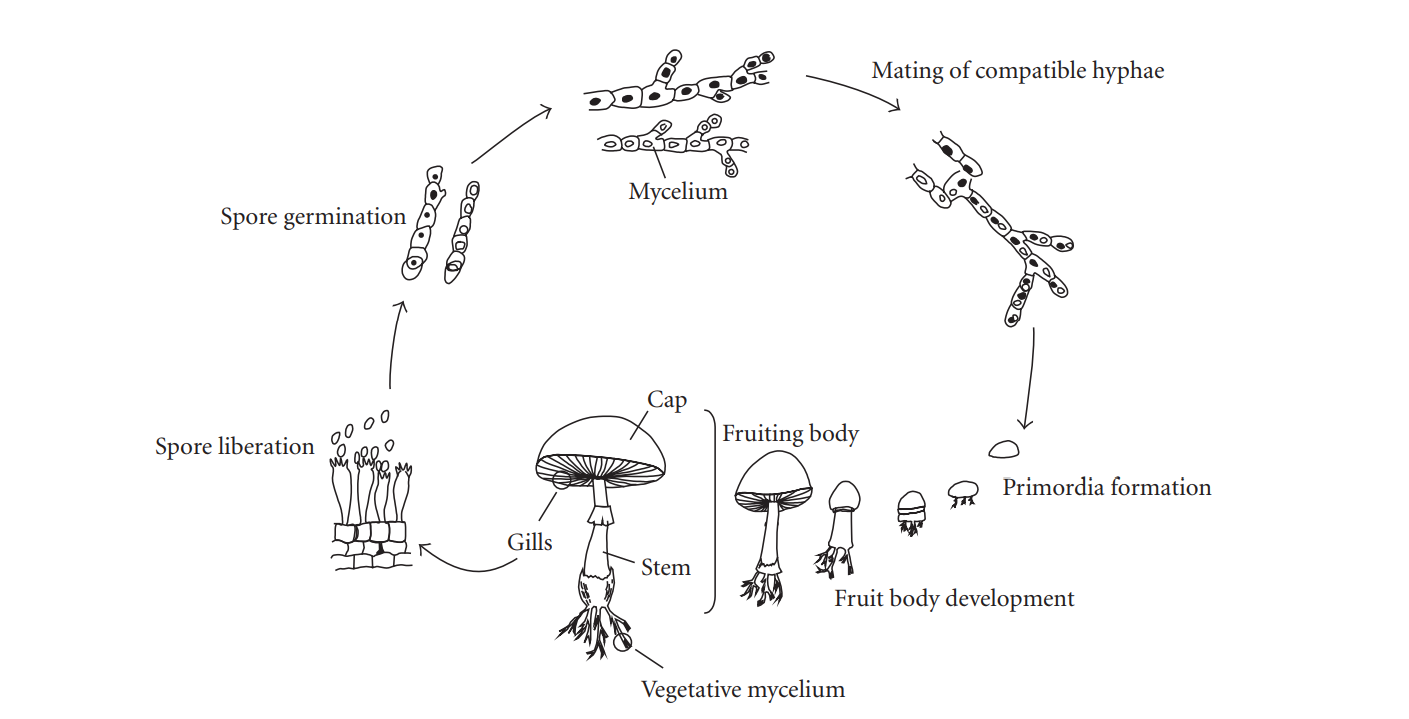
The lifecycle of the fungi
Species
The taxonomical kingdom of fungi is vast. Within the this kingdom you can find species that act as food, produce medicine or in case of this research as building material. Form all the different taxonomical divisions on division is particularly intressting, this is the basidiomycota division. The reason why this division is so intressting is because of its ability to break down long and complex organic moleculs. The species that are most often used within this field are the Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus, "Oesterzwam" (NL)), the Split Gill (Schizophyllum commune, "Waaiertje" (NL)), Lingzhi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, "Gesteelde lakzwam"(NL)) and the Turkey tail (Trametes versicolor, "Gewoon elfenbankje" (NL)). The choices for these fungi are chosen due to their benifitial properties towards growth, strenght and ability to consume specific nutritions for example (Tazelaar, 2017).
Pleurotus Ostreatus
Schizophyllum Commune
Ganoderma Lucidum
Trametes Versicolor
Structural properties
The usage of mycelium as a building component is relatively new. Therefor there is not much research available involving this subject. Besides that mycelium is a biocomposite with many different possibilities for substrate, that fact makes it even more harder to determine average structural properties. In the table below structural properties are shown of mycelium in comparrision to EPS and concrete. EPS is shown since the characteristics of mycelium and EPS are very similiar as are their usages within product development. While concrete is shown as it is a widely used within the build environment.
As seen the structural properties are very similair when it comes down to their compressive strengths. While the young's modulus shows that mycelium is more flexible than EPS. With the mycelium flexibility it is also able to better deal with flexural forces than EPS. But the best the reason why mycelium is better for usages than EPS is its low energy consumption for production and it's biodegradable properties.
| Mycelium Composite | EPS | Concrete (C53/65) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density [Kg/m3] | 122 | 20 | 2500 |
| Compressive strength 10% [MPa] | 0,12 | 0,10 | 65 |
| Tensile strength [MPa] | - | 0,15 | 2,13 |
| Flexural strength [MPa] | 0,23 | 0,15 | 4,30 |
| Young's modulus [MPa] | 1,14 | 6,00 | 37300 |
This table is based on information from (Cement&BetonCentrum, n.d.;Tazelaar, 2017)
Acoustics
Fungi based composites show great potential in the usages of sound obsorption. As seen below its absorption properties are depending on the composite material used.
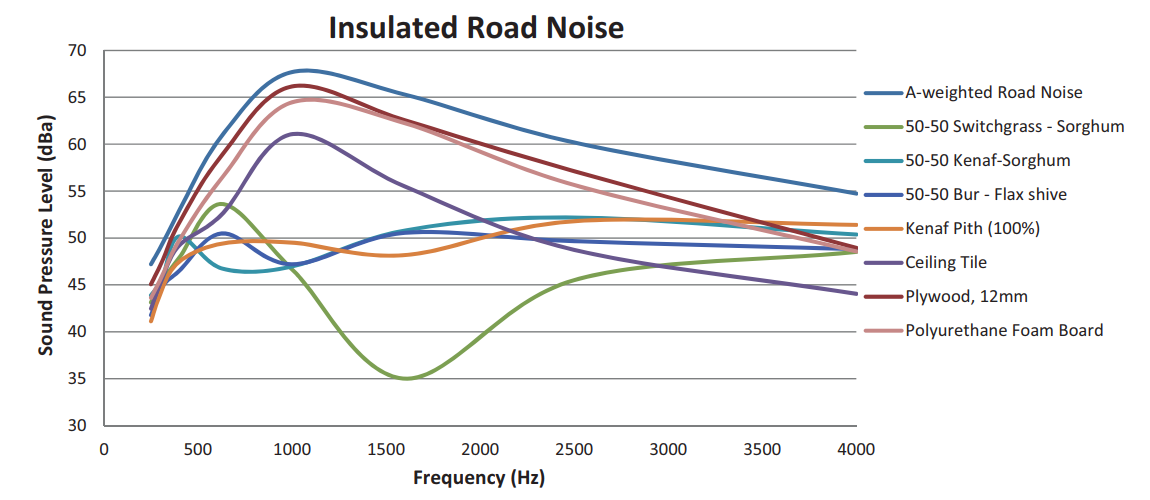
Acoustic absorption of different mycelium based acoustic panels.
Pelletier, M., Holt, G., Wanjura, J., Bayer, E., & McIntyre, G. (2013). An evaluation study of mycelium based acoustic absorbers grown on agricultural by-product substrates. Industrial Crops and Products, 51, 480–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.008
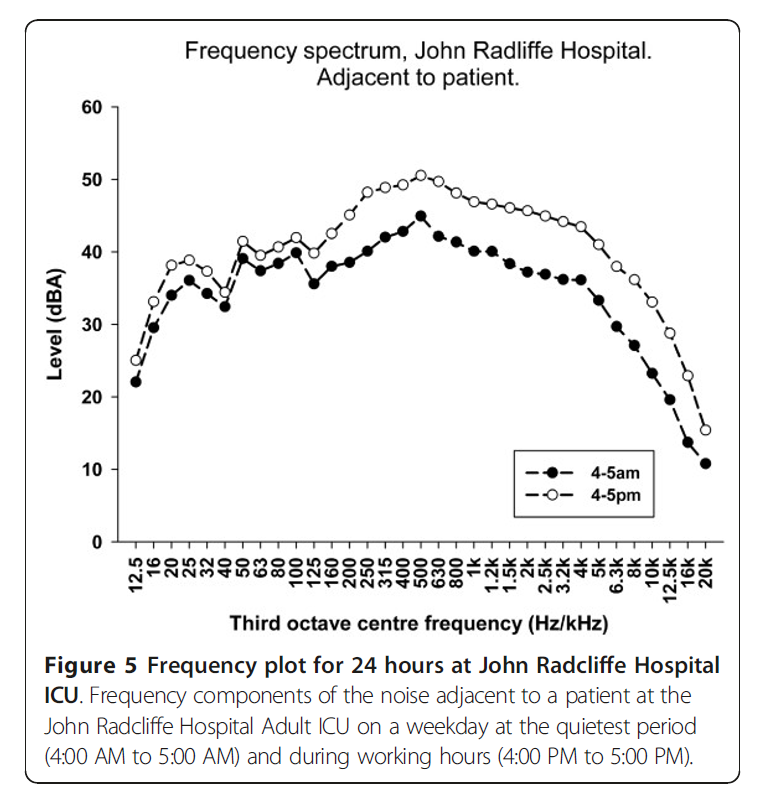
Frequency in patient care units.
Darbyshire, J. L., & Young, J. D. (2013). An investigation of sound levels on intensive care units with reference to the WHO guidelines. Critical Care, 17(5). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc12870
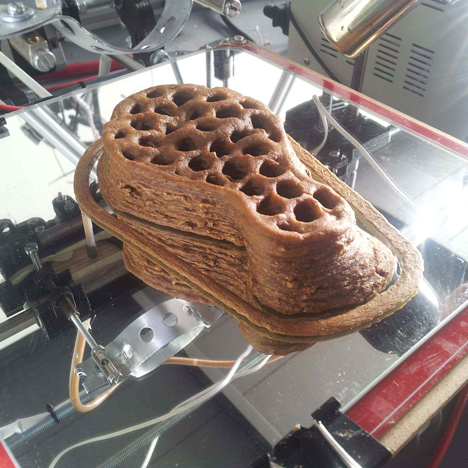
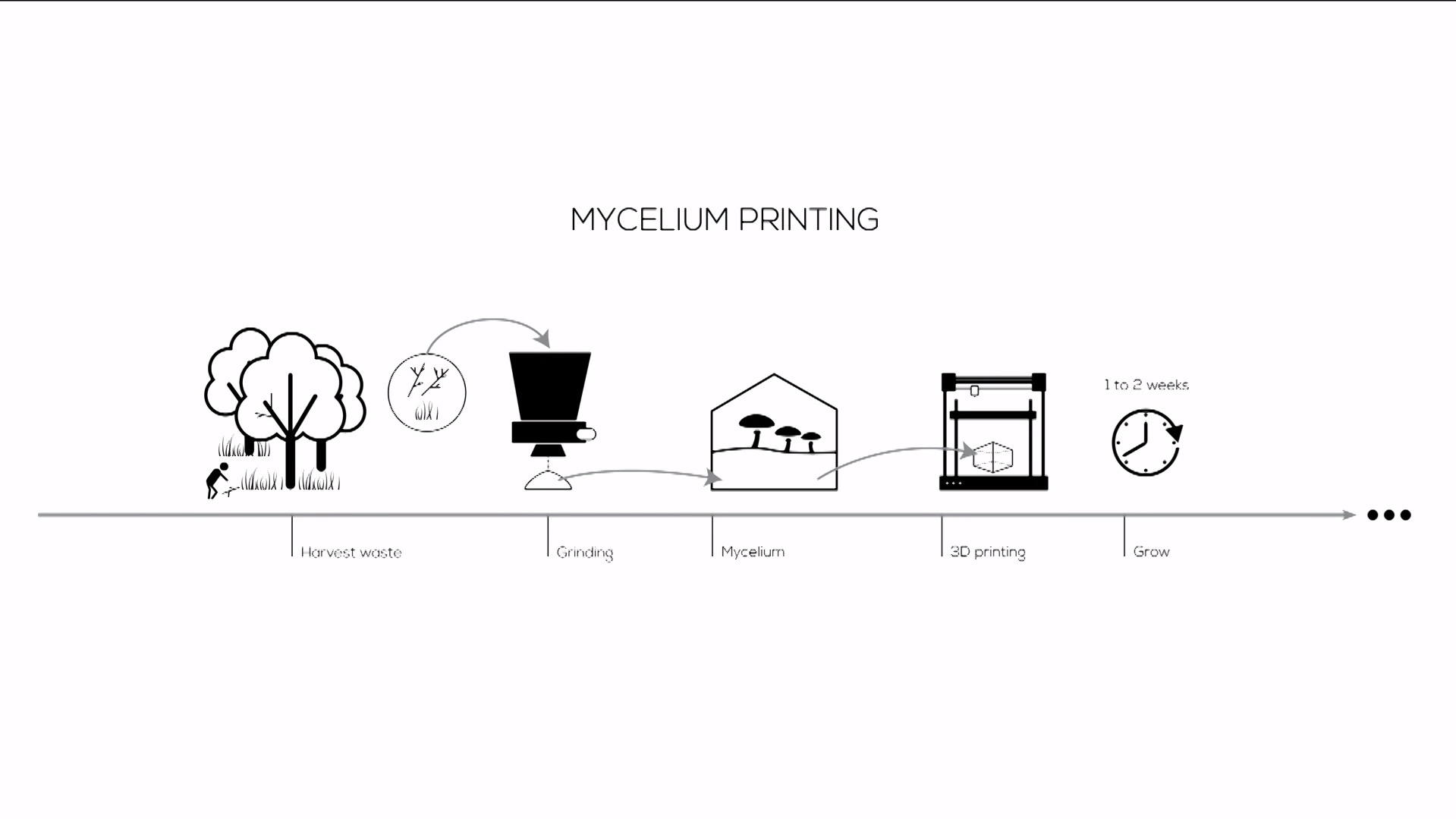
Production
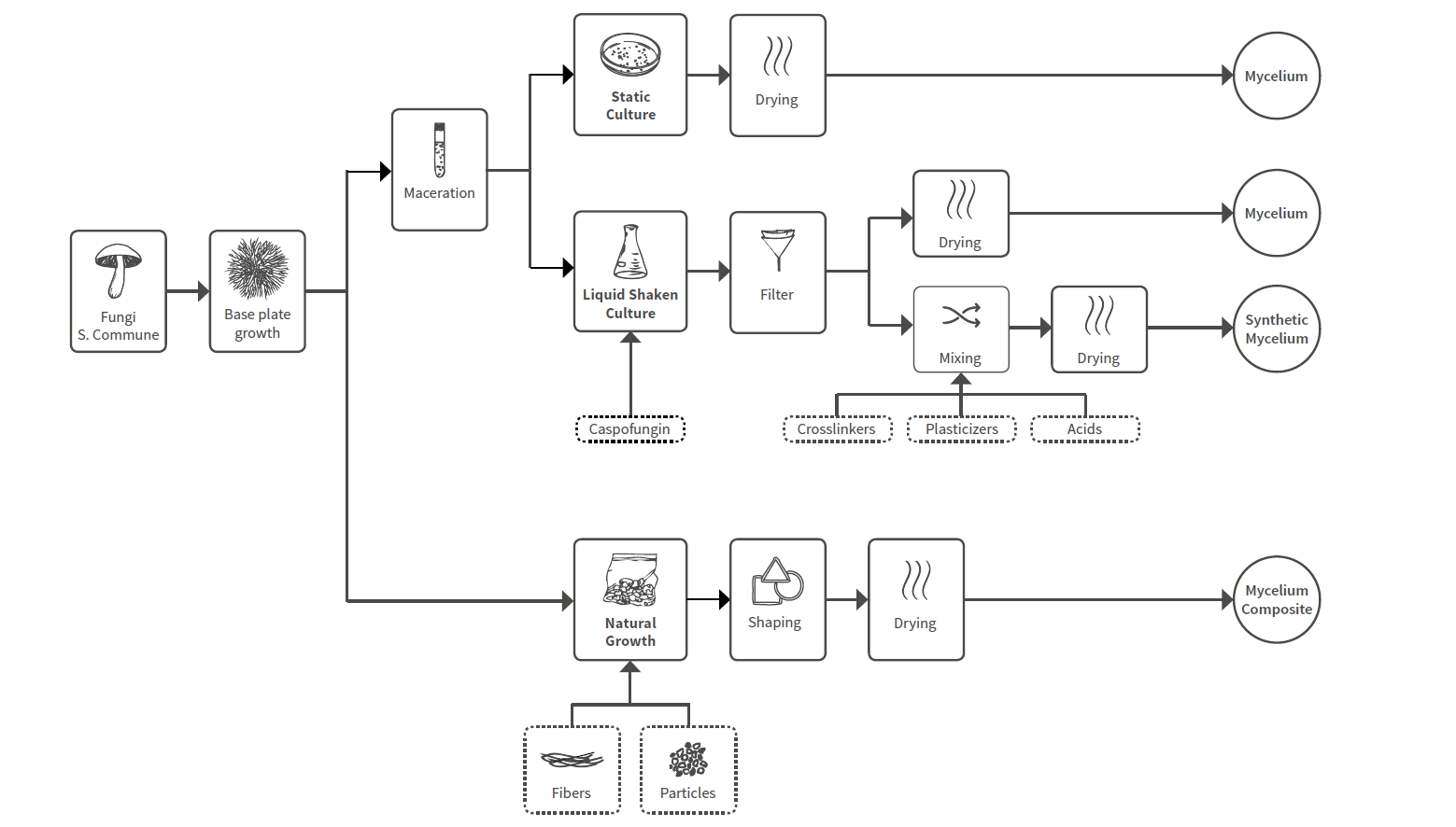
The production of mycelium composites.
Blauwhoff, D. (2016). Mycelium based materials, a case on material driven design and forecasting acceptance. Retrieved from http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:6851aae6-9a46-410f-9f75-91a547770c50
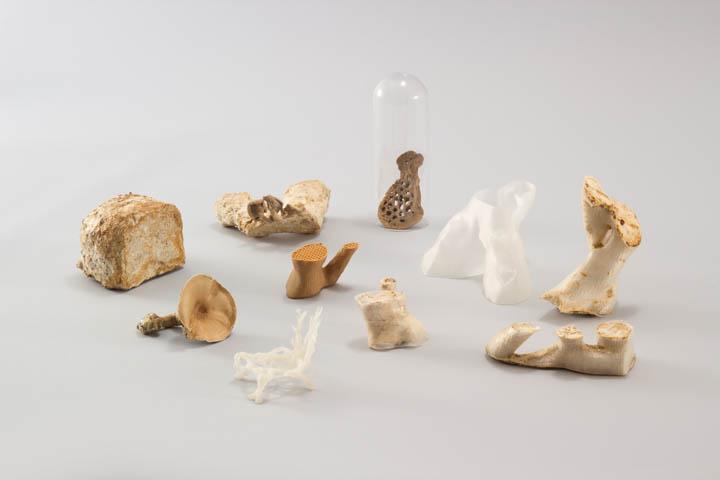
Other useful fungi applications
Various useful fungi applications
Material Cycle
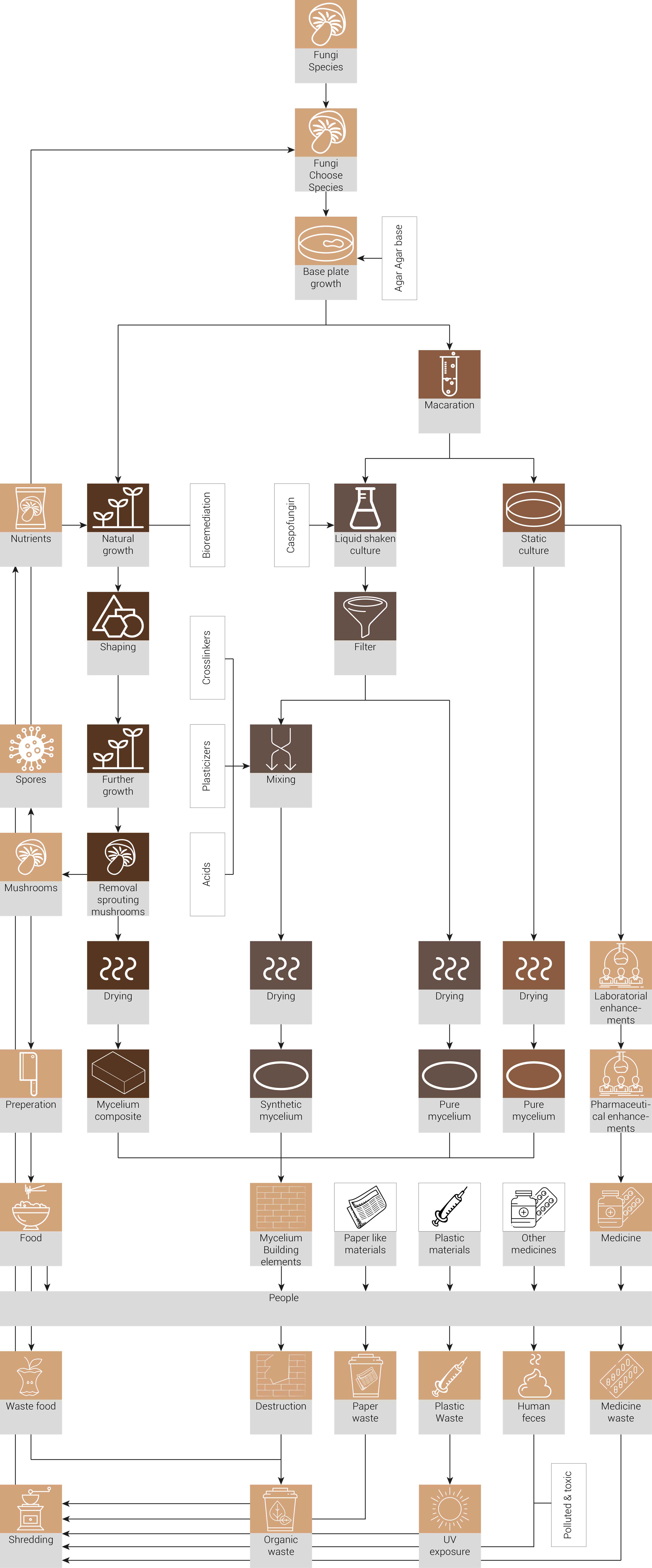
The material cycle proposed for within the AMC
Own image based on Blauwhoff, D. (2016). Mycelium based materials, a case on material driven design and forecasting acceptance. Retrieved from http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:6851aae6-9a46-410f-9f75-91a547770c50
Computational strategy
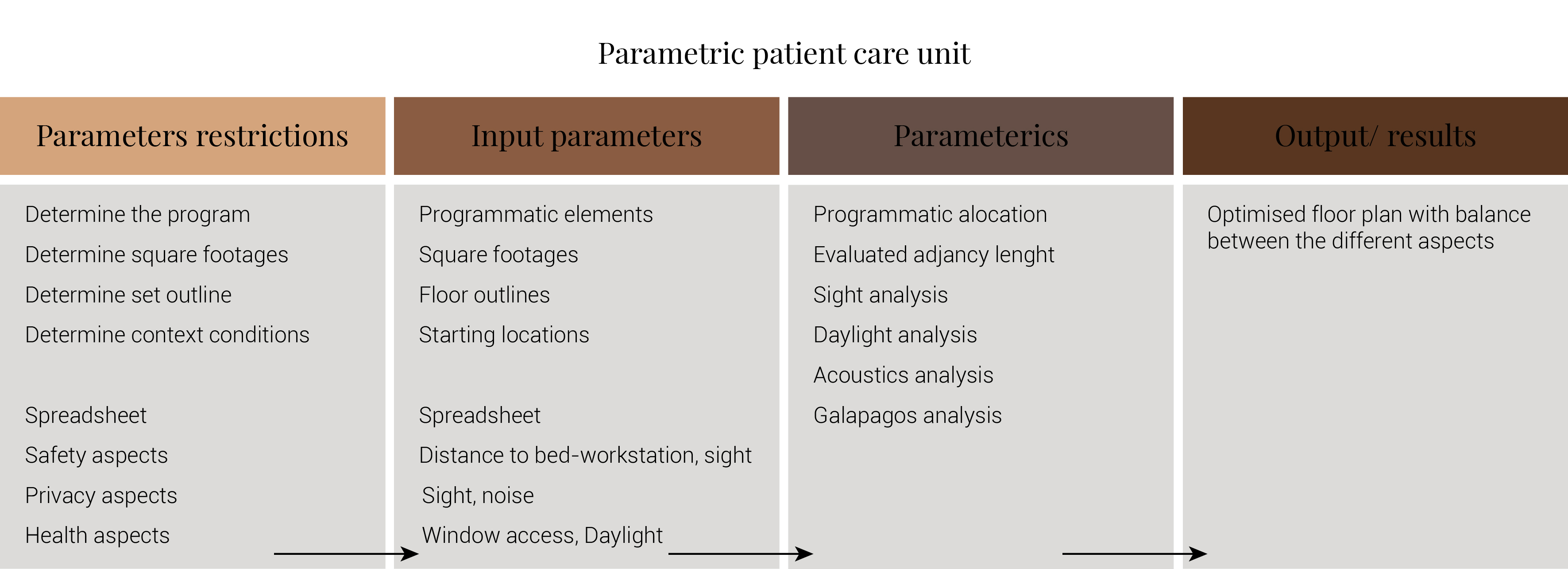
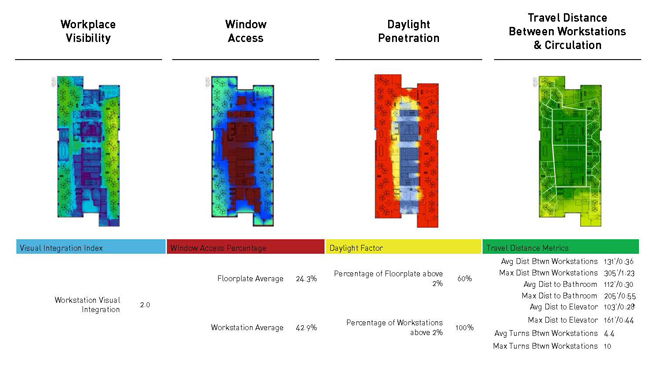
The design of a hospital is very complicated. A hospital is a agglomeration of many different functions and there for very difficult to design manually with focus on the effectiveness of the layout. There for I would like to do an adjancy analysis to optimize the distance between various hospital functions. Therefor I will develop a matrix of all the discrete programmatic elements required for the AMC. The matrix forms a hierarchy of space in terms of priority and ranks the adjacency requirement of each element in relation to all other elements in the chart. The main construction and streets will be form the boundries for the adjancy analysis. The optimization through galapagos should therefor result in a collection of various masses with the least adjaceny.
https://www.christopherboon.com/adjacency
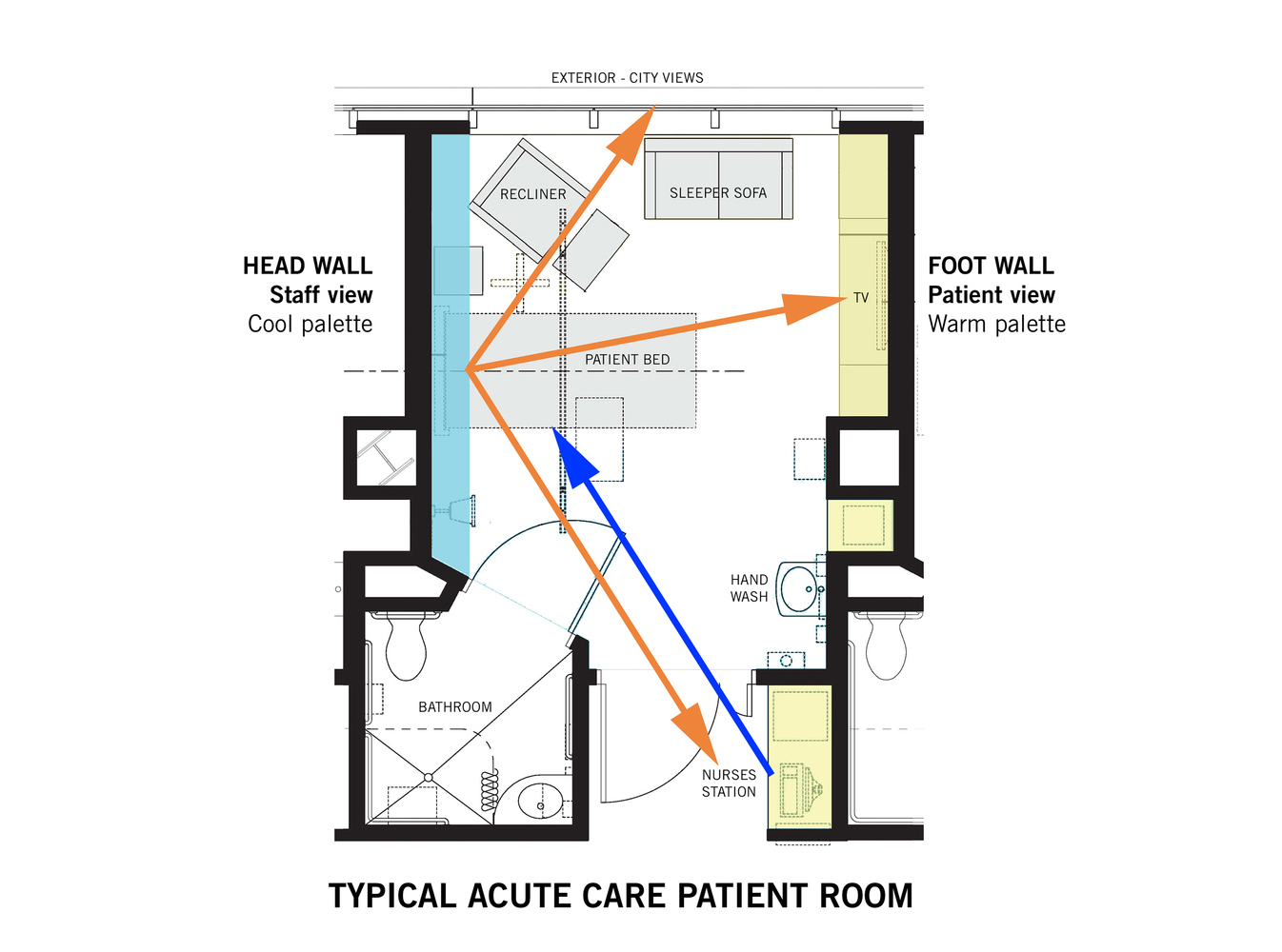
When it comes to the patient room the computational strategy is different. Here it focusses on the aspects of safety, privacy and regeneration through the minimalising acoustics, the optimasation of visual connectiveness and bed work station distance.
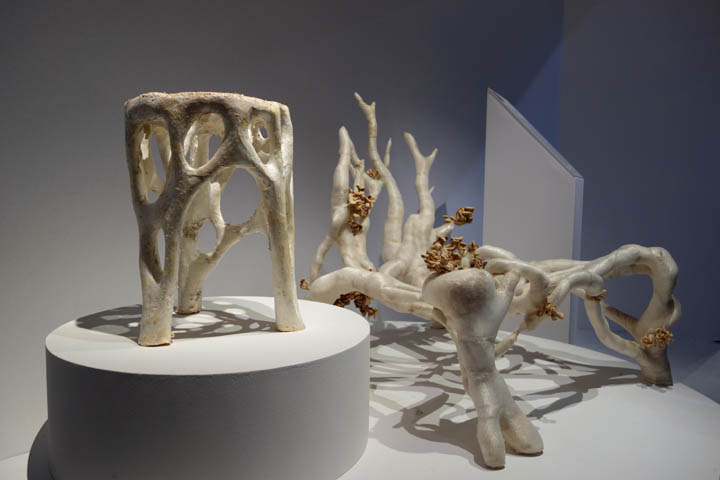
When the form of the patient care unit has been determined. The structure will be divide into segments. Each of these segments will than be 3d printed and grown until a certain phase. Than these are cooled down to stop the growing proces. After the segments are printed, the fungi composite is once again warmed to startup the growing proces. Than the models are stack and joined through the fragment growth. This forms the designed patient room. When this is build, patient data is monitored to if the patient room works as it is supposed to work.
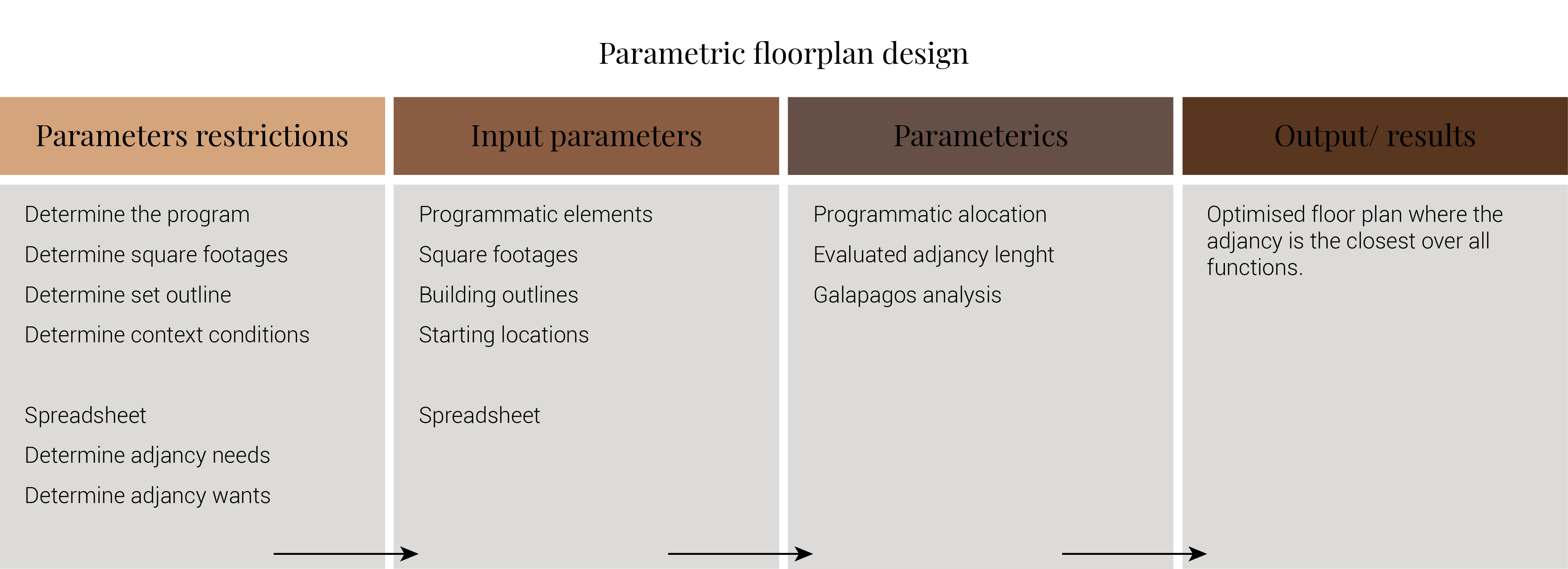
Example by Christopher Boon

References
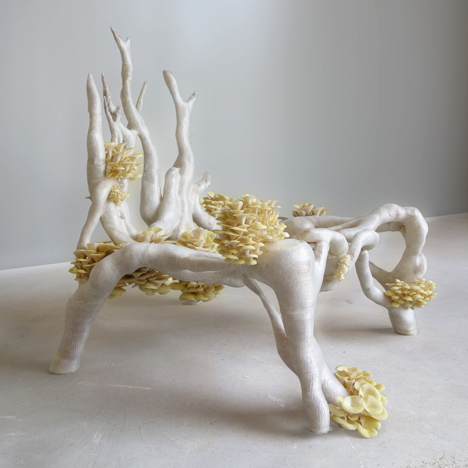
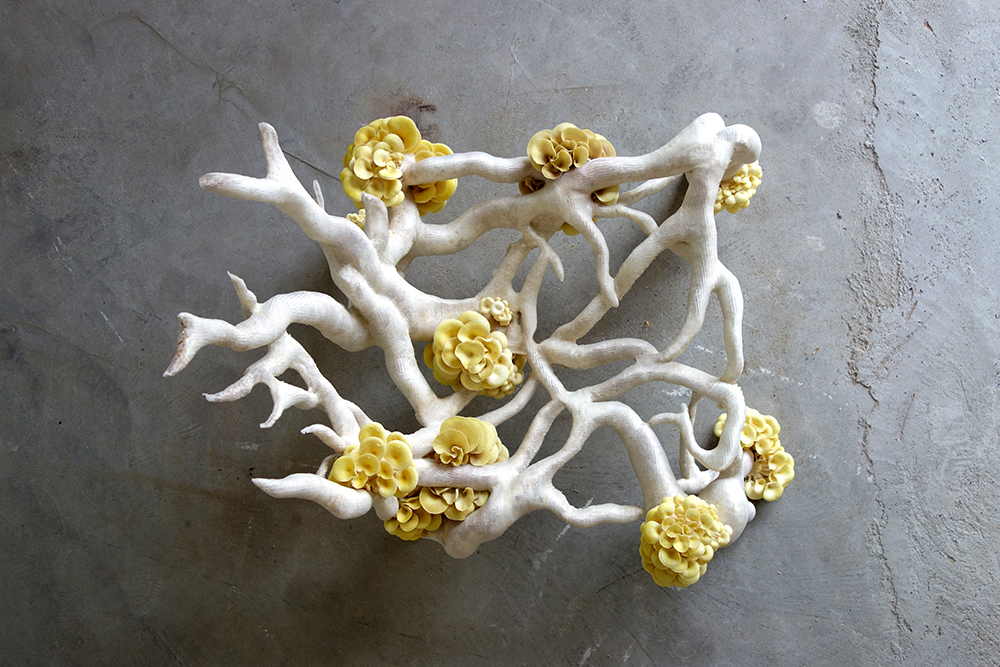
Veiled Lady 2.0 - Studio Eric Klarenbeek
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found on their own respective websites
Klarenbeek, E. Veiled lady. Retrieved from http://www.ericklarenbeek.com/
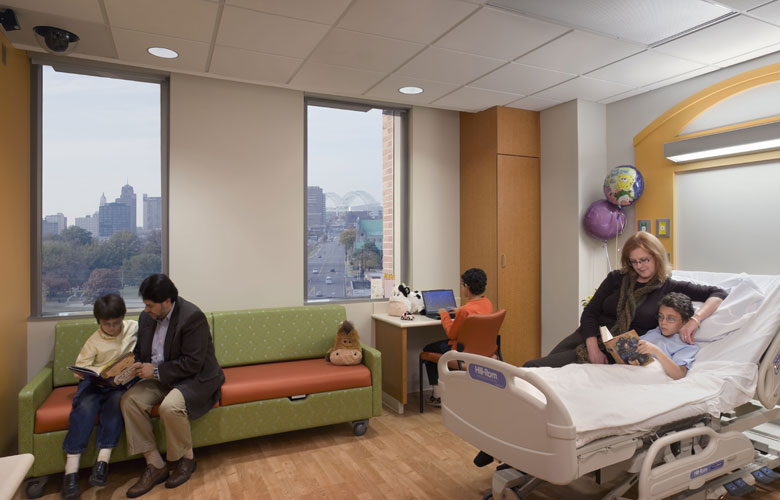
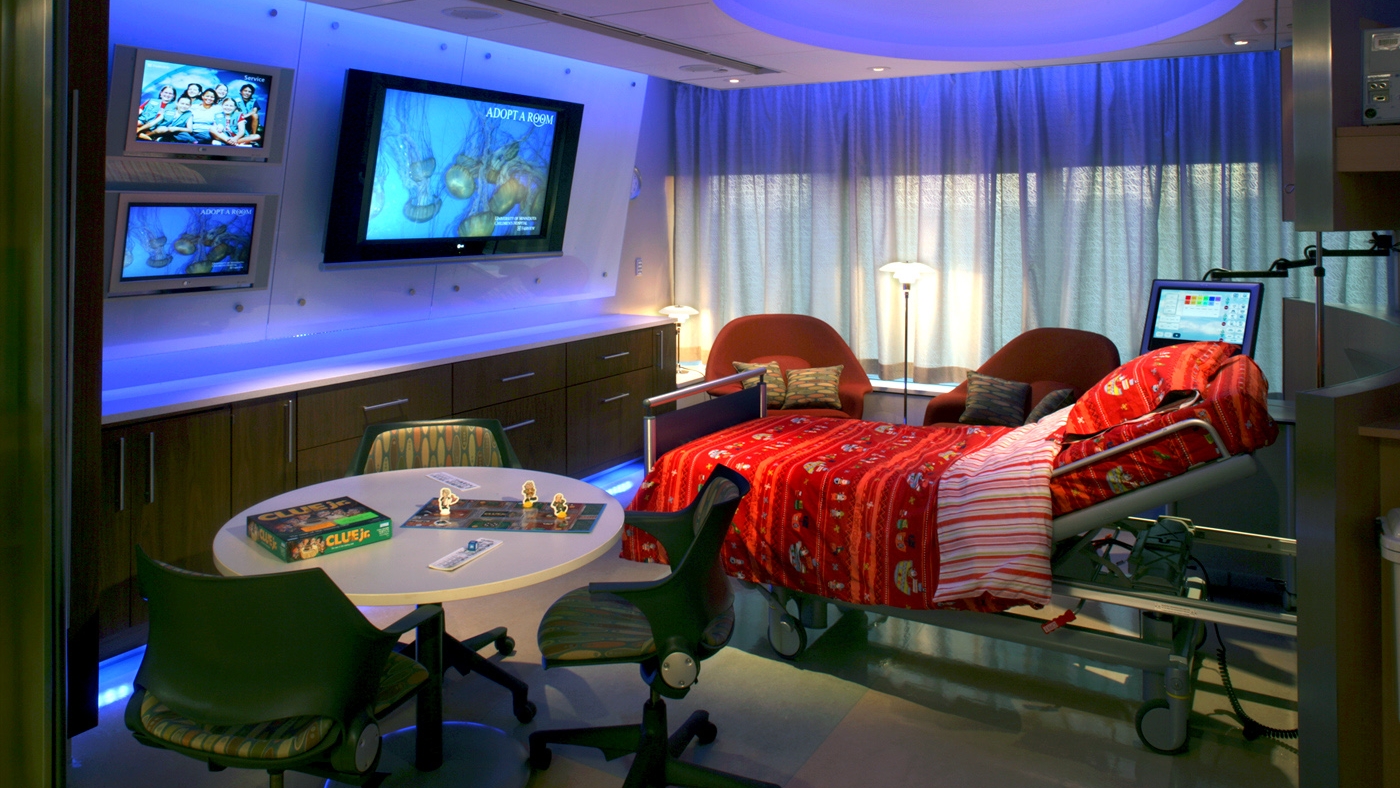
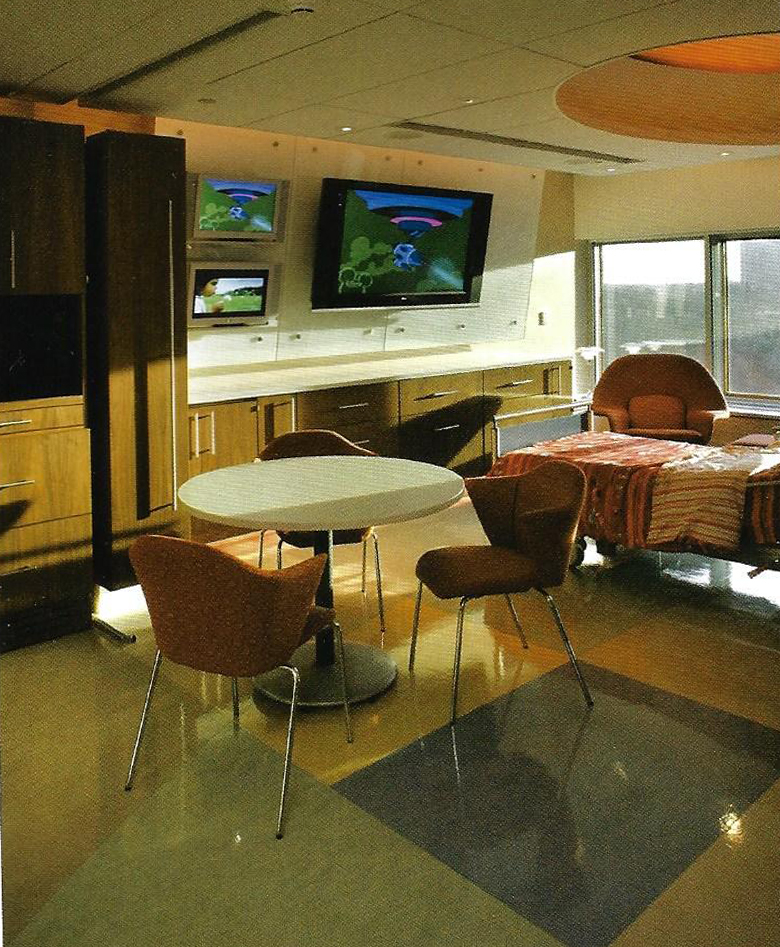
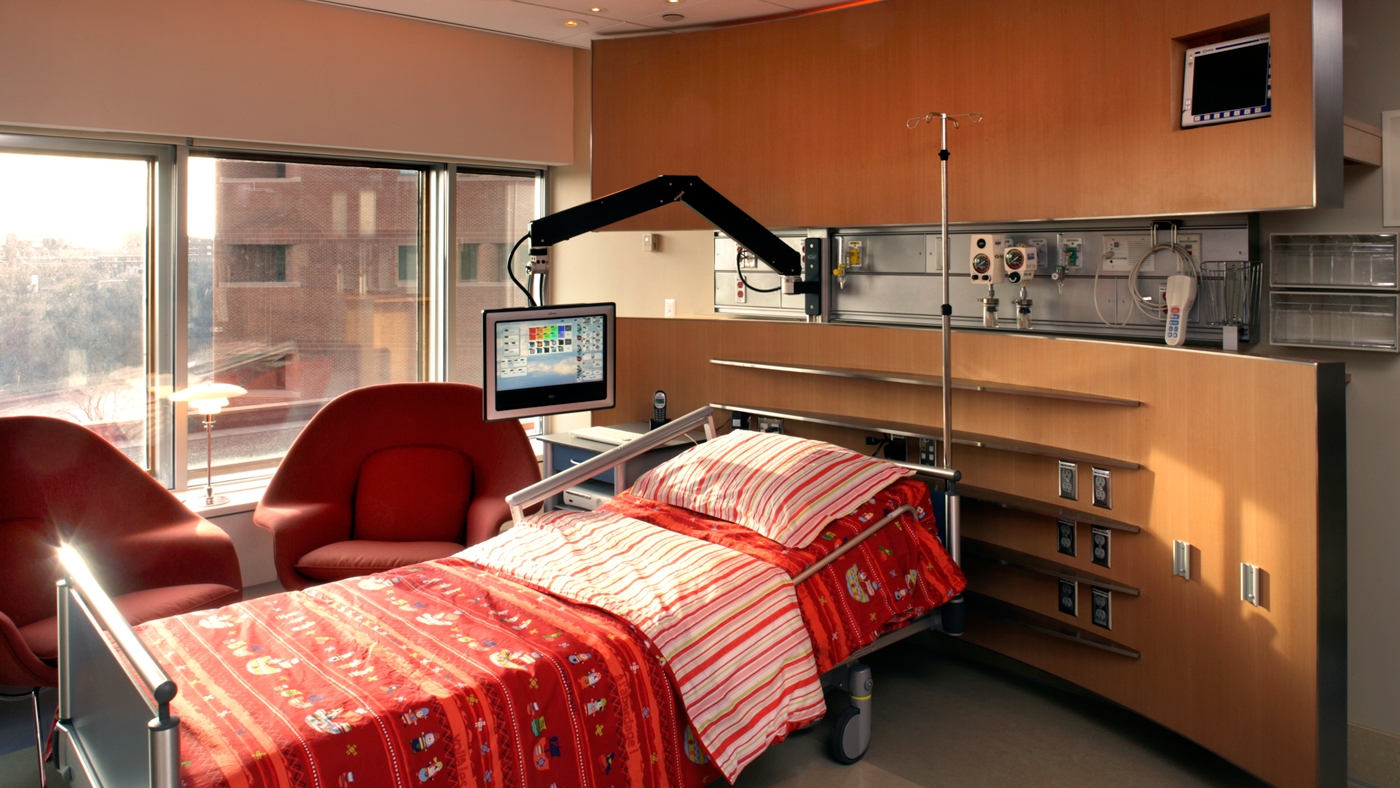
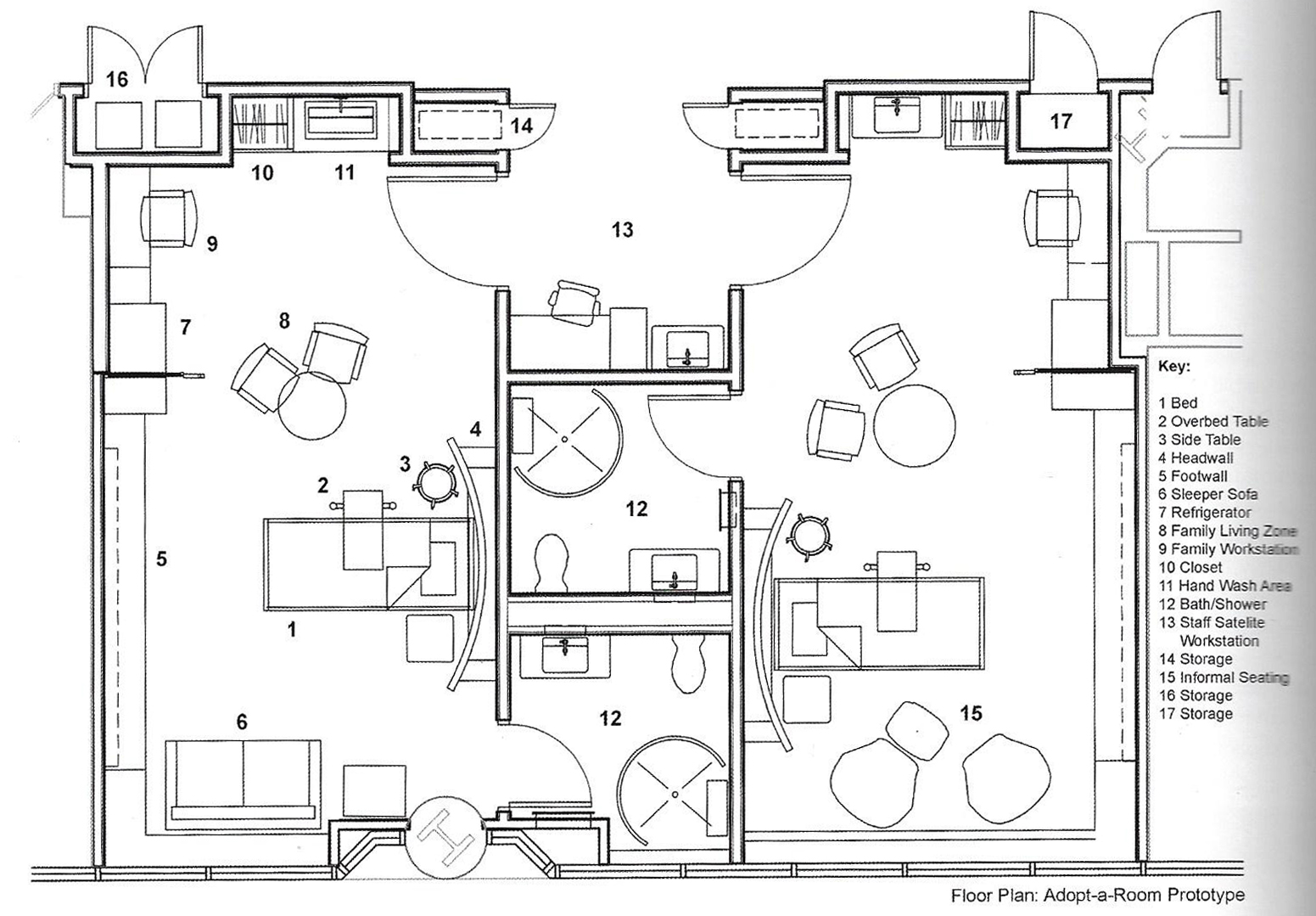
Adopt a room, Minnesota Children's hospital - Perkins+Will
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found on their own respective websites
University of Minnesota Children's Hospital, Fairview, Adopt A Room [Photo]. (2018, 30 januari). Retrieved 1 April 2019, van https://perkinswill.com/work/adopt-a-room.html
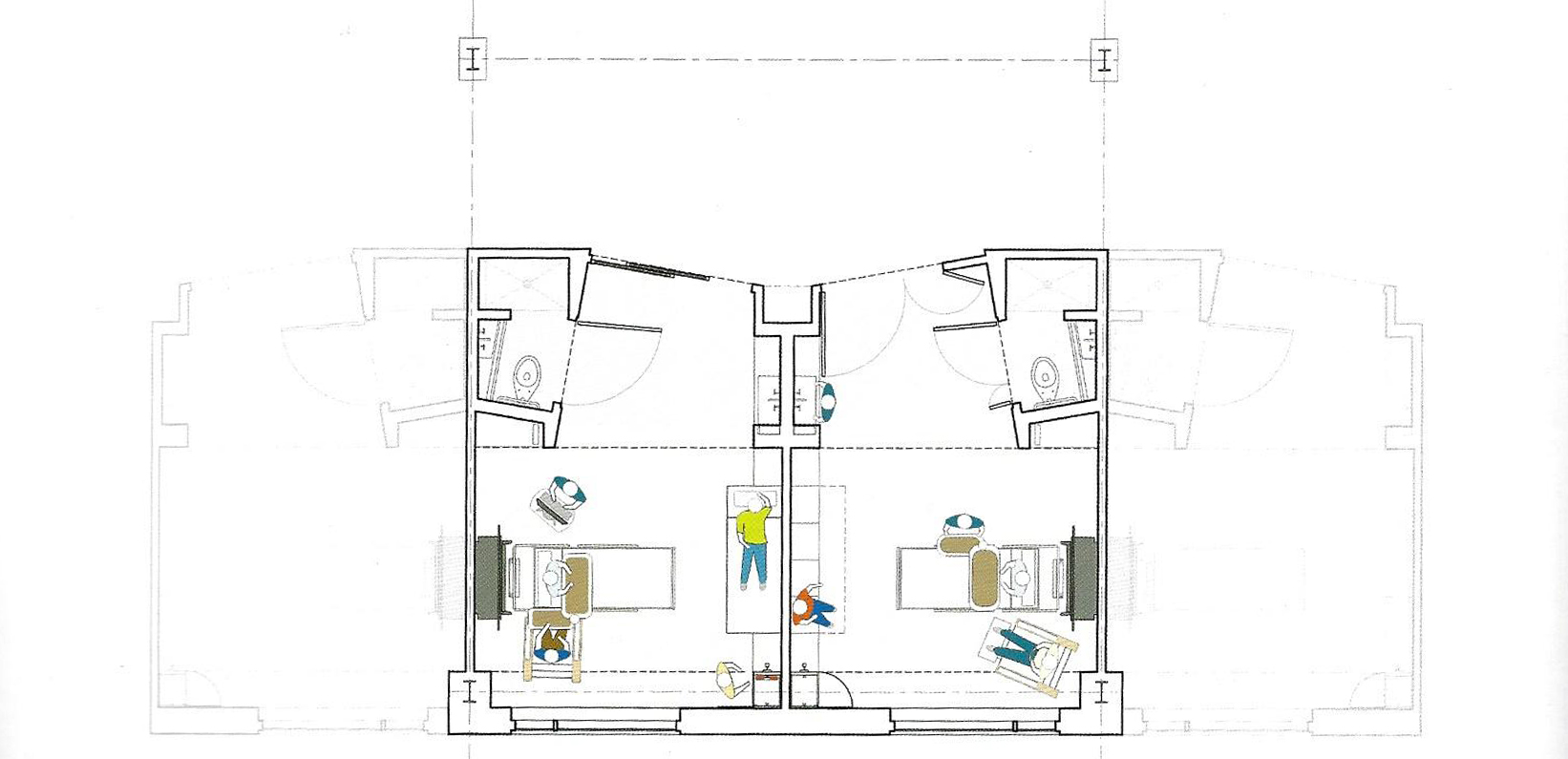
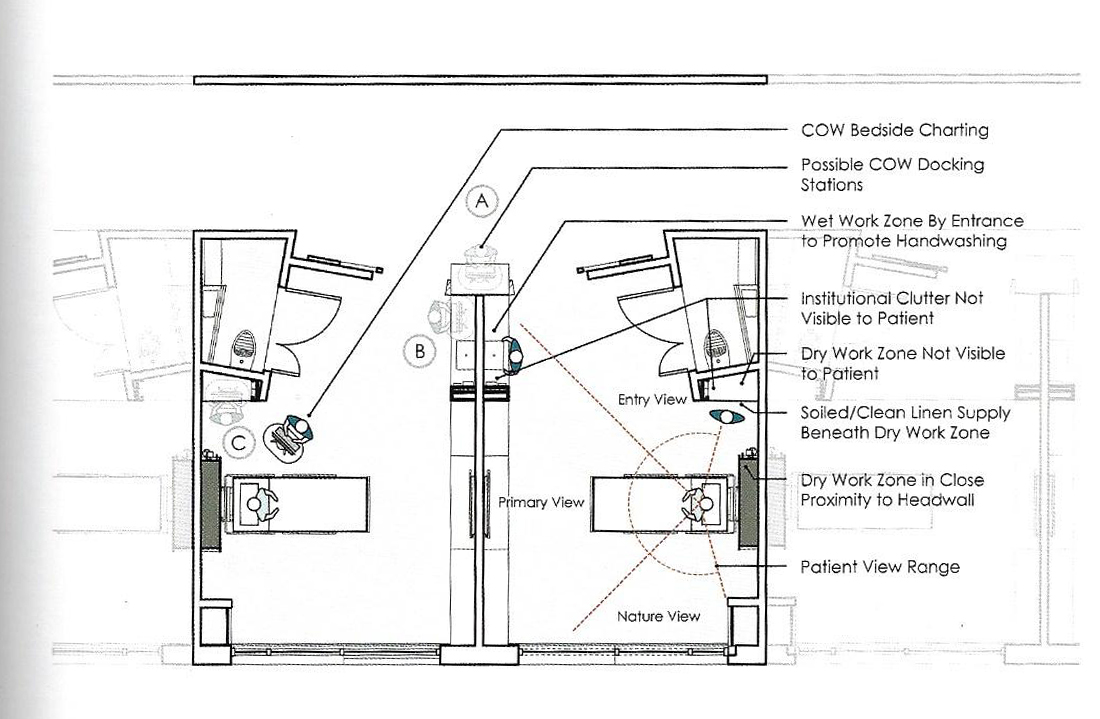
Research Spartanburg regional health care system - Clemson University
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found with in the following book.
Verderber, S. (2010). Innovations in Hospital Architecture. New York, United States of America: Taylor & Francis.
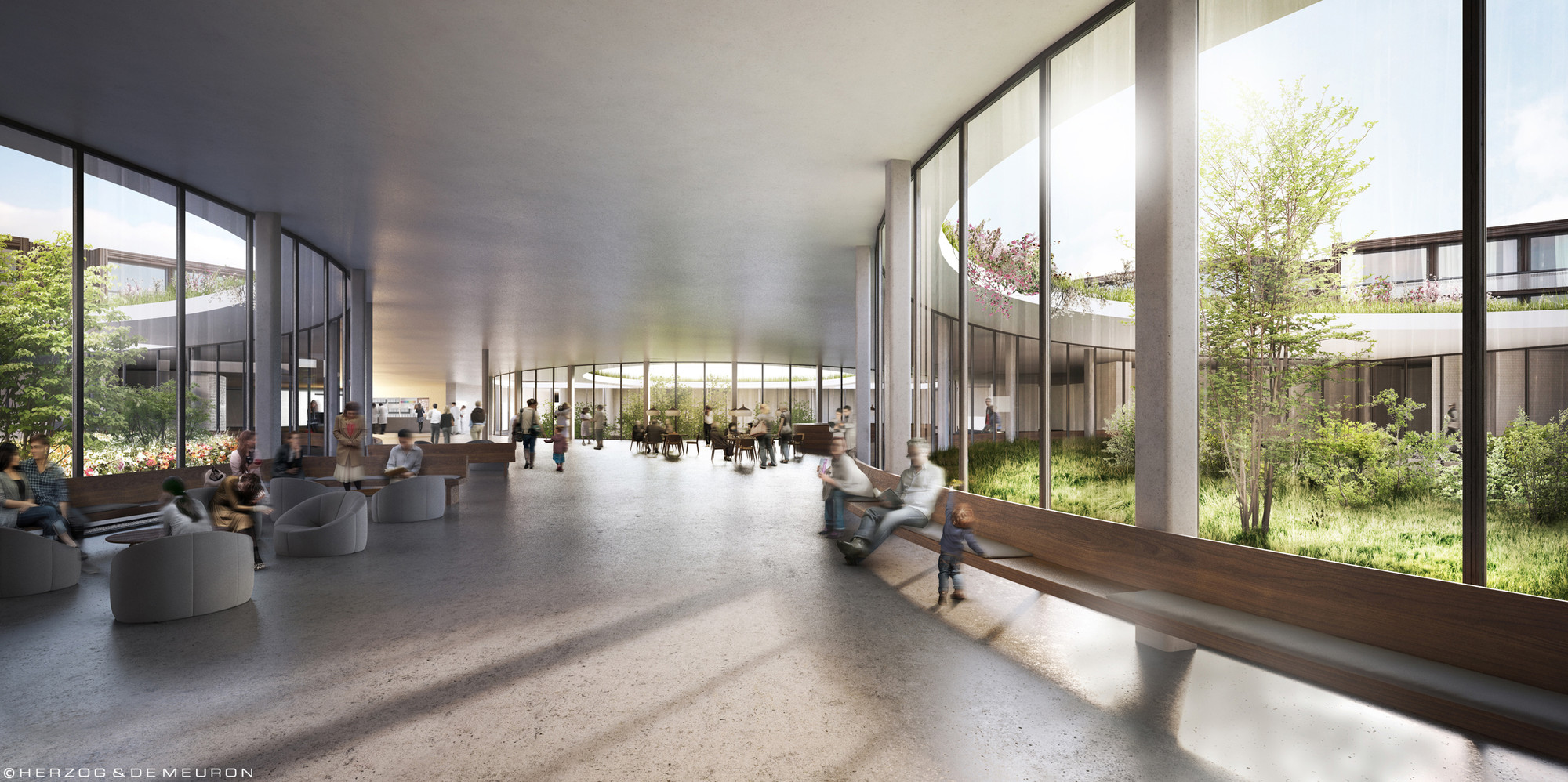
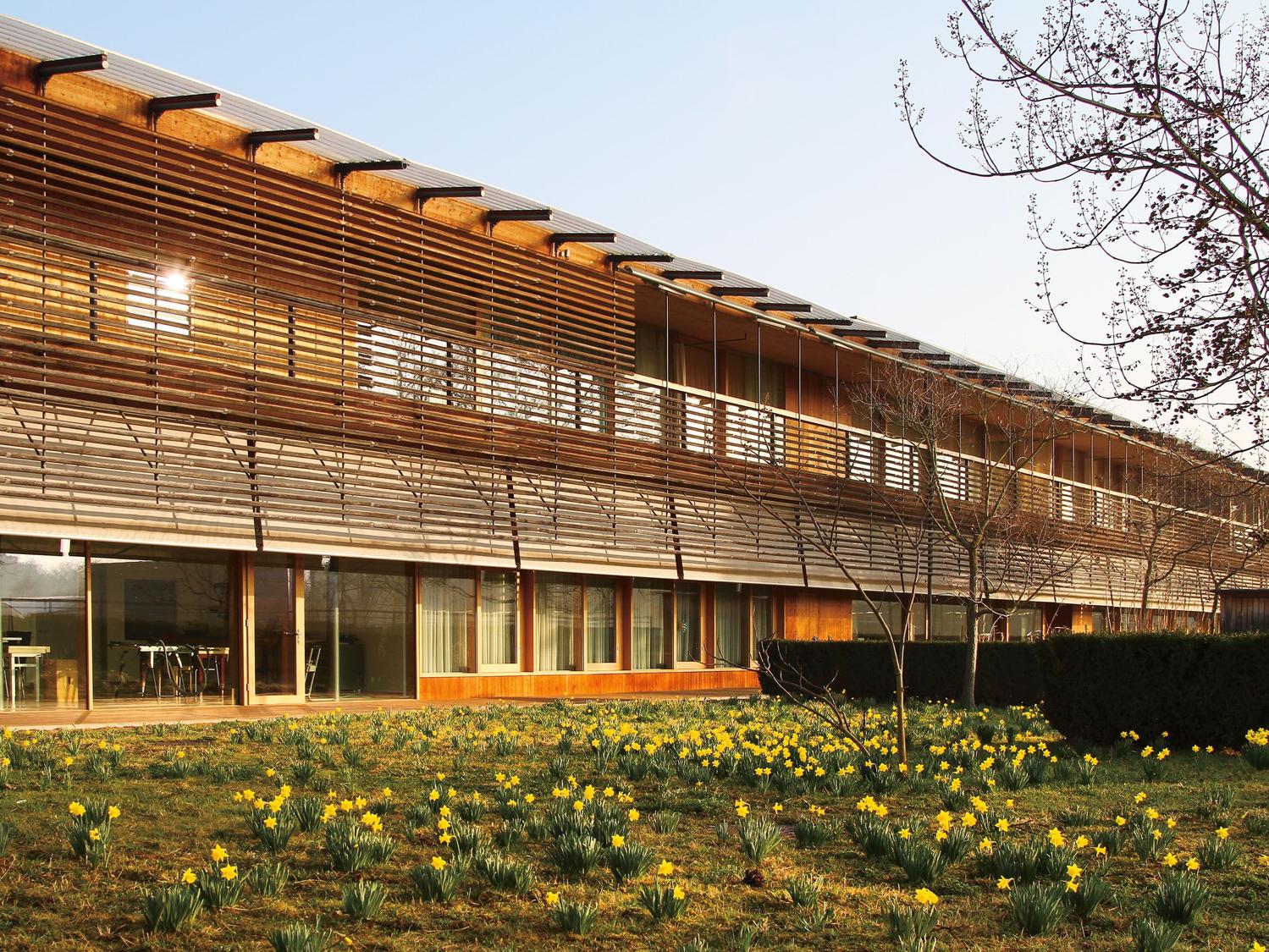
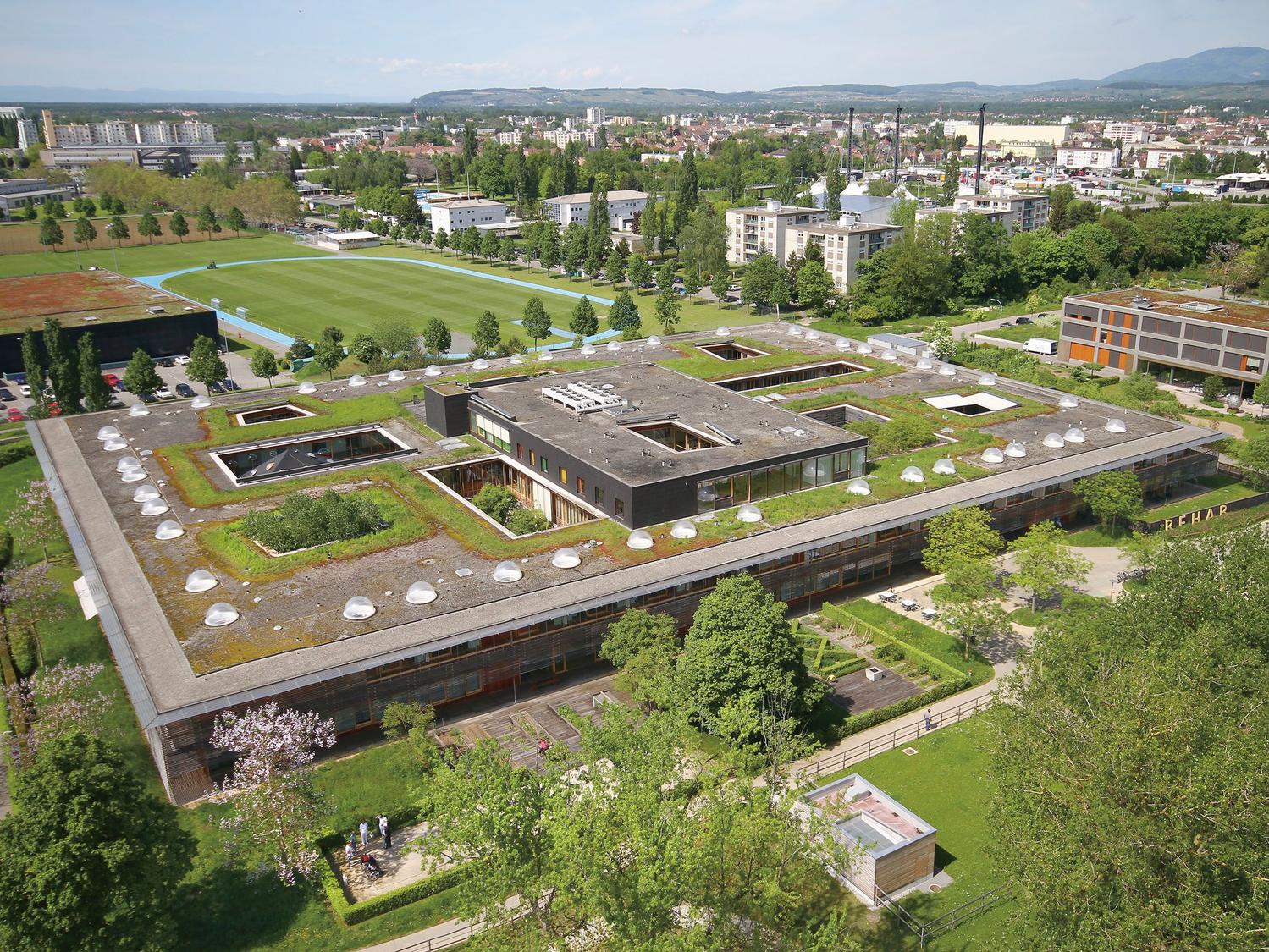
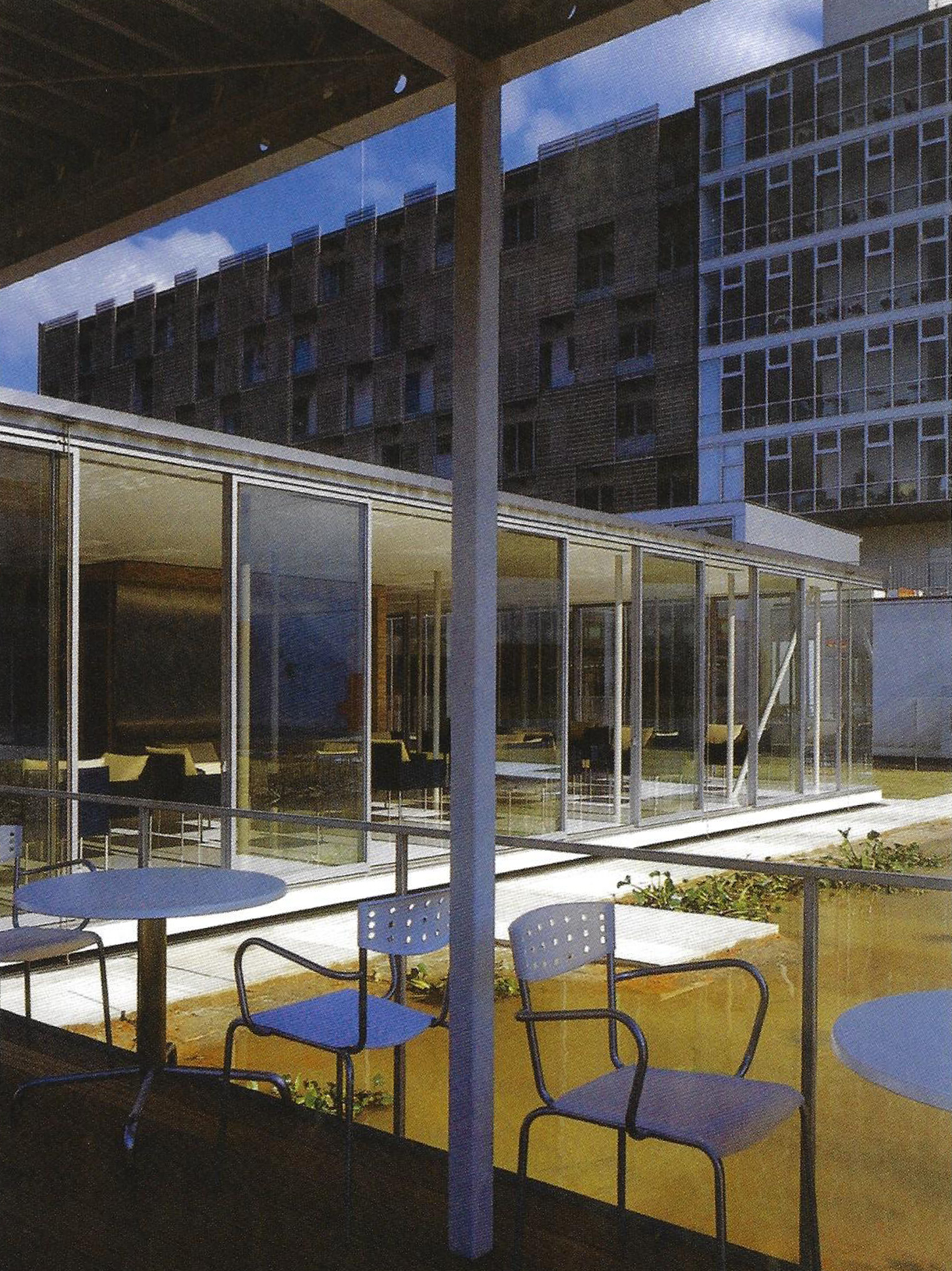
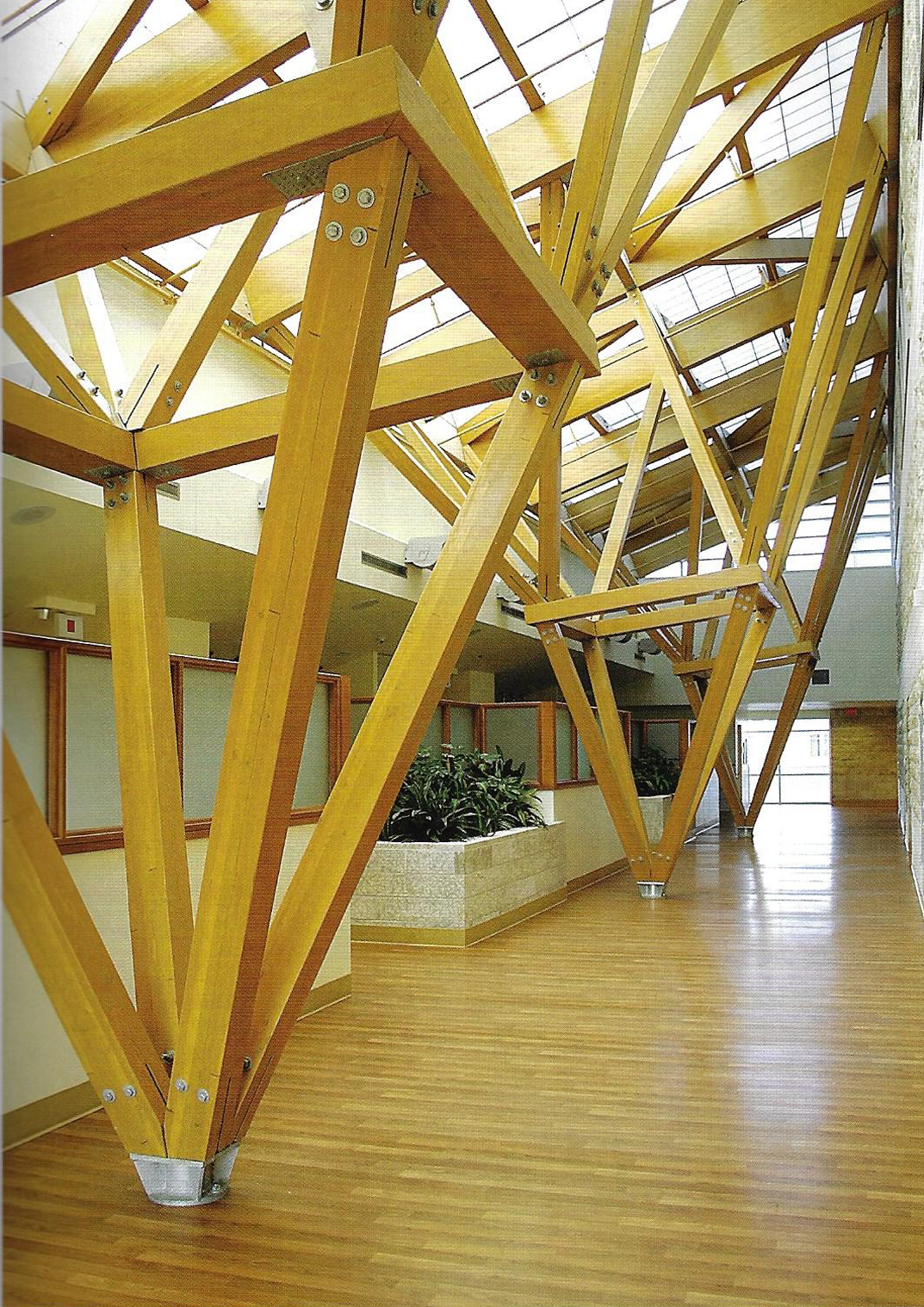
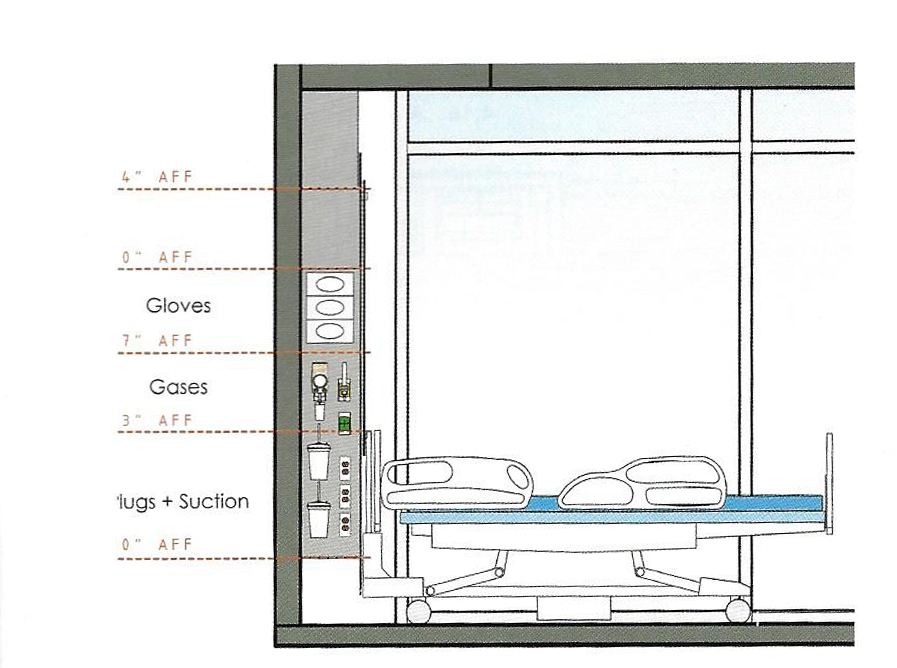
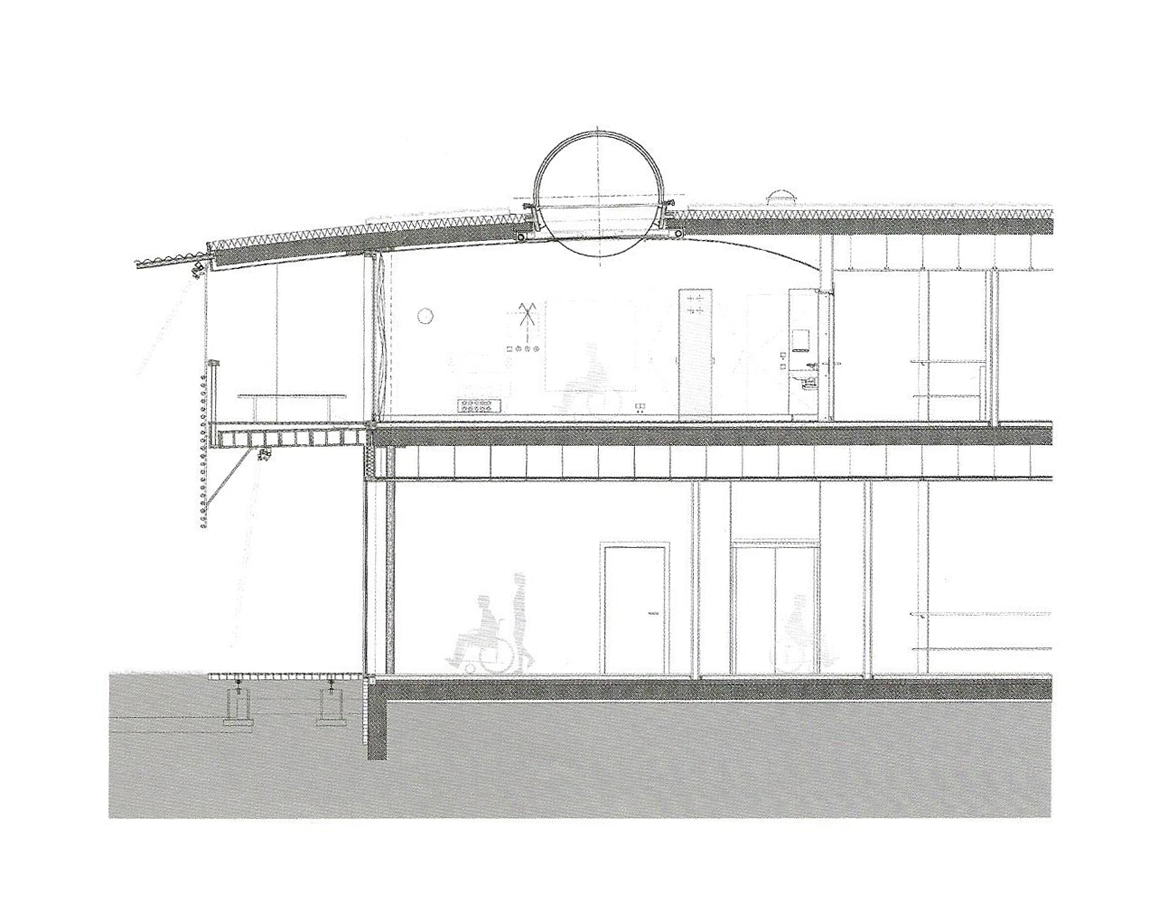
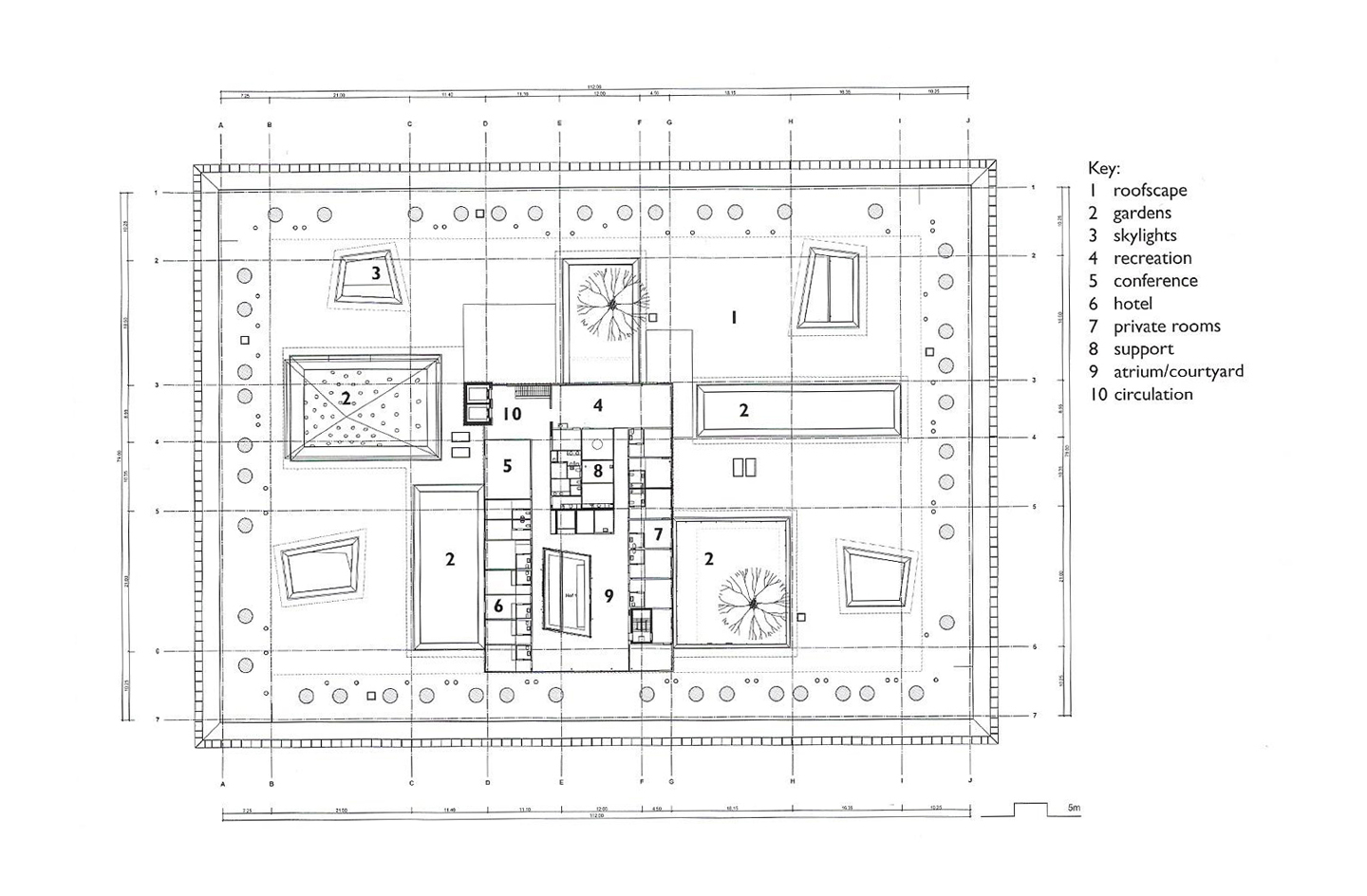
REHAB Basel centre for spinal cord and brain injuries - Herzog & de Meuron
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found with in the following book.
Verderber, S. (2010). Innovations in Hospital Architecture. New York, United States of America: Taylor & Francis.
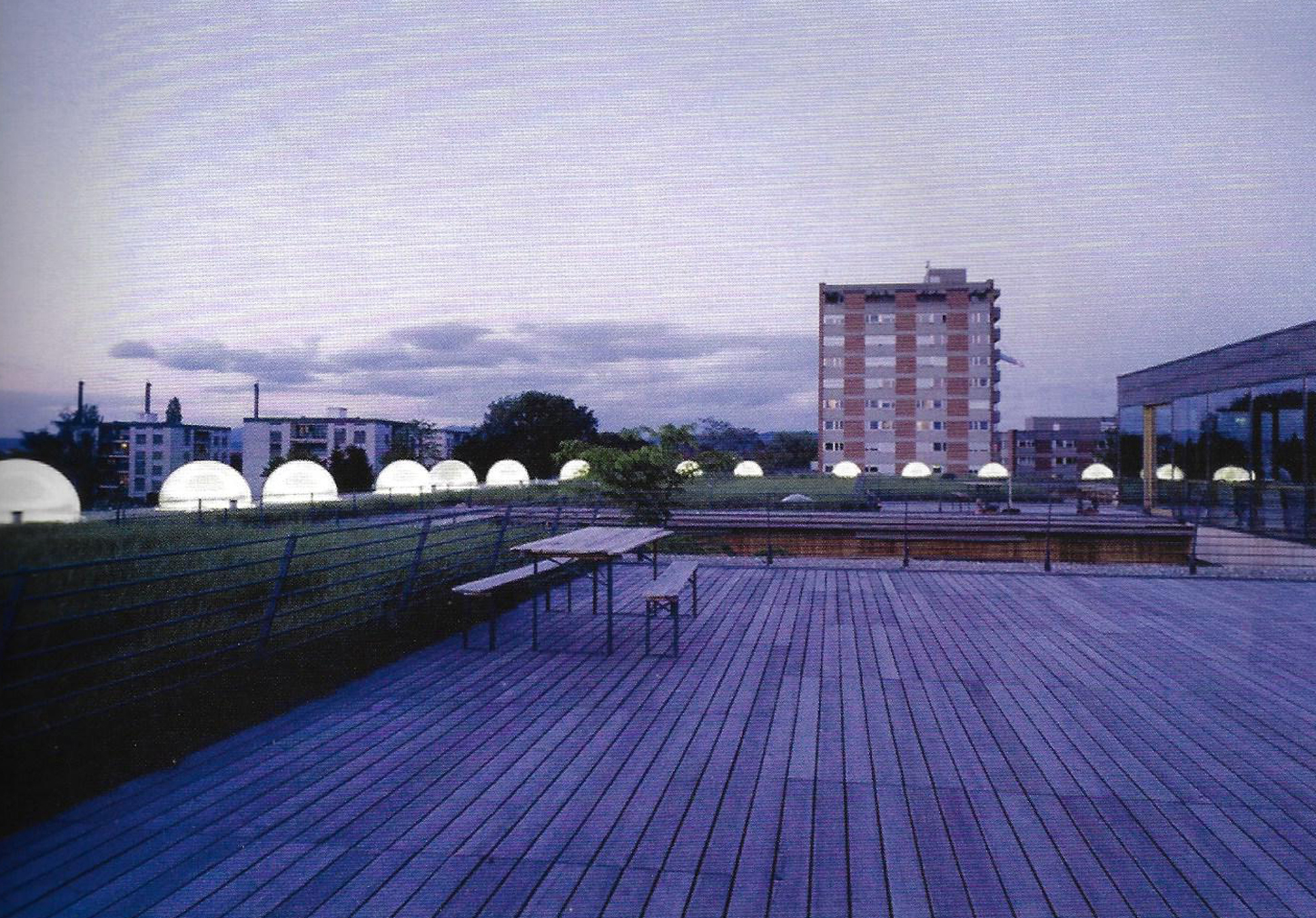
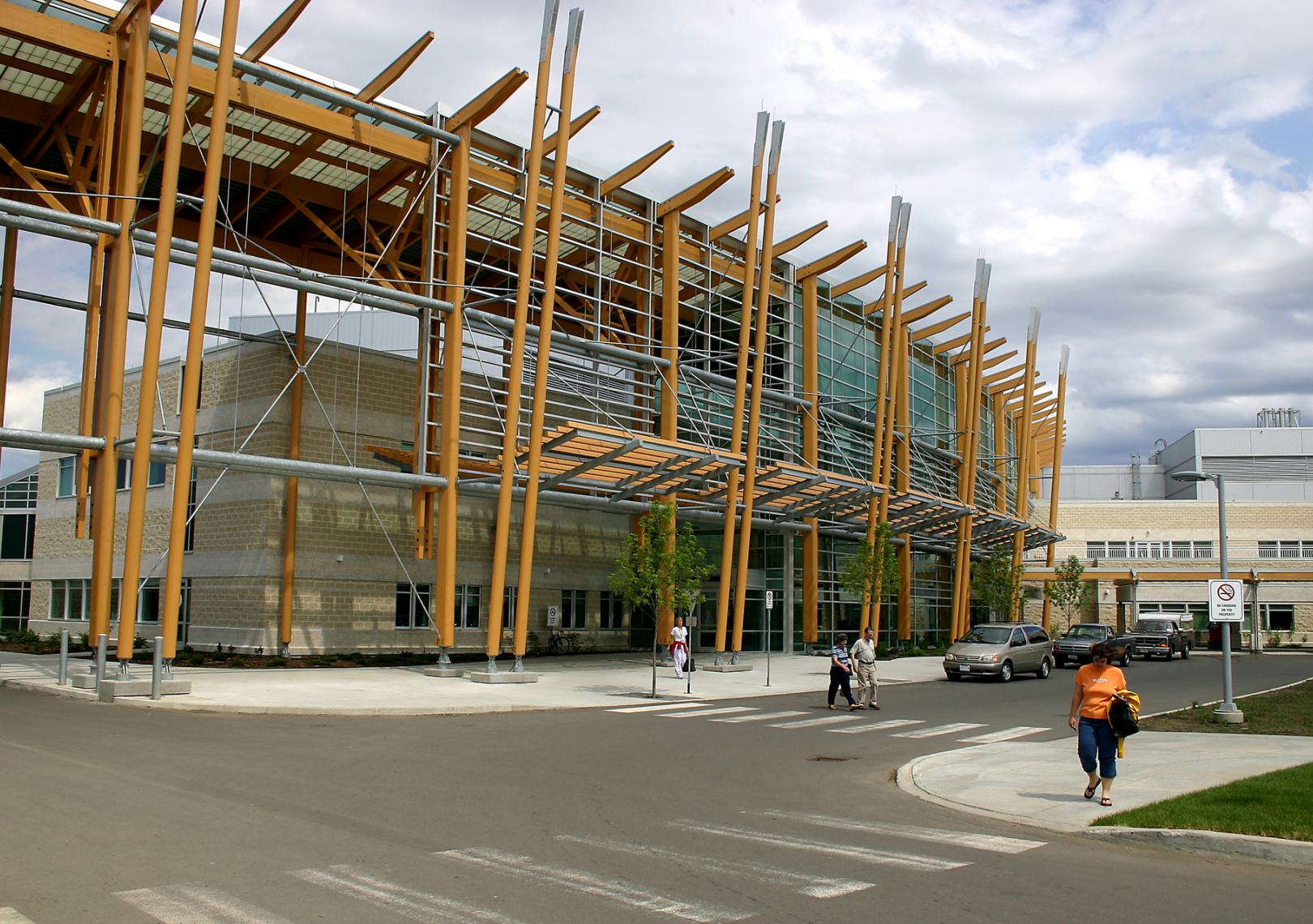
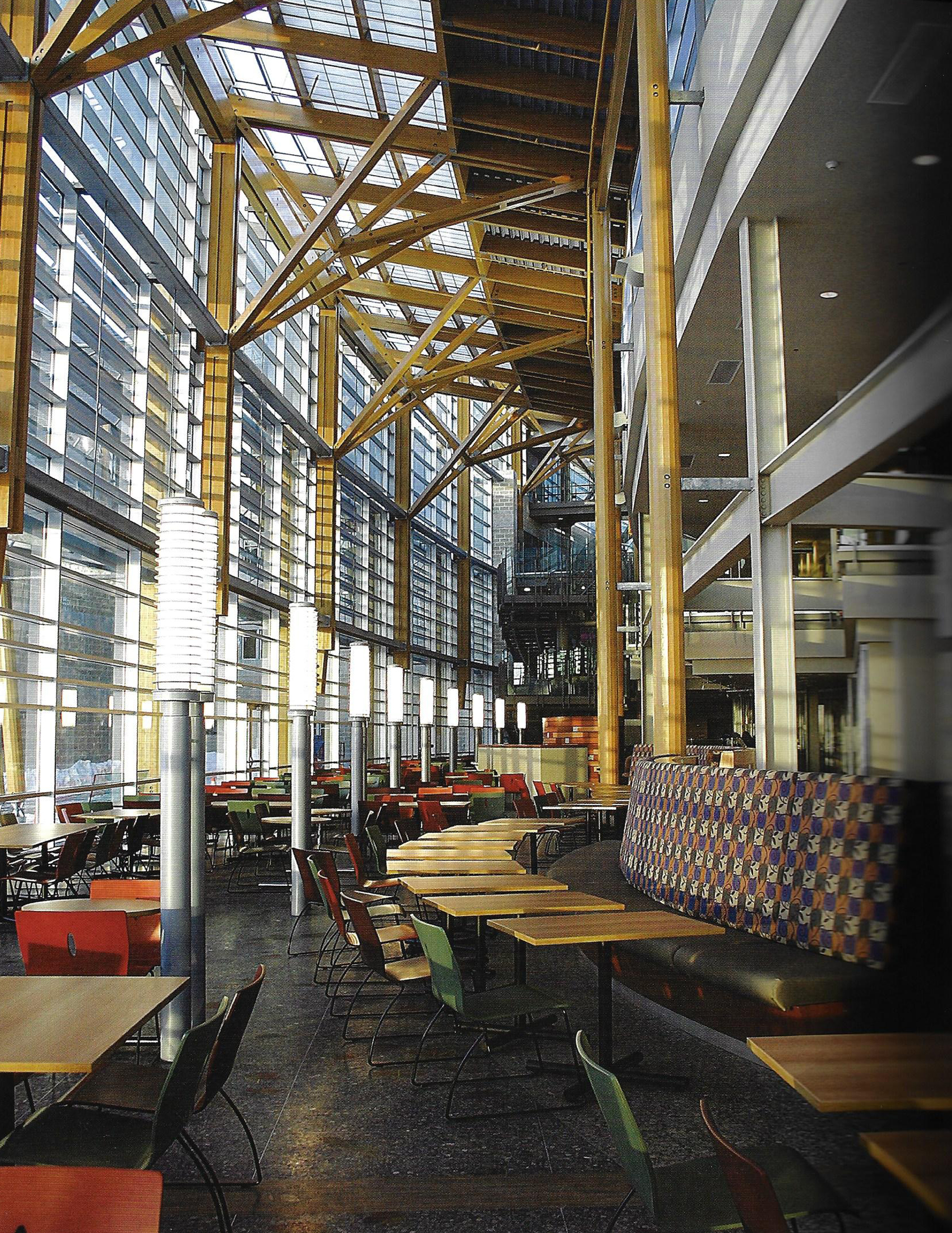
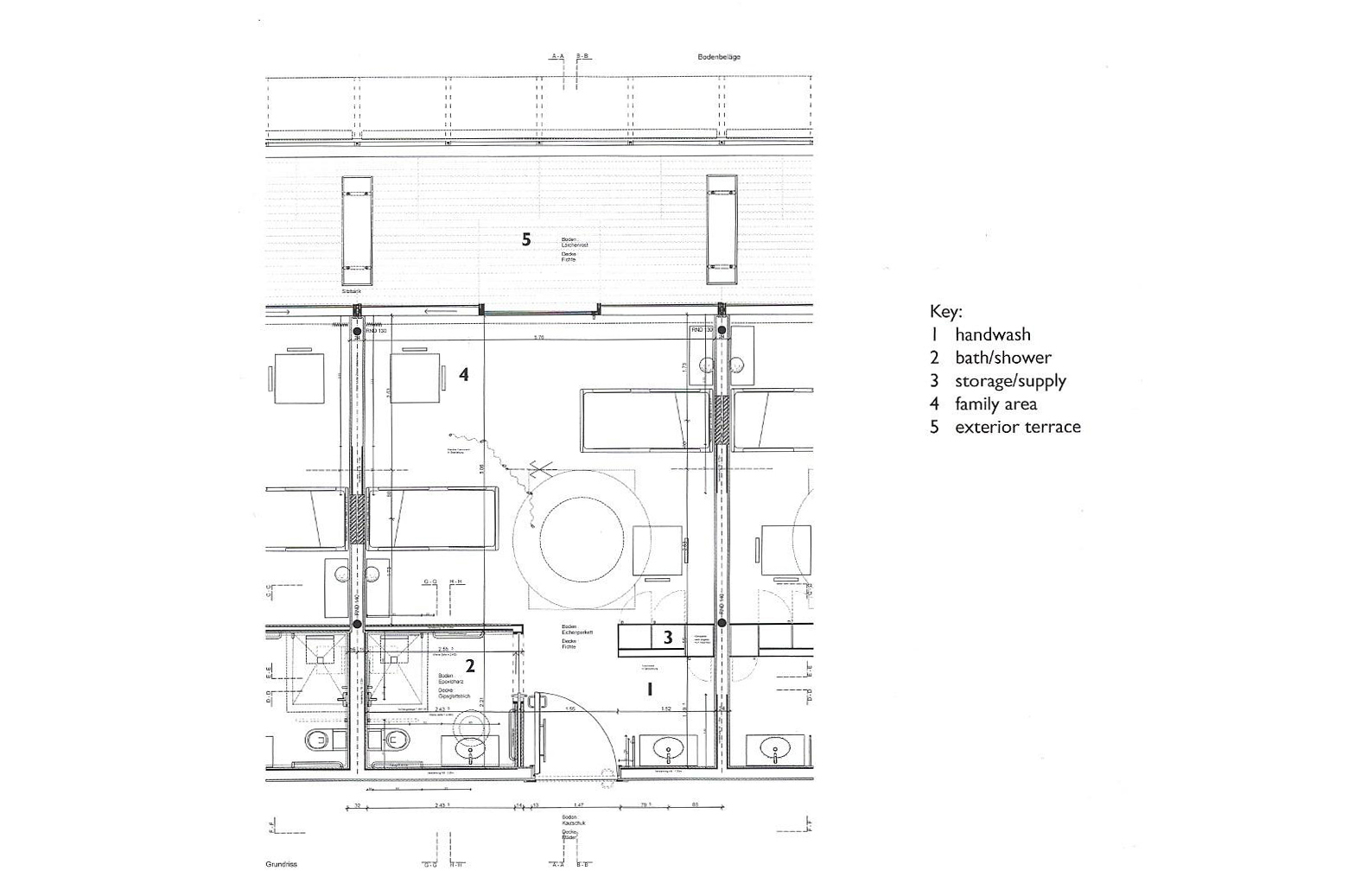
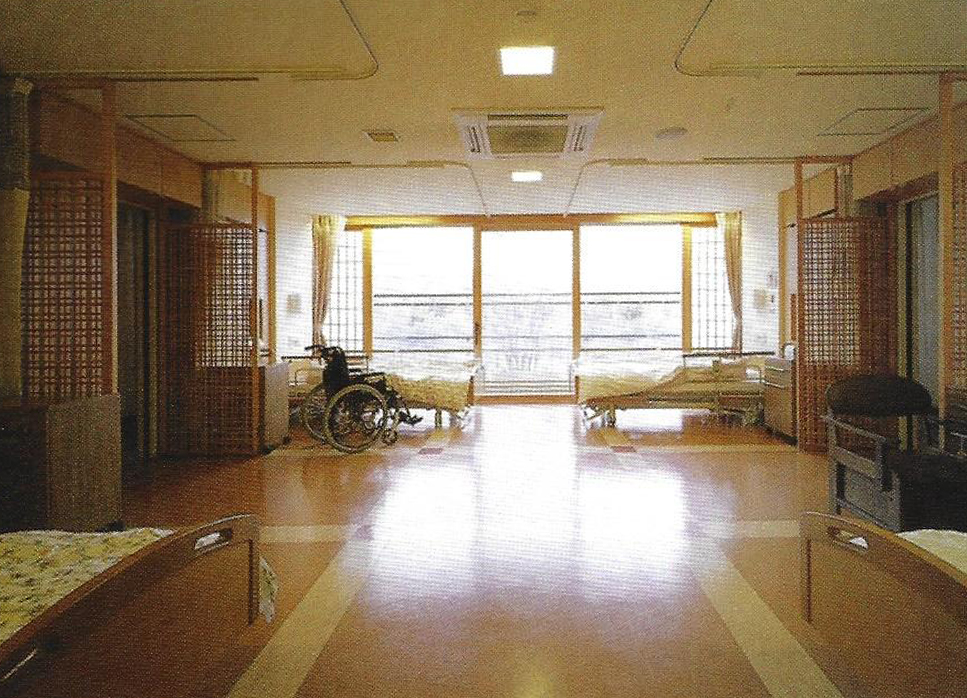
Kokura rehabilitation hospital - Yasui Masahiro and associates
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found with in the following book.
Verderber, S. (2010). Innovations in Hospital Architecture. New York, United States of America: Taylor & Francis.
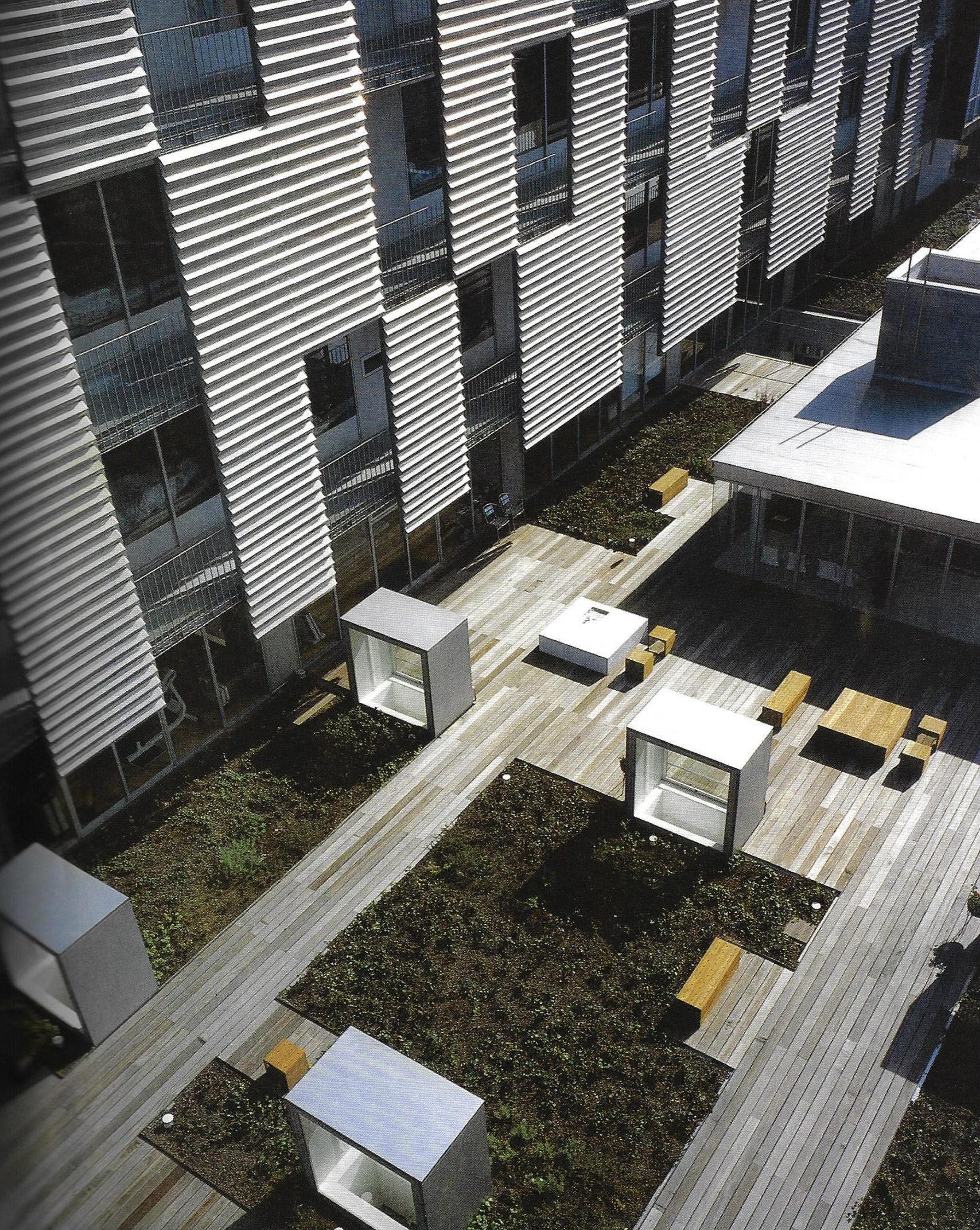
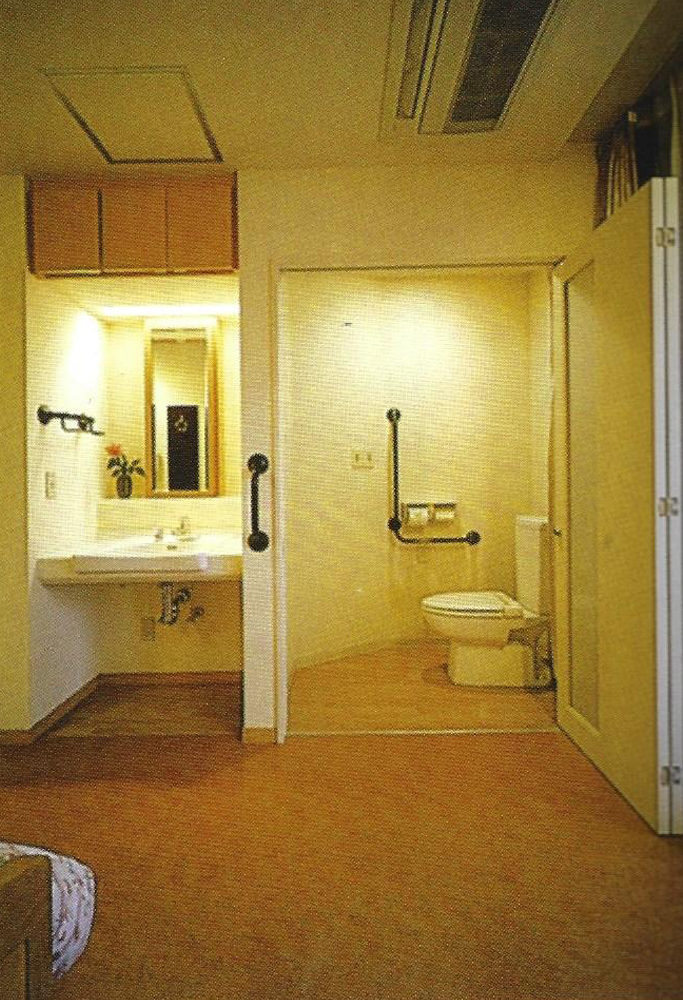
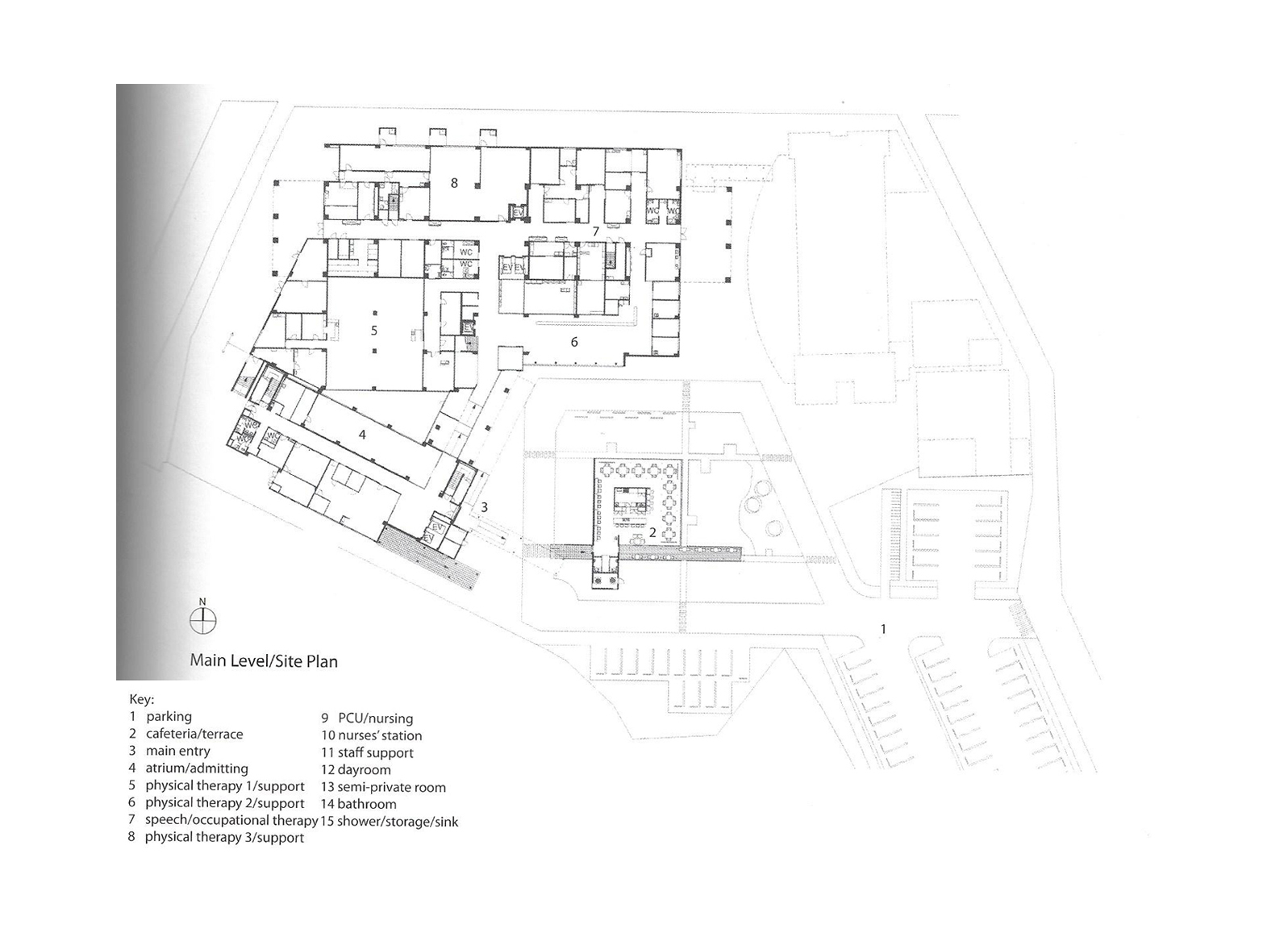
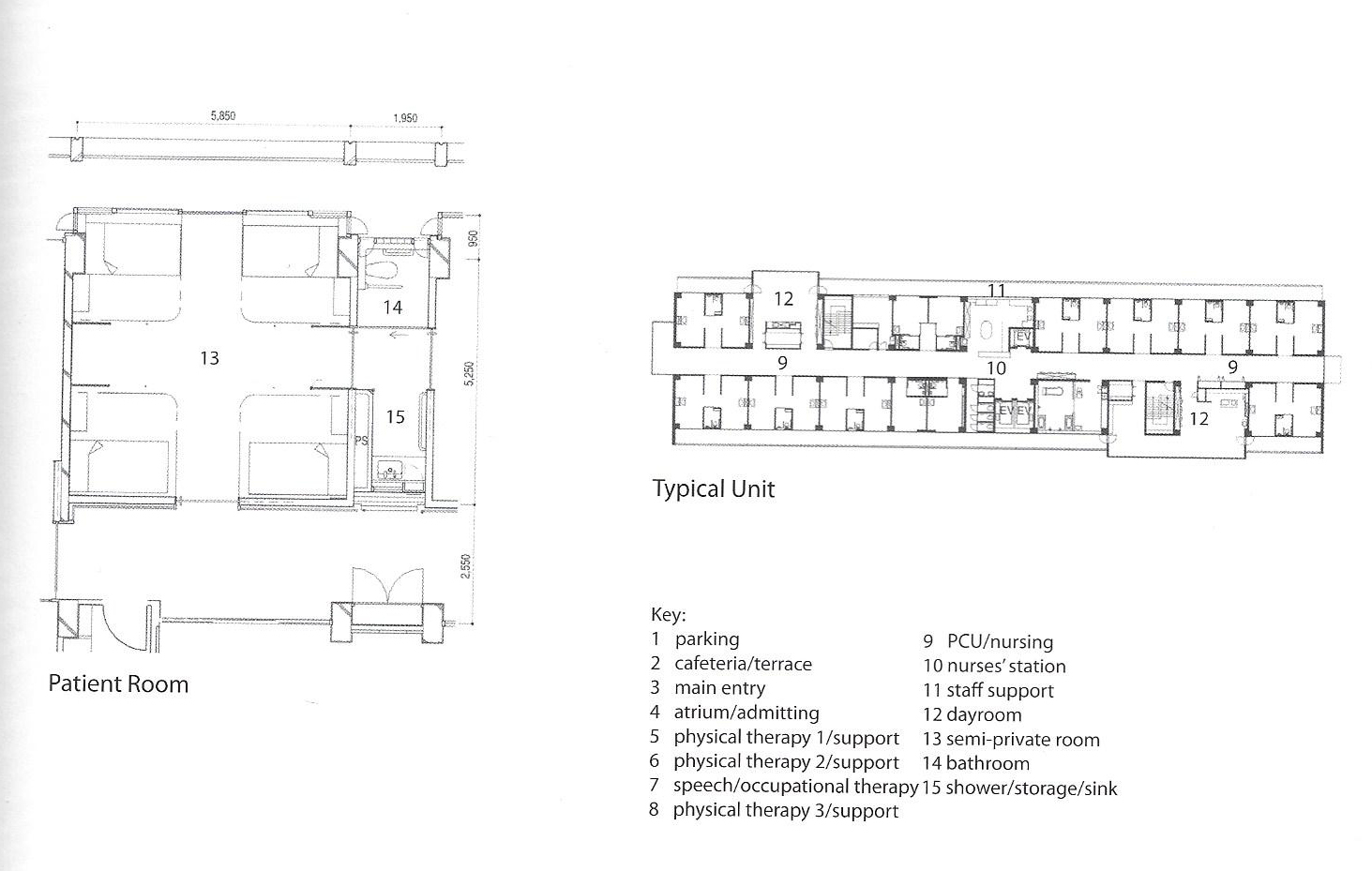
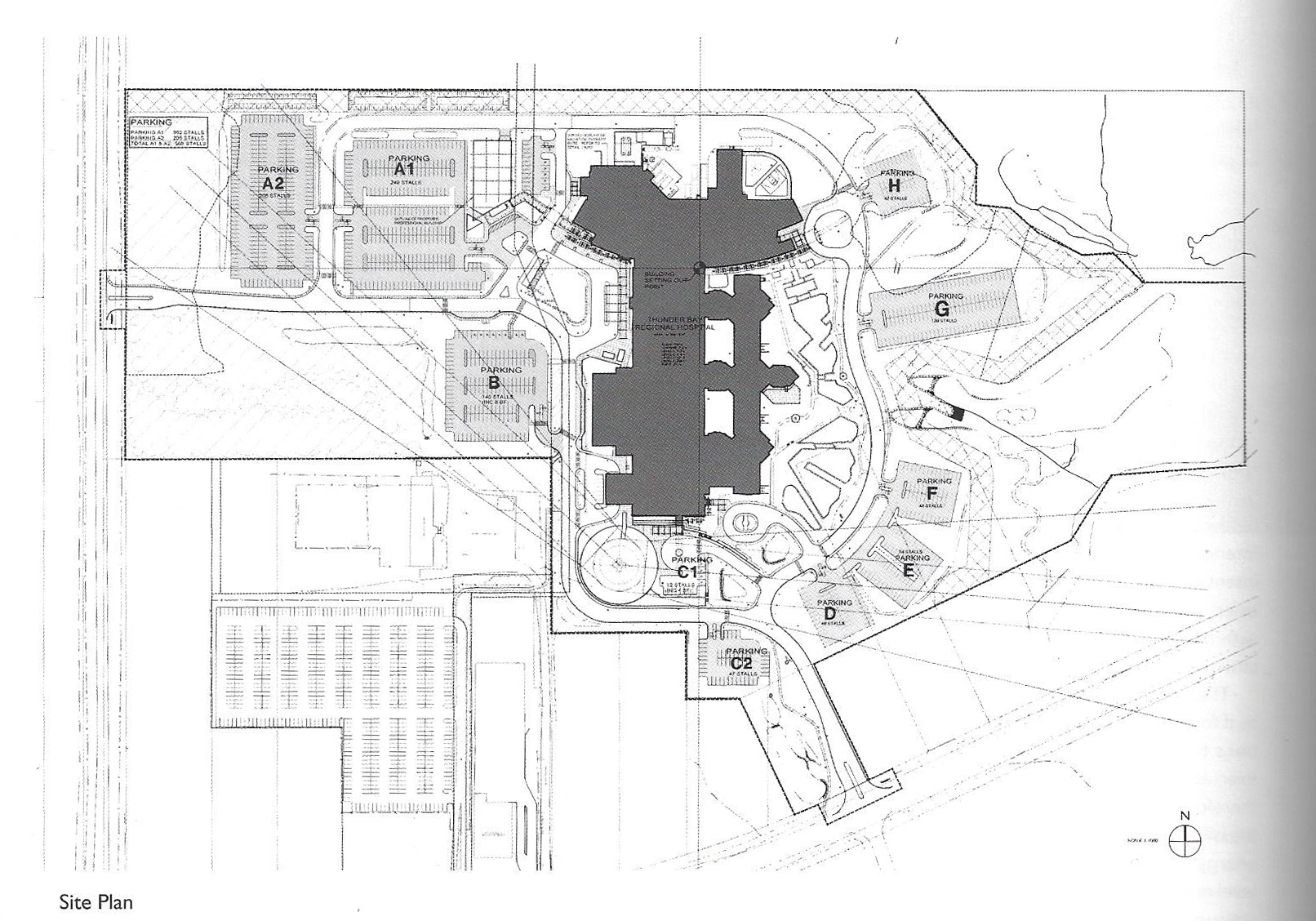
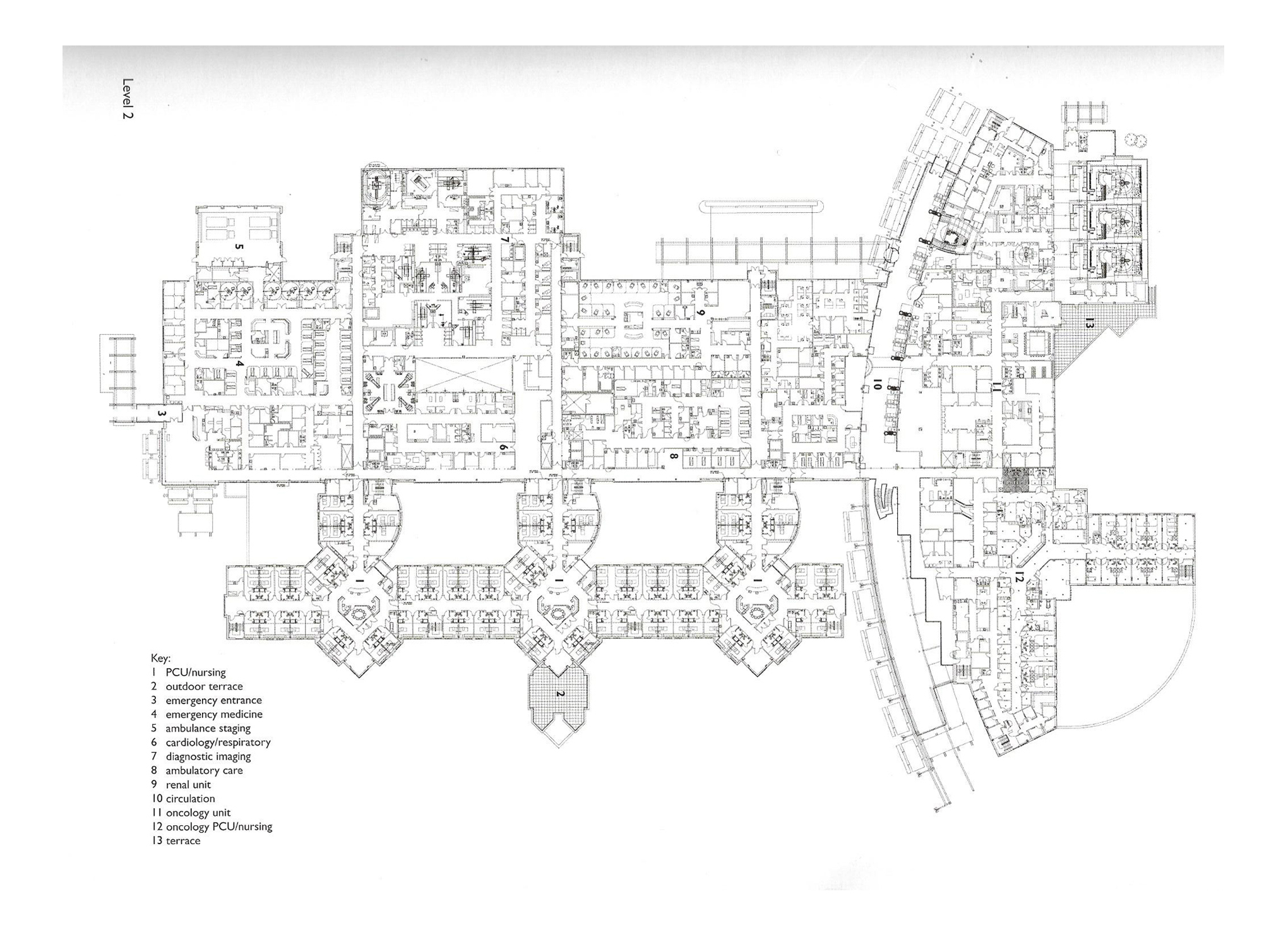
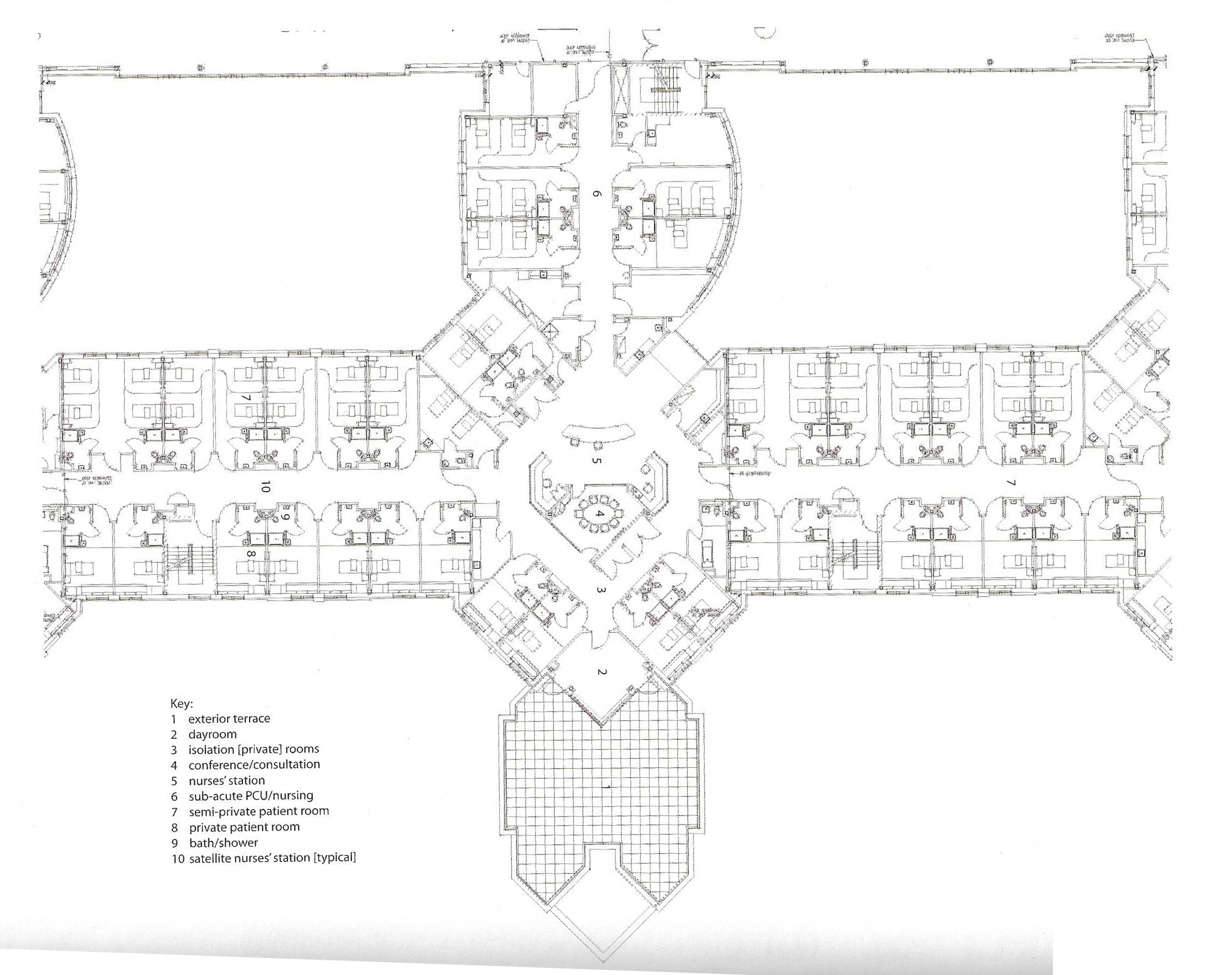
Thunder bay regional hospital - Salter Farrow Pilan Architects
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found with in the following book.
Verderber, S. (2010). Innovations in Hospital Architecture. New York, United States of America: Taylor & Francis.
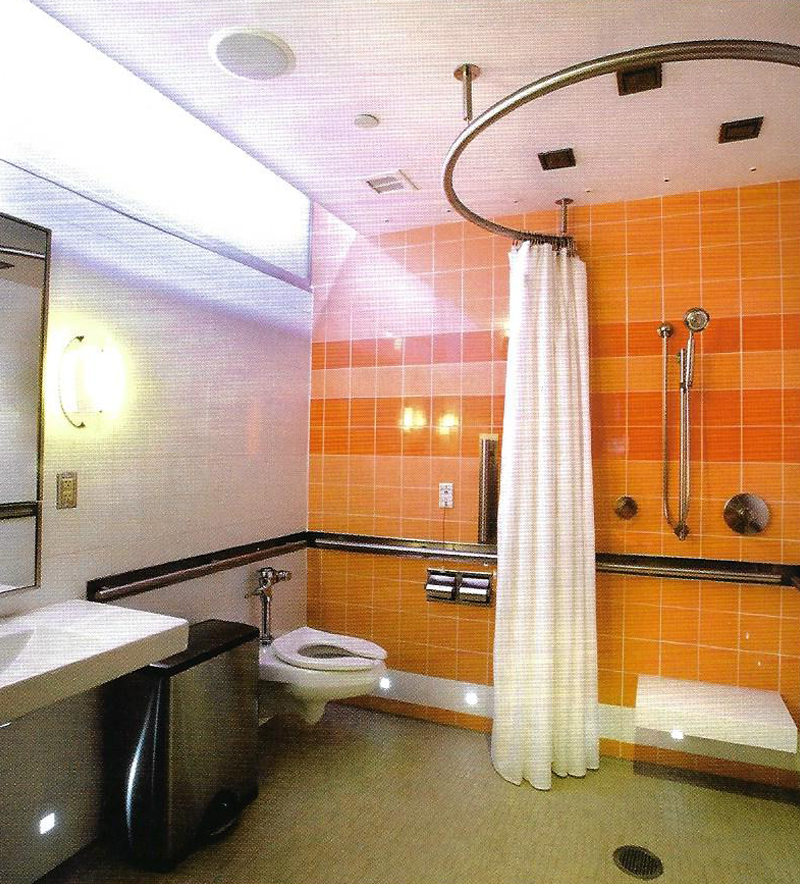
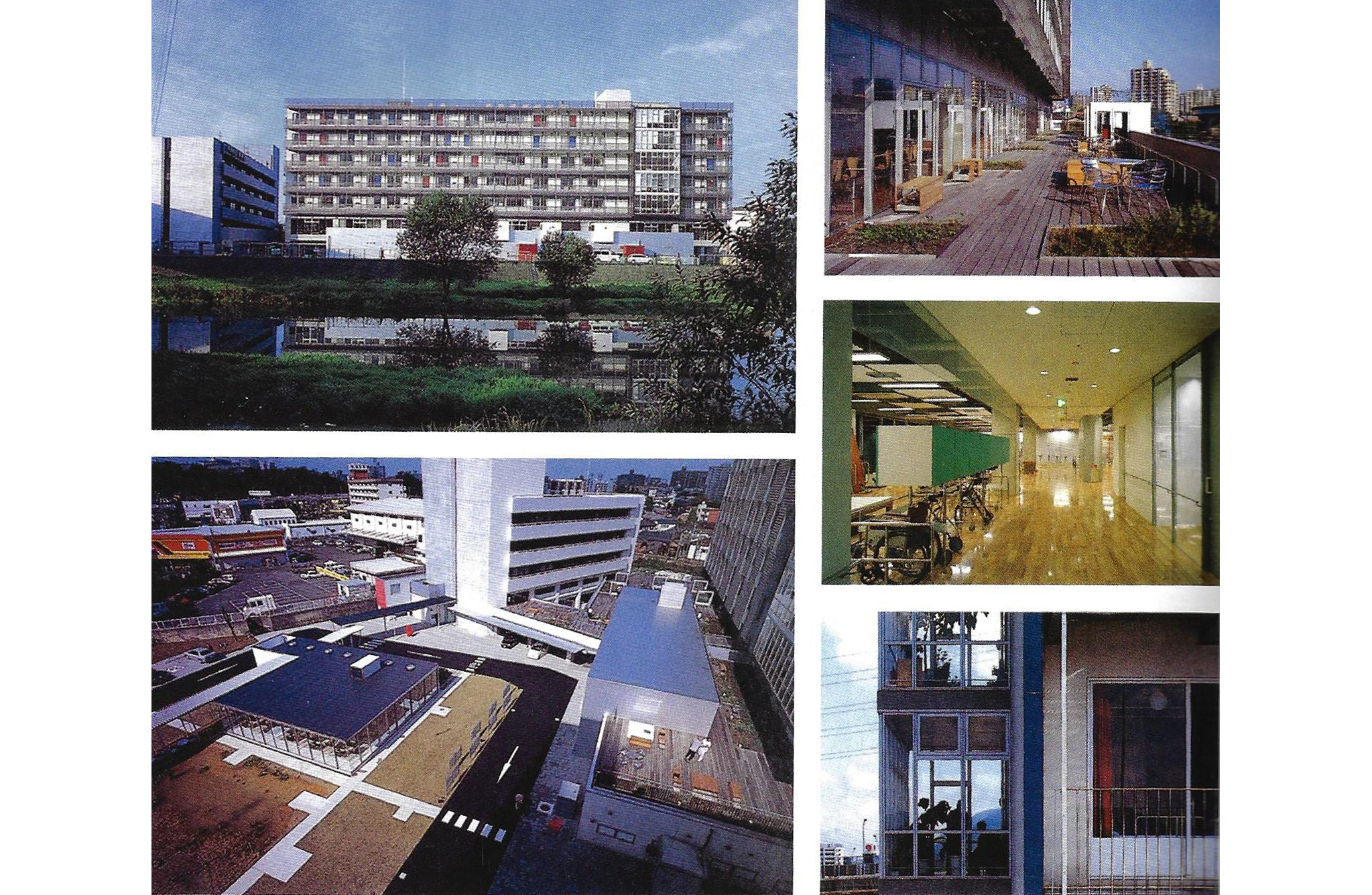
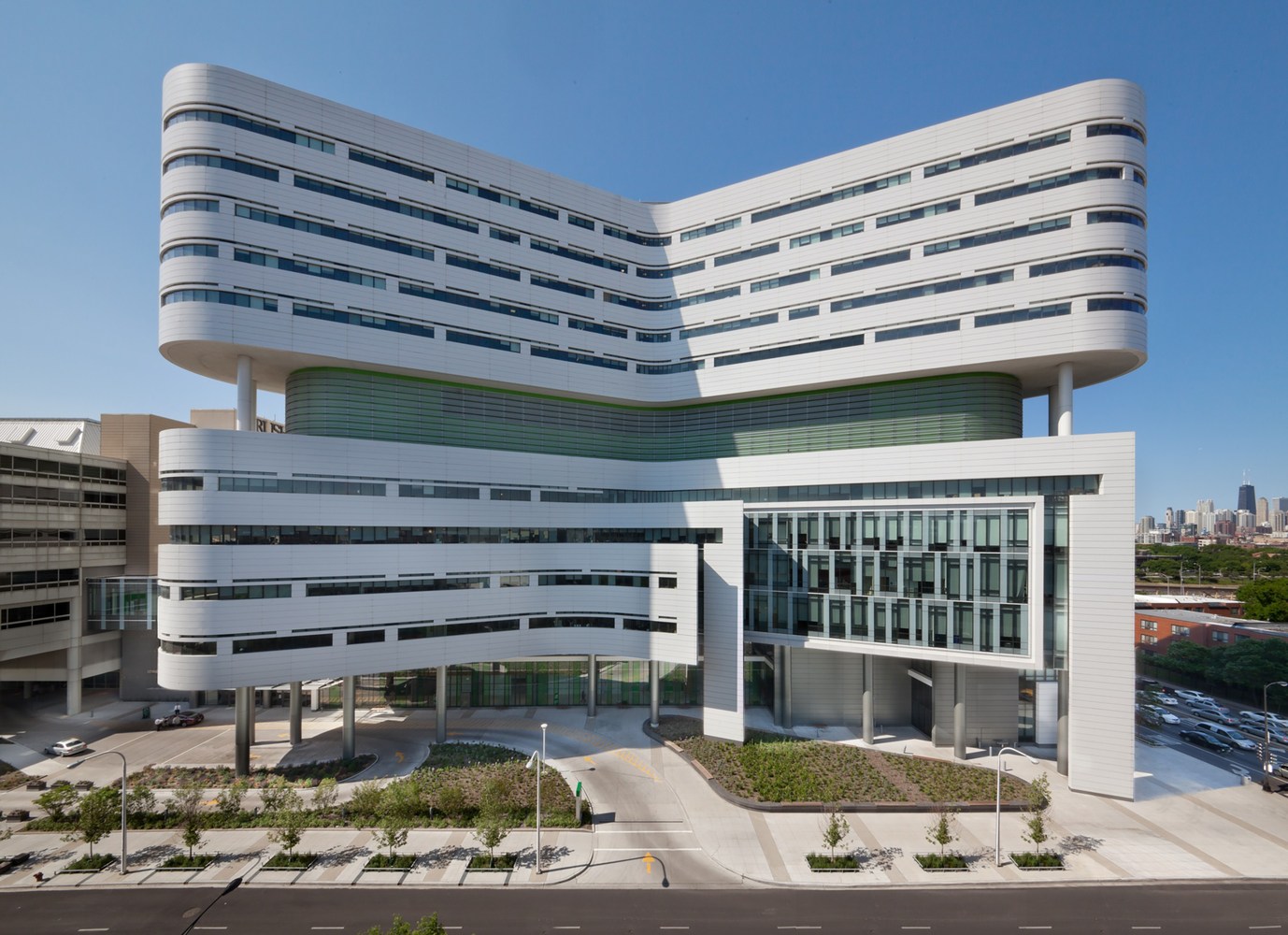
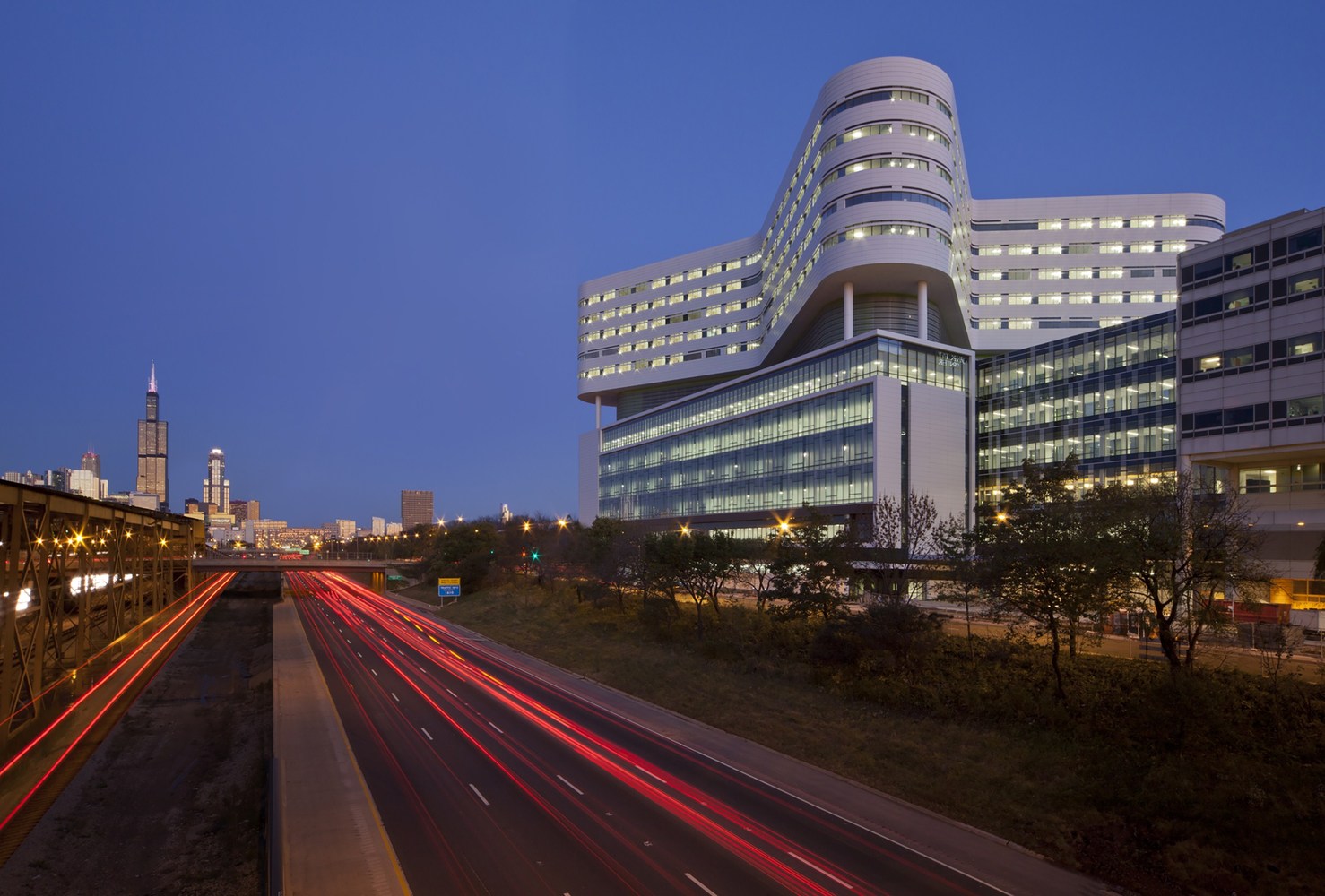
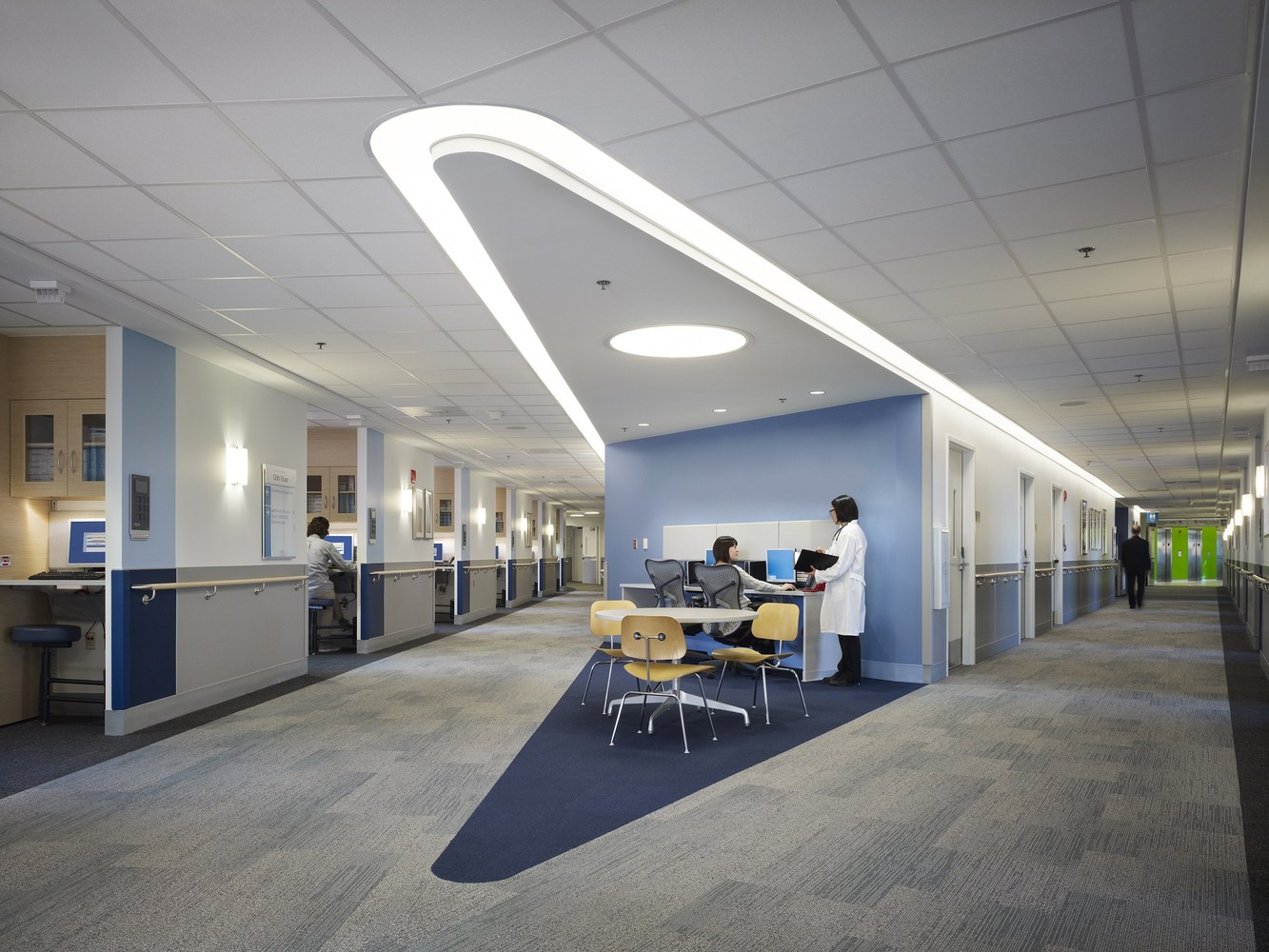
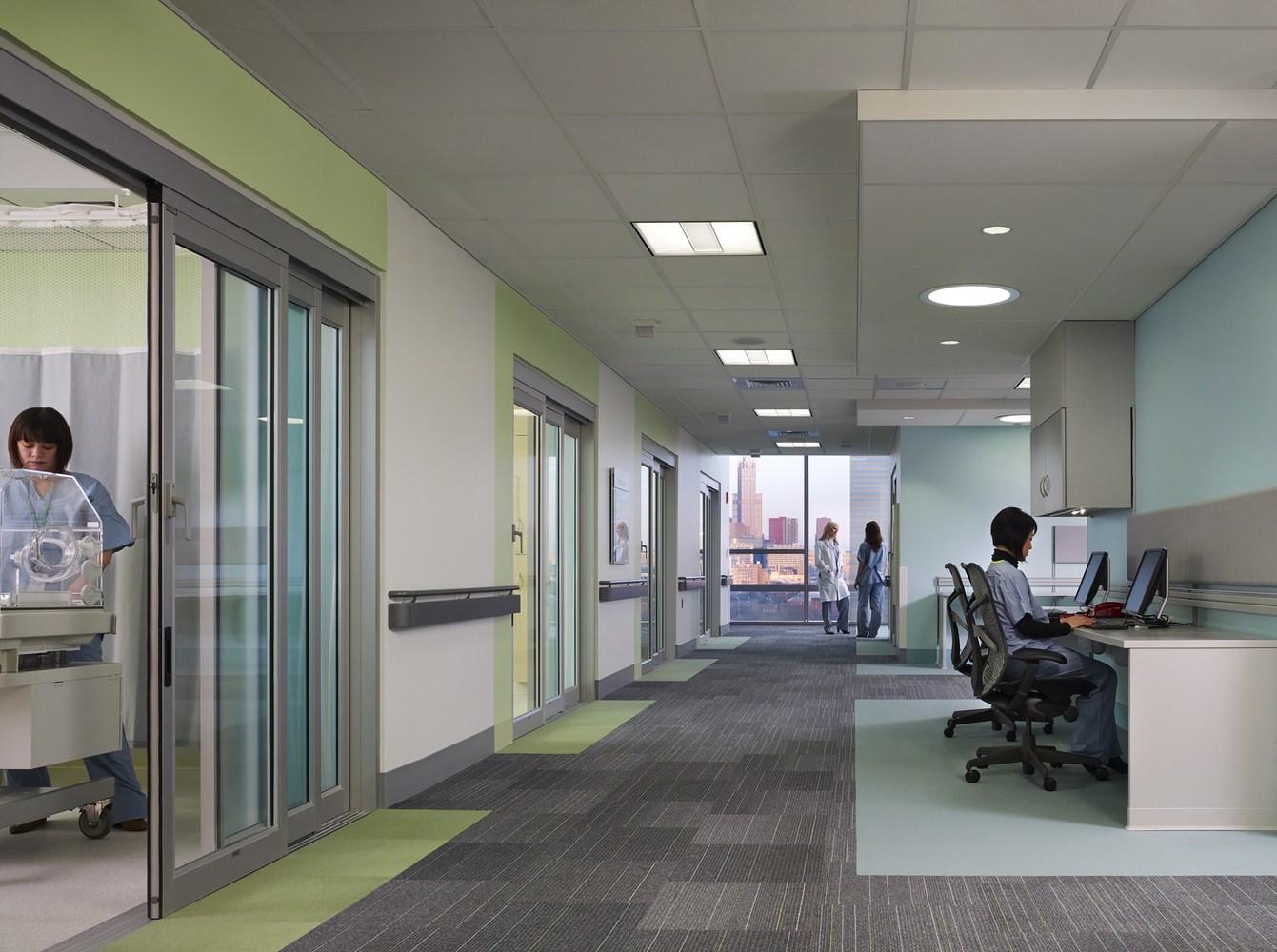
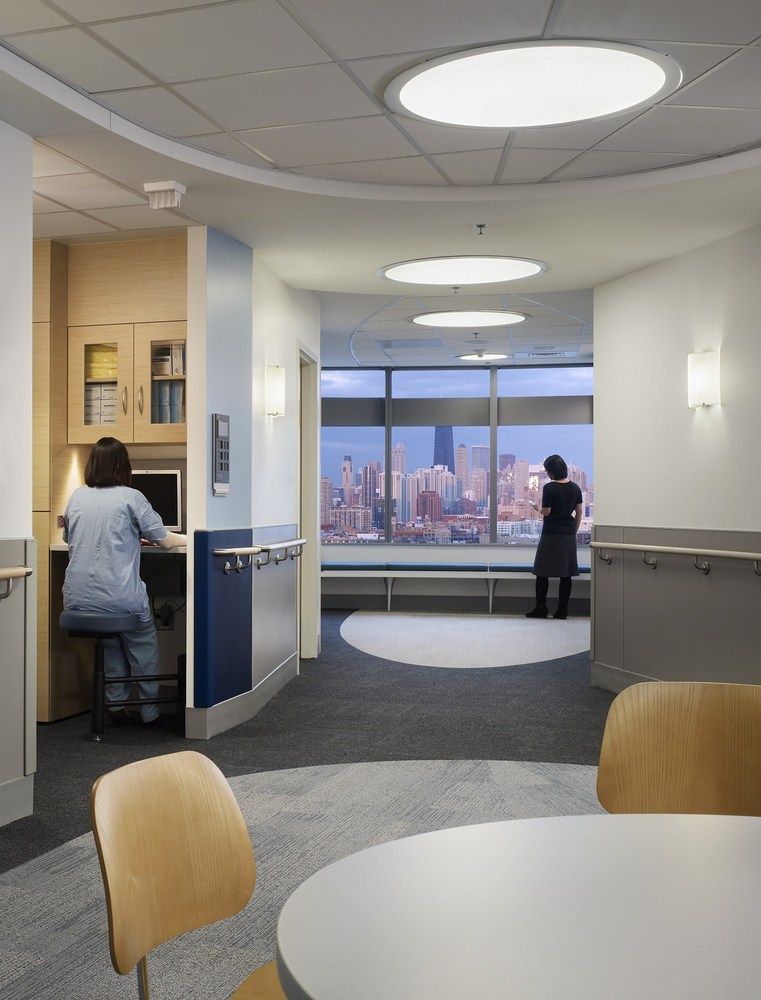
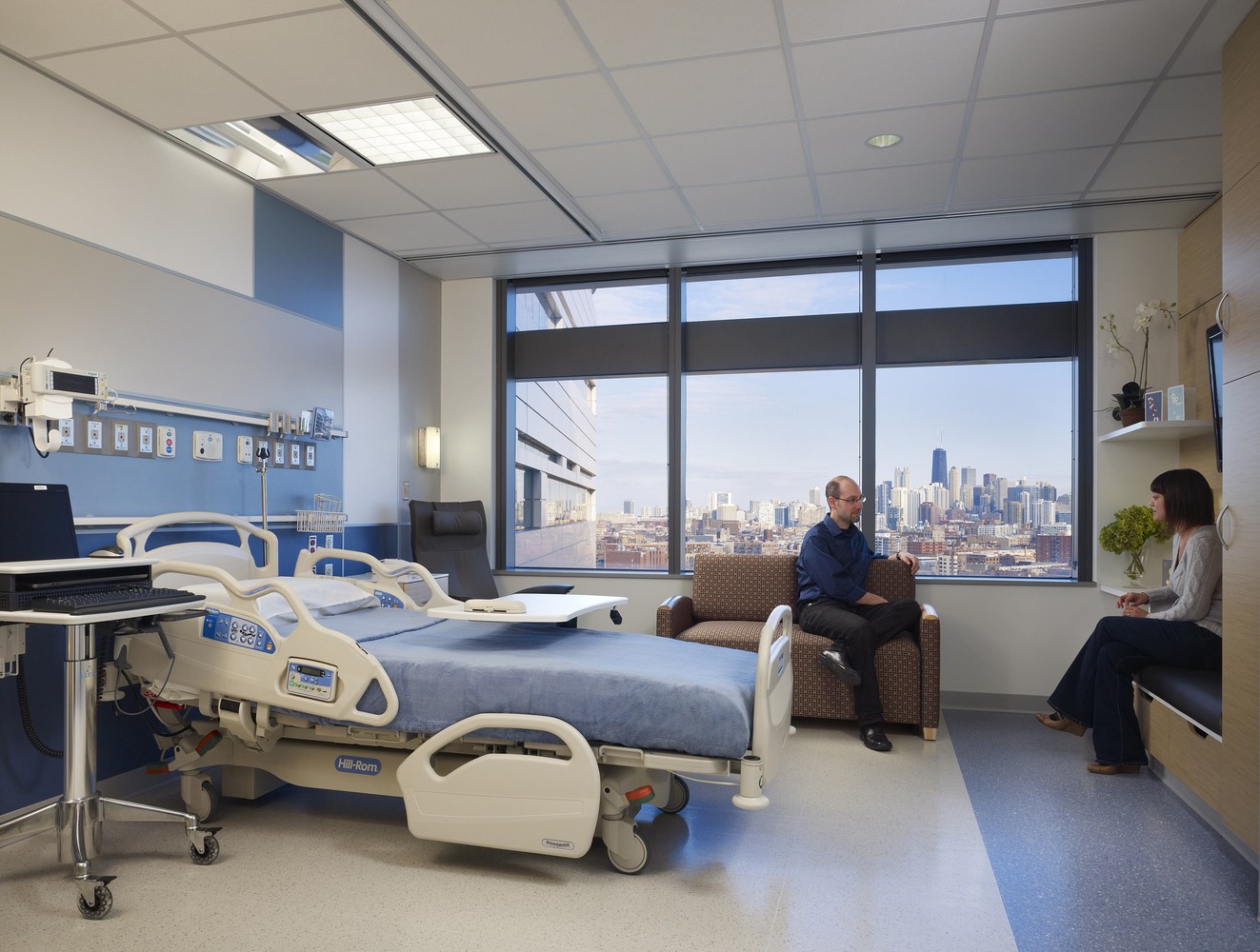
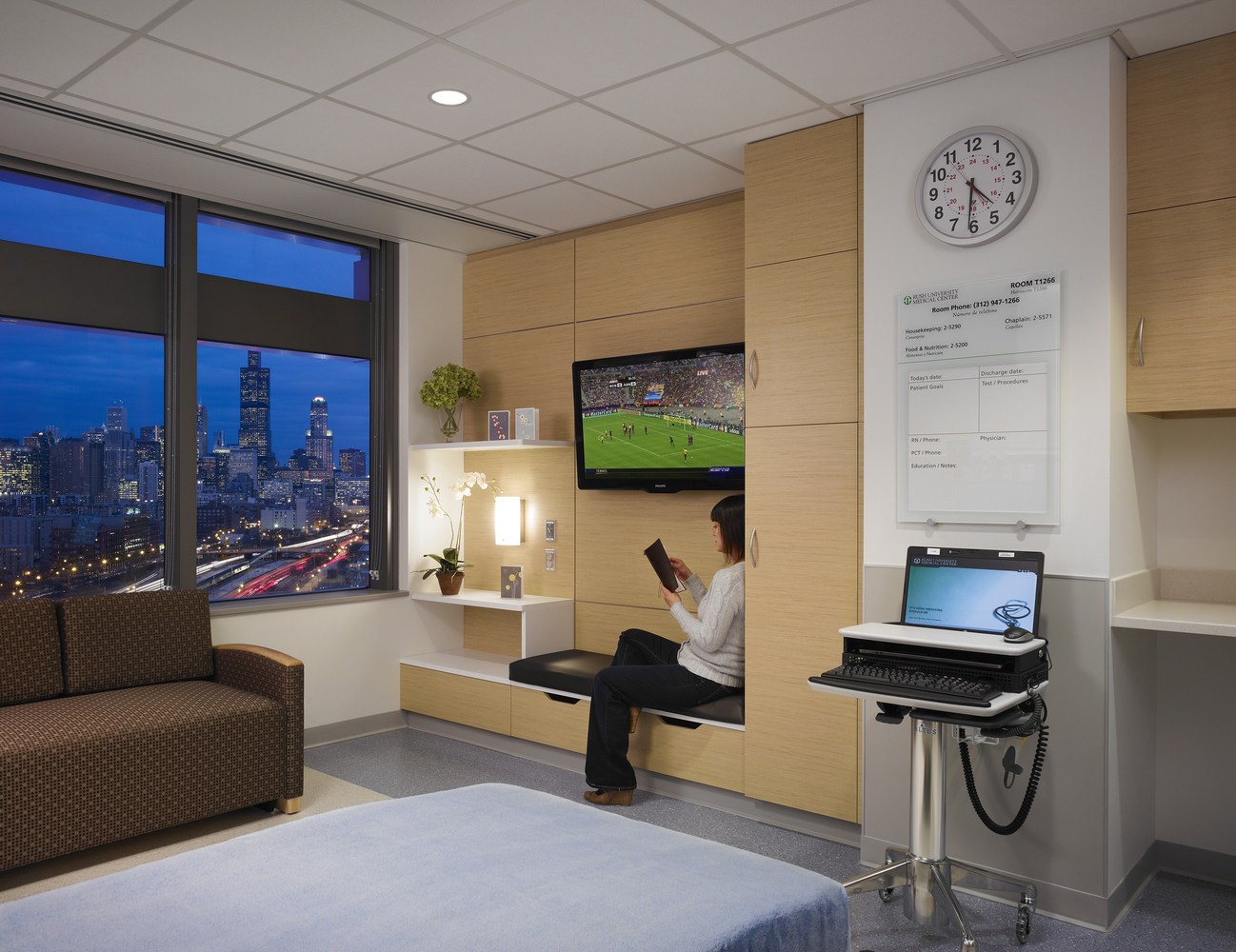
New Hospital Tower Rush University Medical Center - Perkins+Will
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found on the following website.
New Hospital Tower Rush University Medical Center / Perkins+Will [Photograph]. (2013, November 4). Retrieved April 4, 2019, from https://www.archdaily.com/443648/new-hospital-tower-rush-university-medical-center-perkins-will
Planning