project04:P2
P2
The Academic Medical Center(AMC) is one of the largest hospitals in the Netherlands. The AMC is among the top medical centers in the world. The building dates back to the eighties of the last century. Up until now various architectural interventions have been made but the currently the quality of the building is right on the acceptable level. To maintain an acceptable quality of the building renovation and transformation is required. Therefor the AMC building has to be renewed to face the future. Designing new state of the art medical facilities as for creating a sustainble hospital with a neutral carbon footprint. Within the Architectural Enigineering graduation track this challenge is explored. This is the second presentation in the graduation track presenting my proposal for the new AMC based on Robotic Building principles.
The Academic Medical Center
The AMC's occupation dates back to eighties, The building, well rather the city like complex, has been subjected to aging and intensive usages. But still functions well due to the well integrated design principles of flexibility and oversizing. Even though the building still functions well, the quality of the spaces has fallen to just an acceptable level. Small transformations have been made to improve fragments of the city, while a large scale renovation remains to happen. Meanwhile advancements in the field of medicine are changing the requirements for hospital architecture and the way we use them. In order to adapt to these changing needs I propose the transformation of the complex.
Key figures
Completed:
Floorspace:
Clinical admissions:
Day care admissions:
Outpatient visits:
Beds:
Employees:
Medical students:
Medical informatics students:
1983.
500.000m2
25.000 per year.
30.000 per year.
356.000 per year.
1.002.
7.000.
2.200.
100.
Impression
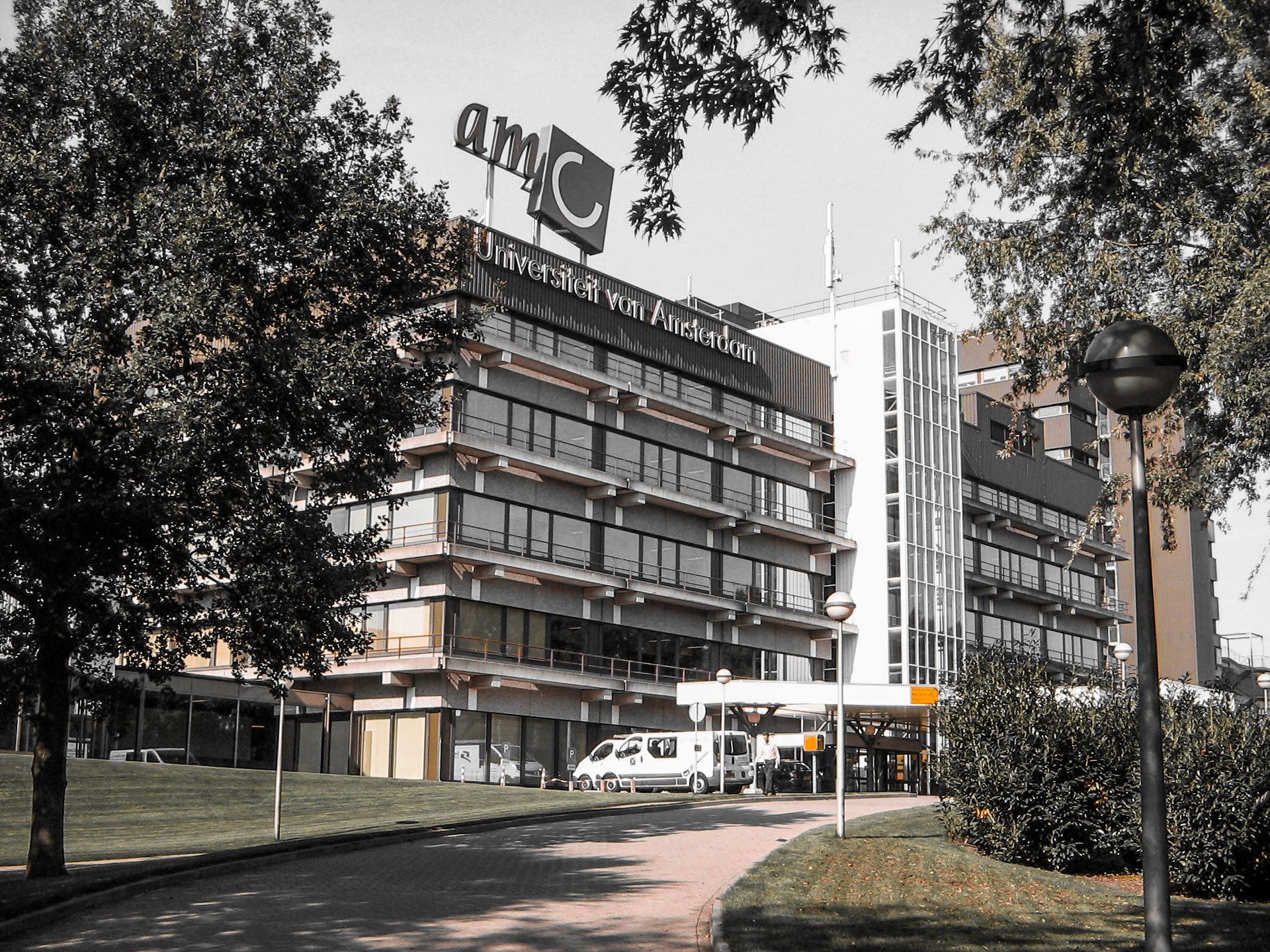
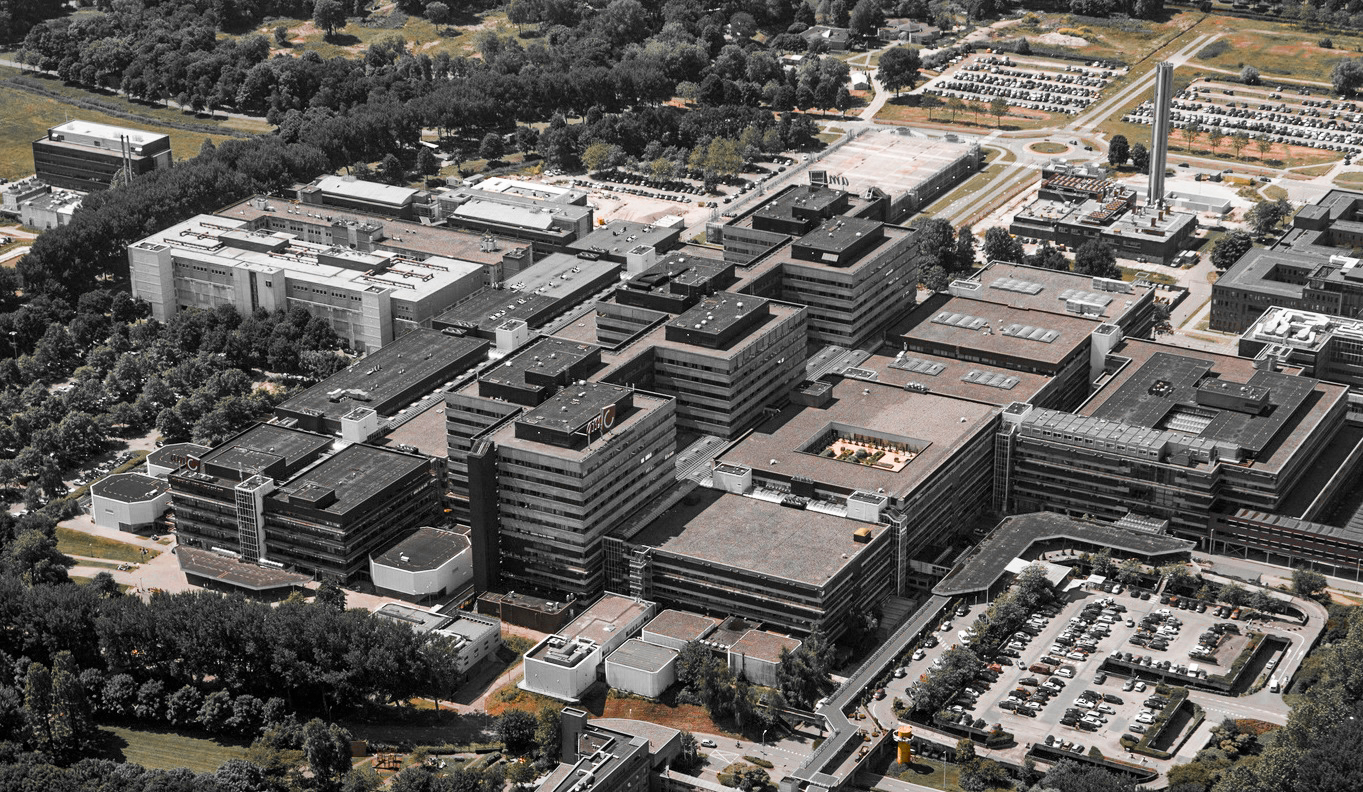
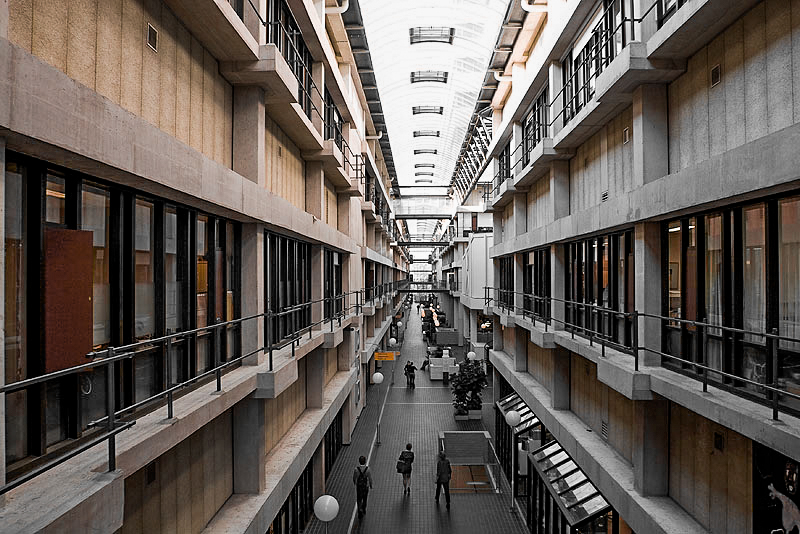
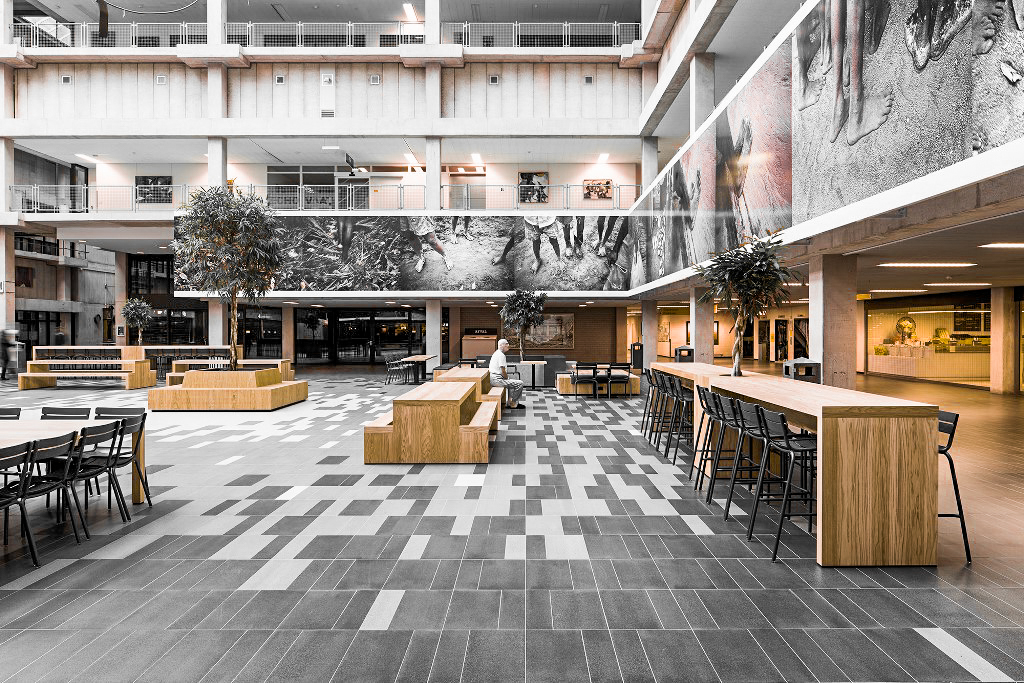
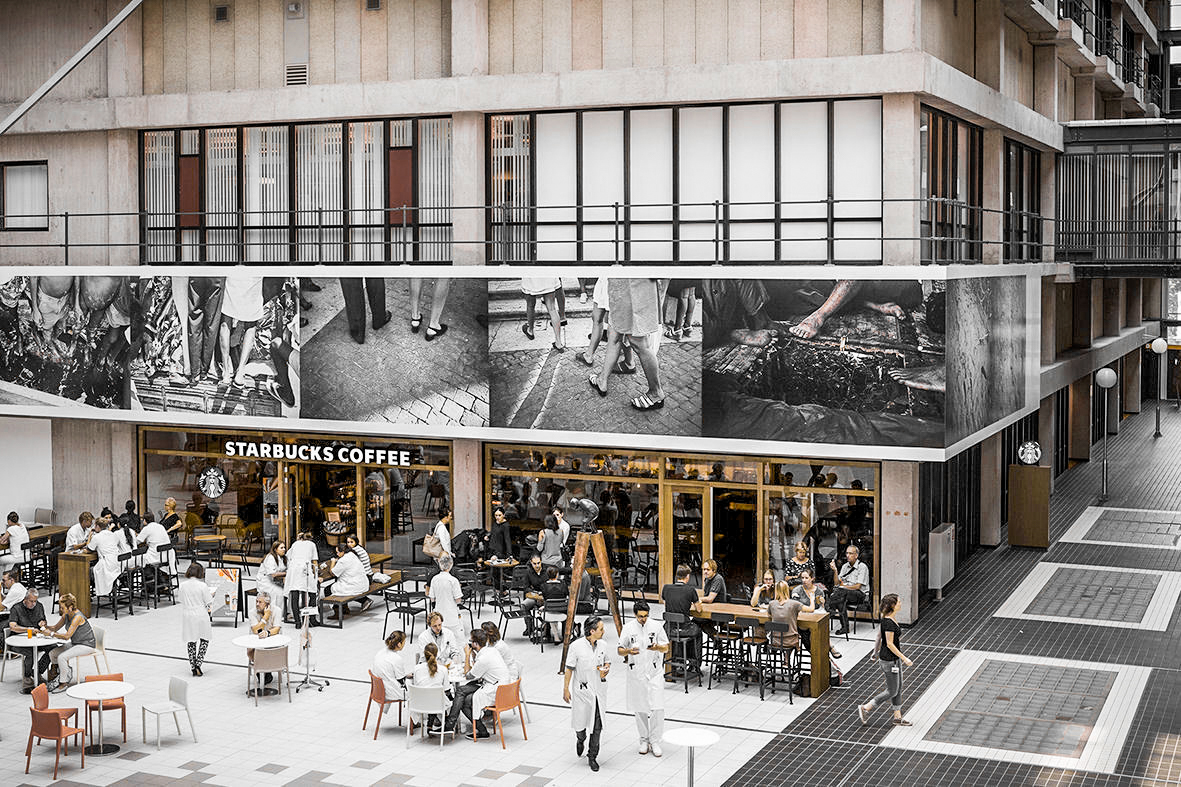
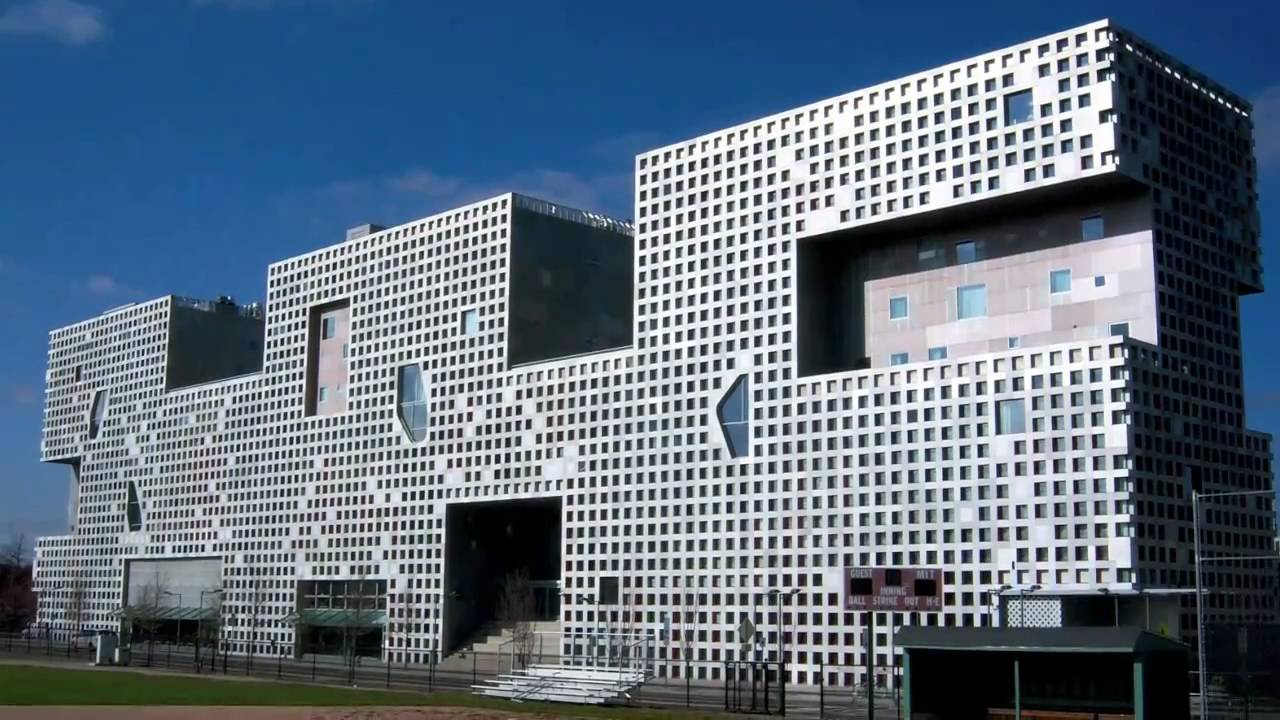
The Academic medical center has a very recognizable architectural appearance. The building shows of the characteristics of the brutalist architecture style. It is the block like structure and their exposed concrete materialization that support the style. the large scale of the building complex can be clearly seen from the bird's eye perspective building. While other photos show the interior quality of the existing structure where the various buildings form the interior public space. This fits in really well with the brutalistic idea where modular elements from distinct masses and functional zones. While consequently forming a unified whole. But it is these qualities that also provide one of the hospitals problems. The building feels cold and discomforting, especially for the ill.
Various images of the AMC.
retrieved from AMC website.
Location
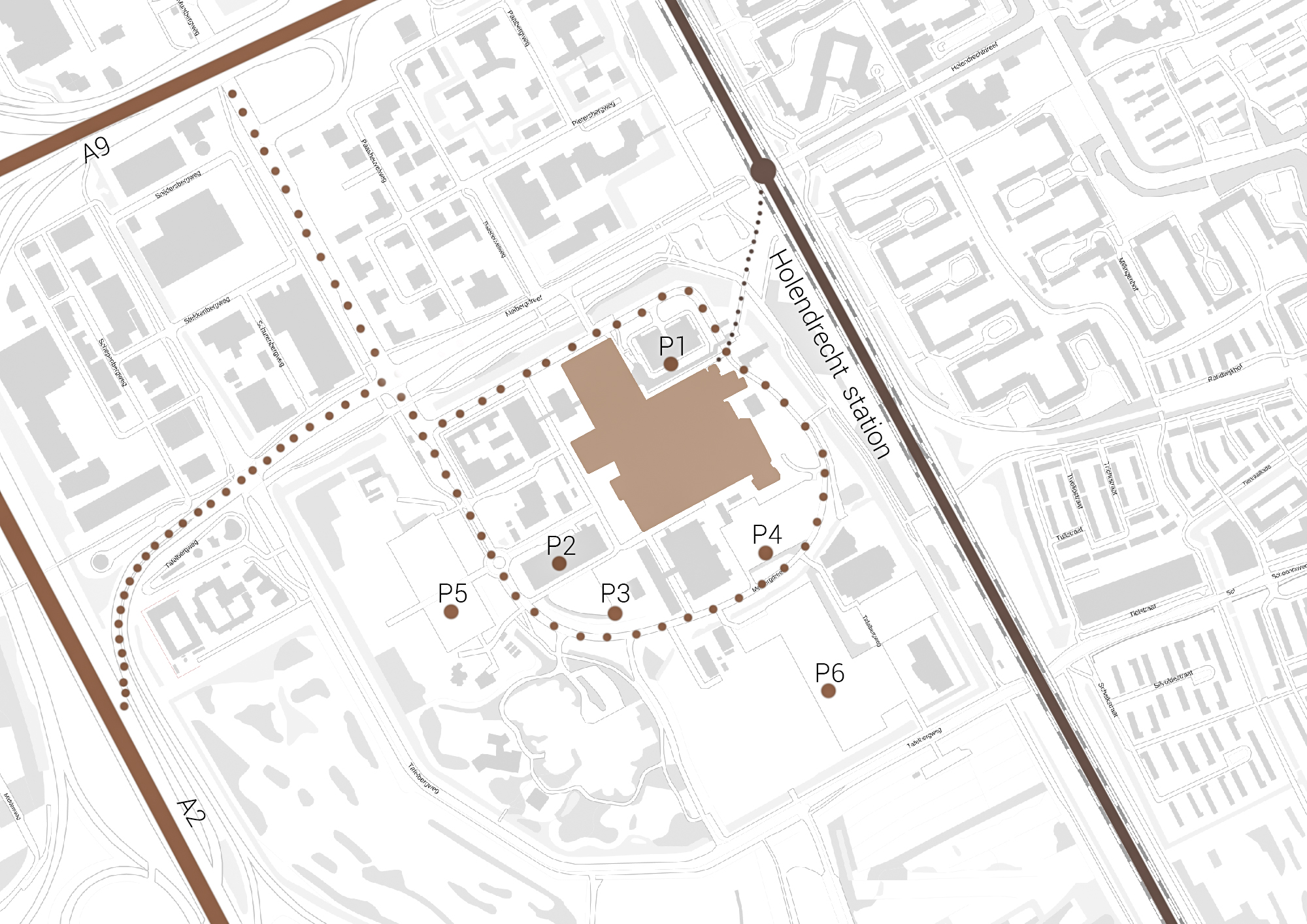
The decision to build this complex dates back to the merging of two hospital with outdated facilities in the city center of Amsterdam. In order to enable future expansion the new building site had been located out of the city center with improved infrastructural access. Over the years the AMC has expended on its plot in order to accommodate more hospital and healthcare function. In the meantime the city of Amsterdam has expanded around the AMC site. Currently the AMC is accessible by the highway network's A2 and A9 and accessible by public transport through Amsterdam Holendrecht station.
Own images showing the location of the AMC and the access to the building by car and public transport
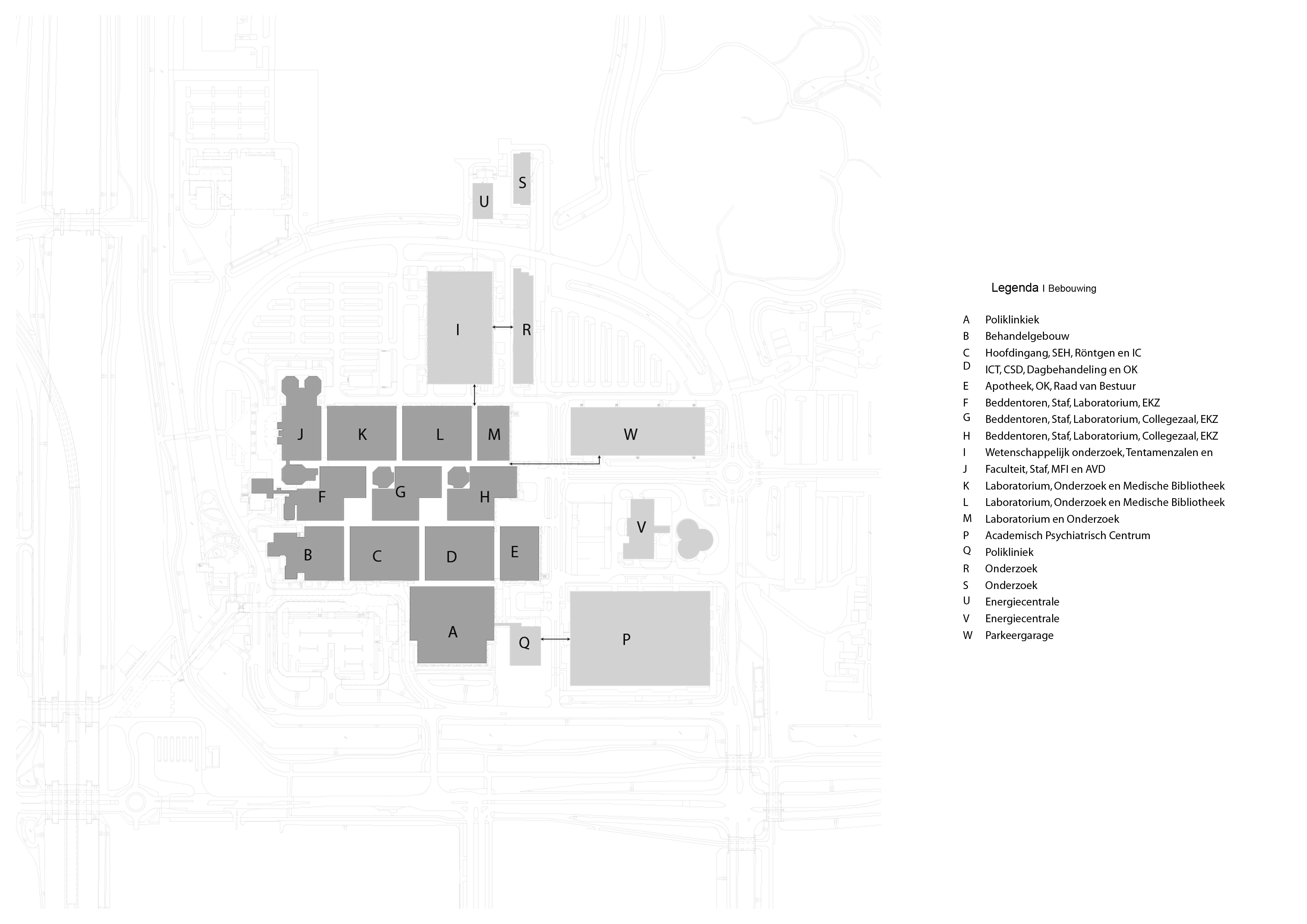
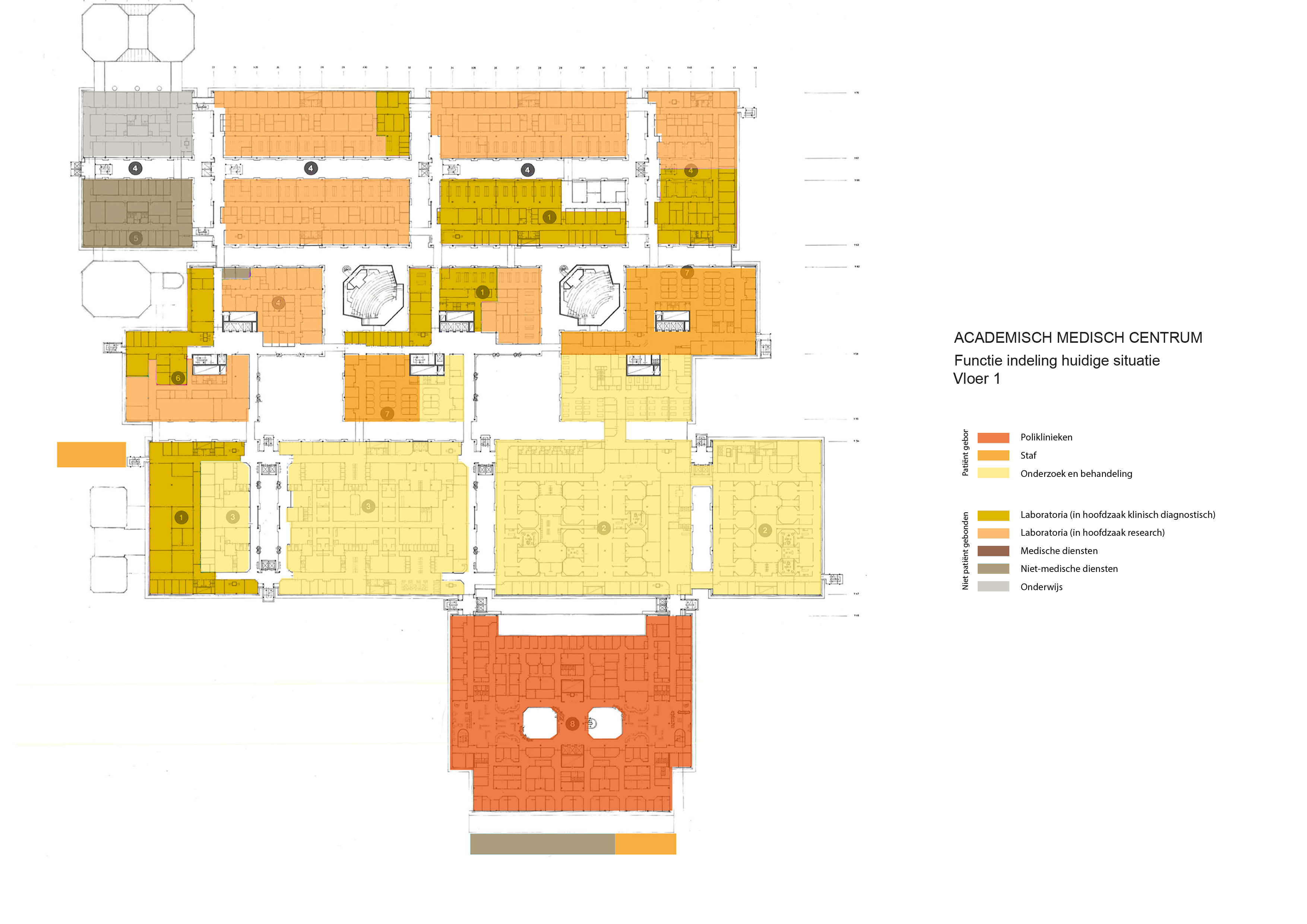
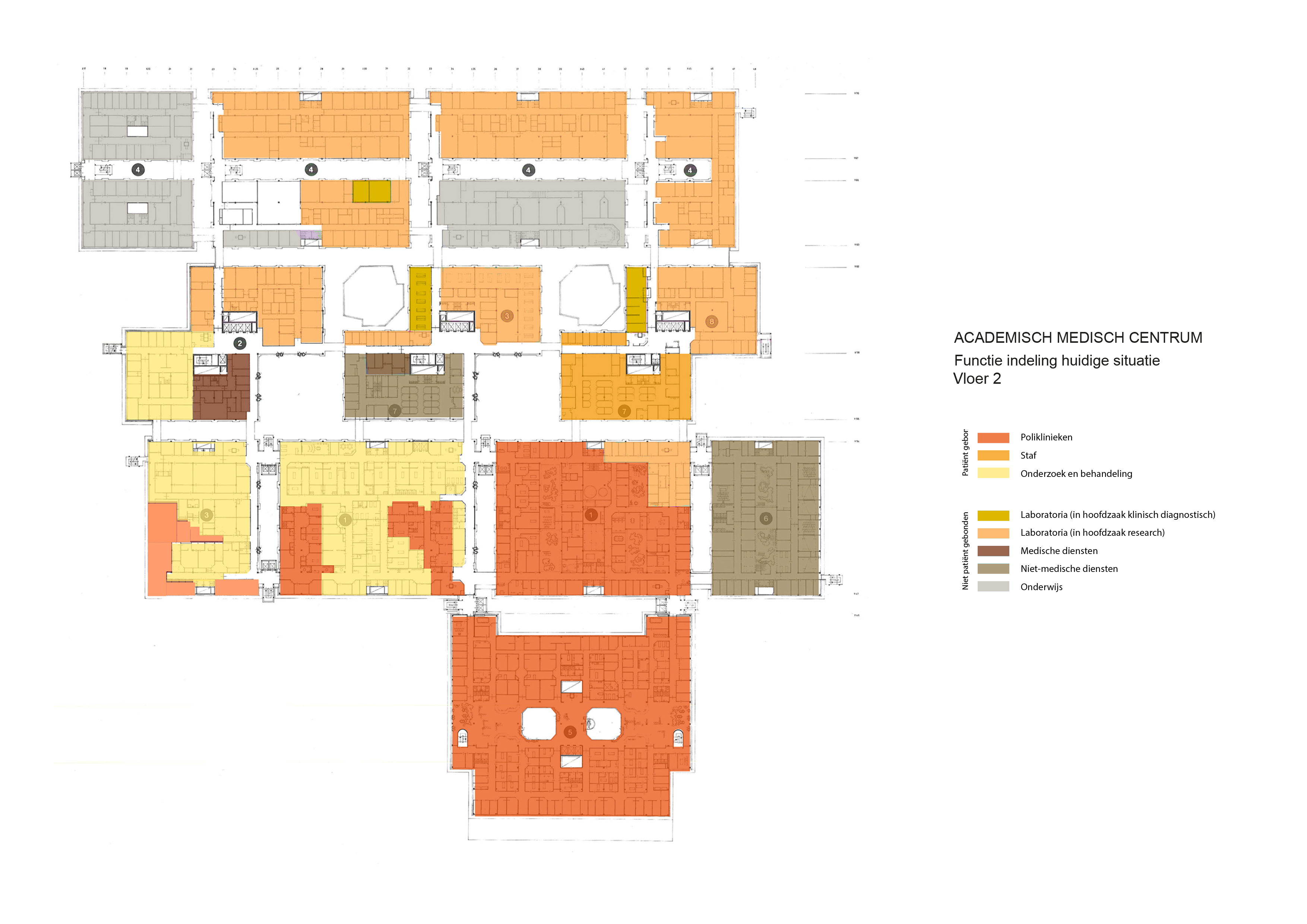
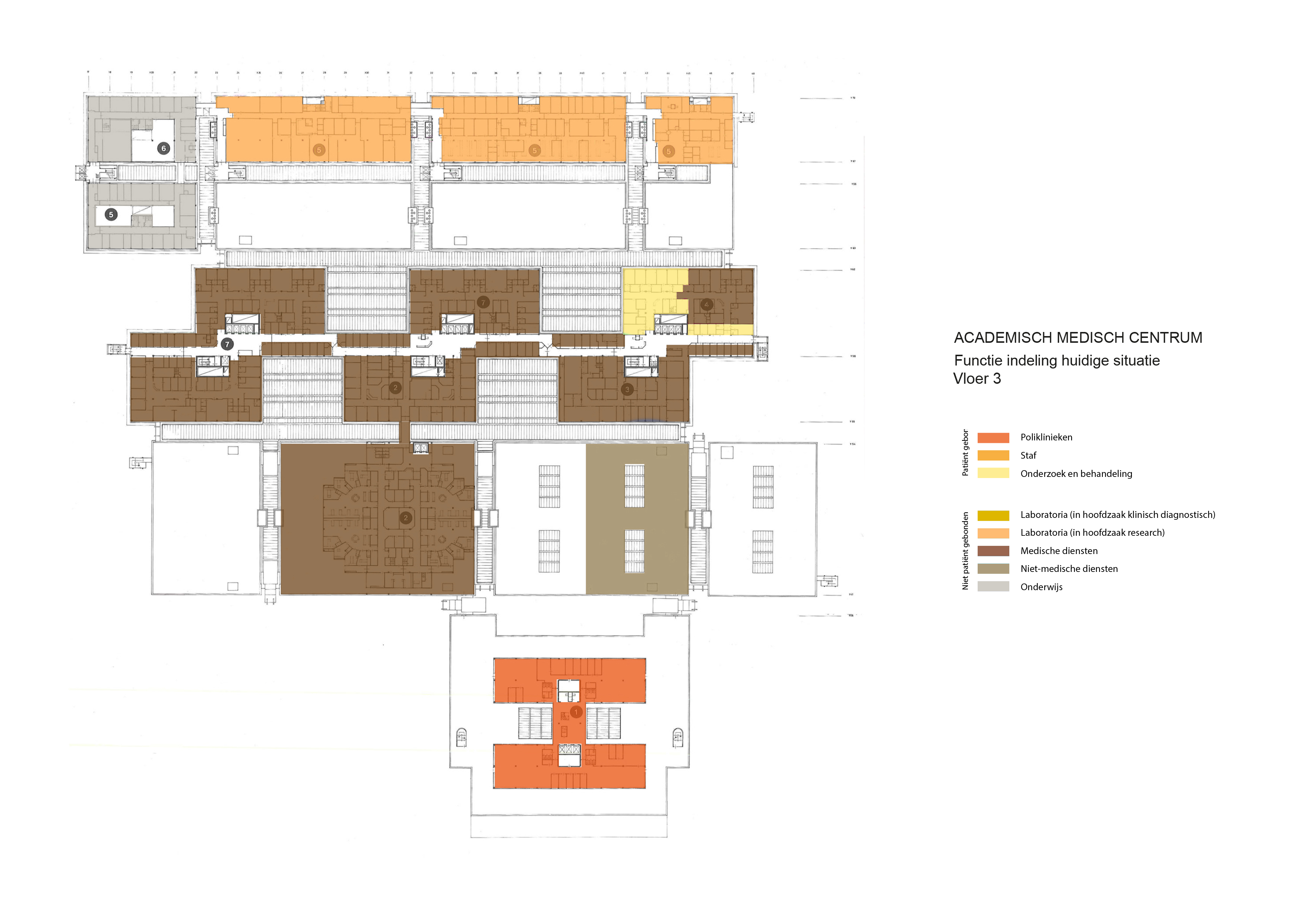
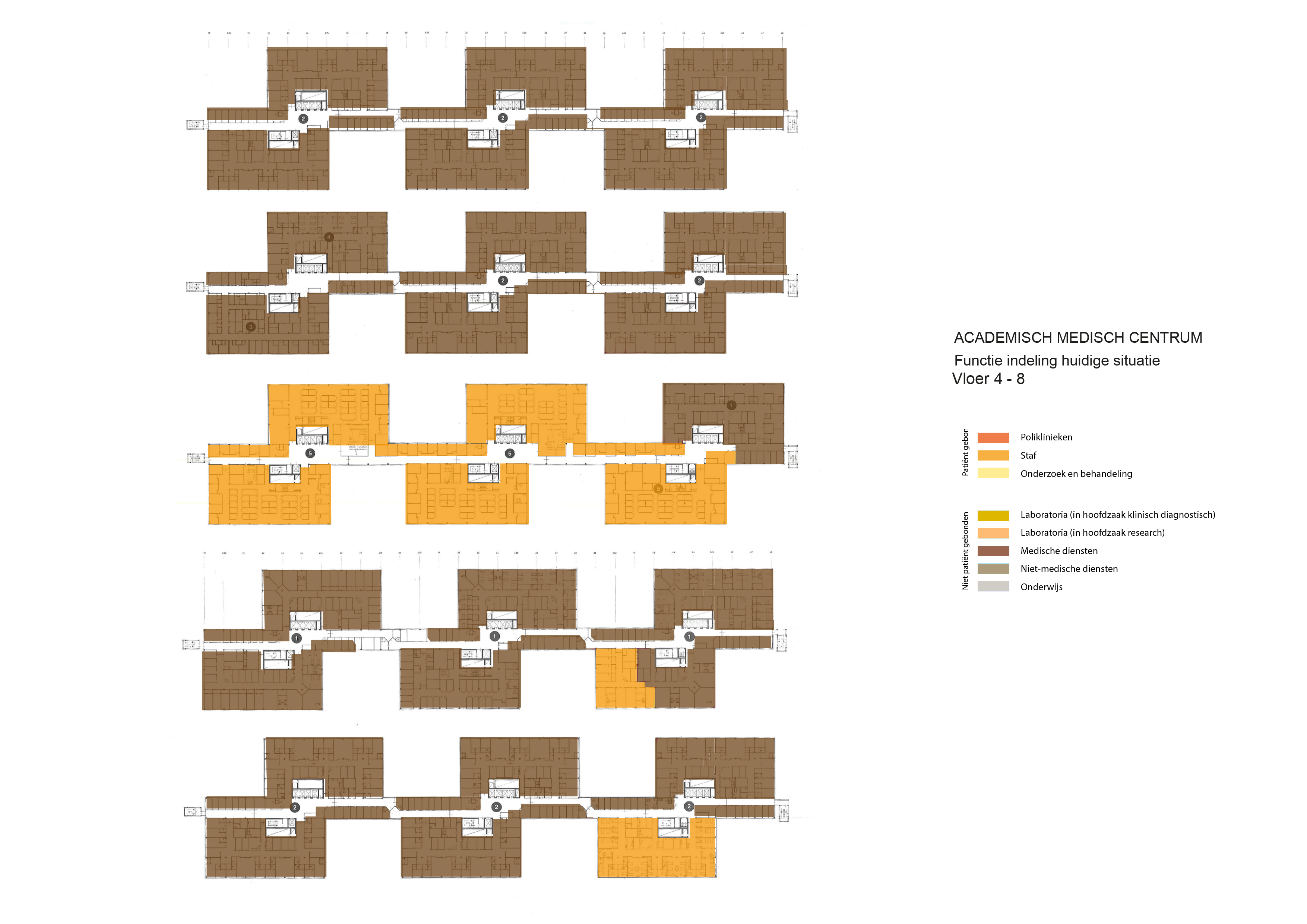
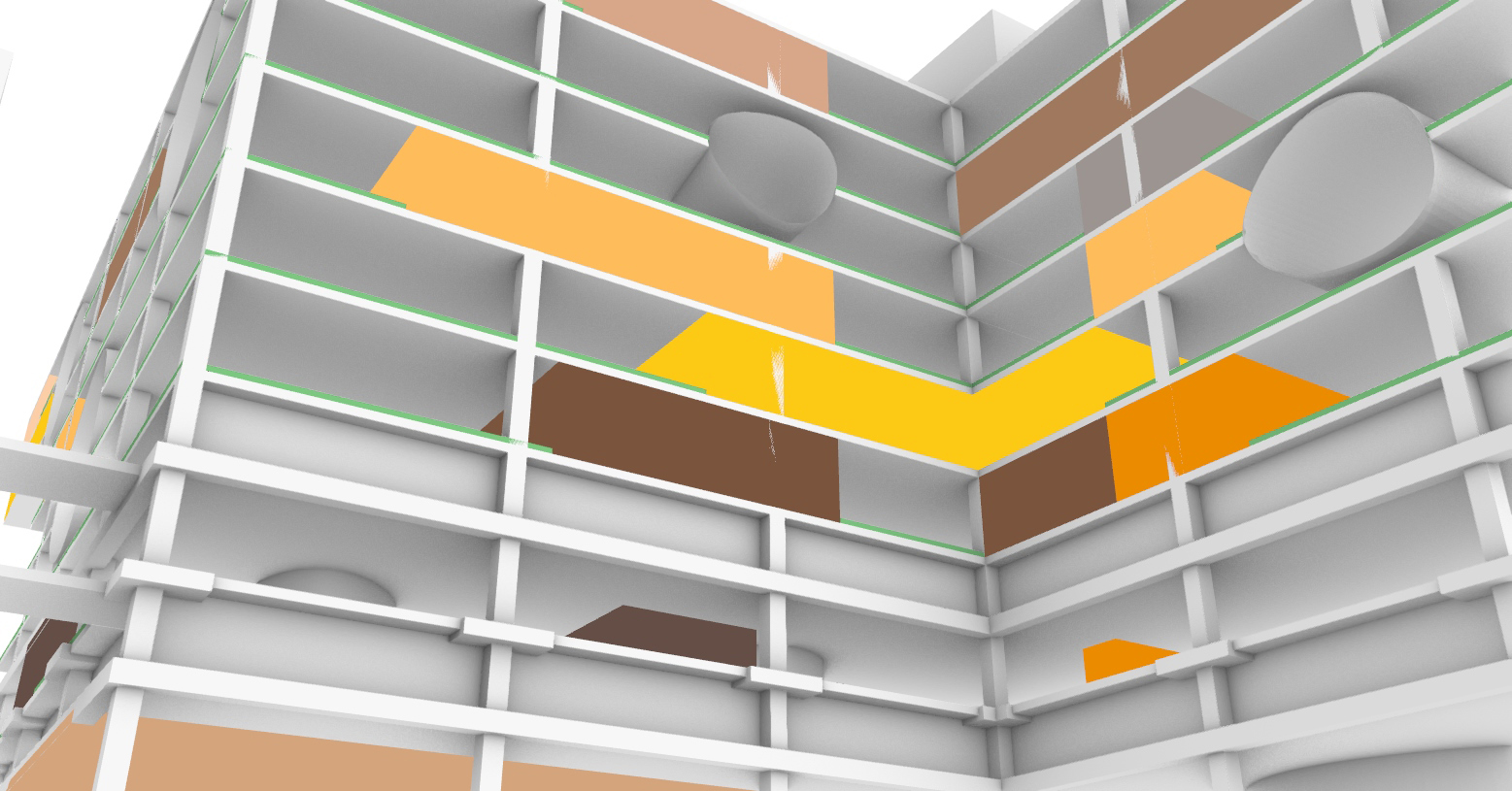
Floorplans
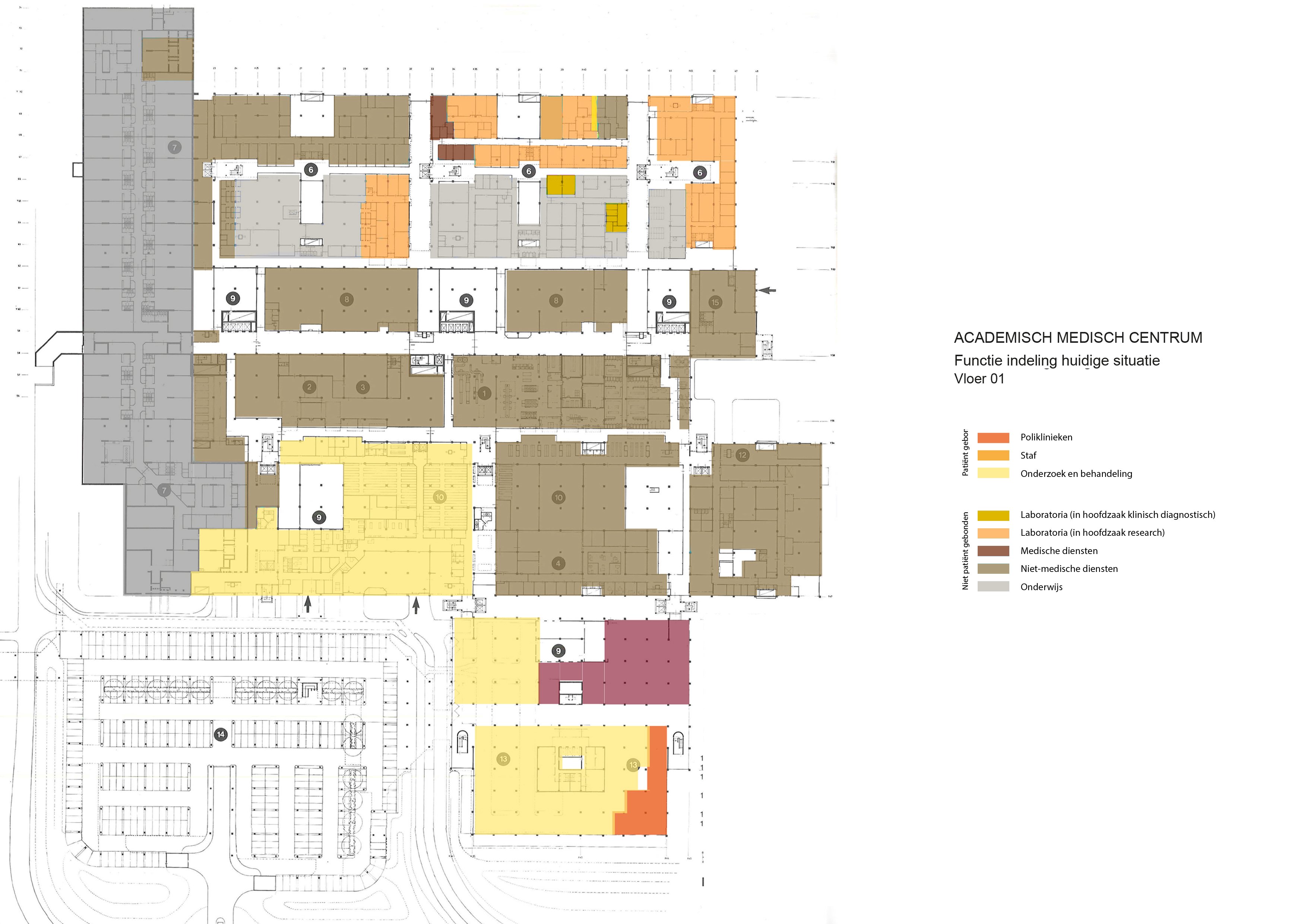
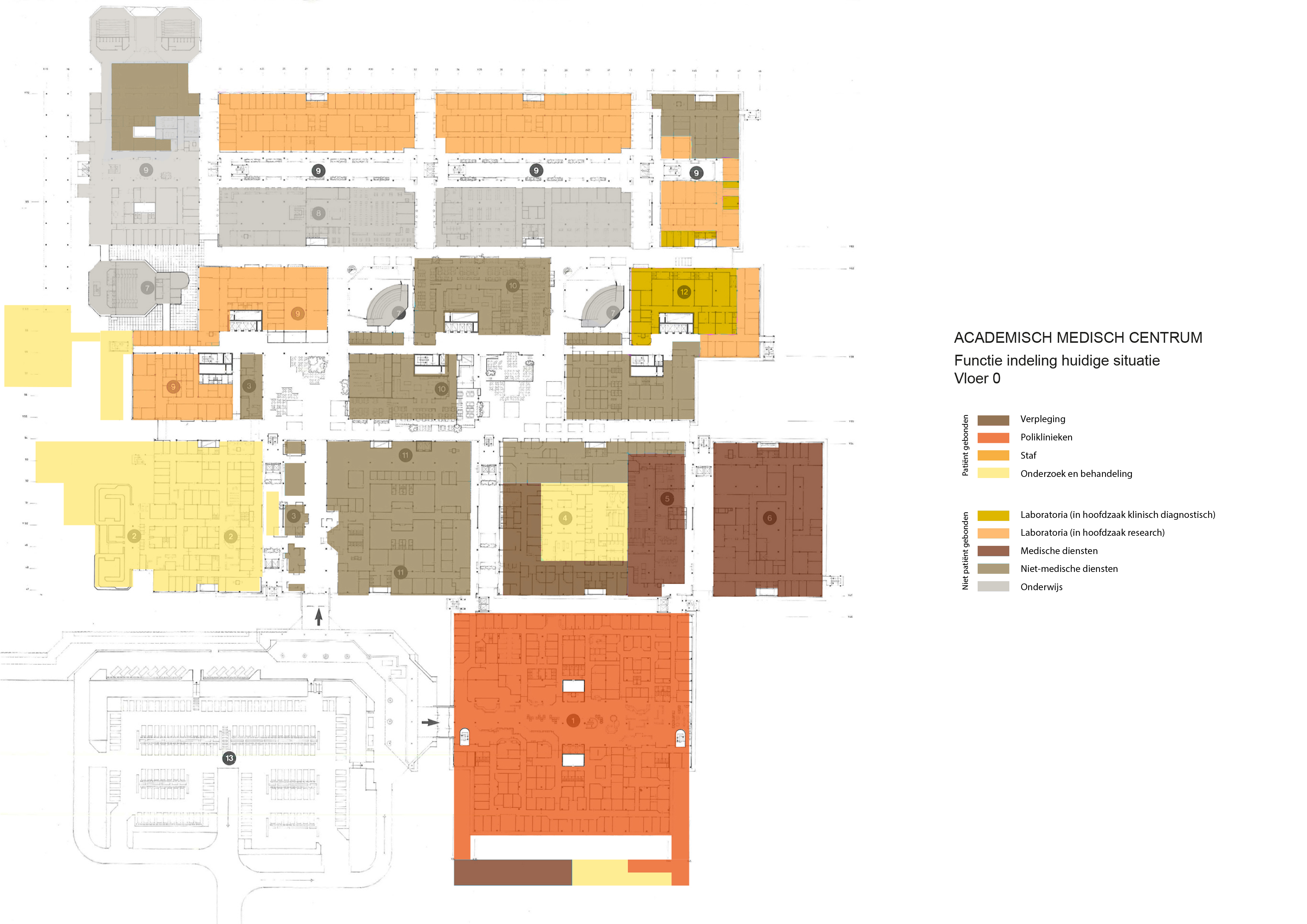
The various floorplans of the AMC are shown below with their colour corresponding to the their respective functions. The brutalistic function distribution is clearly shown. Most function have their own floor in their own building. One of the other things that these floorplans show is there is a distinct division between north and south. The northern part has been reservered for the functions that are non patient related like education and laboratories whil the southern part is meant for patient care. There is also a division in elevation where the higher floors house the nurseries and patient care units and the lower floor houses public and semi public functions like shops and lecture halls. But one of the drawbacks of this distribution is that it does not place its patient central. While this should be where a hospital should revolve around.
The floorplans of the AMC with function analysis.(AMC, 2016)
Specialism
The AMC has various top-referral specialties. These include cardiovascular diseases, immunology and infectious diseases, diseases of the digestive system (surgery and internal medicine), metabolic diseases, gynecological oncology, specialized care in early pregnancy, prenatal diagnostics, pediatric oncology, pediatric immunology/ hematology, vascular disorders of the brain, severe hearing disorders, schizophrenia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and deep brain stimulation for severe obsessive-compulsive disorders. Besides these specialties the AMC has also been allocated various top clinical functions by the Dutch government. These are functions that provide medical treatments and services in limited number of hospitals, this due to high costs and required expertise. The AMC’s allocated top-clinical functions include kidney dialysis and kidney transplantation, open heart surgery, radiotherapy, neurosurgery, neonatology and nuclear medicine.
The AMC tries to distinguish itself from other hospitals through seven core areas of medical research. These are: cardiovascular diseases, immunity and infections, gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders, neurological and psychiatric disorders, oncology and epidemiology & public health. All of these core areas covers the whole spectrum of medical research: from fundamental biomedical, translational and clinical research to the evaluation of new medical methods and techniques.
Infectious diseases and immunity
In a Dutch and international context, AMC researchers are working on the development of drugs and the evaluation of combination therapies for HIV/AIDS. Another line of research focuses on the development of vaccines, and bacterial research concentrates on pneumonia, meningitis and septicemia. Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are also being studied, with researchers concentrating mainly on the inhibition of proinflammatory proteins by means of an inactivated virus. Phagocytes, dendritic cells and T-cells are the central focus of fundamental immunological research.
Oncology
Most of the research in the core area of oncology concerns the molecular and biochemical backgrounds of cancer. There are four lines of research: gastrointestinal oncology, hematological oncology, pediatric oncology and neuro-oncology. The focus of the research is the hypothesis that only cells of one certain type – called cancer stem cells – cause tumors to grow and spread. The pediatric oncology research covers everything from fundamental research (genetic profiling) to clinical research. Much attention is focused on new drugs, and the later effects of oncology therapy.(AMC, 2009)
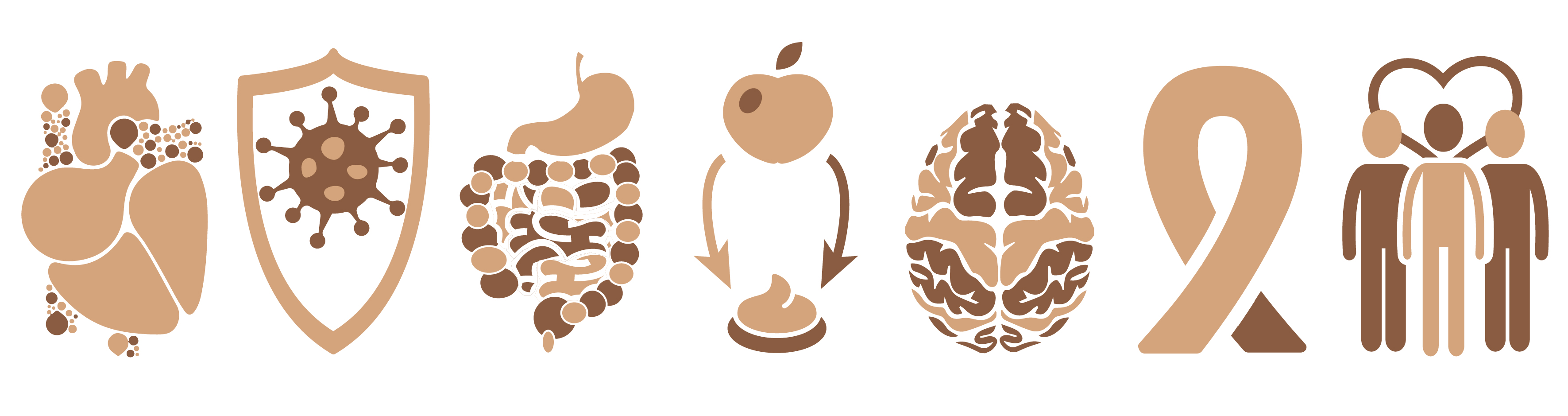
cardiovascular diseases
immunity and infections
gastrointestinal diseases
metabolic disorders
neurological and psychiatric disorders
oncology
epidemiology & public health
The seven core areas of medical research, own image.
AMC's development vision and aims
A hospital is in constant change, to guide this change the AMC has set up a vision and aims, this has also been the case for the redevelopment. Truthful to the original design principles the redevelopment vision for the AMC incorporates flexibility and standardization but also adds the new principles of safety and patient-centrality into its vision. Because of these last two principles the AMC aims to separated the different phases of care and than relocate them accordingly within the health care system. This in order to reduce errors and increase patient centrality. These phases include diagnostics, treatment, screening, after care, nursing and caring. In order to suite patients within the hospitals patient care units redevelopment is mandatory since the current ones have sunk under an acceptable level for modern medicine. While solving that problem another problem of patient care unit vacancy can be tackled.
While one of the AMC's aim is to place a larger focus on patient centrality the hospital currently struggles to do show with its current design. One of the aims therefor is to adjust and change the wayfinding, approach and entering of the hospital area and the hospital. The current main entrance and the polyclinic entrance are out dated, not representative and don't contribute to the welcome feelings patients and visitor should have. It is the AMC that envisions these problematic aspects solved into an embracing routing in- and towards the building.
Important to the hospital is larger growing presence within the world of academical research, in quantity (promotions and publications) as well as quality (research funds and impact scores). It is important for the AMC to remain as one of the top UMC research institutes. Through international cooperation it remains a key player within its core areas as previously mentioned. To increase its international presence valorisation is promoted from start-up companies.
The research and treatment center forms the core of the AMC, these function feature high investment costs, complex housing and growth. The functions feature polyclinics, research centers e.g. but in the future the polyclinic functions need to grow. In order to achieve this sub functions have to be segregated, that would mean that research functions are supposed to be clustered as for the other functions.
Flexibility plays a role within the strategy to make more efficient use of the current facilities. This means that employees will have to share their office facilities with employees from other facilities. Therefore reducing 70 offices spots per 100 employees. Another aim is the redevelopment of internal spaces so that they can be used for one main purpose like offices, waiting, research, consultant rooms e.g. and not just for one specific department.(AMC, 2016)
Redevelopment constraints
The board of the AMC has made the decision to not demolish the building complex. That brings with it that transformation and renovation is a considerable option for them. But with these come restrictions, demands that the AMC has set up in order to maintain an certain appearance and values embedded within the architecture. But transformation and renovation brings difficulties with it, for one is that a hospital is not simply able to shut down for a long period of time while construction takes place. Appointments, surgeries and treatments are scheduled far ahead. While at the same time various functions require sterile facilities. Sterile research samples cannot easily be transported without external factors influencing the sample. In short the transformation of a hospital is very difficult. Luckily the large city like building provides the opportunity to temporary shut down one of their various fragments. The constraints that are set by the AMC are:
1. During transformation the hospital should remain in function. That would imply that a phased development plan should be developed.
2. The redevelopment should remain within the current boundaries of the building. Excluding the entrances of the building and the renewed landscape plan.
3. The concrete structure should remain in place and should remain visible.
While the first and second constraints are very clear and logical to implement in the new design. I believe the third one to more debatable. While the AMC wants to keep not just the interior but also the exterior concrete structure visible. In my opinion a transformation within the architecture of the AMC should result into an new architectural intervention. Therefor part of the concrete structure including the facade should be transformed into the new architectural intervention.
1. Remain active while construction
2. Building boundries
3. Concrete structure
The Design Void
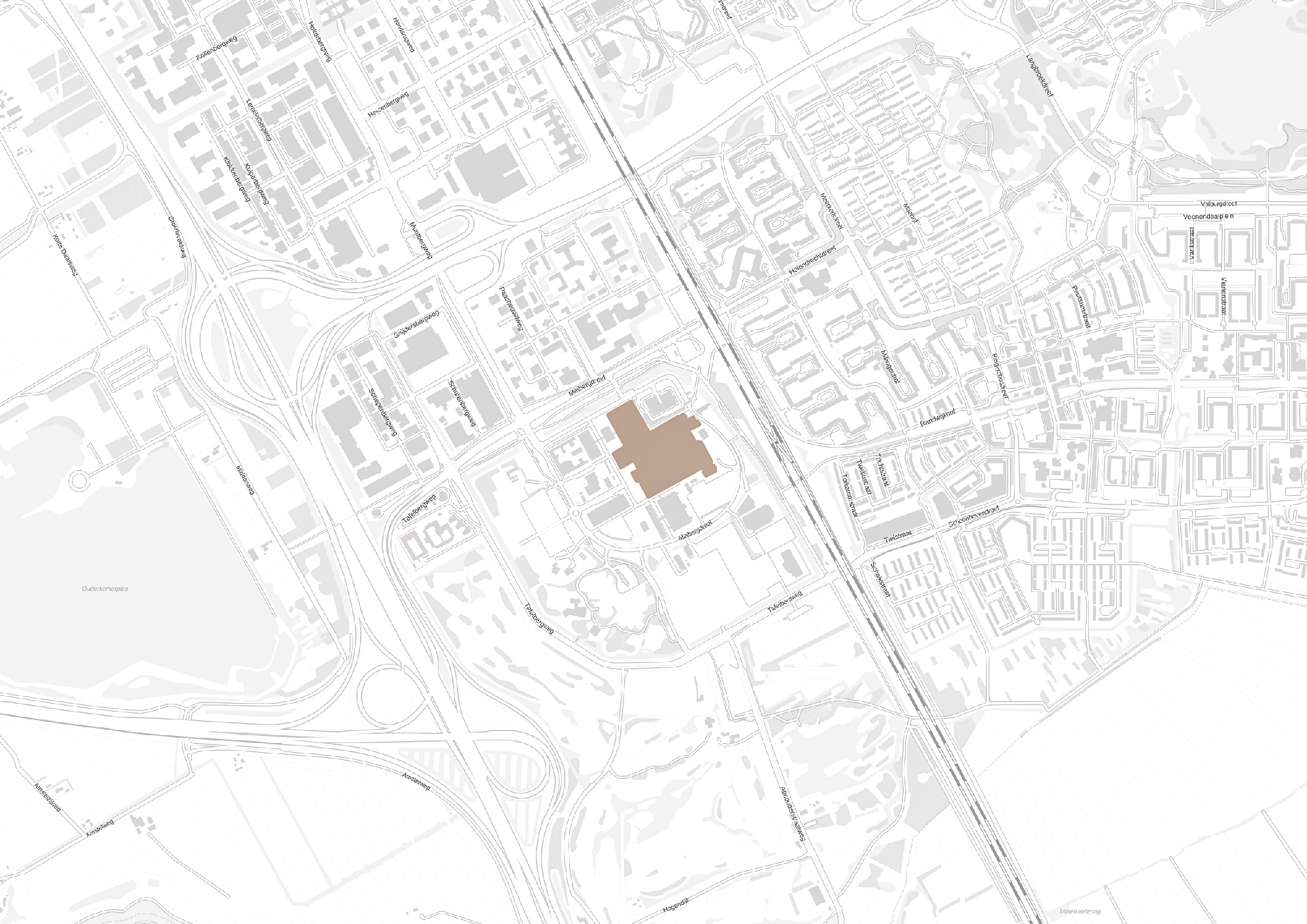
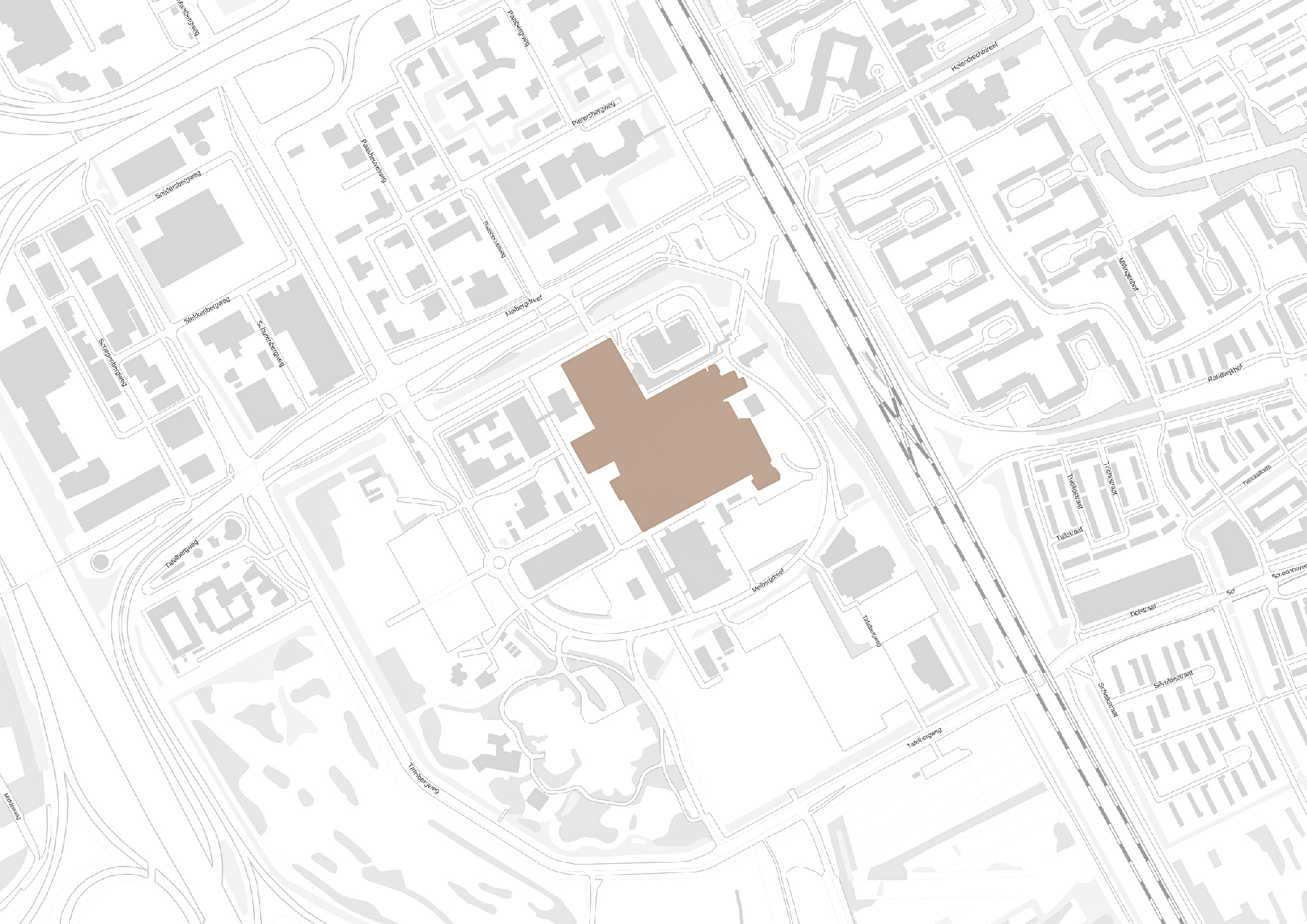
Medical centers are complicated buildings to design, often these buildings house a wide range of different functions with each of them having different requirements. In order to house these functions hospitals tend to be very large. This can clearly be seen when someone looks at the Academic Medical Center. Therefor a (re)design of a hospital building is very time consuming. Unfortunately this assignment is being done within the graduation track and there the time that is required for this redesign is not available within the graduation course. Therefor the design will be focused on a specific fragment.
It is this fragment that I will redesign into a state of the art hospital design. Incorporating the previously mentioned restrictions, aims and visions set by the AMC.
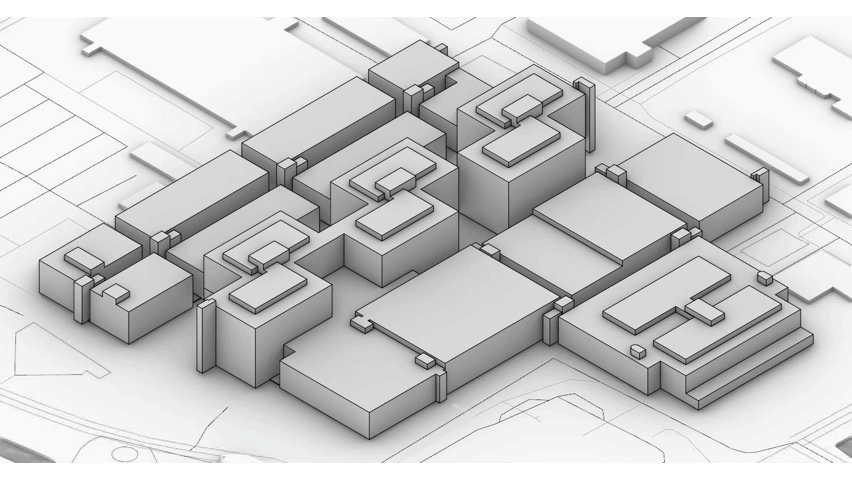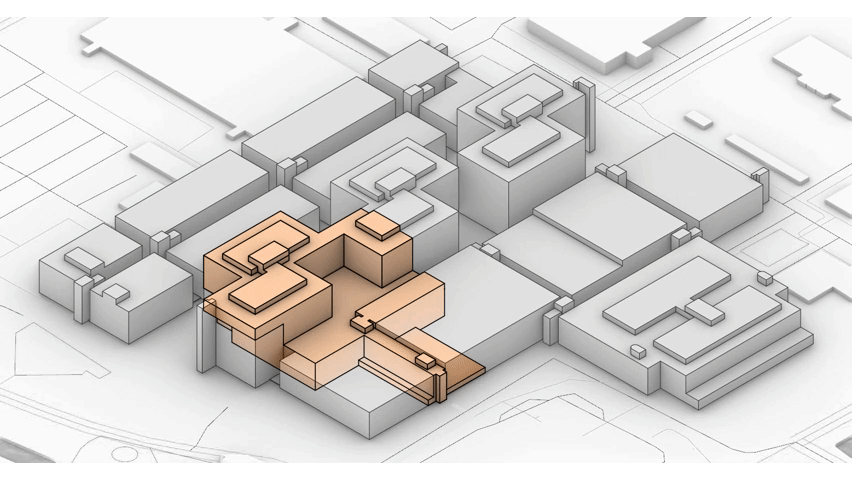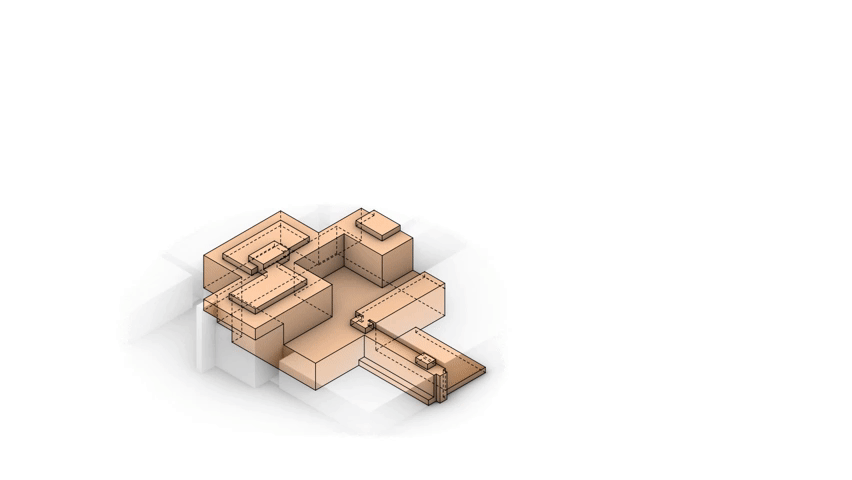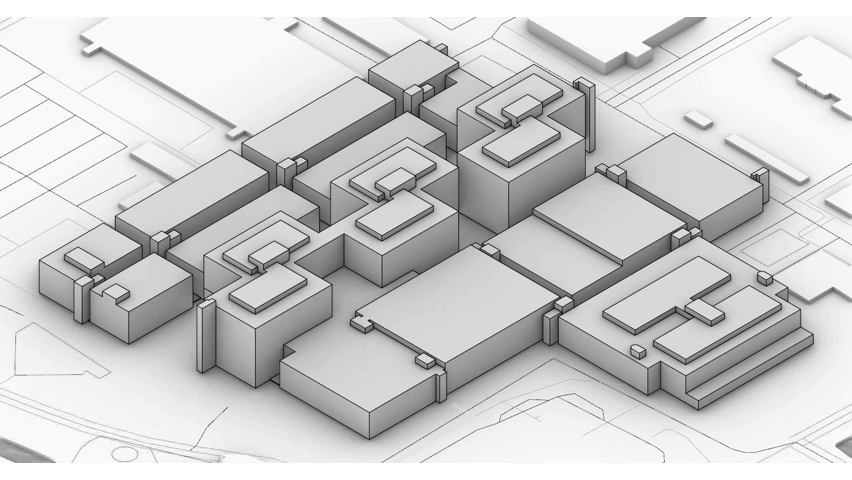
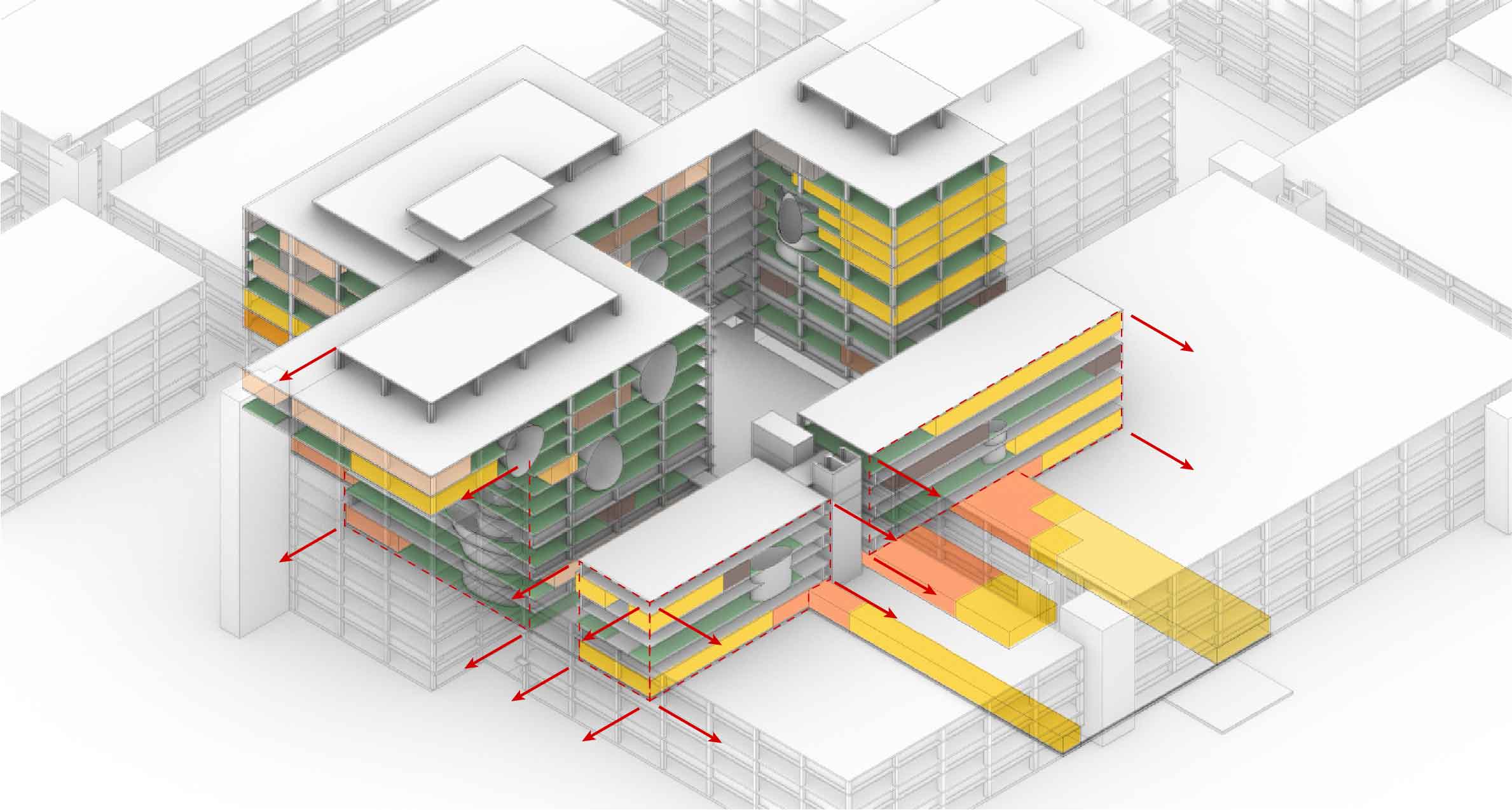
The design fragment of the academic medical center.
The functions
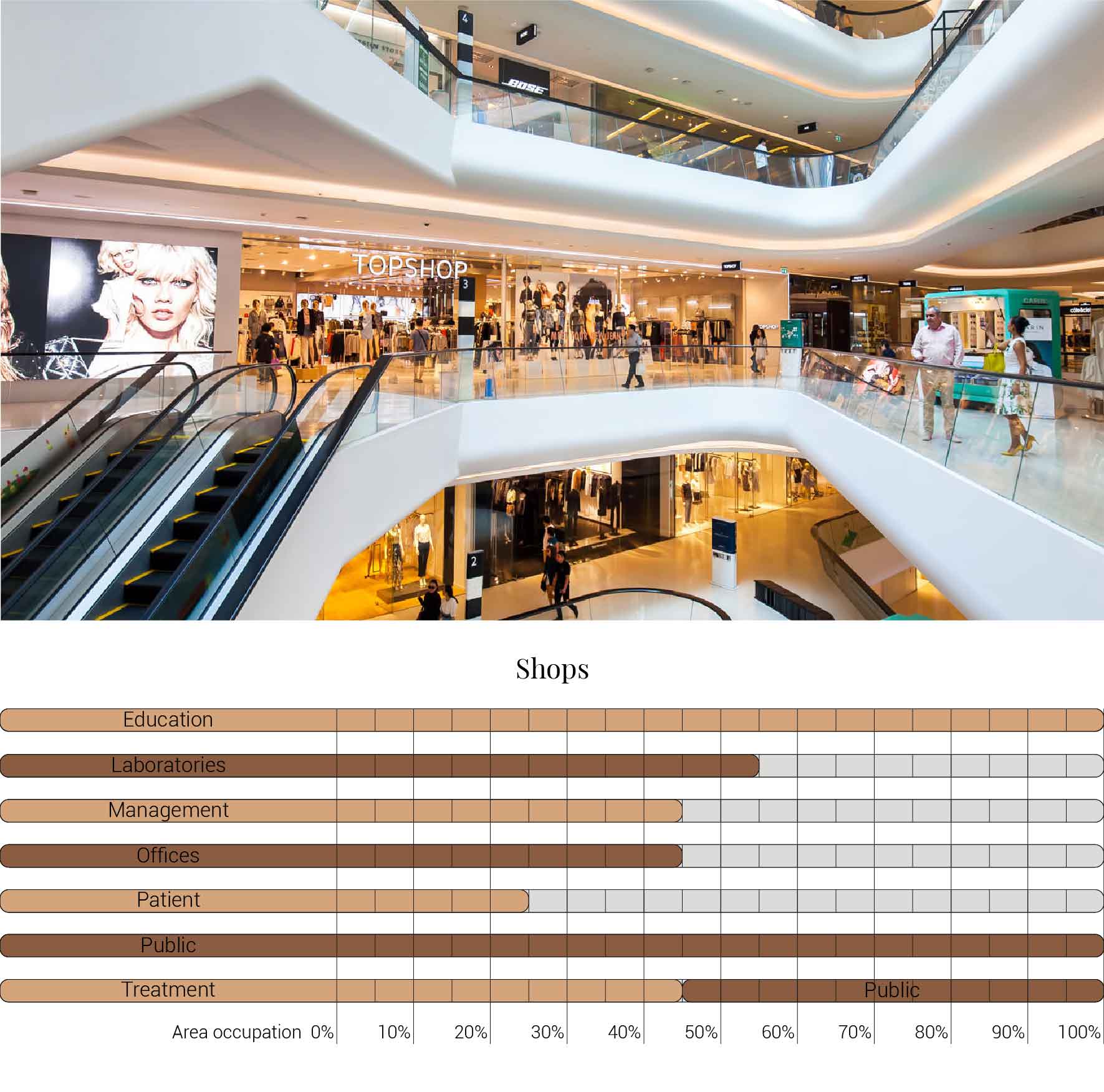
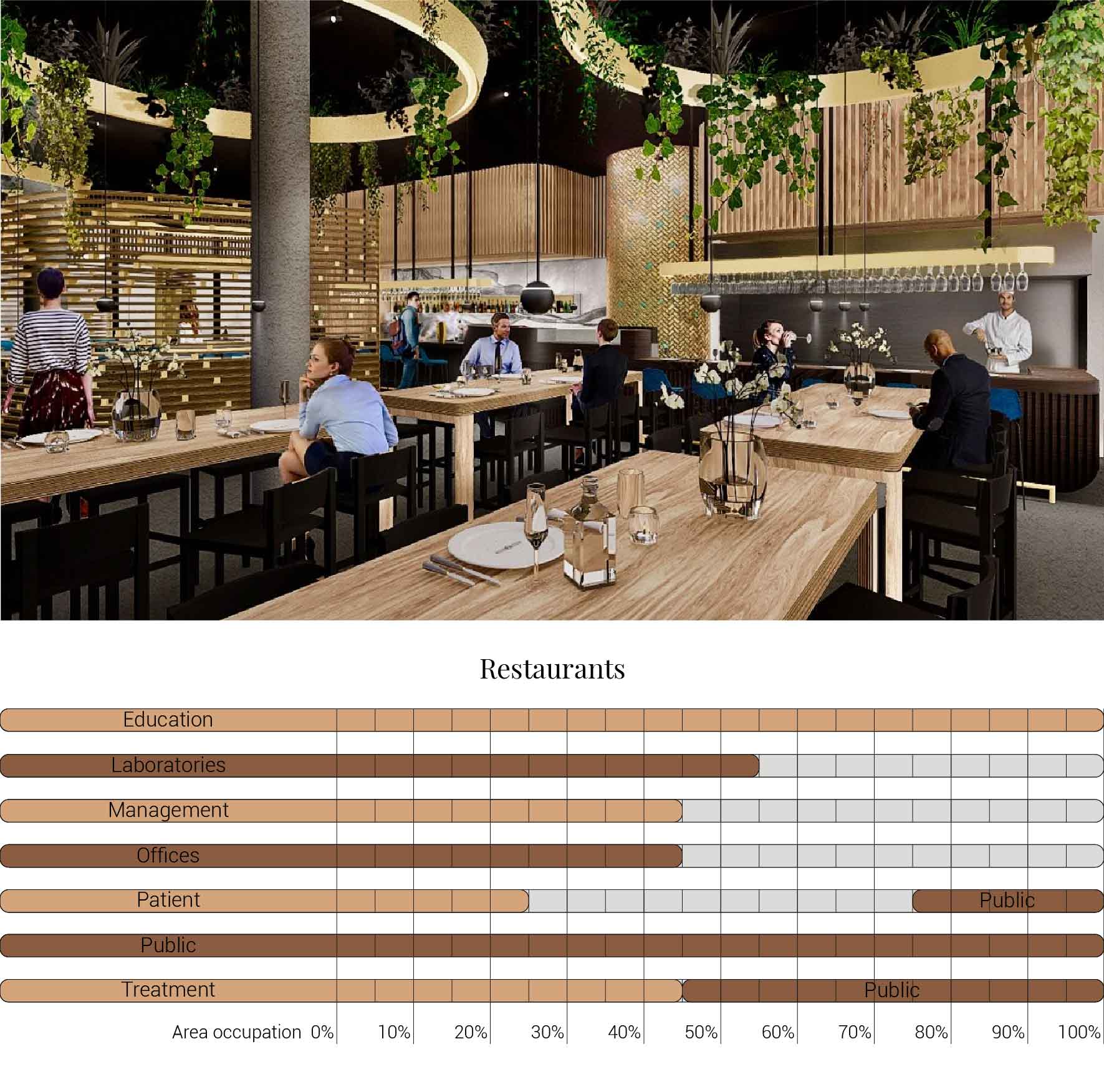
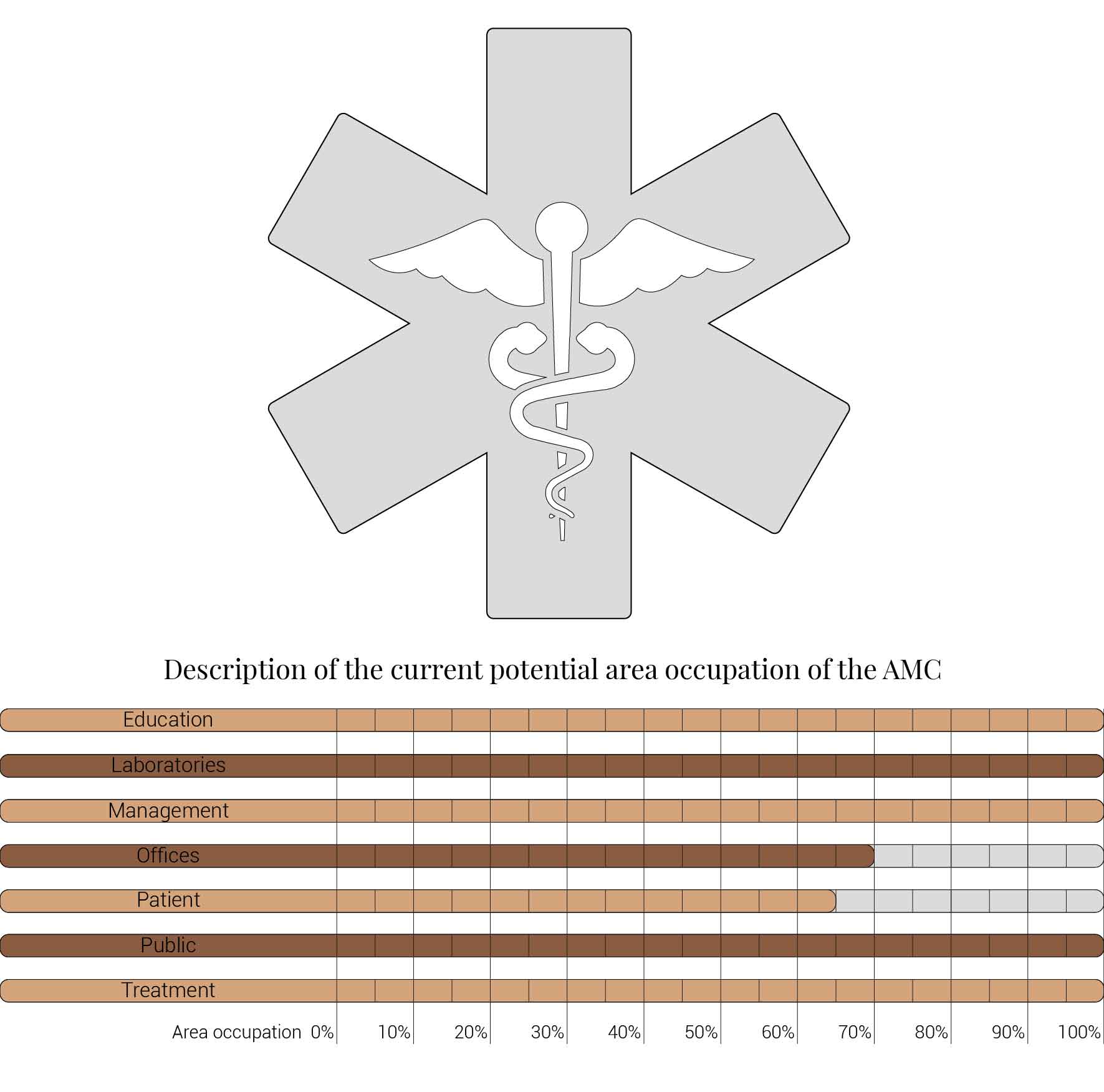
The decision to transform just a fragment of the building implies that I also had to reduces the amount of functions that I am able to incorporate into the design. The original fragment is home to varies functions which I have to decided to once again use as input for the new. The functions that originally are housed in this segment are, the main entrance, lecture arena, lecture rooms, toilets, varies laboratories and treatment facilities with their own specialism, shops, restaurants, offices, patient care units, nurseries and many more. But the basically can be reduced to the functions as shown below. What this image also shows is that these functions and areas are used as relative for comparing the area occupation of the building to the new situation.
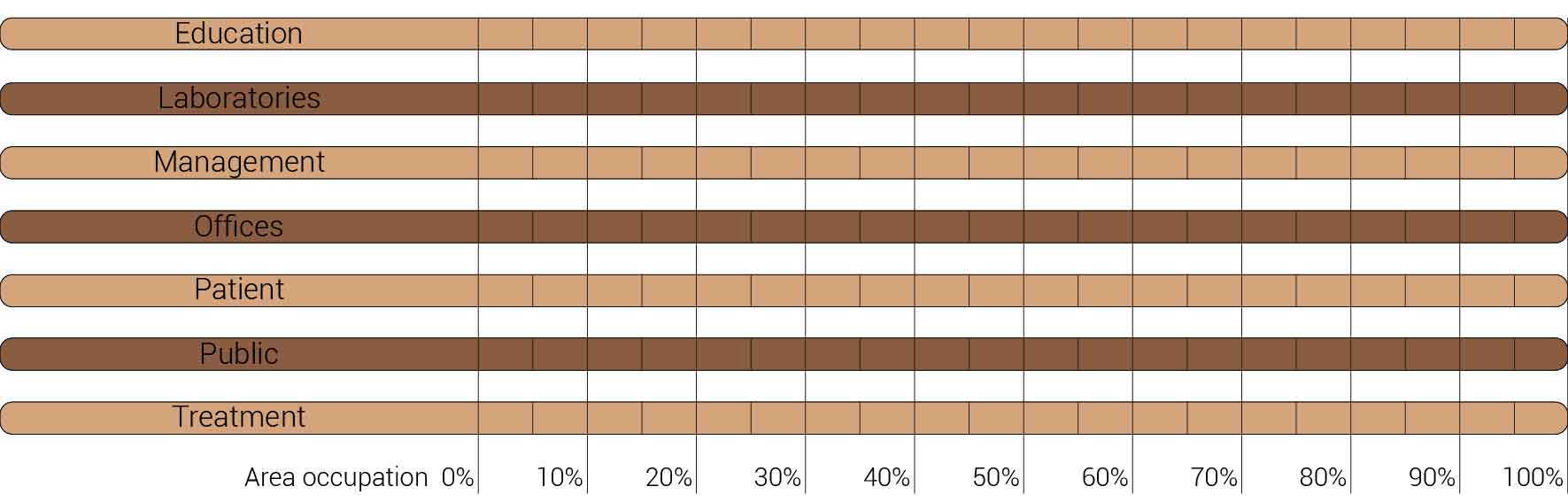
Overview functions and their occupation.
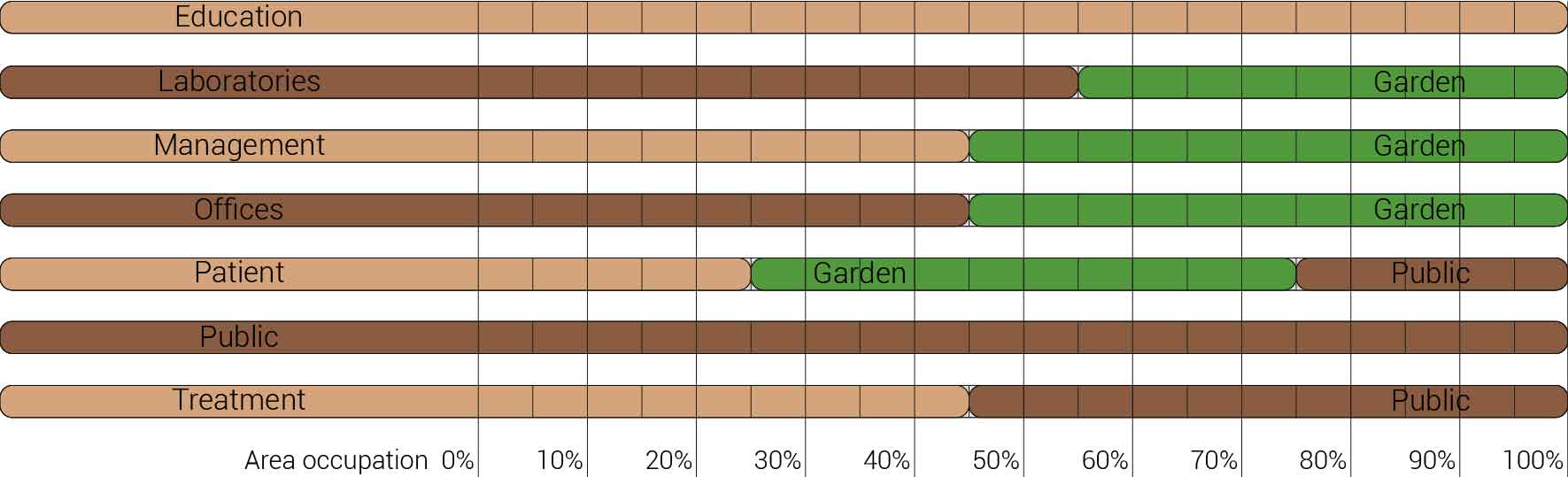
Within the section about the AMC's vision and aims it already had been stated that currently the AMC is struggling with hidden patient care unit vacancy. As a result of this vacancy one out of the three pcu towers could be repurposed. Since my fragment houses one tower the area occupation can already be reduced to sixty six percent. But it does not stop there the AMC aims to reduce the amount offices currently in used from hundred office places for hundred employees to seventy offices places per hundred employees. Therefor also leading to a reduction of thirty percent resulting in the area occupation as shown below. This area occupation will form the basis for the further space reductions since the continuing technological advancements also influence the area occupation.
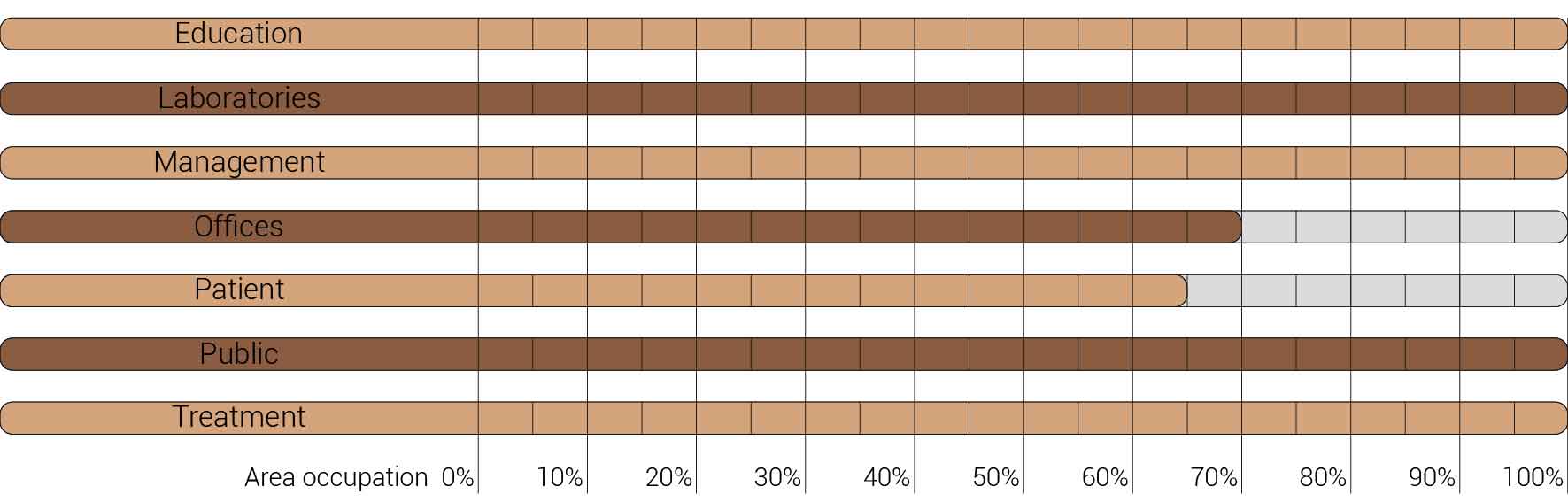
Overview functions and their occupation, renewed.
The future of healthcare and the hospital
Survivability is at the core of every human being. Everything we do we do to survive and prolong our existence as humankind. In order to live longer and survive diseases we have developed a large and complex healthcare system. One shackle within this system is the hospital. This place is designed as a last resort, a last chance for the ill to get better. Since the hospital is a place for healing and becoming well, it would imply that being within a hospital would be experienced as a pleasant experience. But on the contrary people often experience anxiety and discomfort.
This is due to that same survivability, it is when we become ill we become uncertain. We lose the control of the situation of health. As a consequence of this uncertainty it becomes difficult to predict what will happen next. Which then can result in feelings like isolation, alienation and depression. As a consequence patients can suffer from increased blood pressure, stress, reduced sleep. All of these consequences not being beneficial the potential recovery of a patient's health. But this is not what a hospital should cause to any patients. Therefor the hospital architecture should change and with technological advancements the future of hospital design will change. This section will present the future prospects for hospital architecture.
Design characteristics for future hospital architecture
To prevent these negative impulses from occurring in future hospital architecture, research has been done to find out which design factors matter to patients in order to create a healing environment. It proposes six themes with their own associated design characteristics to improve the healing environment; Spatial comfort, Privacy, Autonomy, Sensory comfort, Safety and security, and Social comfort. It is these characteristics that should be taken to heart while designing the new hospitals and especially the patient care units.
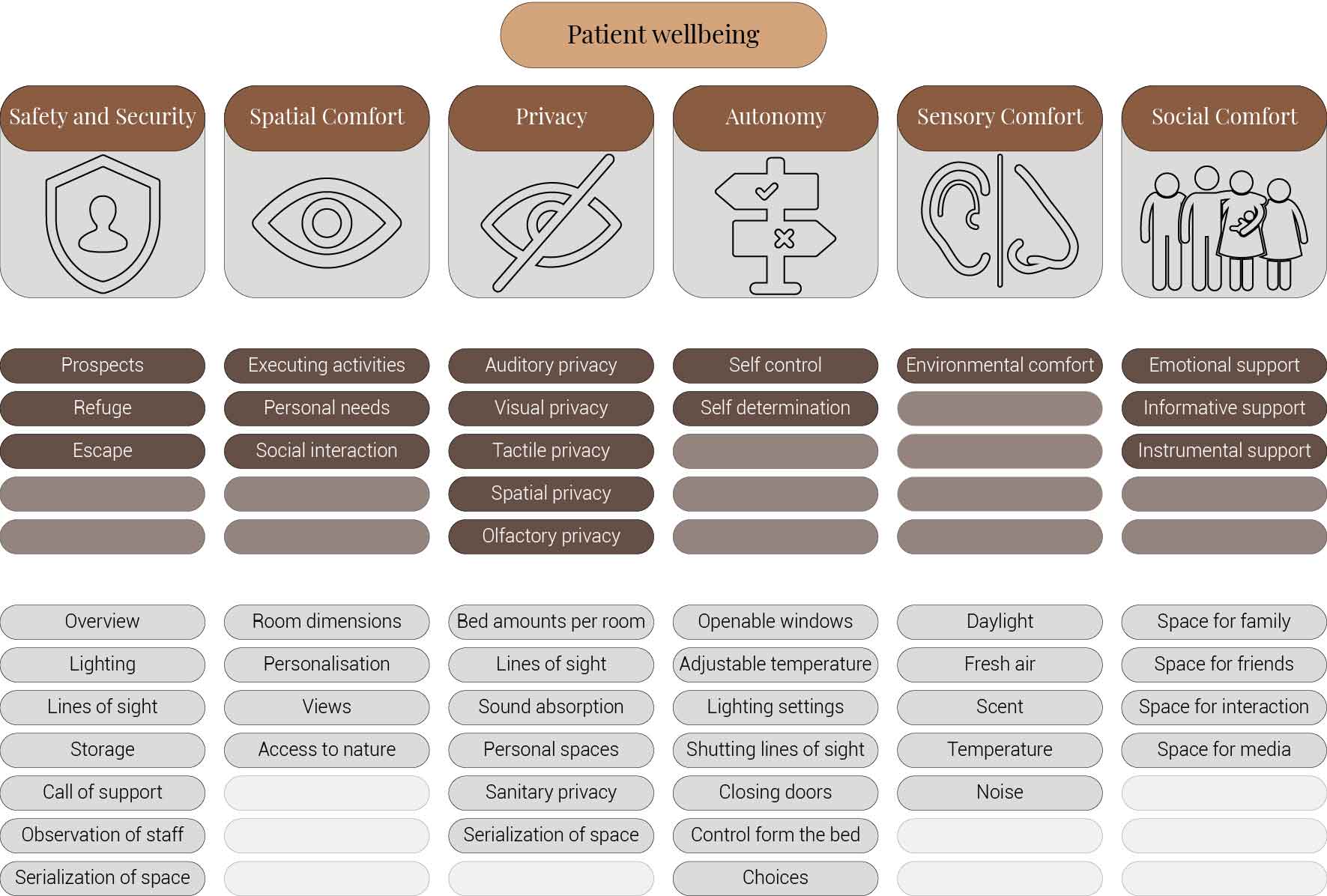
A summary of design characteristics based on the six themes
This image is based on (Schreuder, Lebesque, & Bottenheft, 2016)
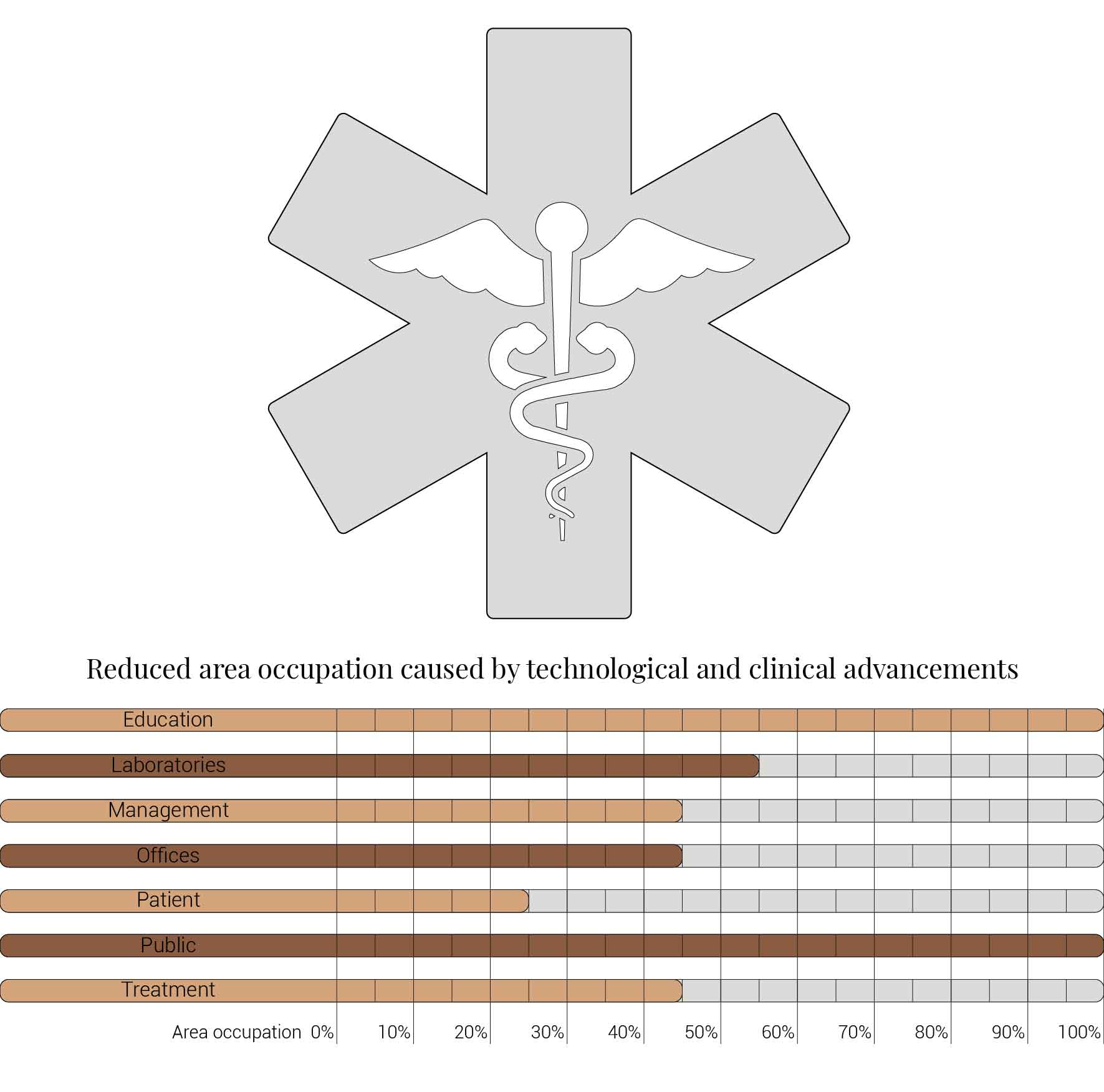
Hospitals will be smaller
It is expect that hospitals will shrink in size in the coming future. This reduction is caused by various different influences. Often caused by technological and clinical advancements with each influencing different functions within the hospitals. That also implies that my design fragment will be subjected to spatial shrinkage.
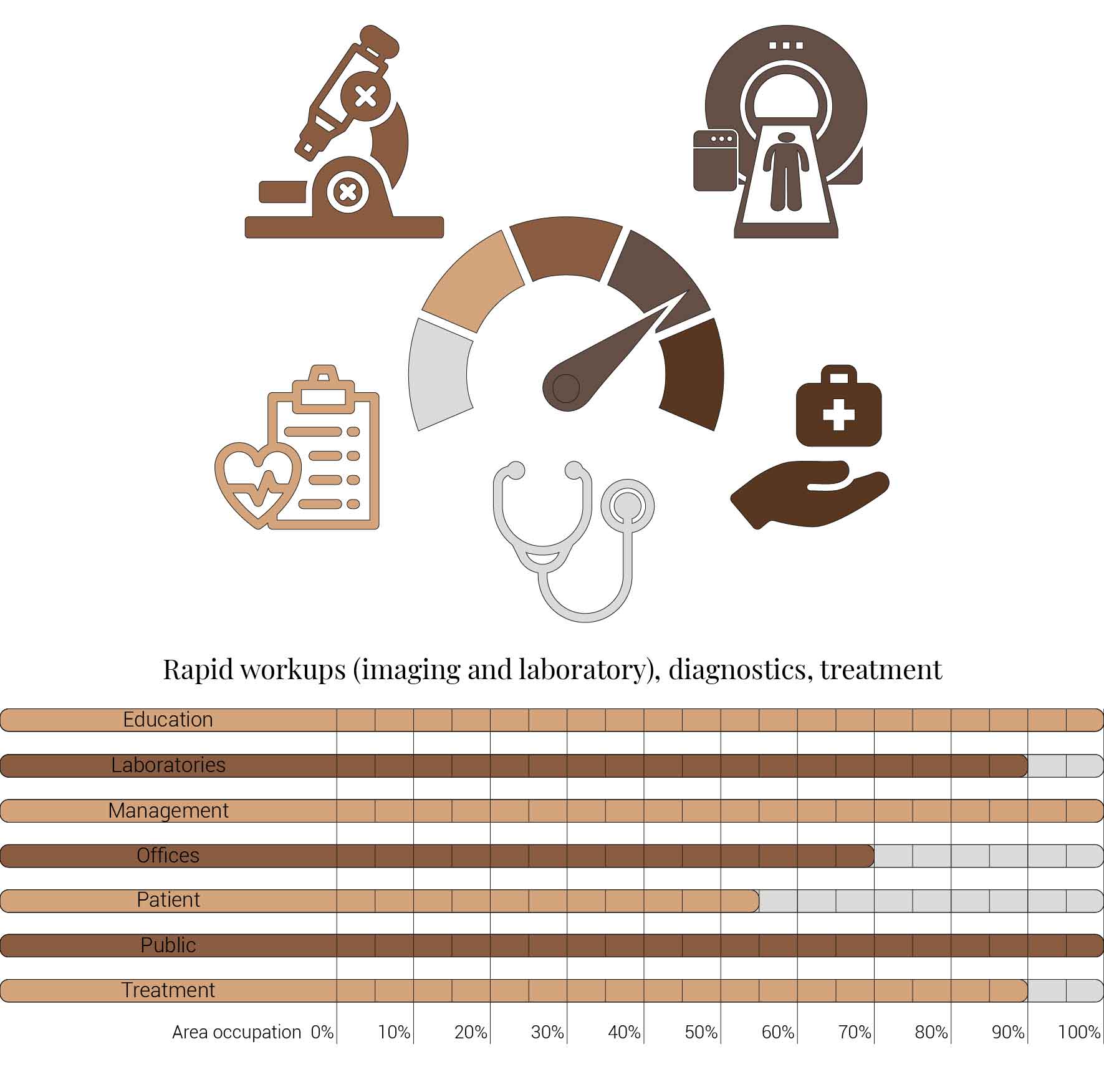
The first influence is increased speed of patient work-ups (imaging and laboratory), diagnostic tests, and treatments. This has as a consequence that patients don't require to stay as long within the hospital as they used to do. Reducing the need overnight rooms for patients. While simultaneously decreasing the amount of machines necessary to preform and process these work ups in the laboratories. As does it reduce the time that the treatment functions are occupied by single patients.
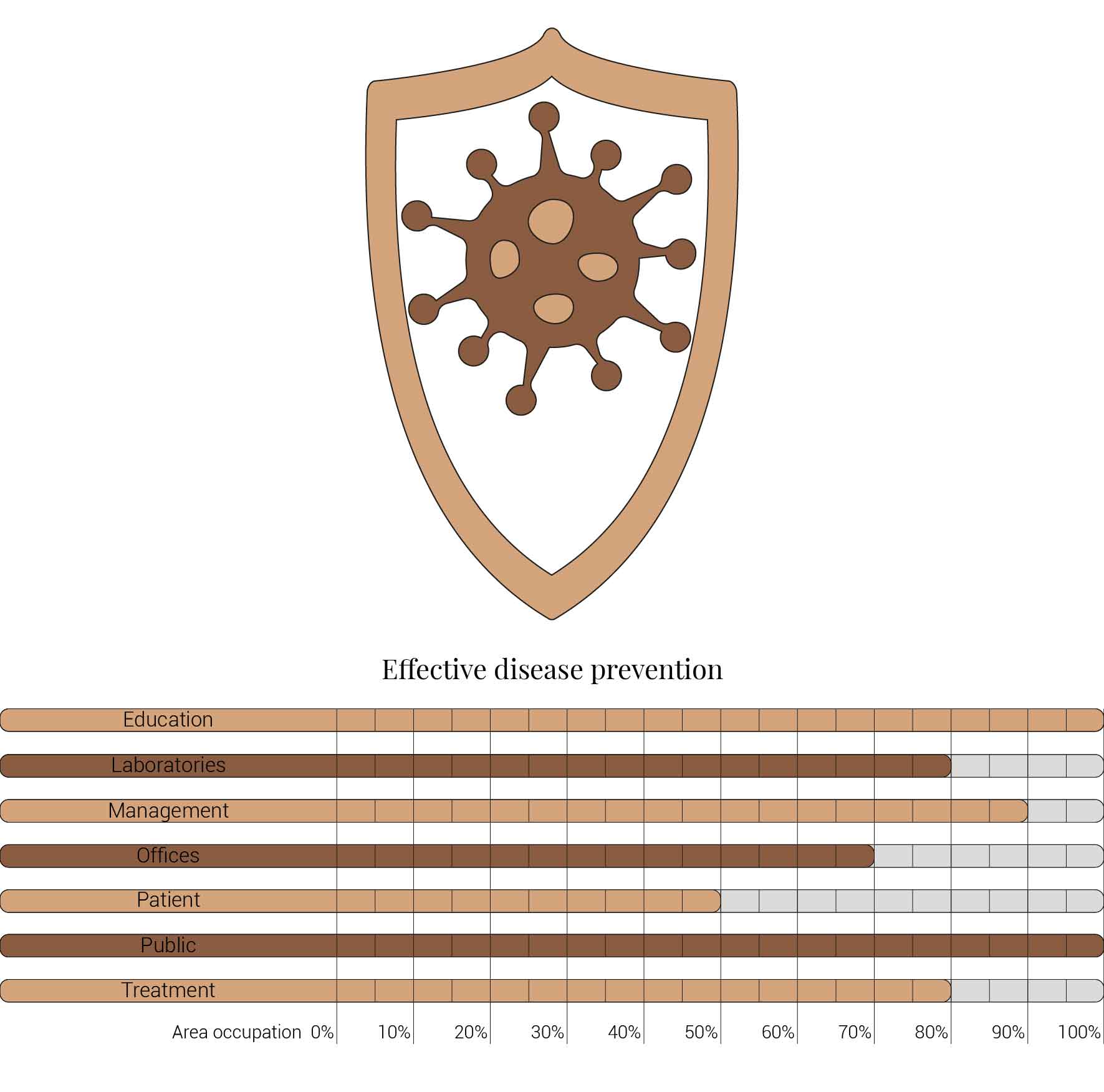
Another aspect has already been mentioned before, the effective disease prevention. Hospitals, including the AMC, are trying to relocate different phases of within the whole healthcare system. Therefor are symptoms of diseases can already be noticed and treated in the early stage of the disease., therefor not requiring the patients to referred to hospitals at all. Furthermore this effective disease prevention could even prevent some disease from even occurring at all. Thus resolving in a reduced need for treatment, laboratory and management facilities as reducing the patient care unit need even more.
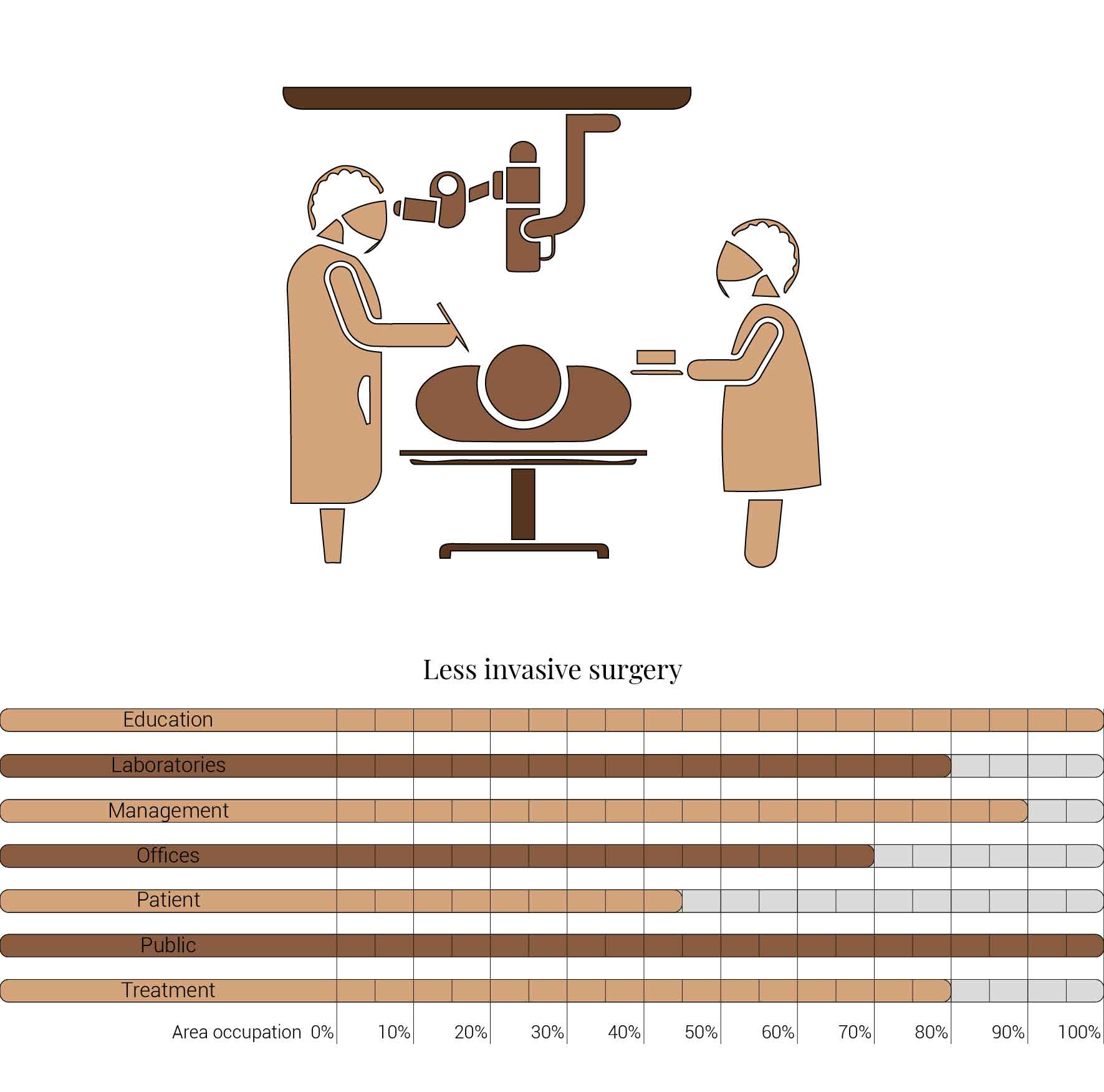
Technological advancements have enabled surgeries to become less invasive. Where back in the day certain surgeries where life threatening because of their large invasiveness into the body and the risk of contamination and collateral internal damage. This has now change to more safe methods with a larger prospect of recovery. This trend will continue to such an extend that once life threating surgeries and long and risky recoveries will become surgeries that can preformed within an hour while the recovery will happen before the end of the day. Therefor no longer requiring the patients to stay overnight. Thus decreasing the area occupation of patient care facilities.
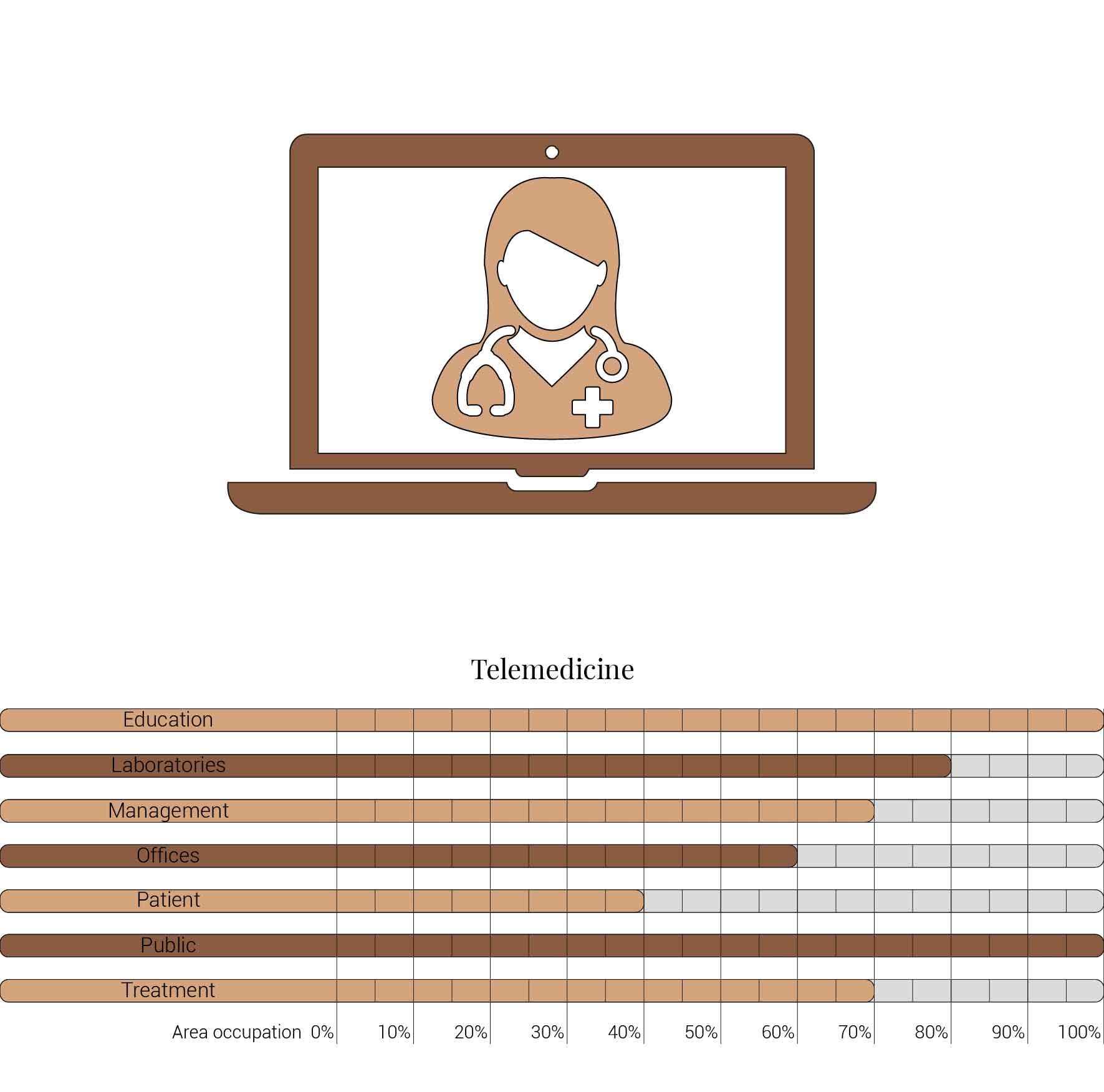
The increasing digitally connectiveness of humankind will is also starting to impact healthcare. Telemedicine, e-health and care are becoming more and more used. But this trend will continue. This will eventually result into a global teleconsultancies, enabling patients to be treated by experts from one country in another countries hospital while not having to be physically near. Another consequence is that patients can be able to stay in the comfort of their own home for treatment and recovery since they will be connected digitally. With supportive technologies of augmented and virtual reality techniques to enable these trends to advance even further. Therefor reducing the management, office, treatment and patient facilities for the individual hospitals.
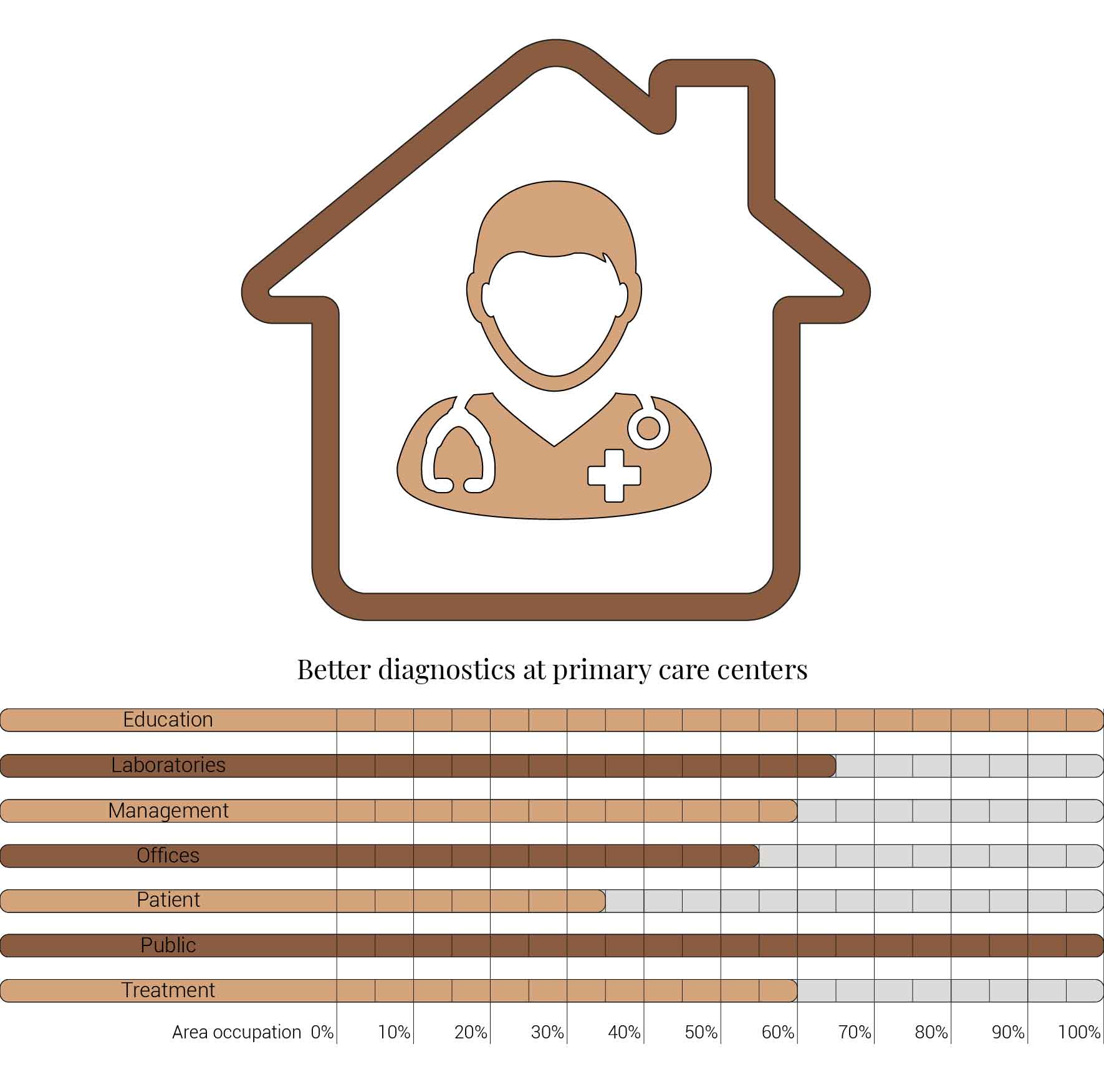
Better diagnostics at primary care centers has been slightly touched upon while introducing the disease prevention aspect but this theme continues to hospitals area occupation even further. The first step when noticing you are feeling ill is of course googleing your symptoms only to get even more worried. This leads people to take the next step and visit their general practitioner. Nowadays often the general practitioner cannot diagnose you due to his lack of equipment and refers you to the hospitals. As a consequence improving the pressure on the hospitals. But this will change, primary care centers will be equipped with better diagnostic capabilities. Therefor the general practitioner is to treat the patient himself or refer the patient to the specialized hospital. Once again leading to an reduction in space occupation for the laboratories, management, offices, patient and treatment facilities.
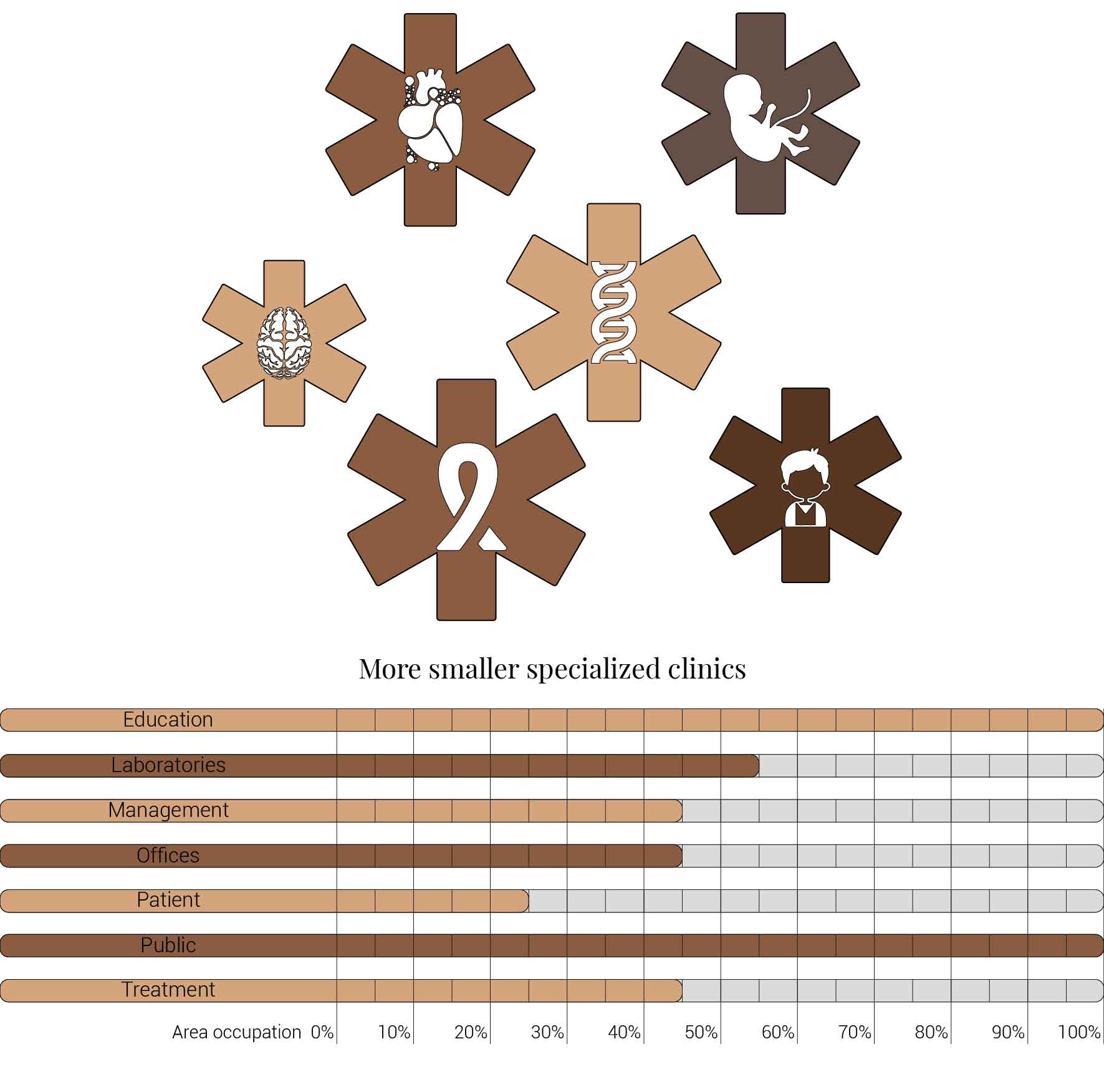
Last but not least that the general hospitals like the AMC will see most of their seven specialism branch of into smaller specialized hospitals. Due to the interconnectiveness of telemedicine, these hospitals won't lose their knowledge and skills in those fields of medicine. And therefor can still be called upon in request of consultancies. Thus providing the last space reduction for laboratories, management, offices, patient and treatment facilities.
Causes for hospitals to become smaller.
The user friendly hospital
As mentioned in the introduction, hospitals are often experienced as unpleasant impersonal healing machines. Touched upon before, that experience will change in the future. Hospital architecture is shifting towards patient centrality, just as the AMC envisions. Reducing the negative impacts and influences on health while simultaneously improving the aspects of recovery. While I have already proposed design characteristics that influences patient experience and recovery. This segment will elaborate on the patient centrality within the hospitals. While the last segmented showed reduction in area occupation some of these patient centrality aspects will increase area occupation rather than reduce the occupation.
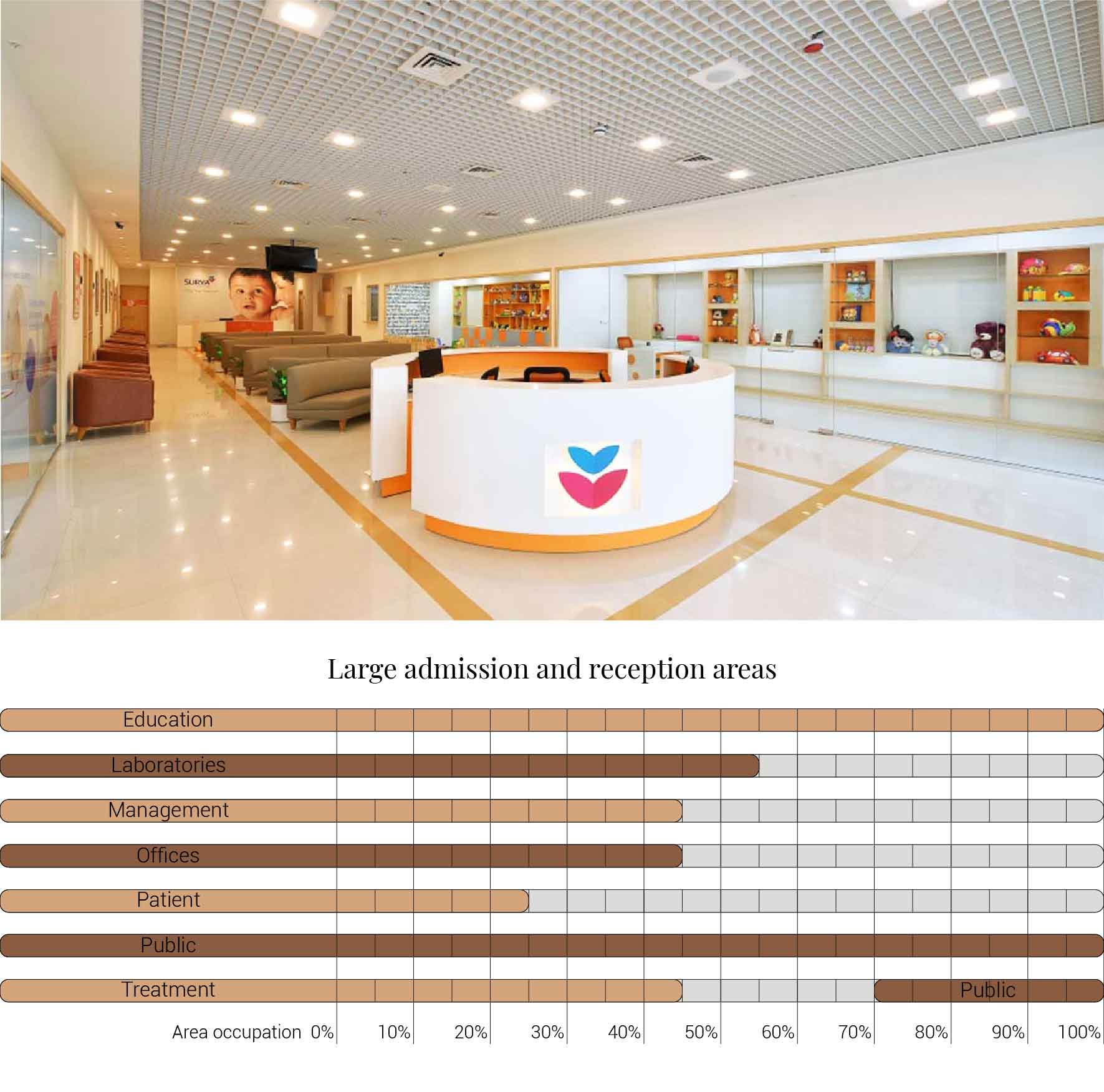
The patient centrality should be immediately noticeable. That would mean that even before entering the building the design should be based on providing an pleasant and welcoming feeling. It is that moment when you enter the building where this feeling should continue. Therefor the admission and reception areas should be spacious and designed in an elegant manner for the user to find their place in order to wait for further instructions and help. This therefor increases the area occupation for the public functions within the hospital.
Patient that are not just in the hospital for a brief period but also for the longer stays will be mobilized early. Essentially reducing their own patient care unit usage to just sleeping at night. To encourage patients to do so, patients should be stimulated with attractive and interesting things to do within the hospitals, like an wide variety of shops, restaurants and garden spaces. Due to smart monitoring these patients will not be lost within the hospital, but are free to go where ever they please within the hospitals borders. But these functions require space.
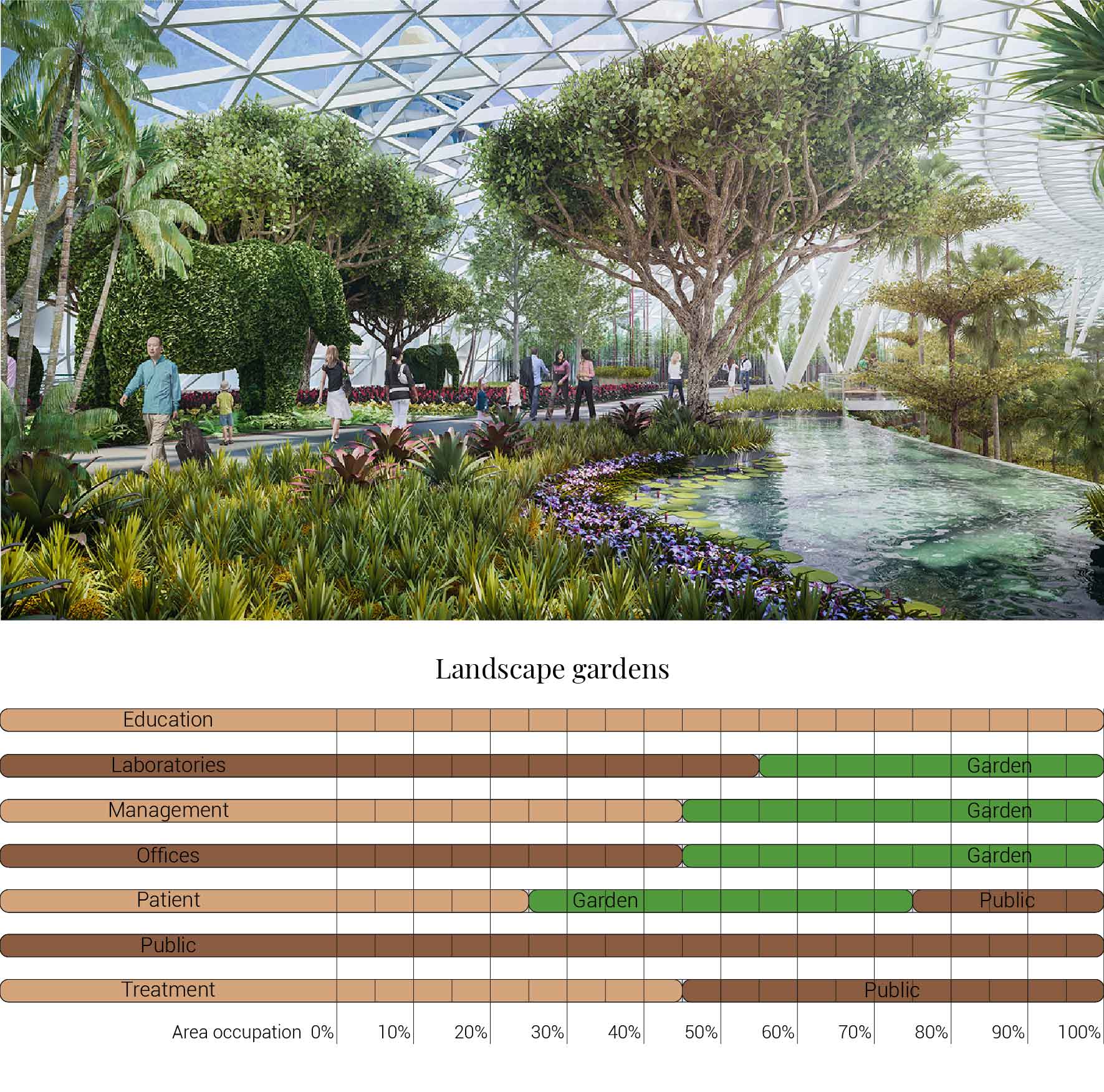
With in my opinion green taking up the most amount of space. It has been scientifically proven that view on and presence of greenery improves the well being of patients. Greenery reduces stress and therefor makes people feel more at ease and thus improves the speed of recovery. Besides green offers patients distractions from their often unstable situation. Because of the many benefits green will occupy the unoccupied space within the hospital.
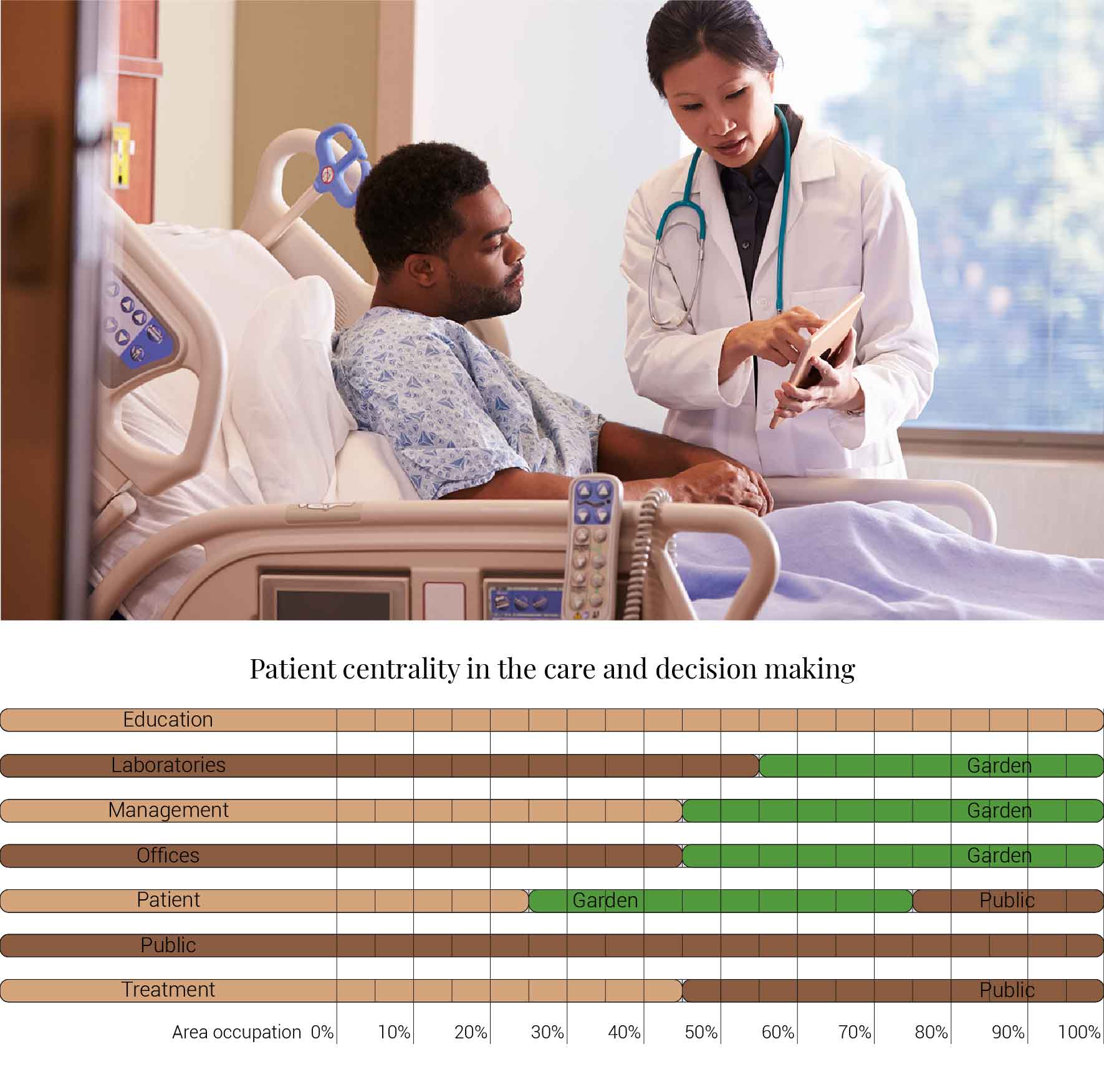
Another effort to make the hospital user friendly is the involvement of patients within their treatment. This returns the lost control they experience while becoming sick. It enables patients and doctor to discuss the recovery track and letting the patient chose their recovery track. To make sure patients are aware of the possibilities will be provide with interactive screens showing relative information about the illness and the opportunity to consult experts and other patients as an interconnected whole. But that would not be complete without the involvement of the patient family. The future patient care units will therefor integrate space for family members to stay overnight.
The various aspects of a user friendly hospital.
Other future advancements in healthcare
Besides these previously mentioned prospects there are plenty more changes coming to healthcare. But it is hard to predict what their impact will be on the architectural component of the hospital. Since they will be of large influence in the future I will mention them to give an extra indication of what is to come. These prospects include: 3d printing of organs, extensive monitoring of wearable technologies and sensors, genetic modifications, integration of AI in healthcare, e.g. personalized medicine, and nanomachinery.
Various future healthcare developments.
The Design
The functional distribution
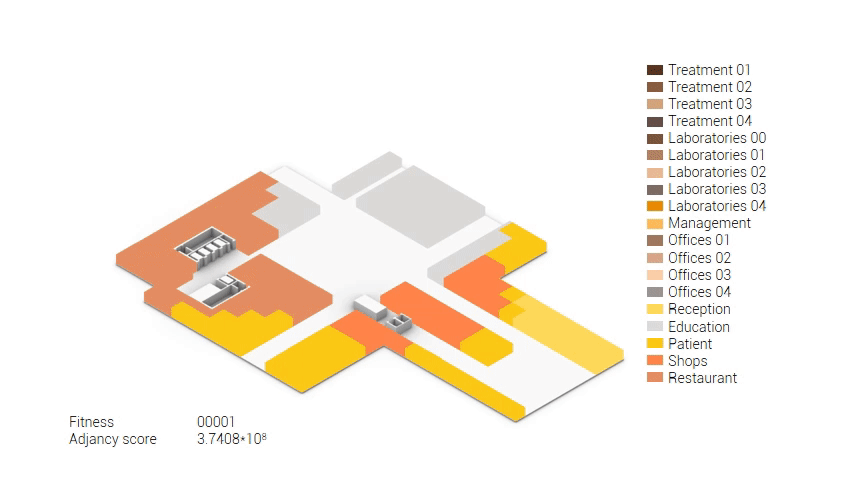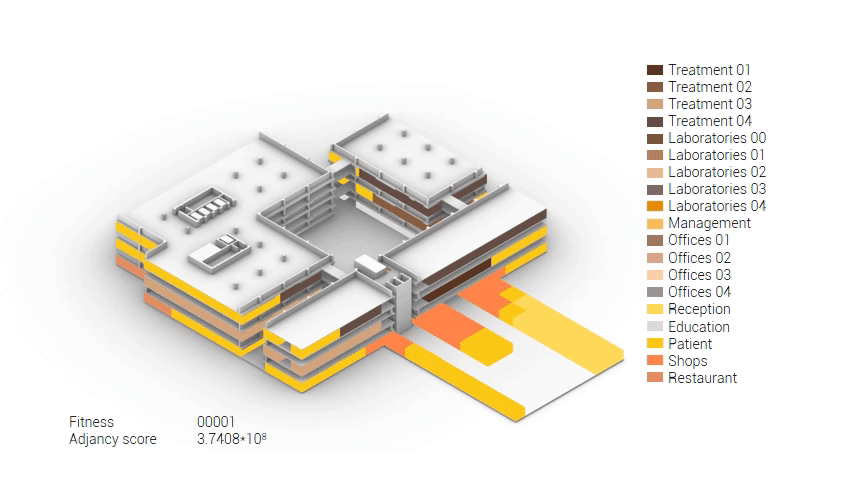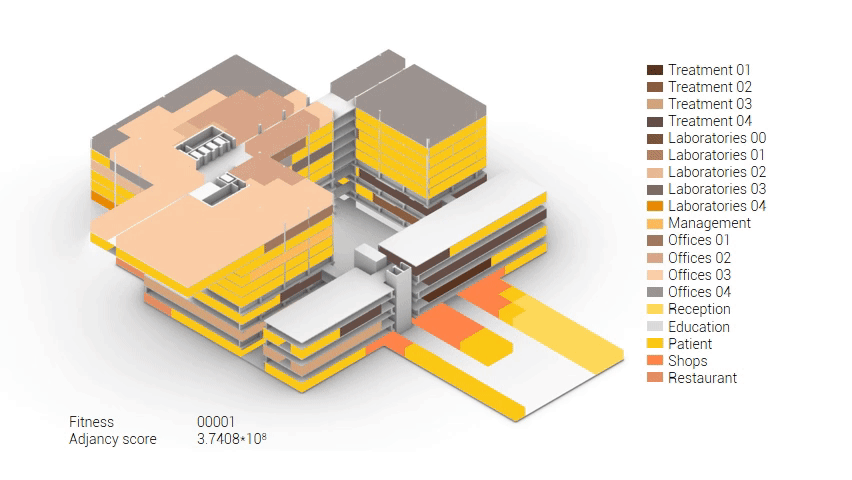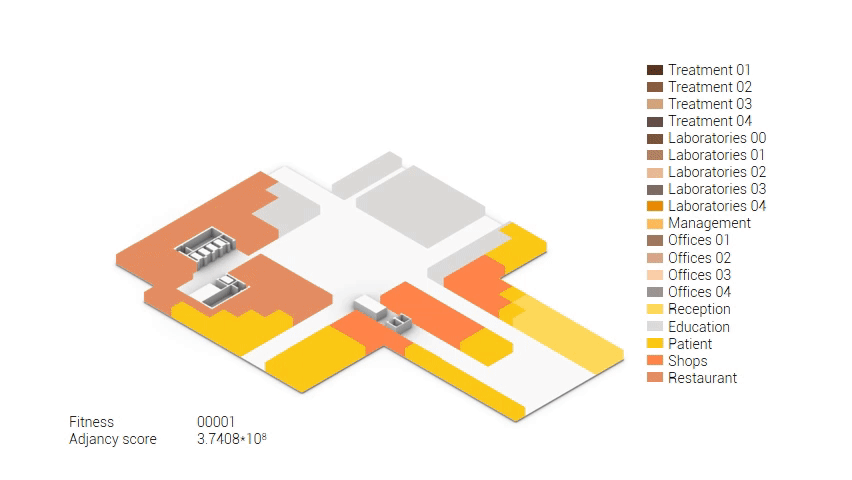
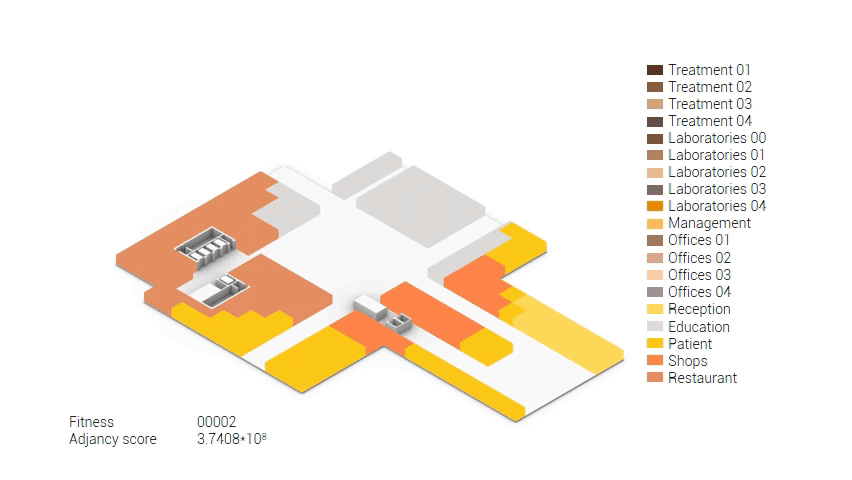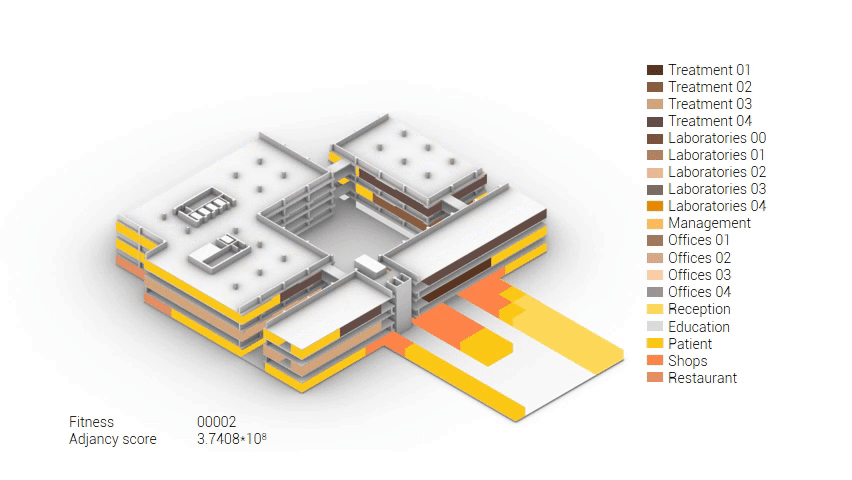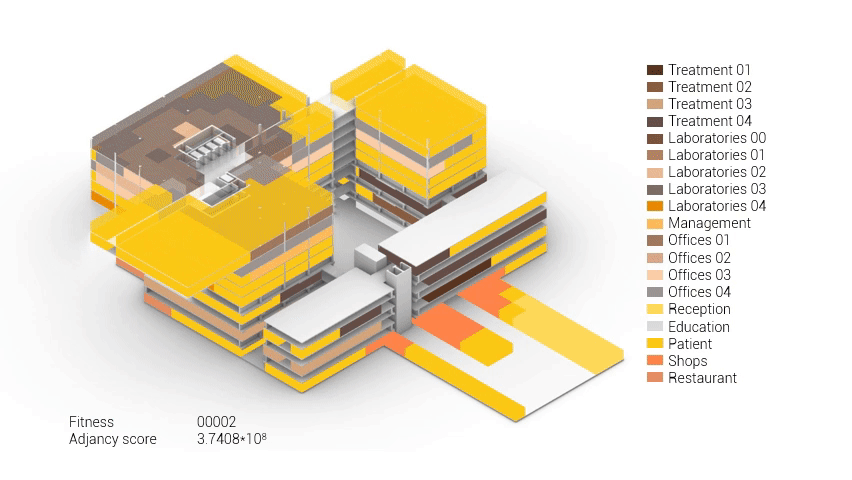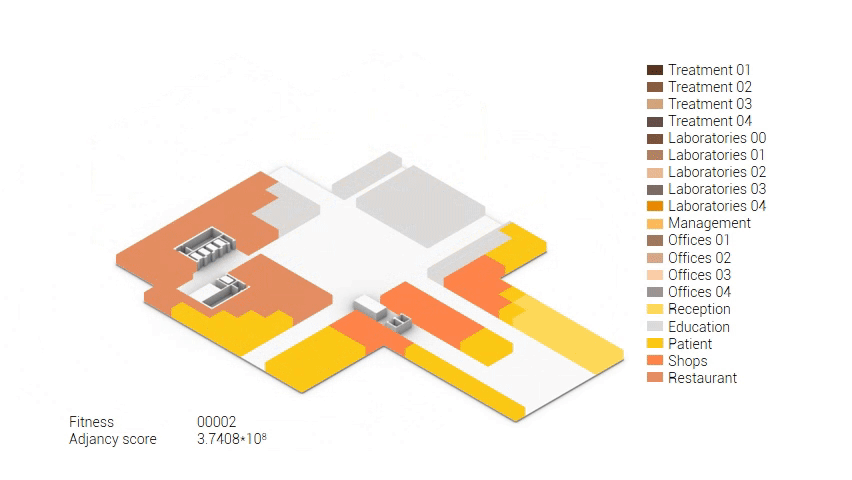
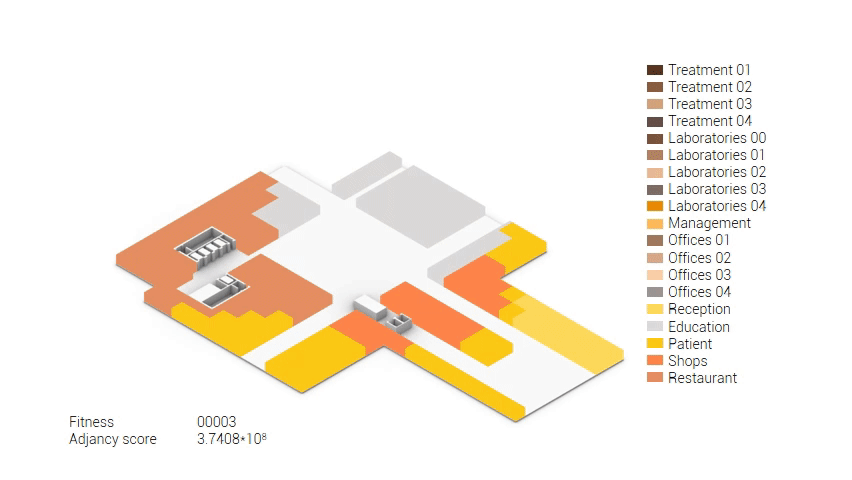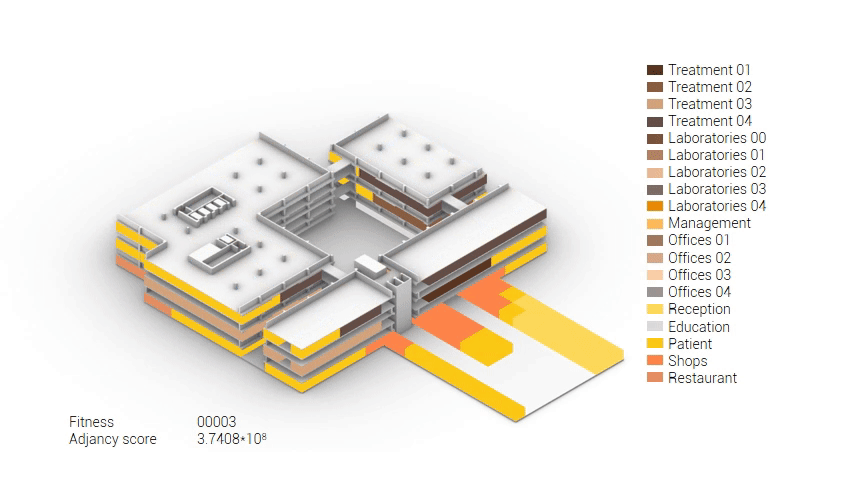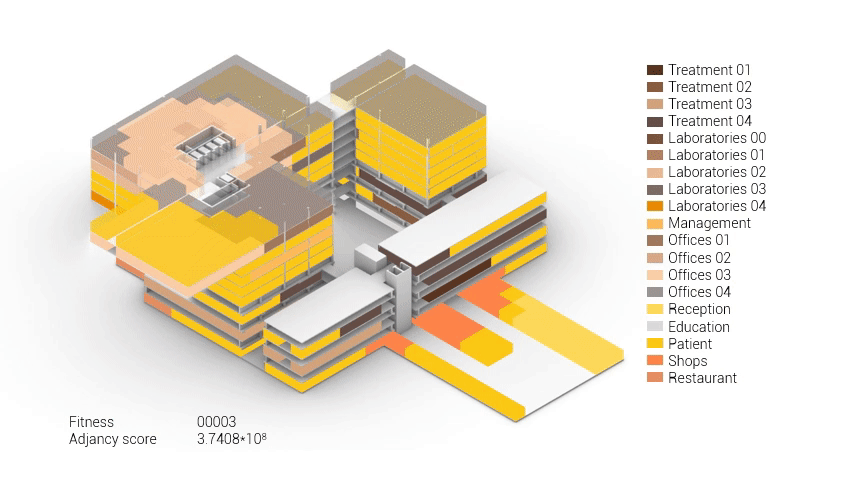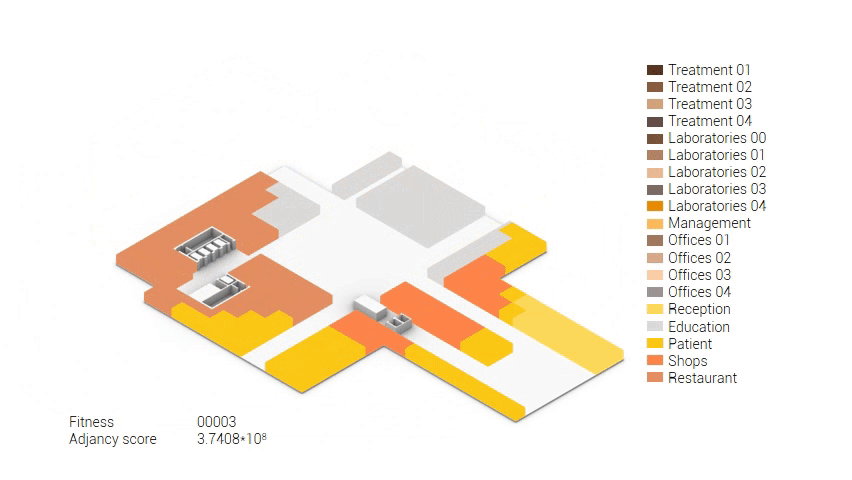
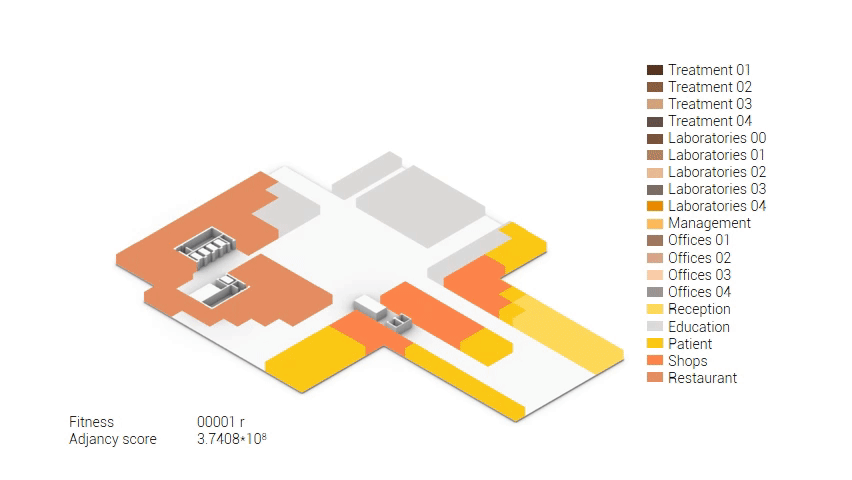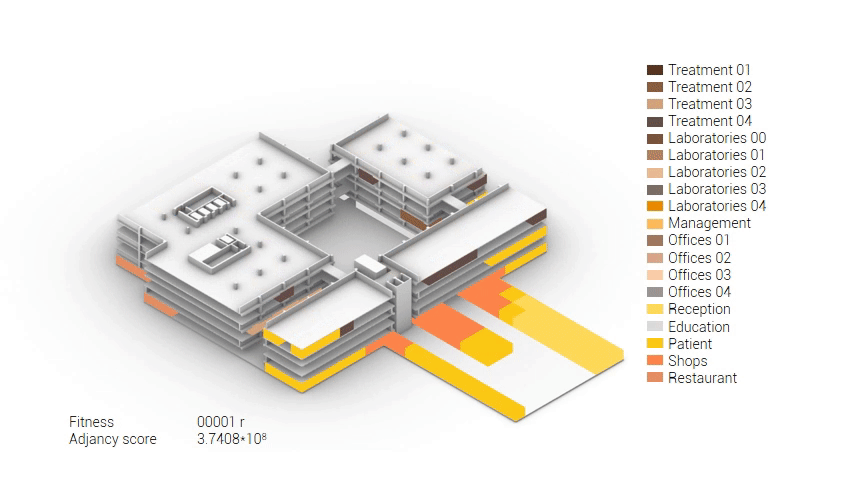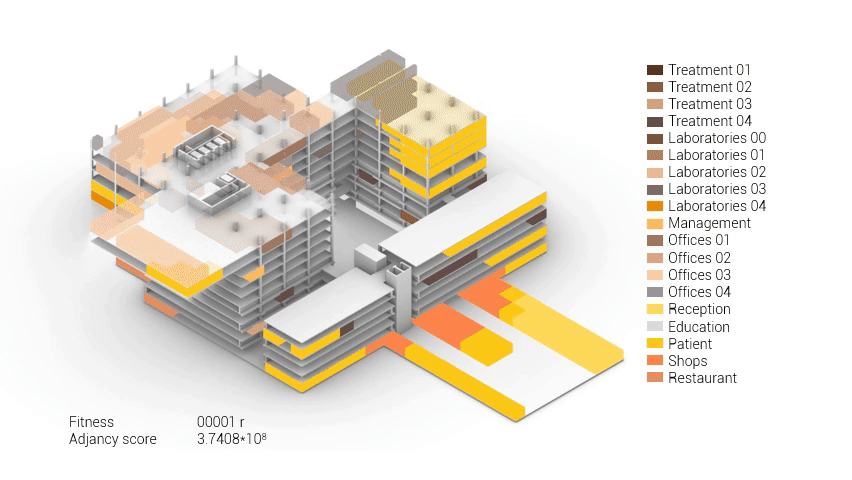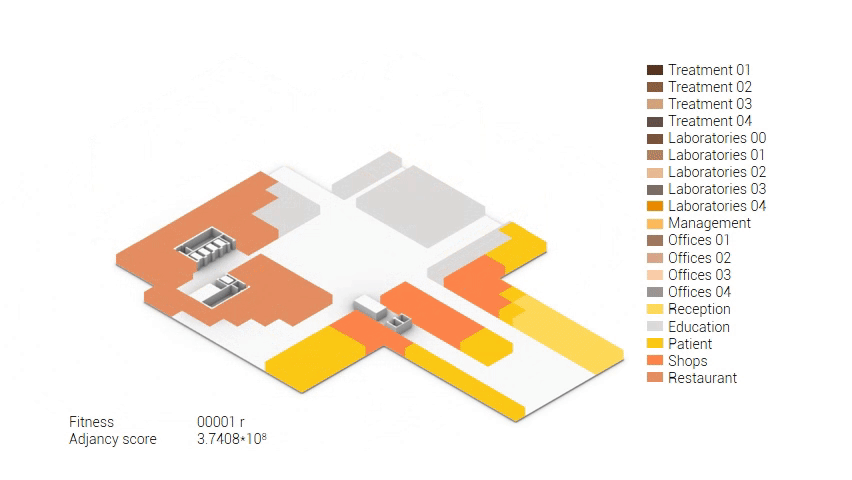
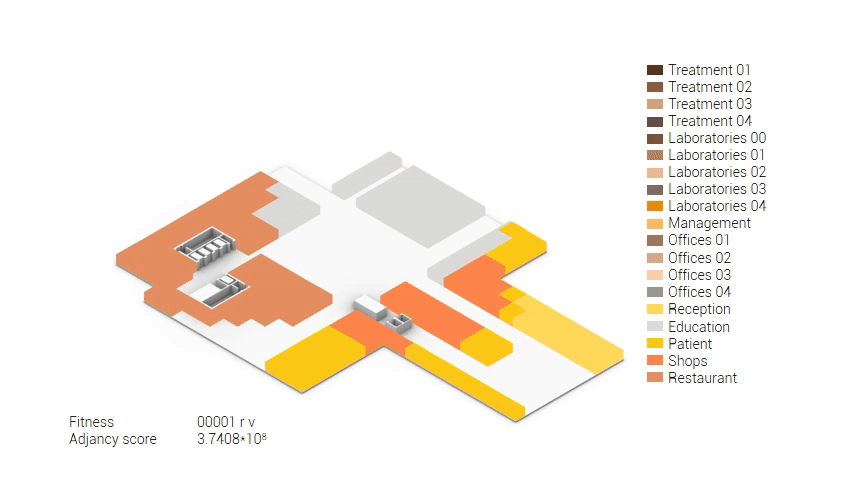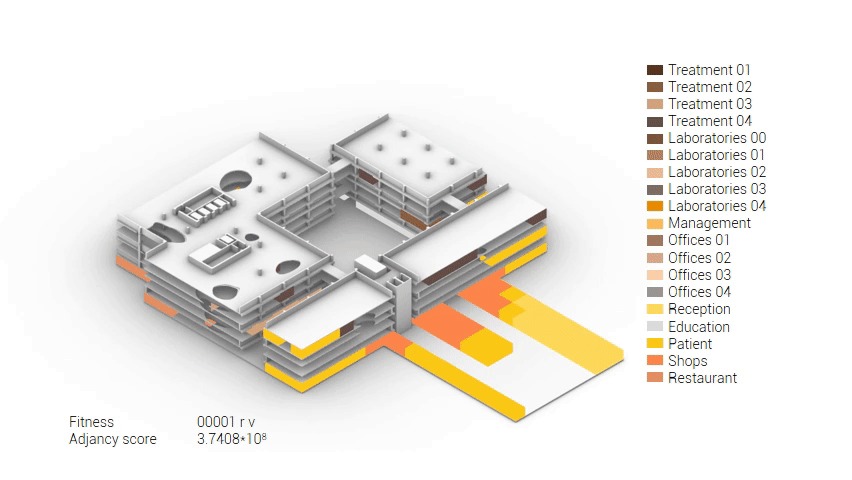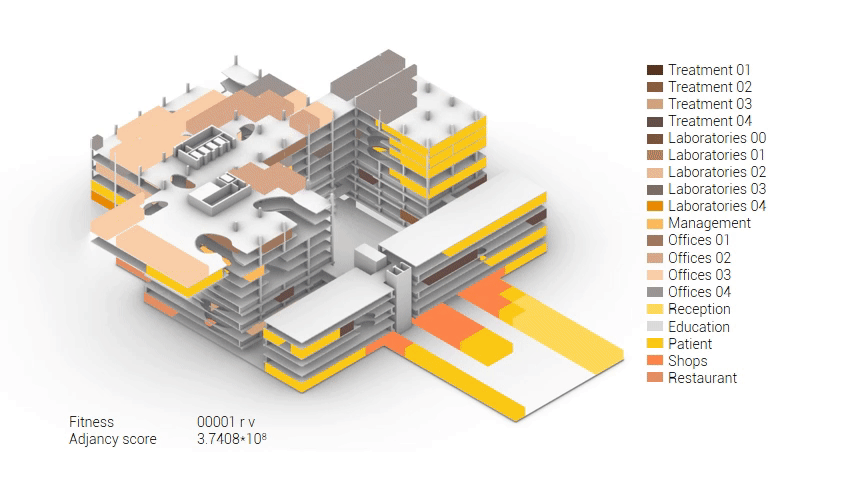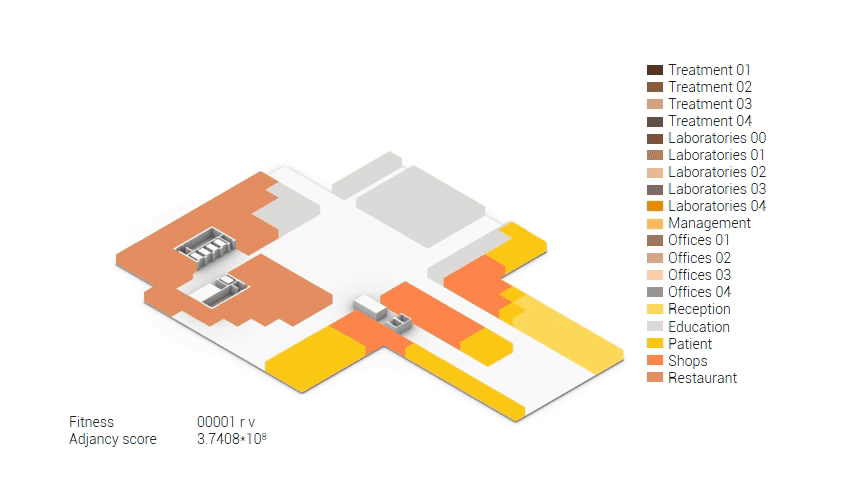
Based on the future predictions the area occupation of the AMC will change radically in comparison to what it is now. Therefor the AMC requires a new functional distribution. It is in this new functional distribution where the patient and nature can once again be centered within the architecture design process. In order to achieve this I have created an grasshopper script which tries to reduce the distances between related functions (see the figure below). These relations are shown in the adjacency matrix below. In the beginning this script does not yet use the reduced occupation and therefor does not provide place for nature but instead uses the current occupation. These functions and their area requirements are distributed on an projected grid. The Galapagos evolutionary solver component then shuffles all these functions on the grid, creating thousands of iterations, each having an different adjacency value. The lower the value the closer the functions should be located to one another and therefor patient walk distance is reduced.
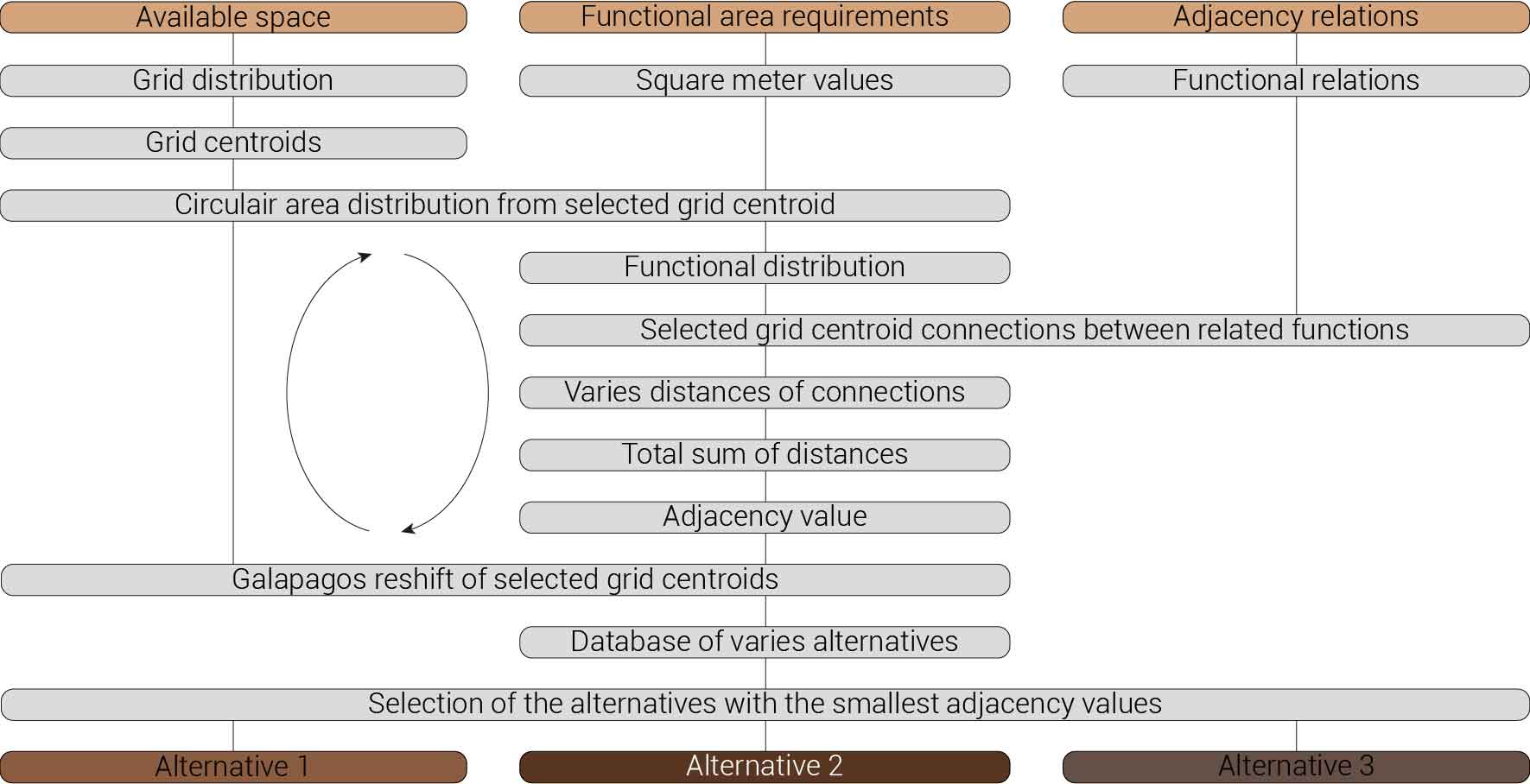
Computational design for the functional distribution.

The design fragment for the functional distribution.
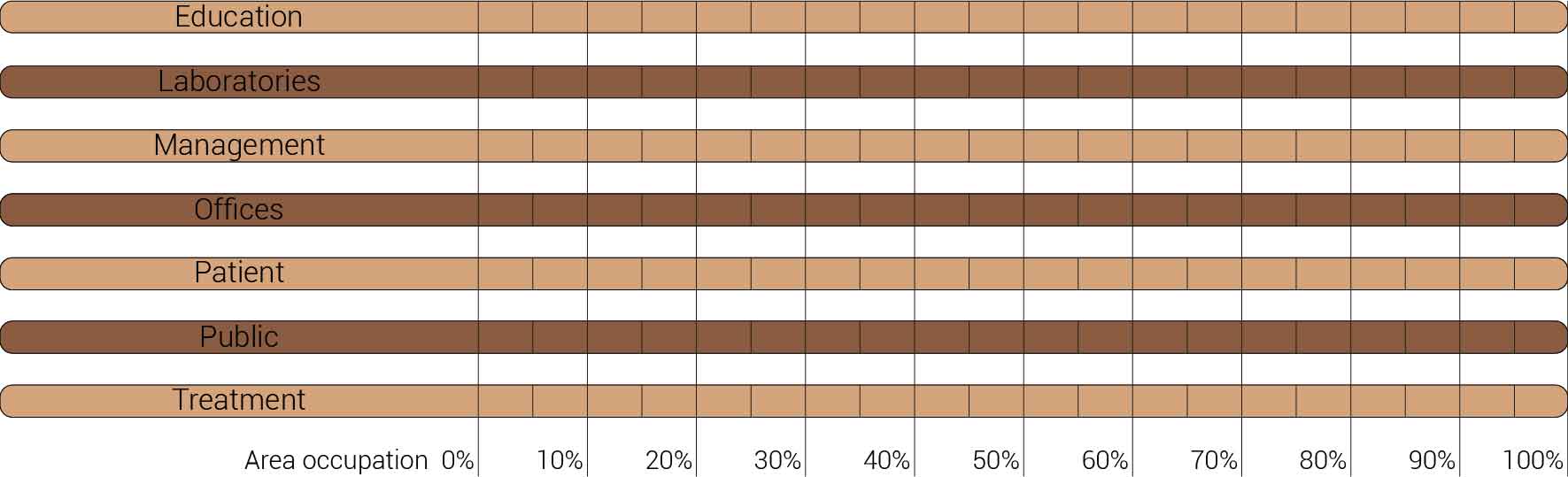
Overview functions and their occupation.
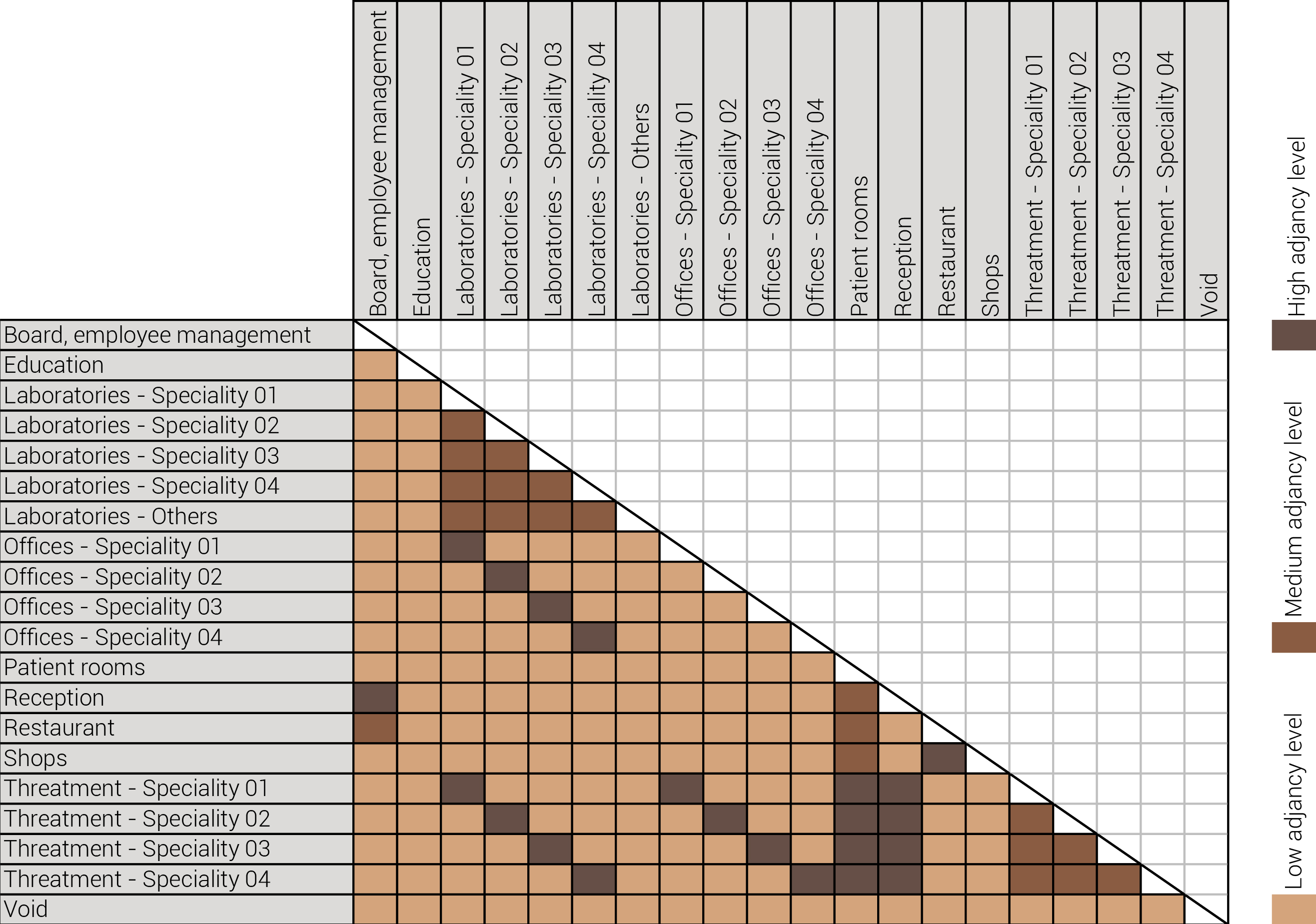
The adjacency matrix portraying the spatial relationship between the functions .
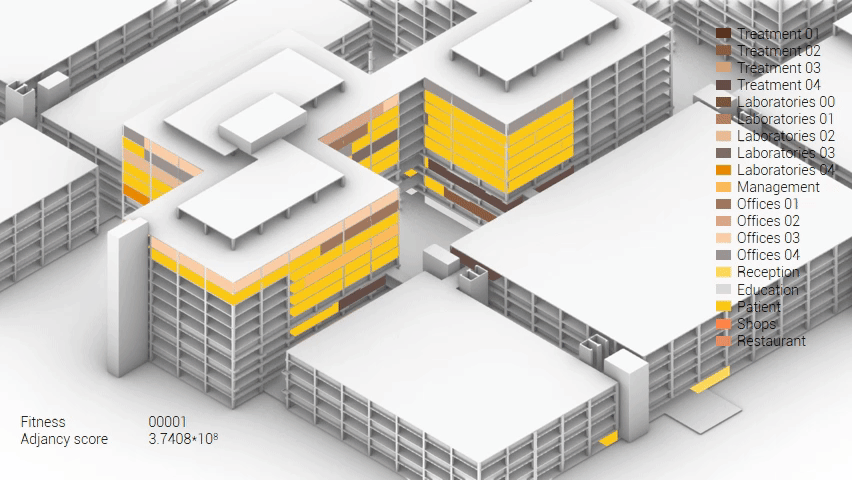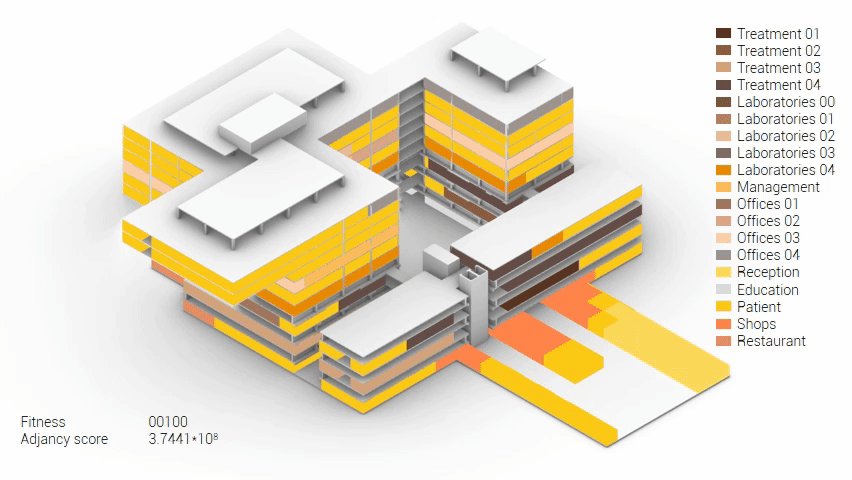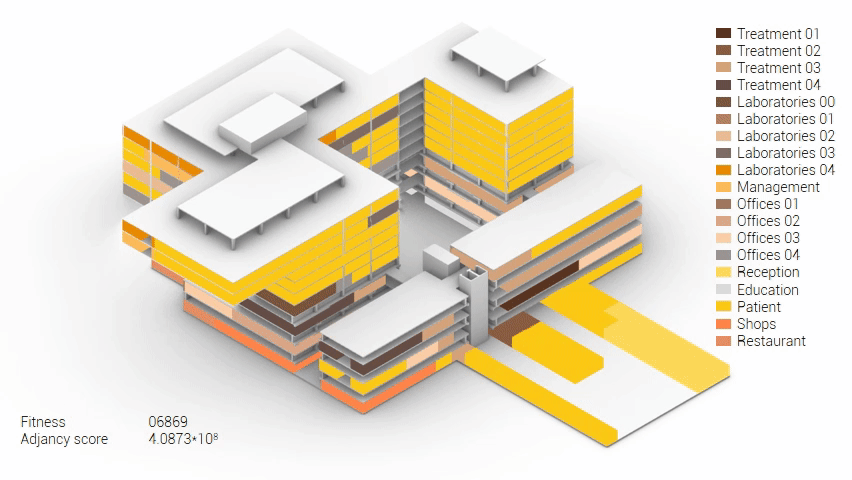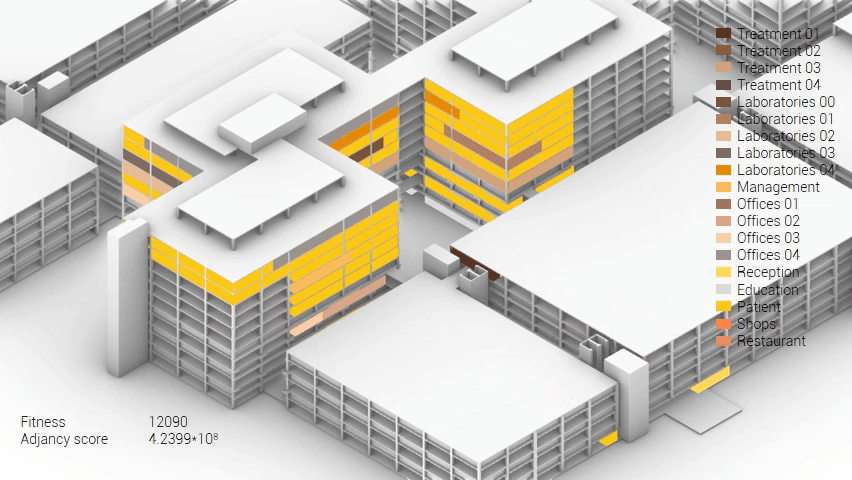
Various design solutions based on the adjacency matrix.
As shown in the gif thousands of iterations have run and with each having a different composition and therefor a different adjacency value. The build up of the three most ideal configuration have been shown below. What is noticeably from these three components is the fact that the office functions in the top tend to be differently positions. Where the first alternative looks better due to the lack of patient functions on the top floor.
Build up of the top three variations.
The functional reduction
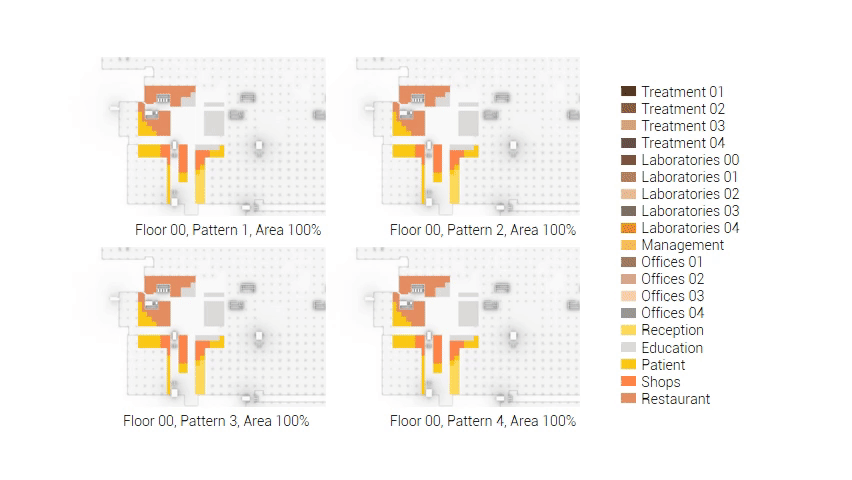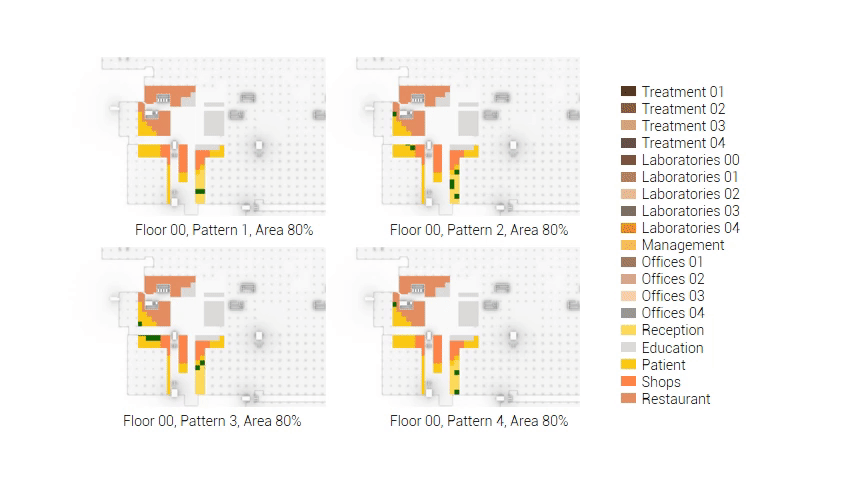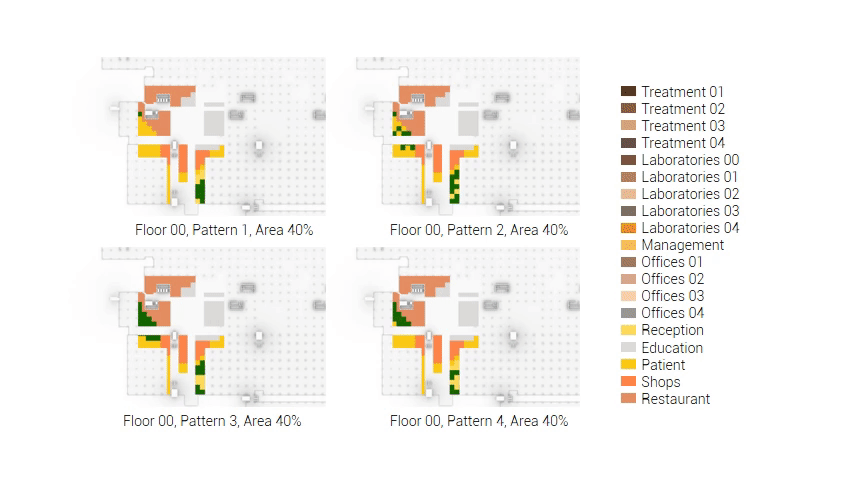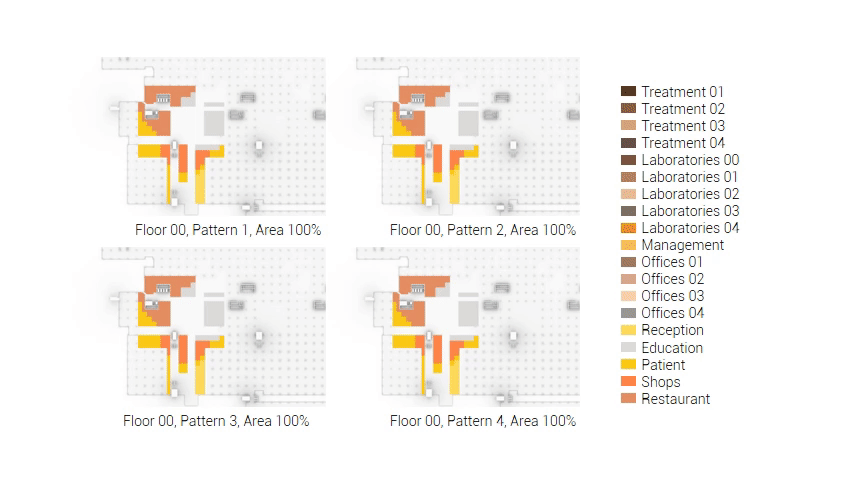
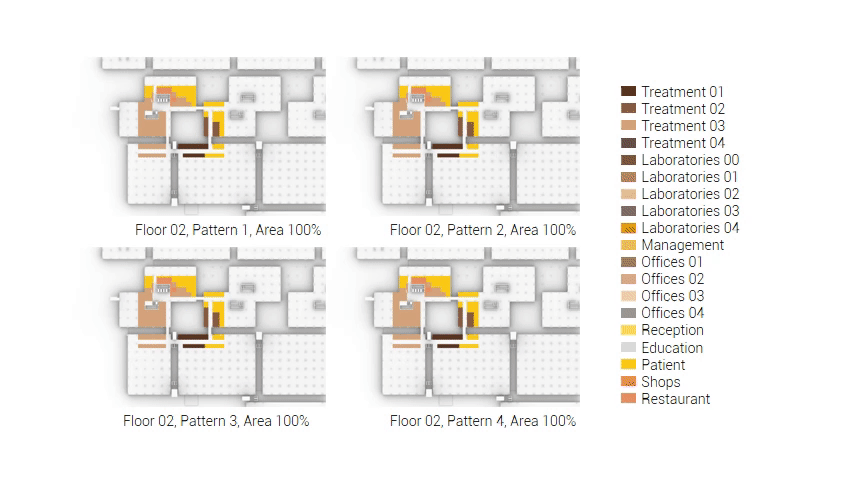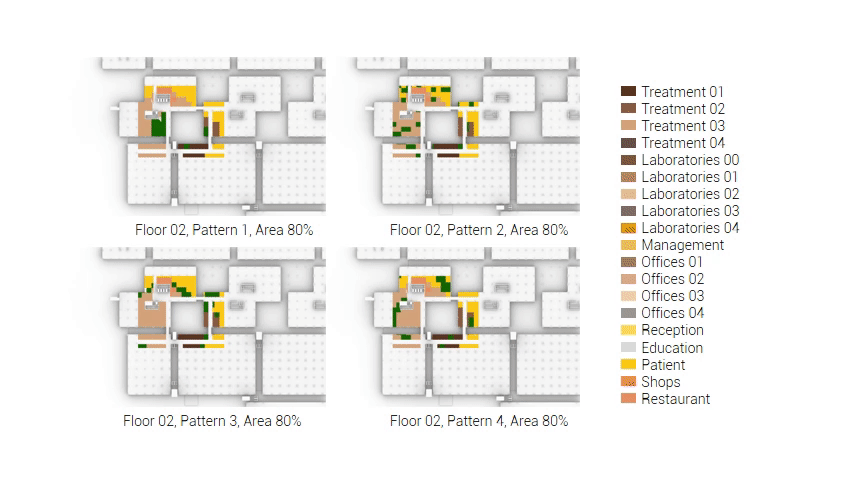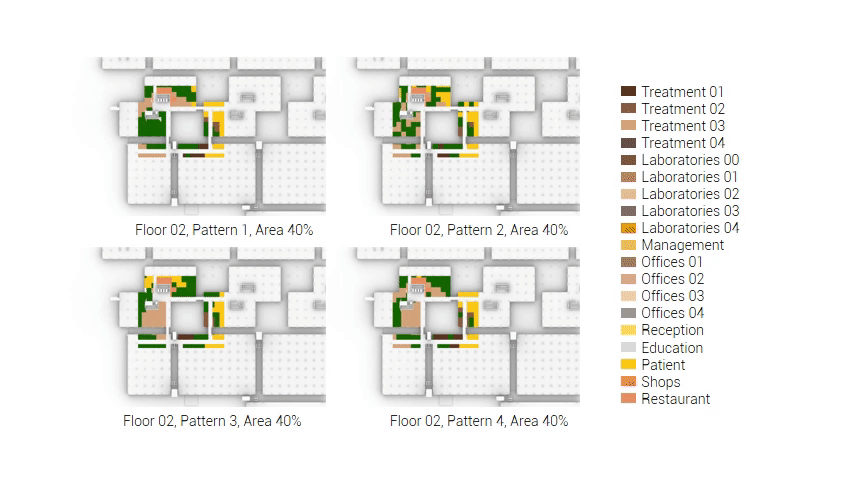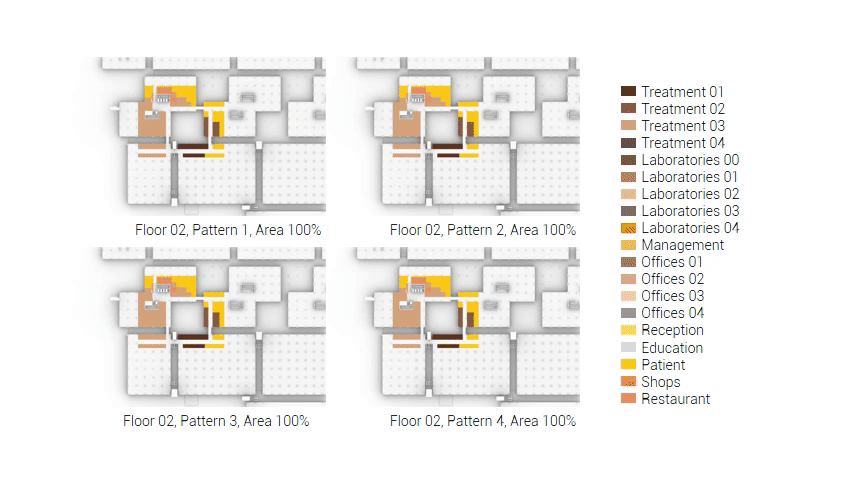
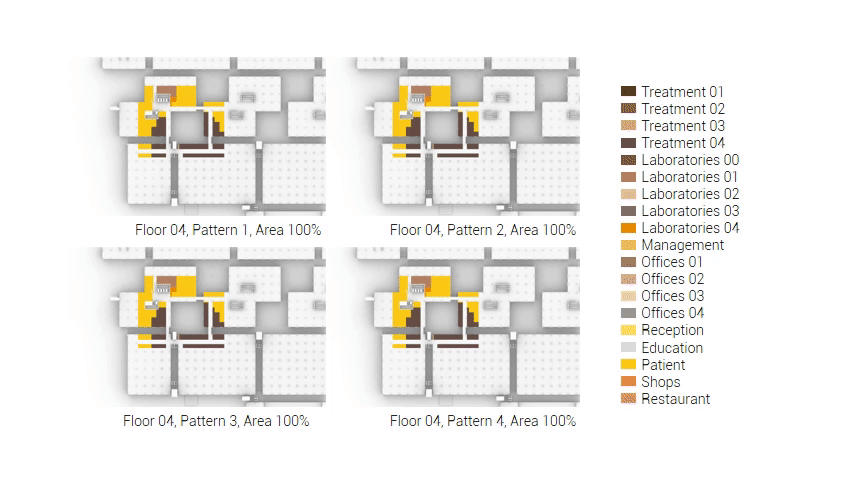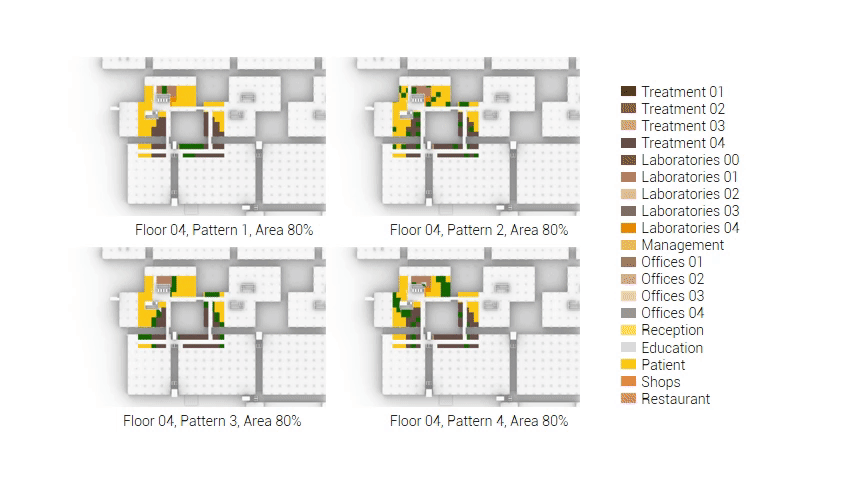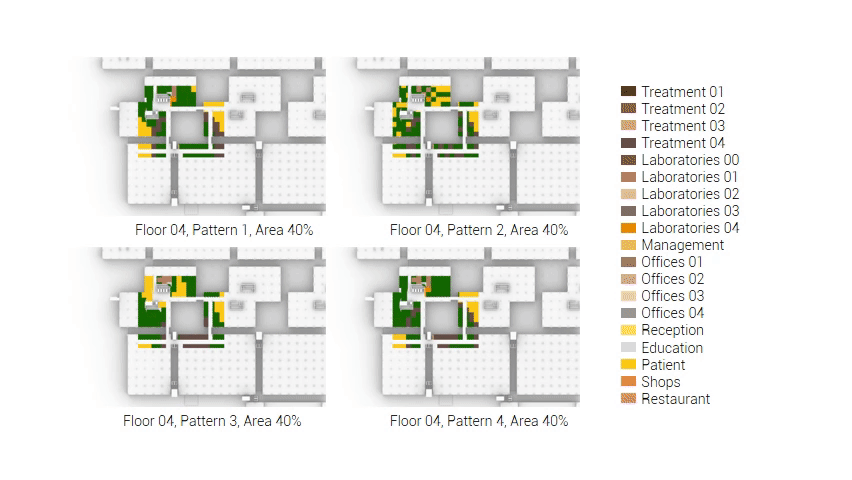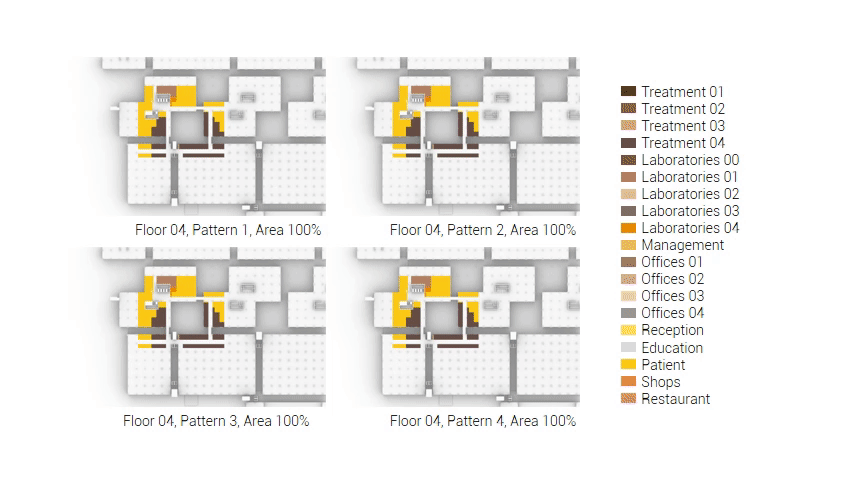
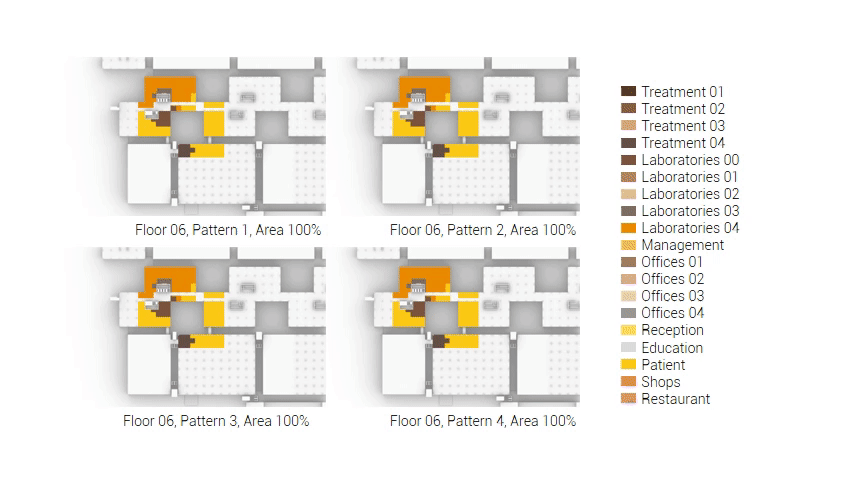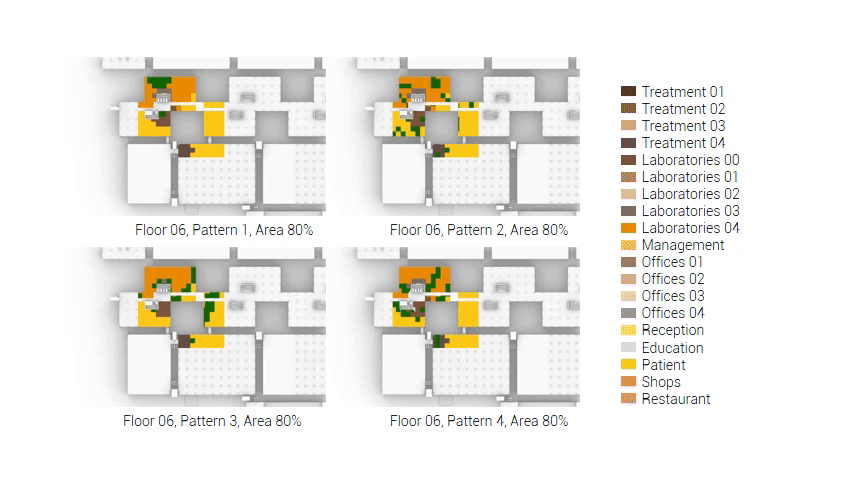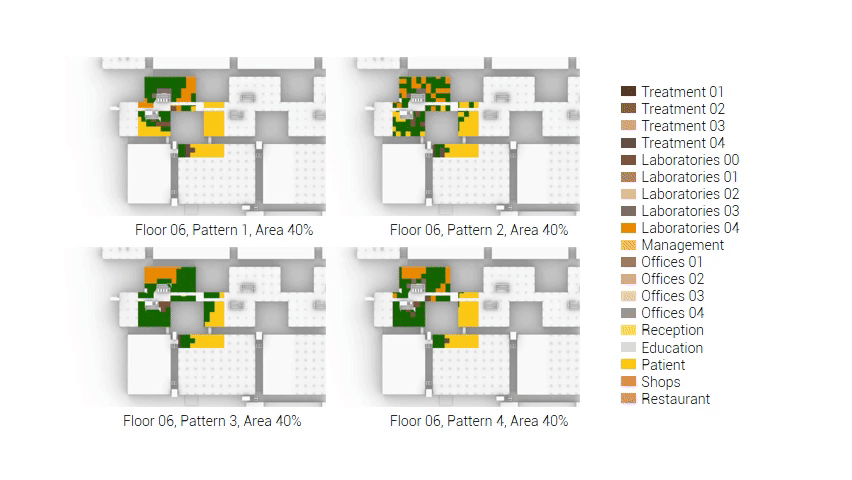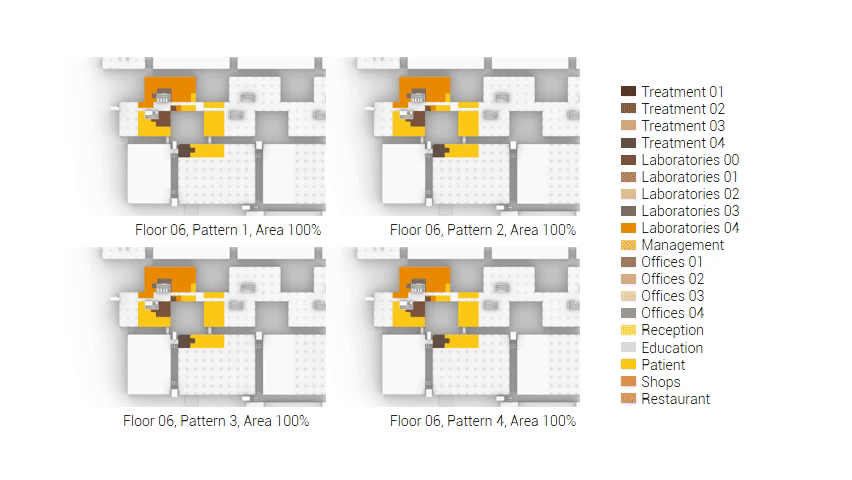
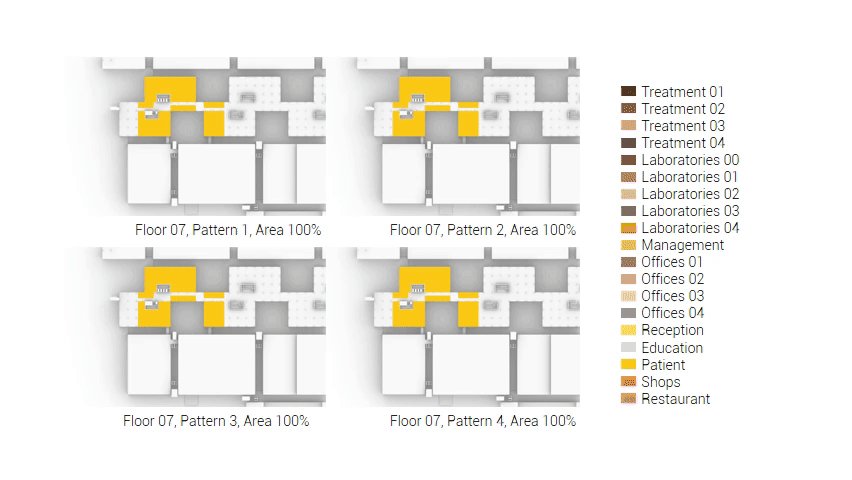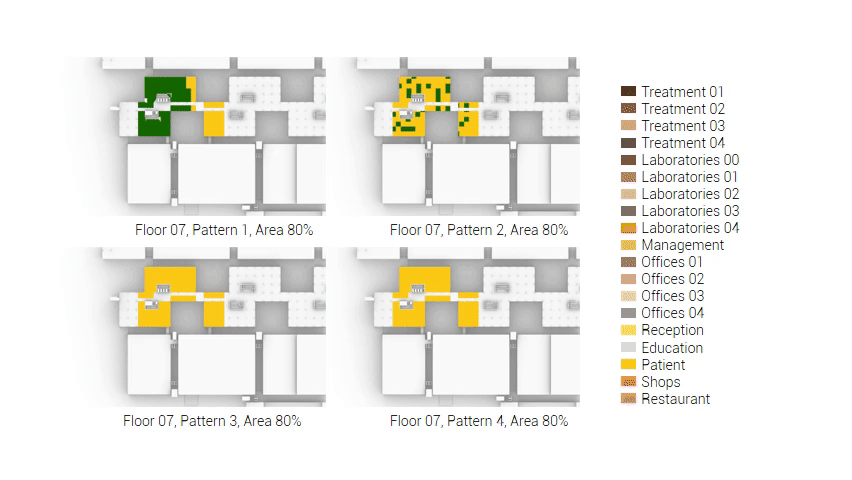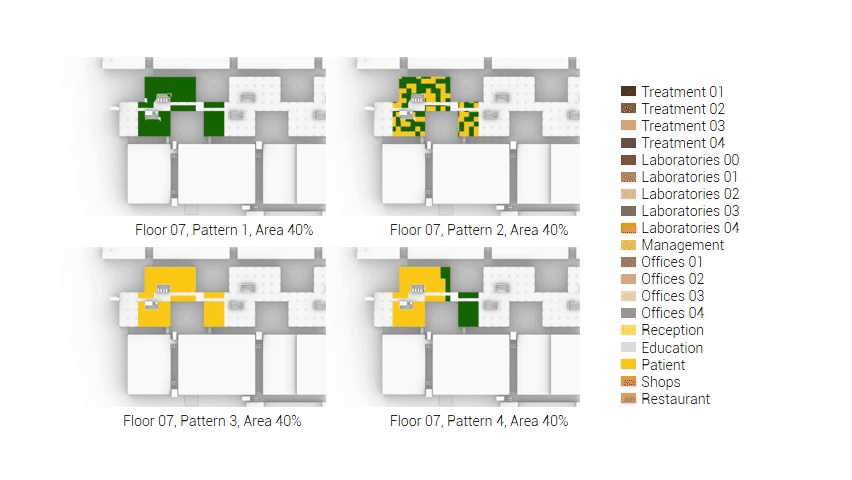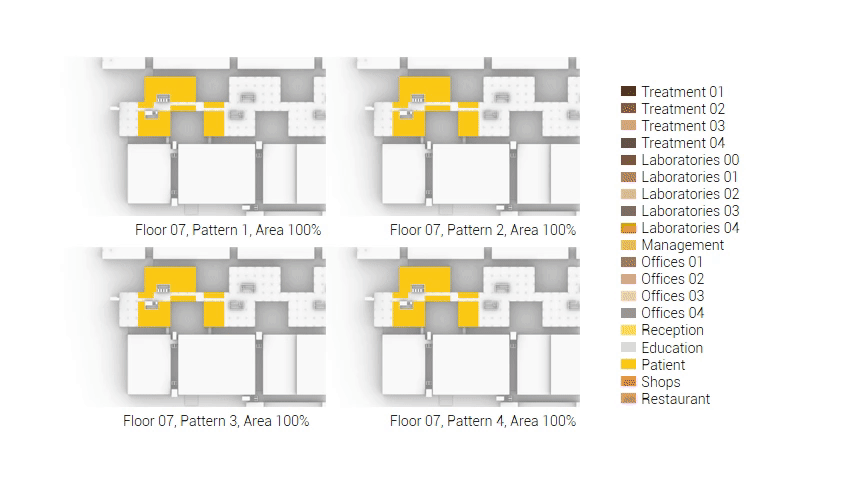
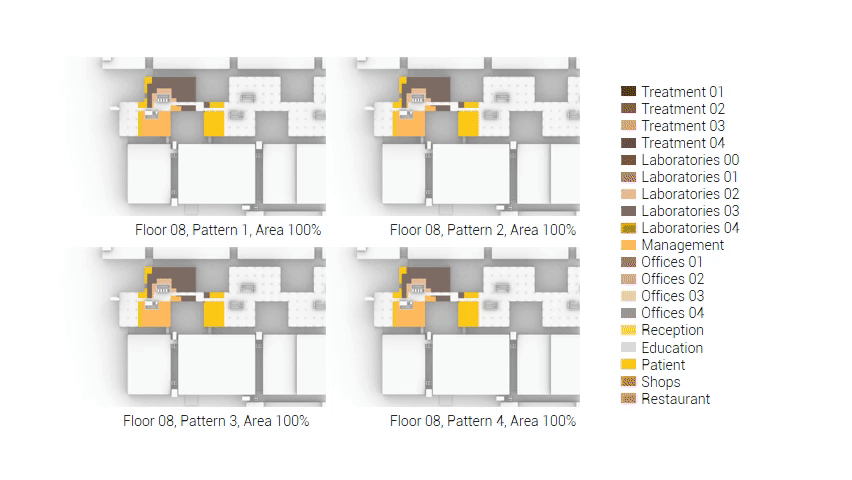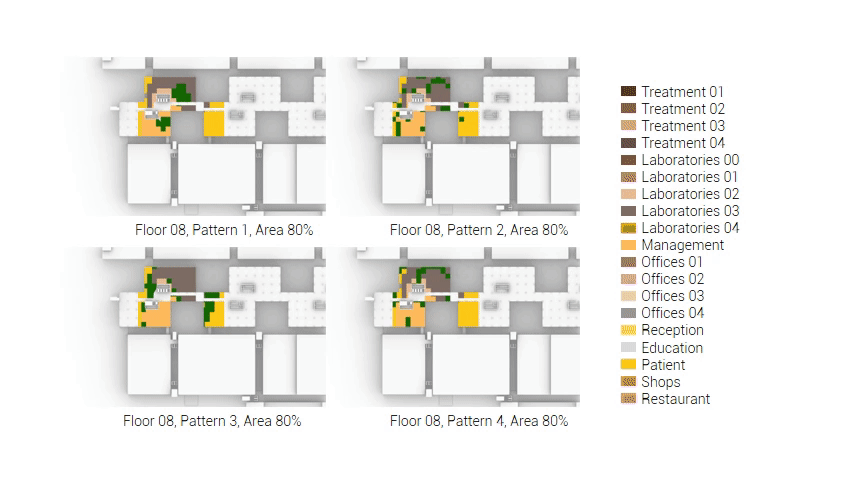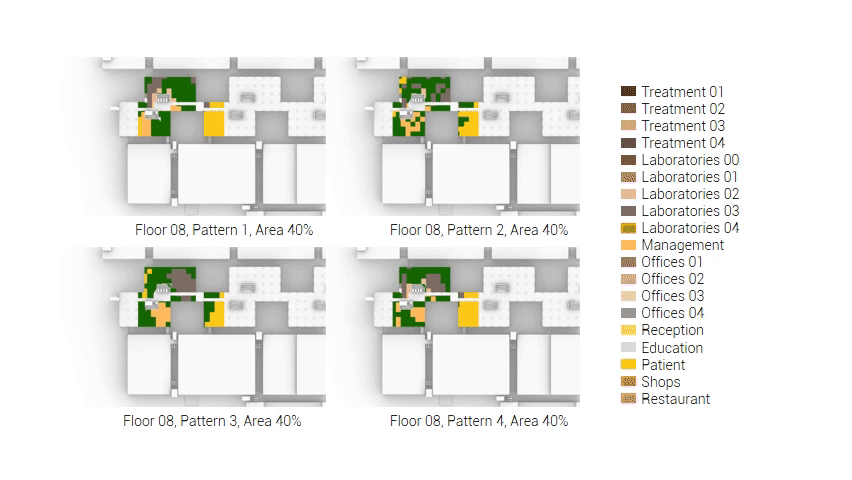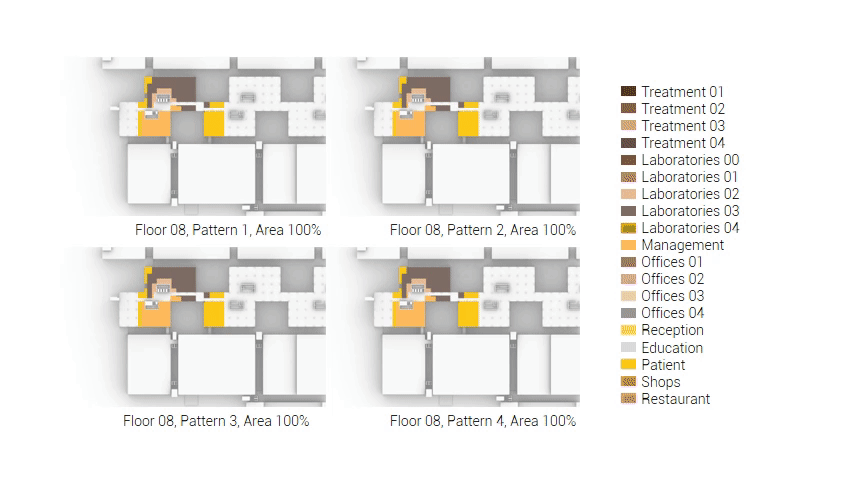
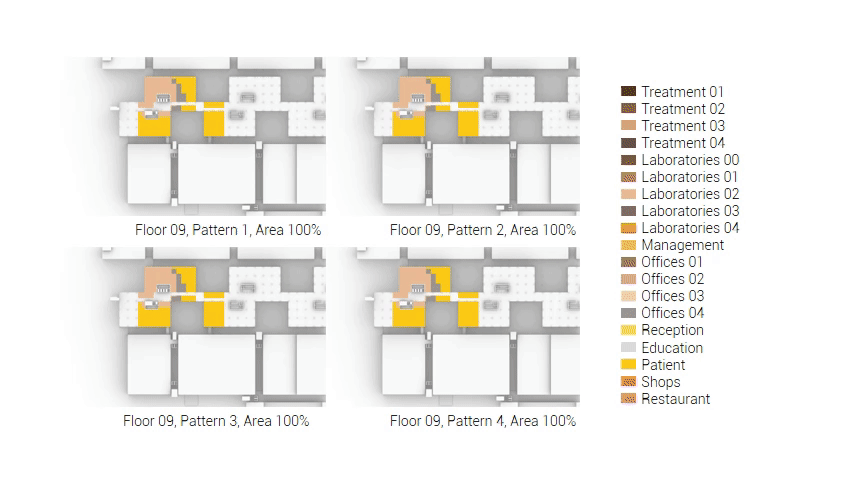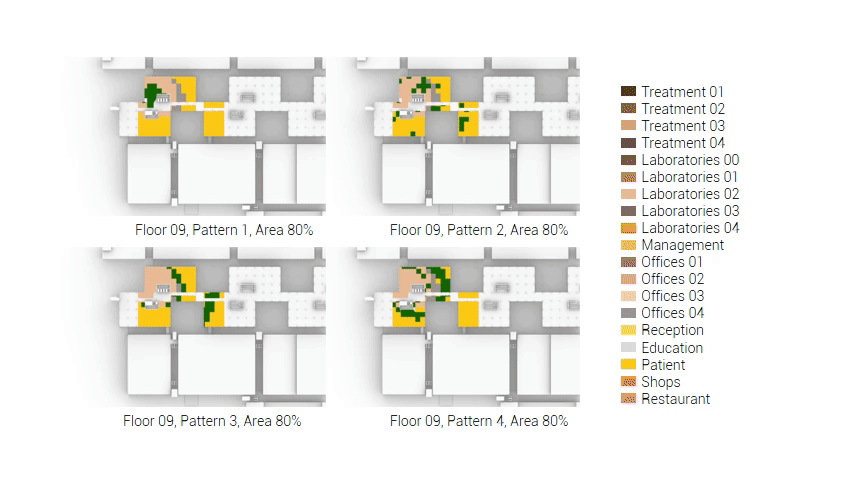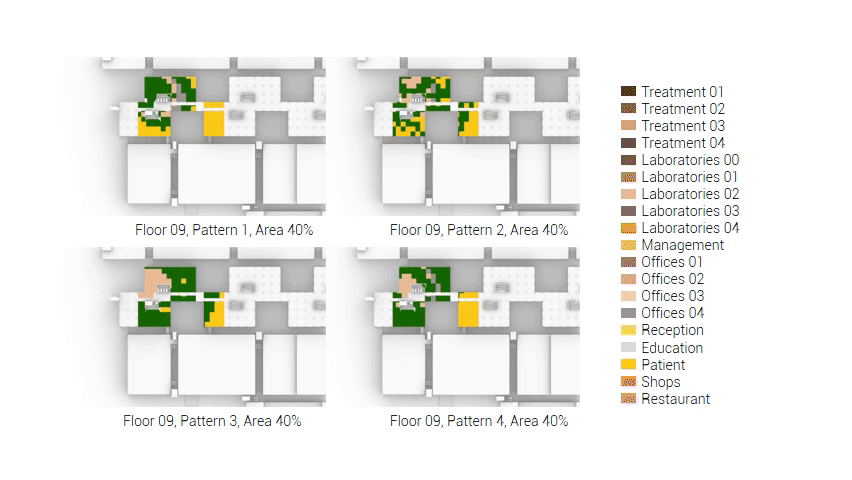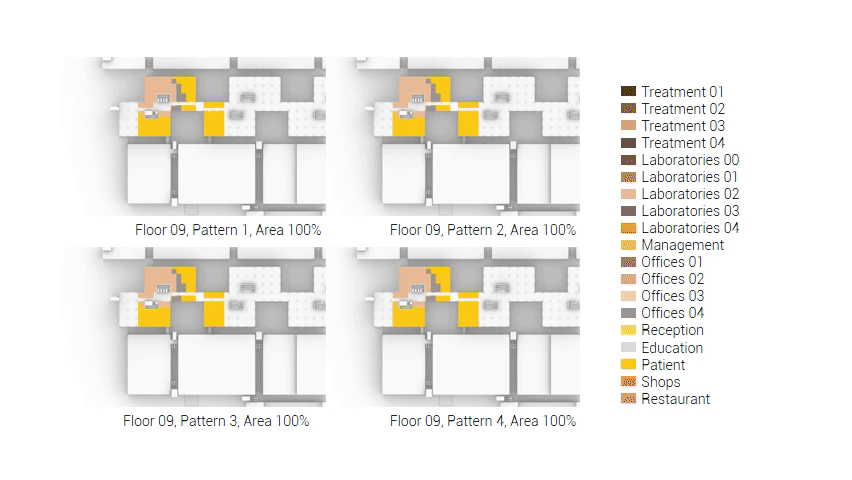
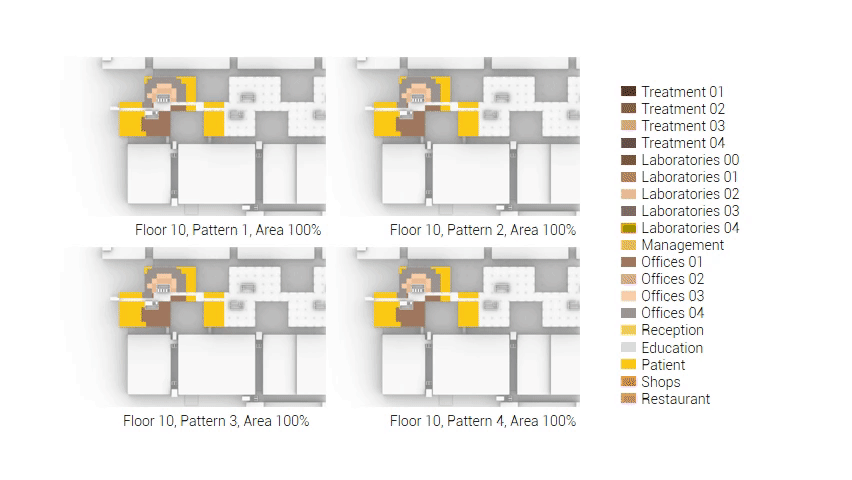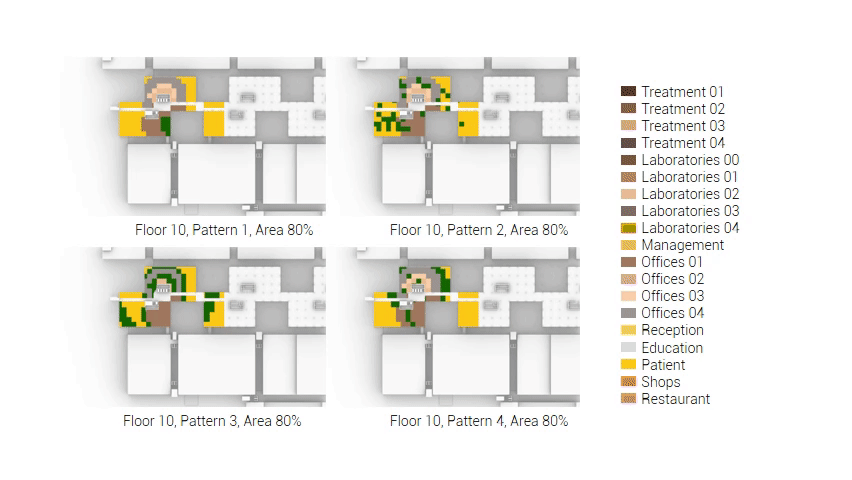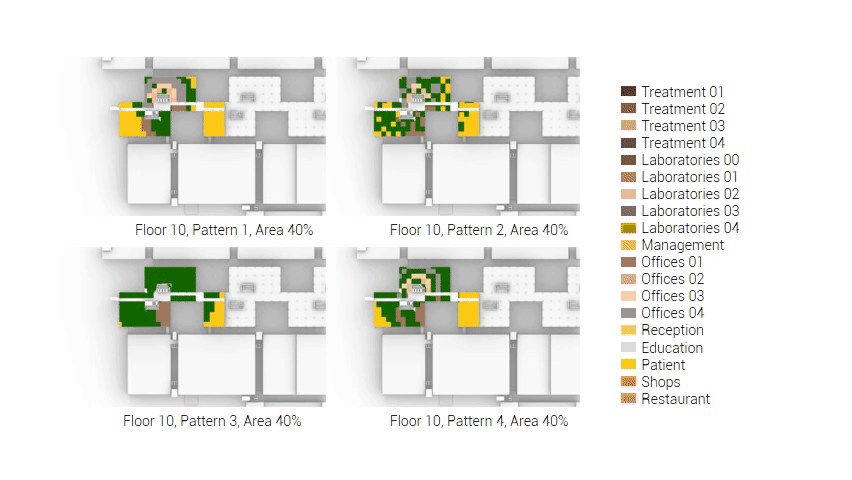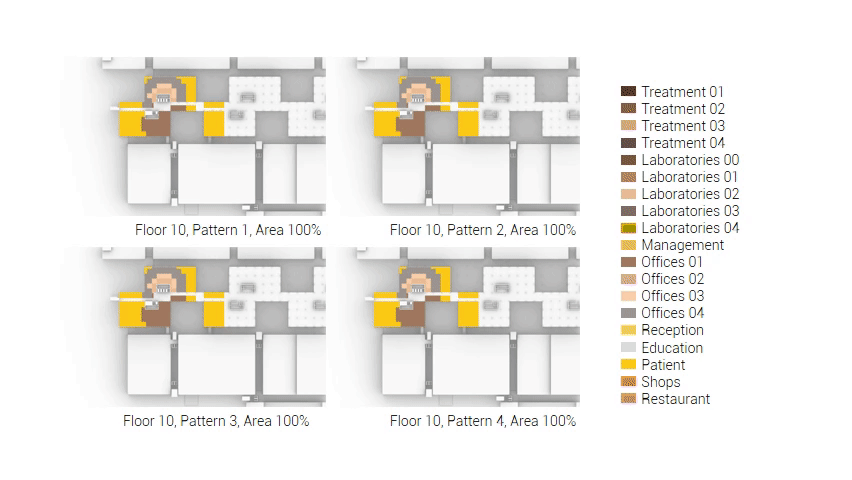
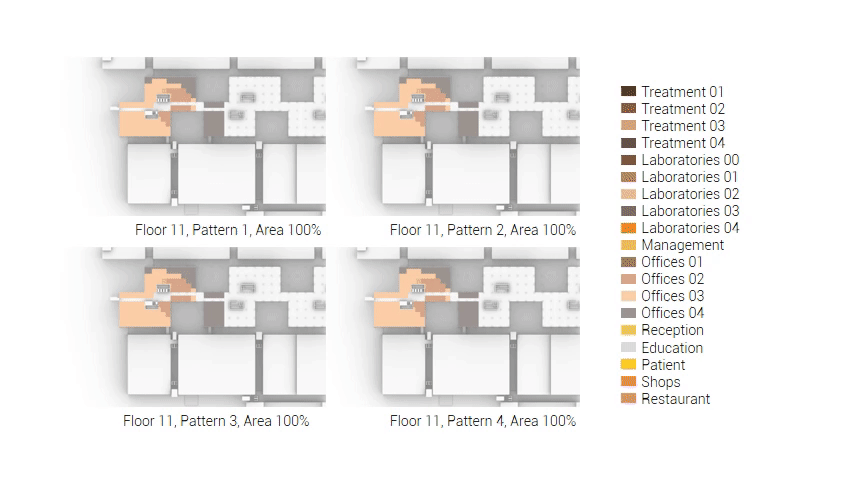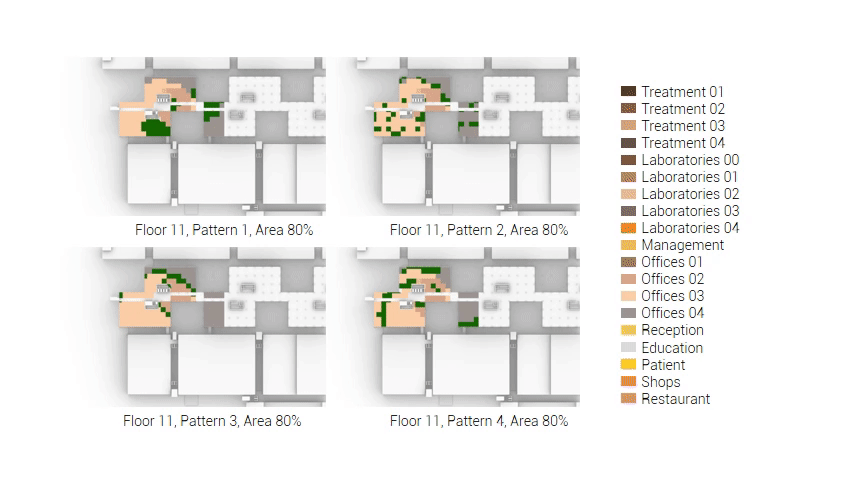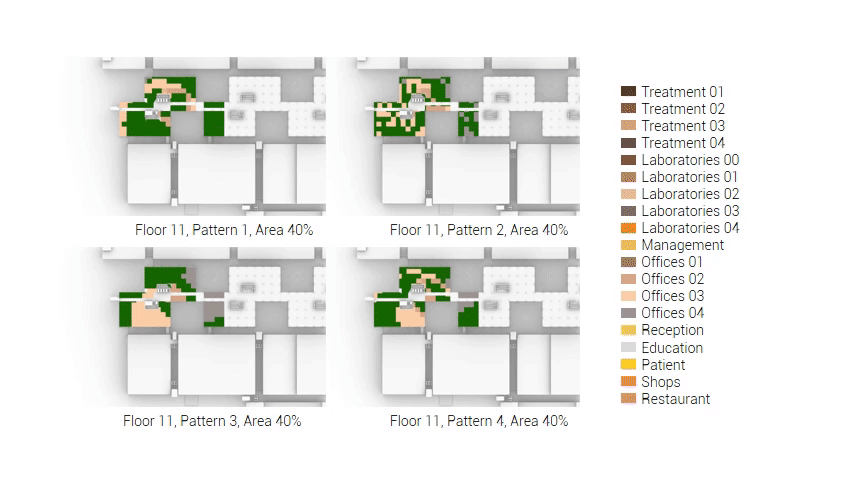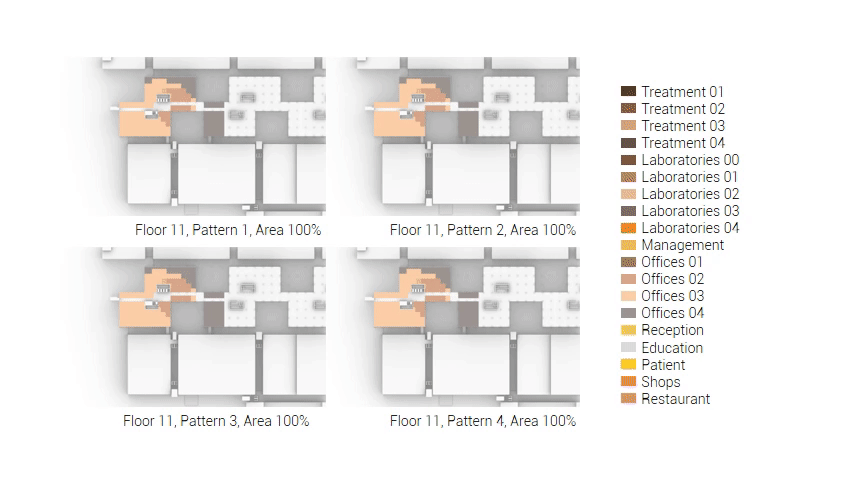
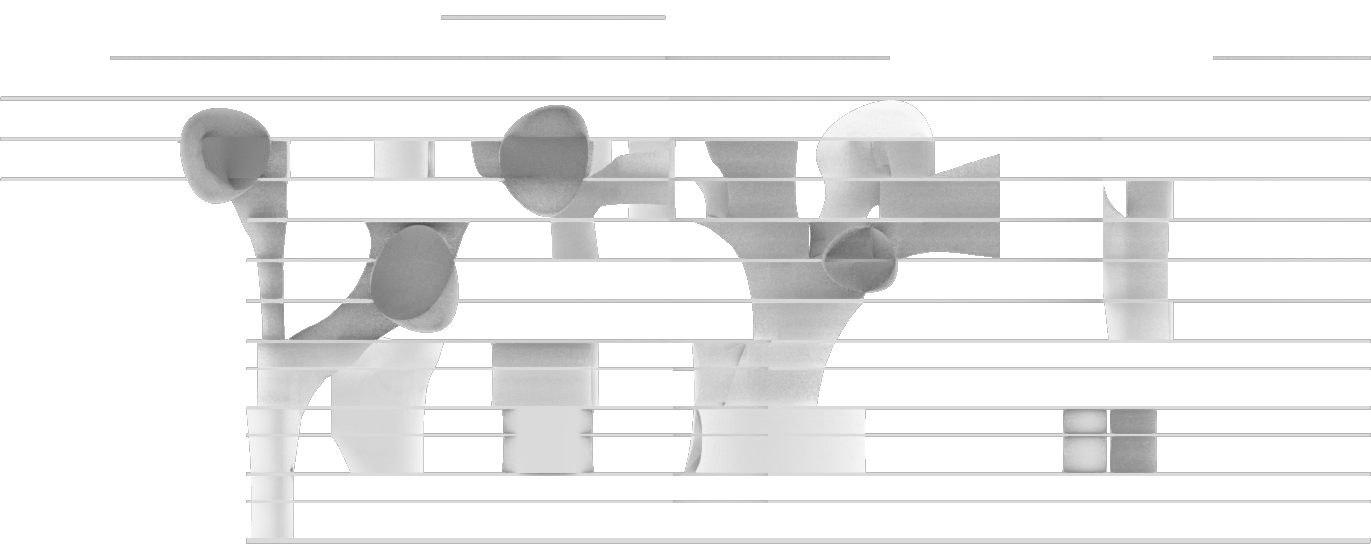
The next step from the functional distribution is to reduce the functions as it was argued before. That result being shown below once again. To arrive at this reduction four patterns are developed each decreasing the area occupation in its own way. These are; pattern one, from the centroid towards the outside. The second one, randomly reducing the area occupation. The third, from the outside inwards towards the centroid. And the last and fourth one reducing the the area occupation from the middle and expands its reduction towards the outside and inside. It is shown below what the impact of these patterns is one the space occupation on each floor. It than is up to me as designer to find the suitable configuration of patterns for each function. Hereby I took into account the impact these patterns have on creating connected open spaces. For this configuration I have used the design alternative with the best adjacency score, which is the first option.
The renewed area occupation of the AMC.
Reduction patterns shown on each floor.
The build up of the first variation based on the area reduction.
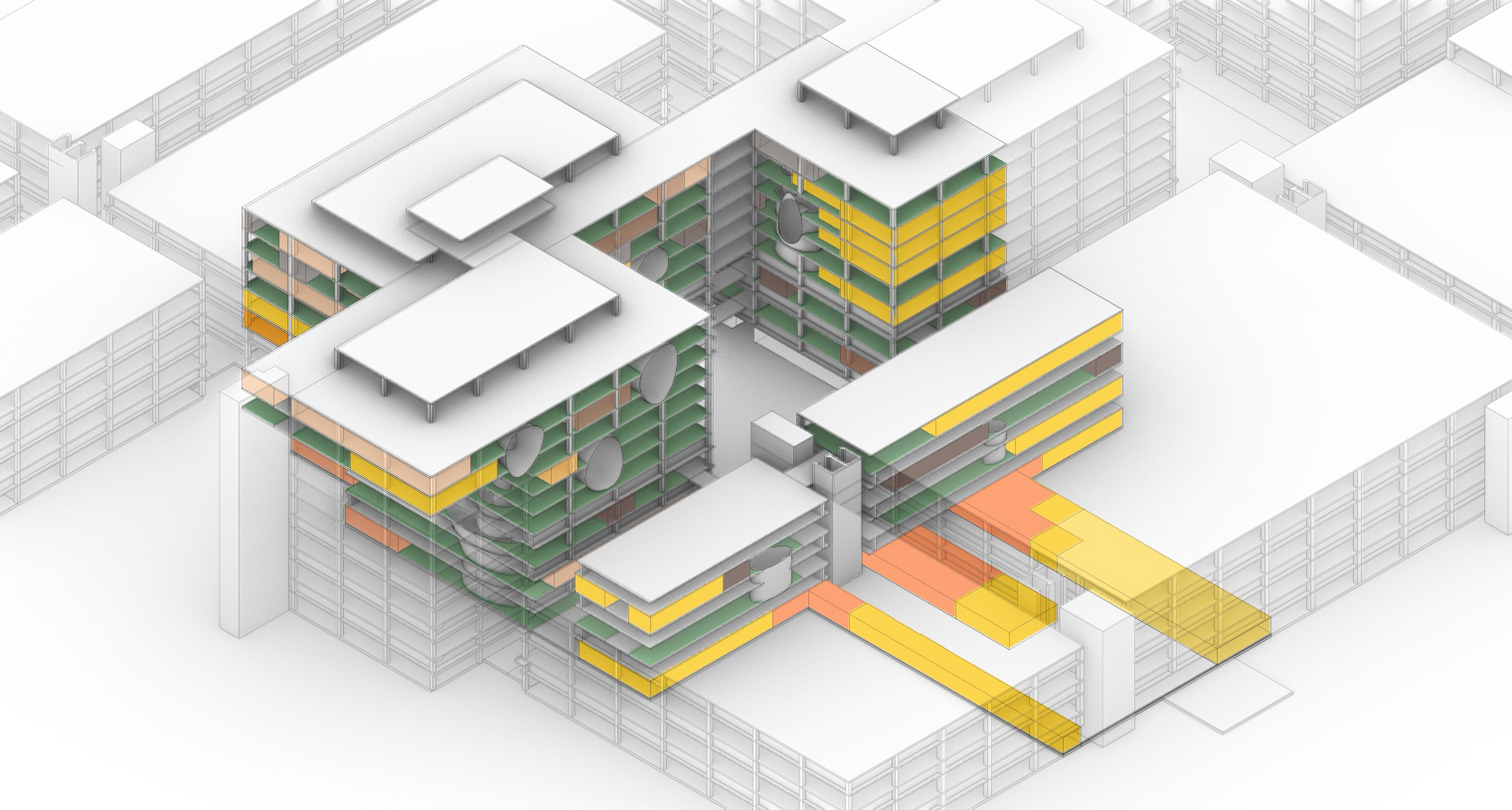
The vertical connection
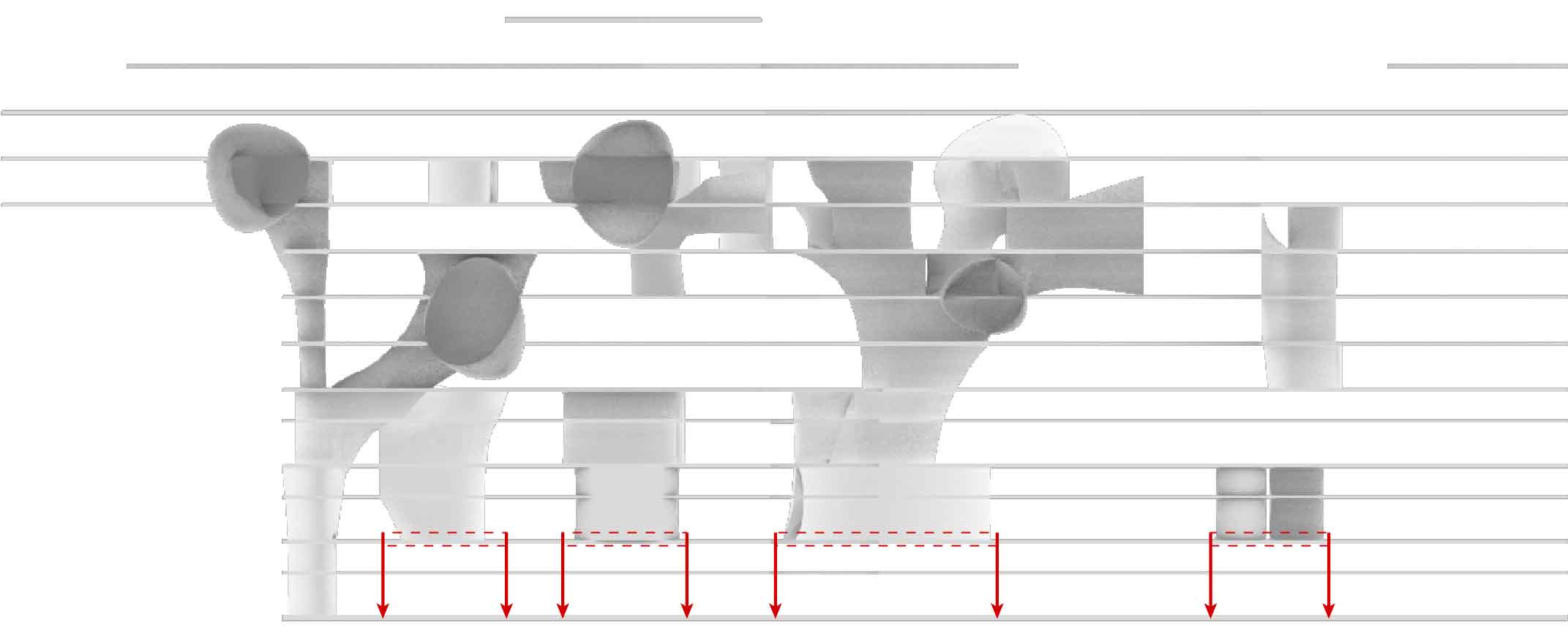
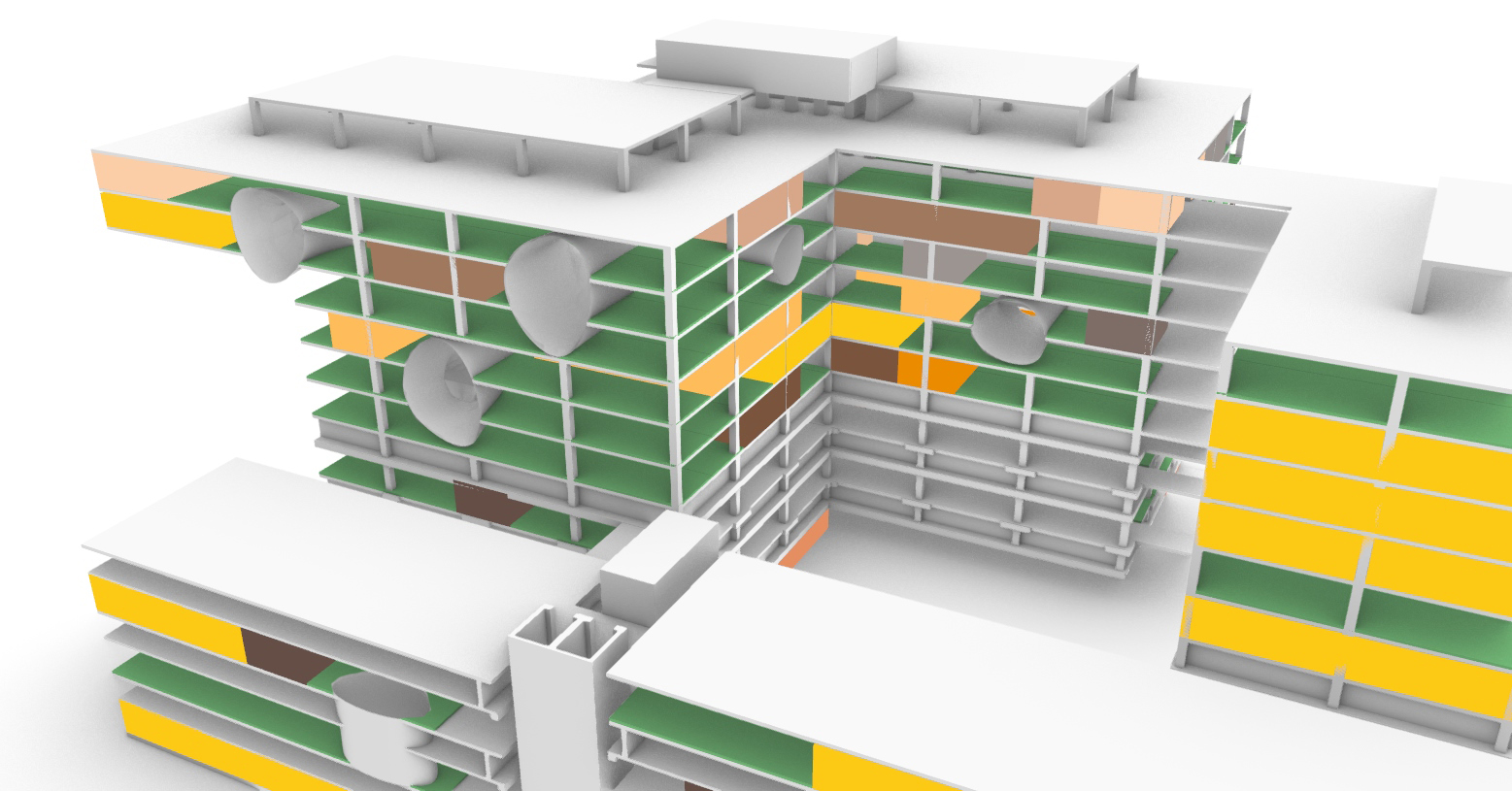
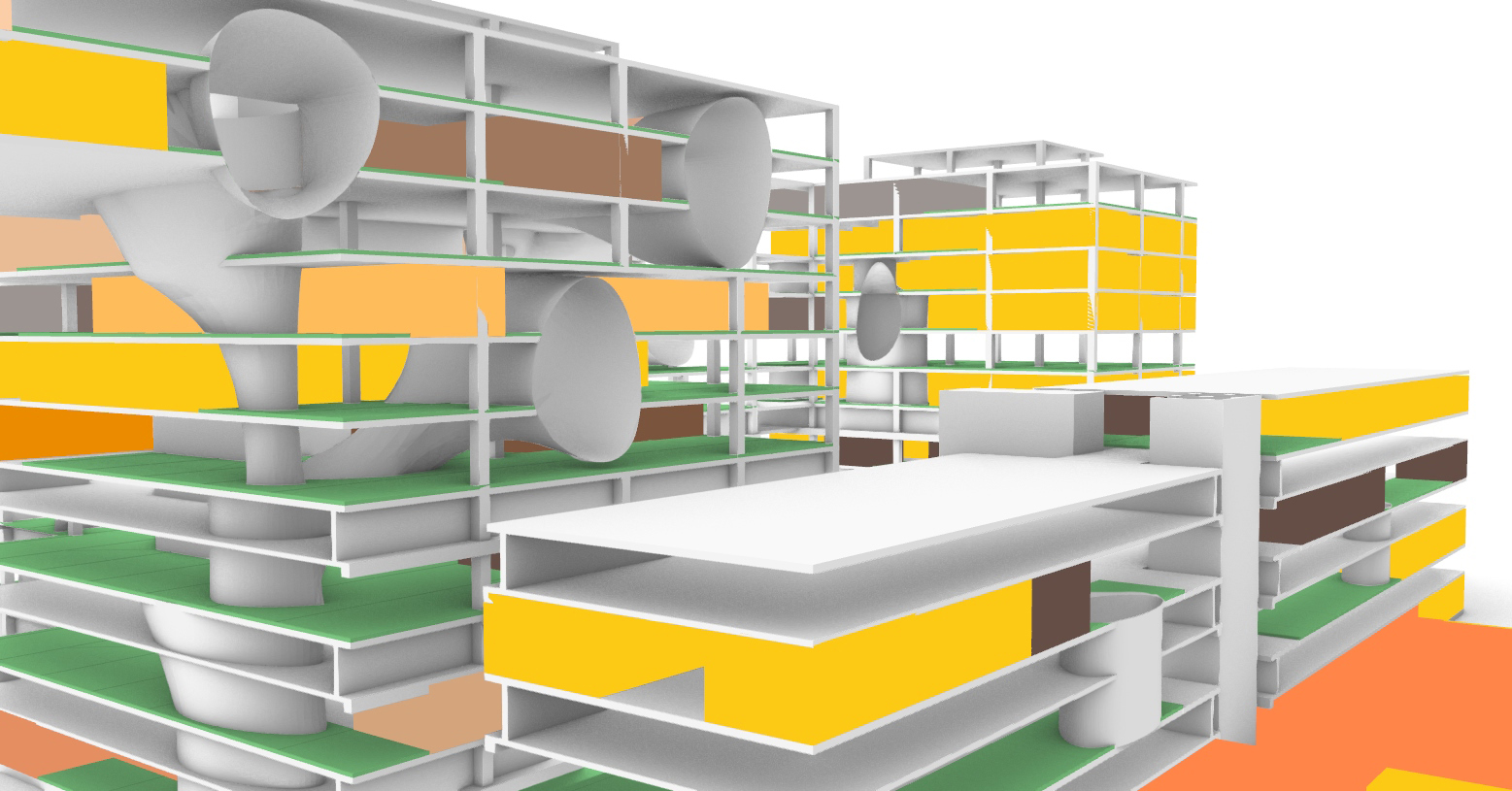
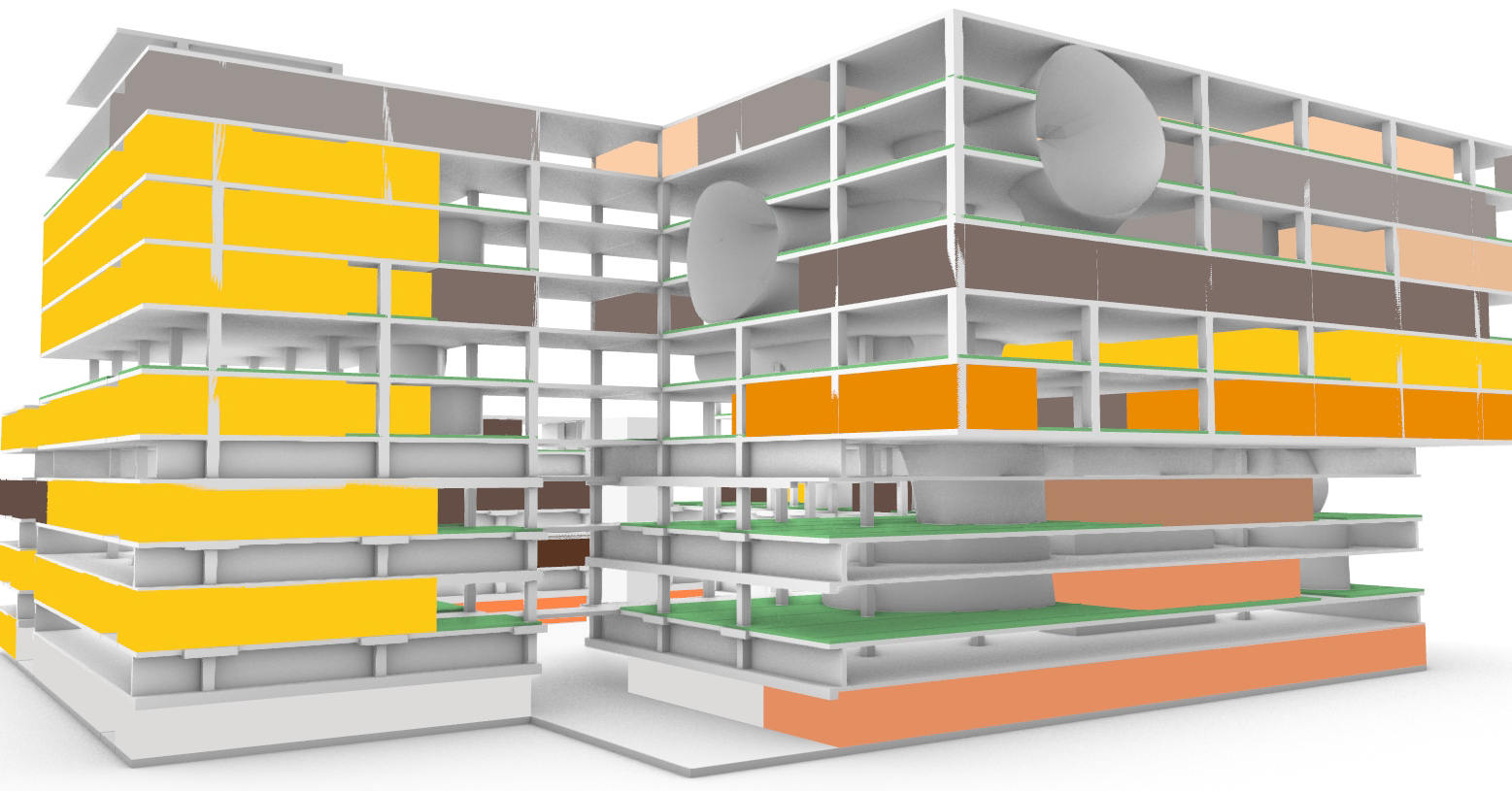
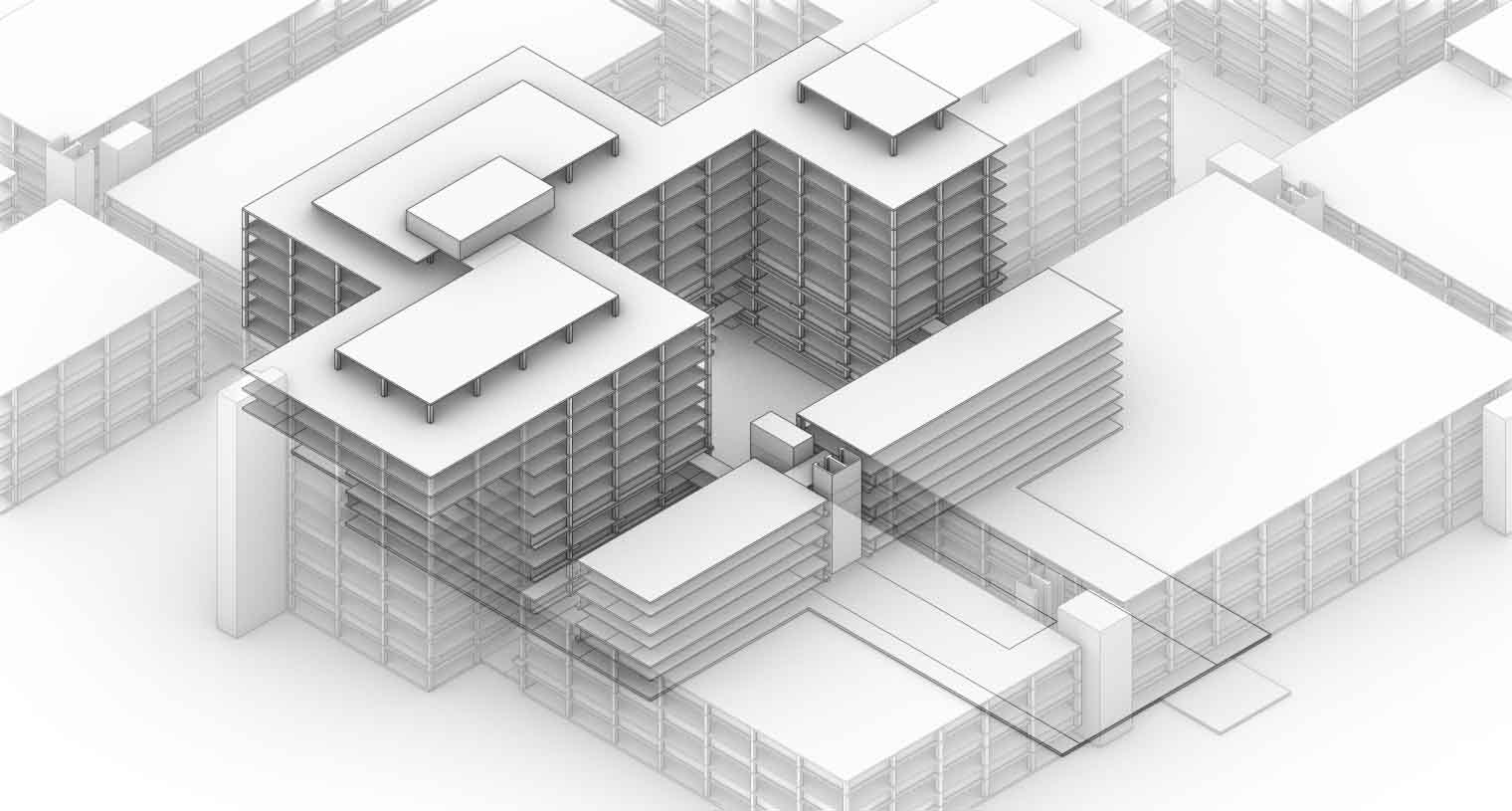
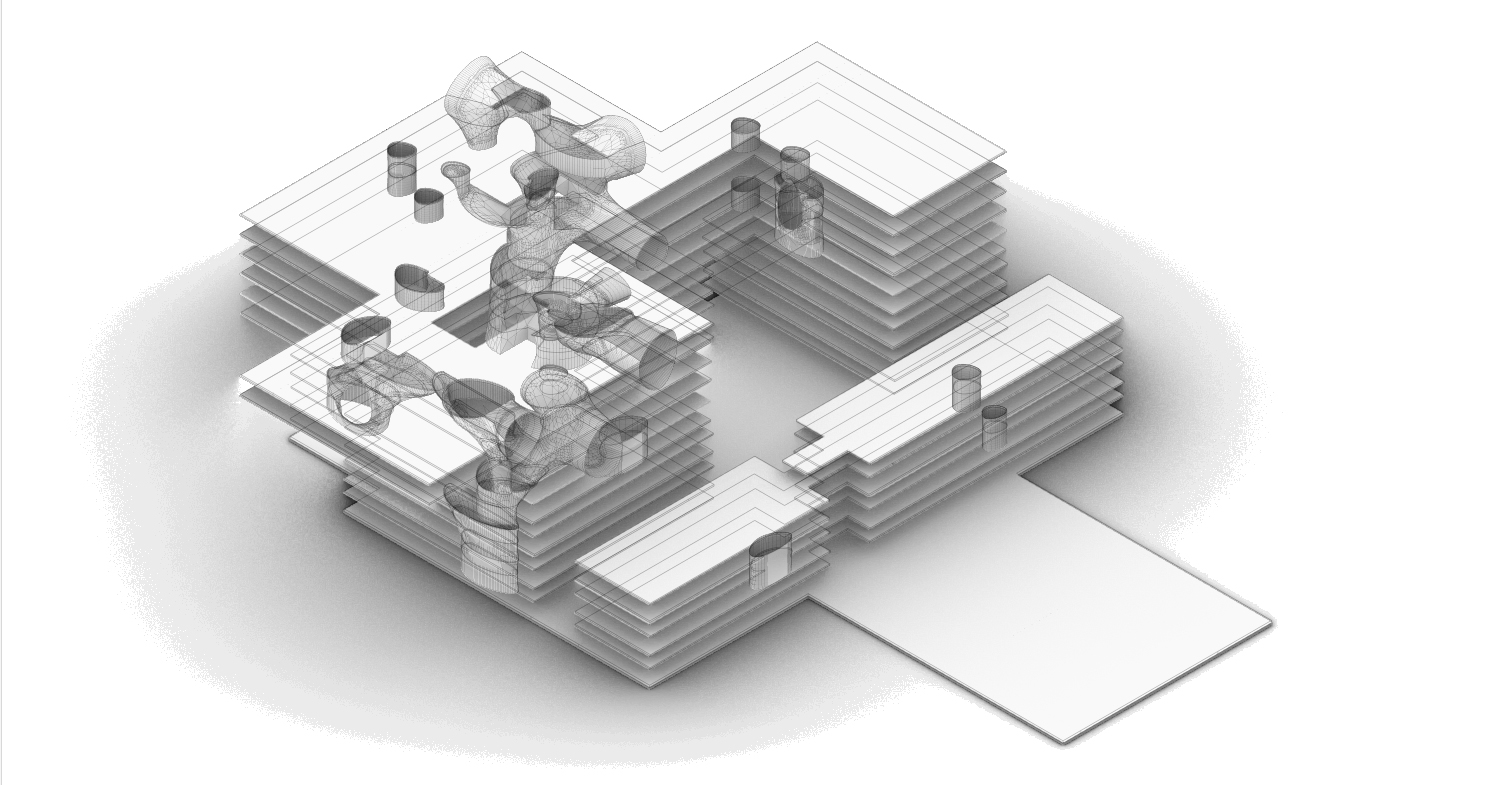
While the original design of the Academic Medical Center has their individual building components with their own function. But it is within these building components where the spatial connection has largely been horizontally. With the new situation providing plenty of vacant space it also offers the opportunity to create vertical interventions. These vertical interventions offer unique qualities. In order the create these vertical connections the vacant grid elements where analyzed by an grasshopper script connecting the grid elements with the shared x and y coordinates through their z component. This results into vertical lines. These lines are than split to form groups within their respective building. The four longest lines are than selected to form the vertical cores. On each floor the four nearest grid areas surrounding each of those lines there four creating different vertical connection between the floors. Subsequently transforming these grid areas into curved lines. These vertical cores are unable to be formed near the edges of the building in order to maintain the brutalistic facade. But at some places these cores break through the facade showing the glimpses of the new intervention.

Computational design for the reduction and creation of atria.
This strategy than results into these tree like atria's of which offer the patients more lines of sight as does it offer interesting routes throughout the building. The only problem with the variation below is the lack of connectiveness to the ground floor.

The atria tree like structure.
The atria shown in relation to the building.
The build up of the design.
Final impression.
Build up of the various variations.
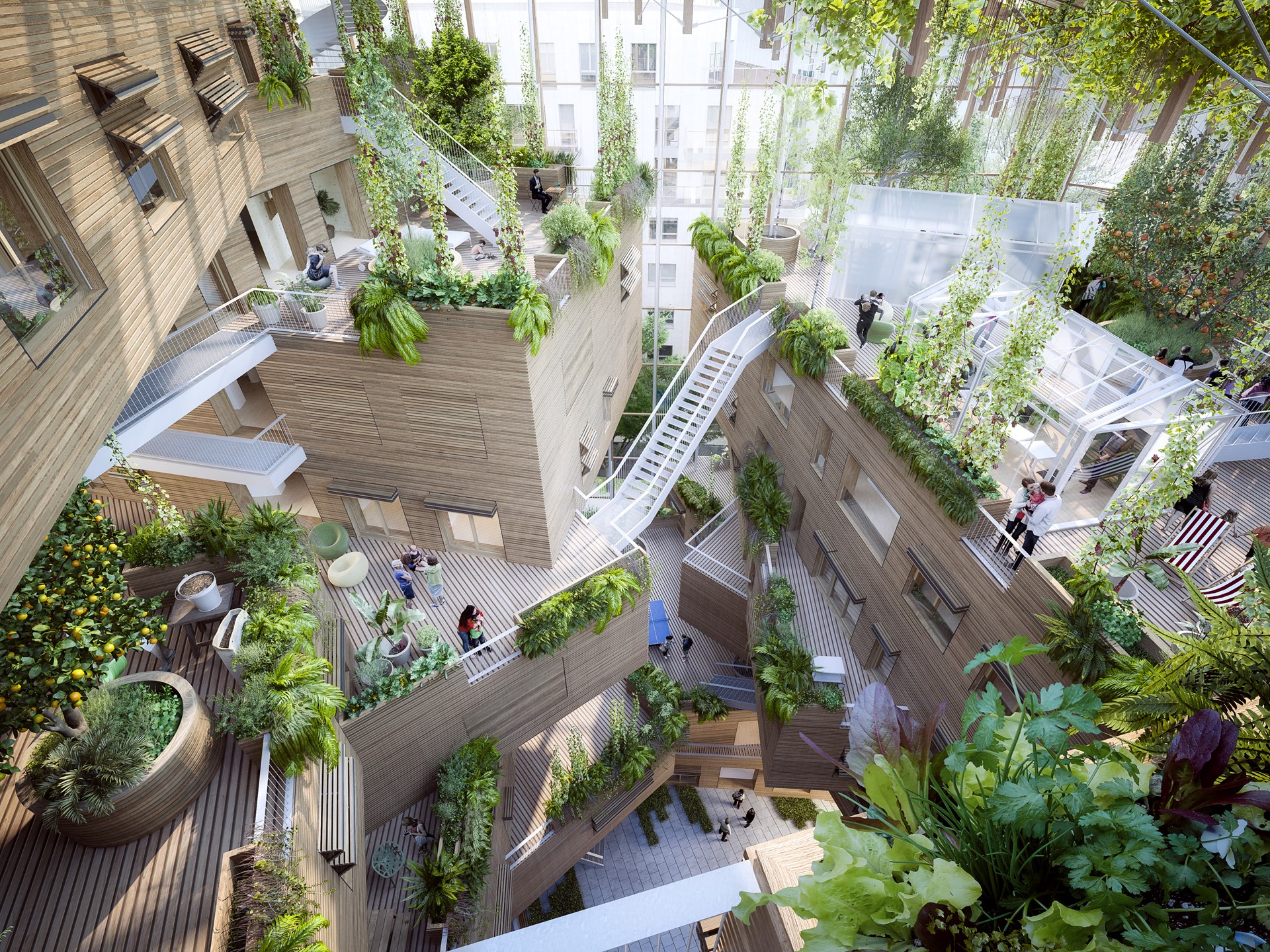
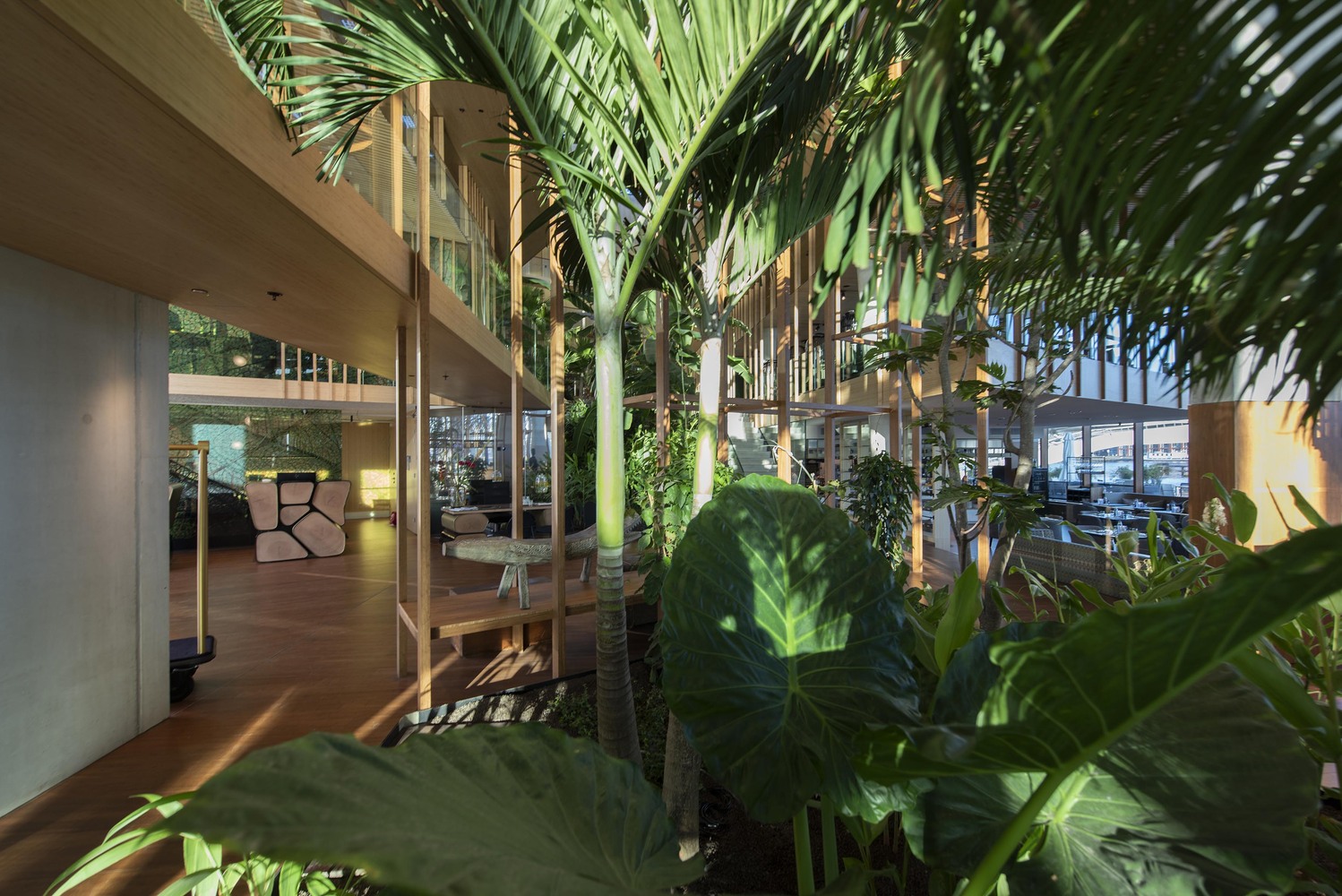
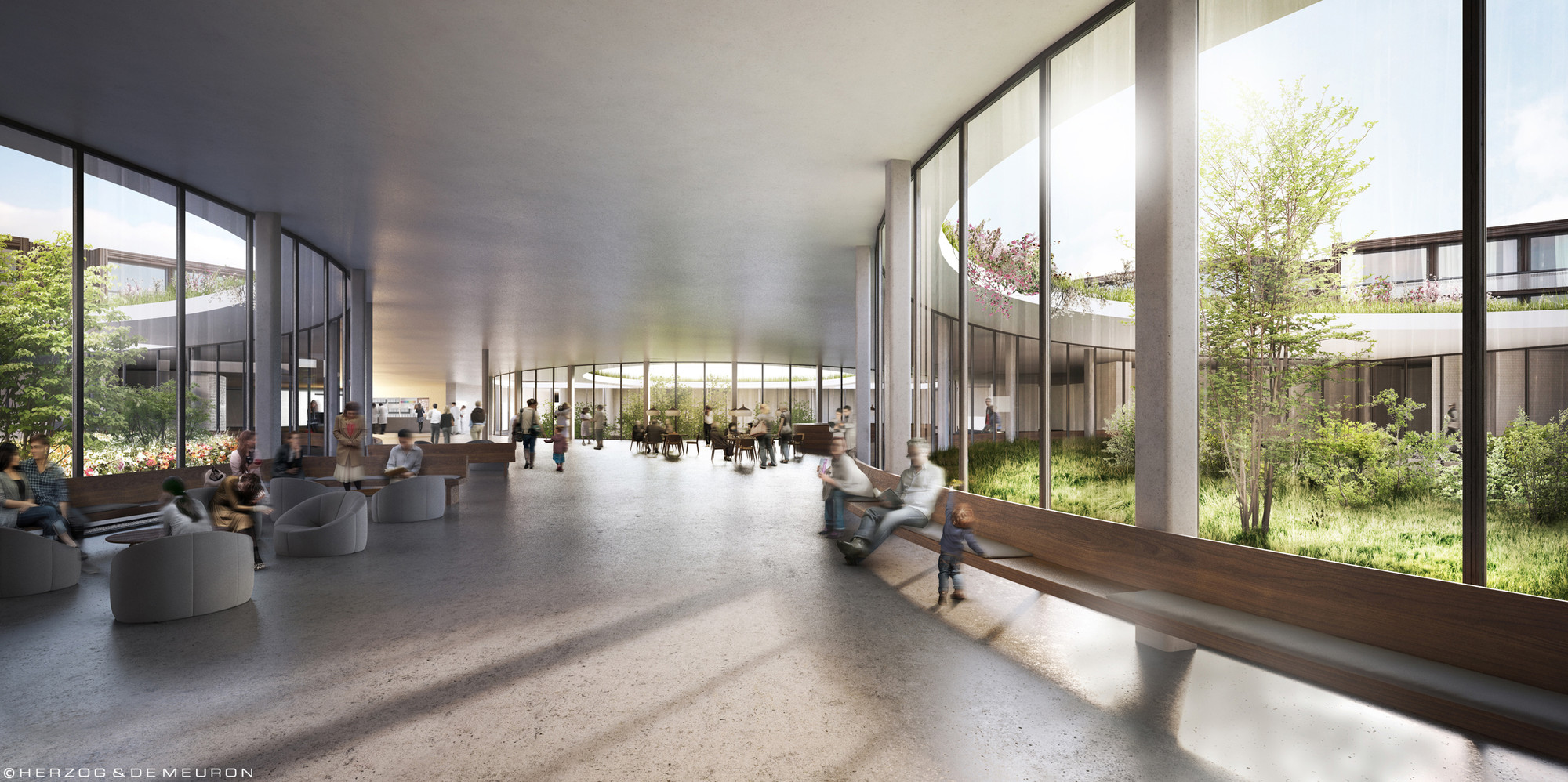
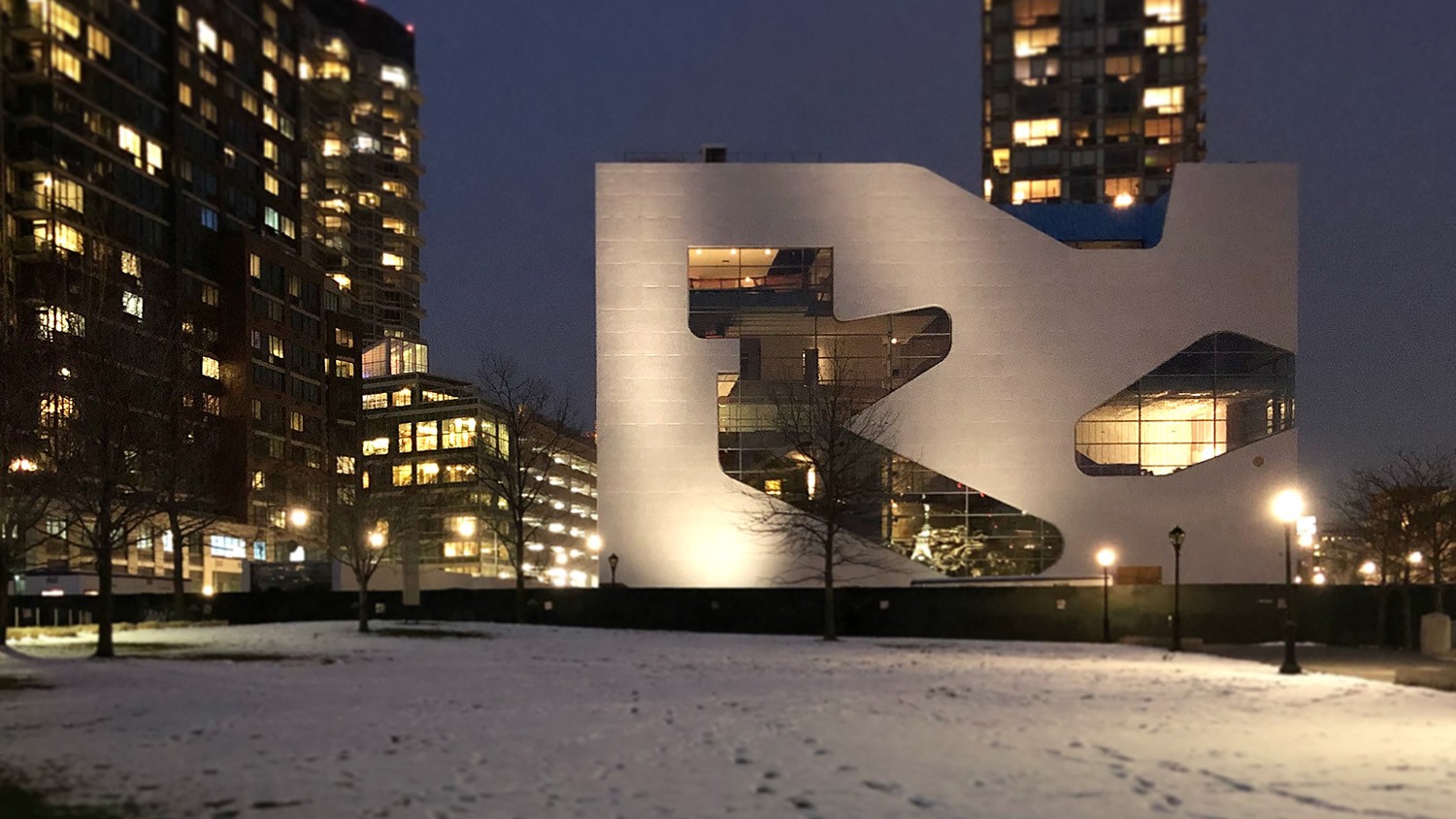
Architectural references
To get an better impression of what architectural image I have in my the slideshow below shows some design which each have qualities I would like to integrate into my design.
Various architectural references.
Materialisation
Biobased solutions
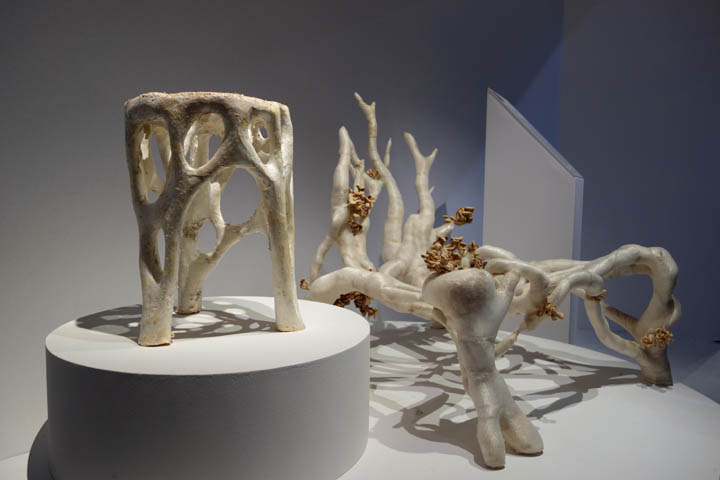
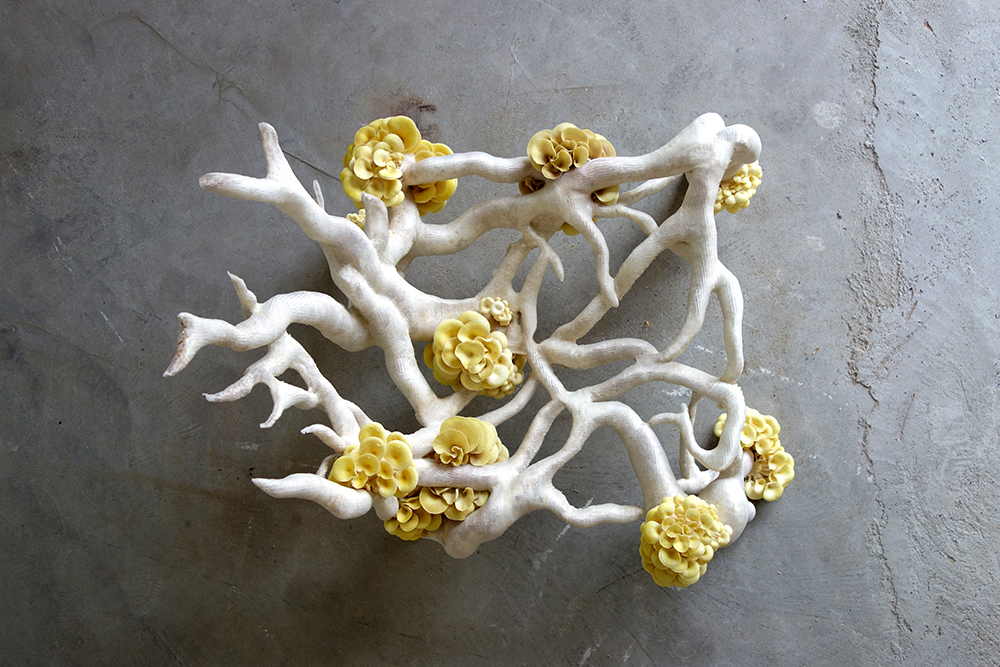
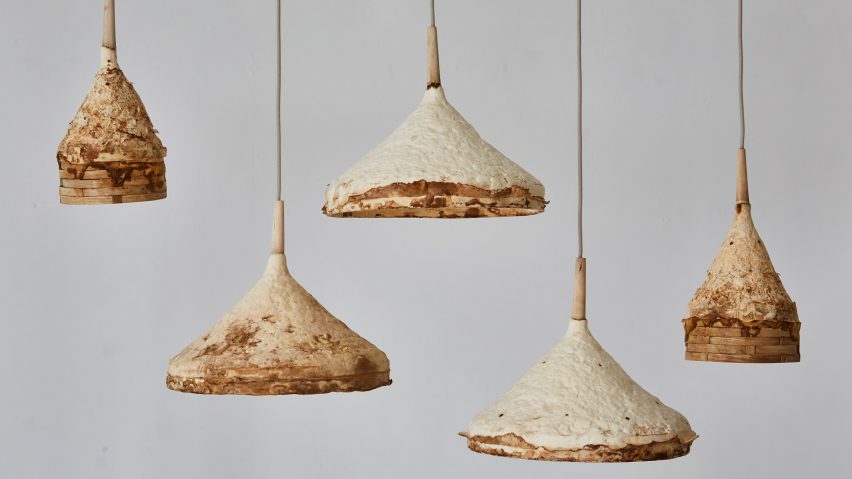
Hospitals are known for their healing capabilities, but mostly for people and not for their environment. With the reintegration of nature within the building. I believe that the materialization of the intervention should also find their origins in nature. Especially the use of growing materials. This search resulted in the usage of mycelium as an building material. Mycelium is the vegetative part of fungi. This biological tissue/ material is composed from tube-like fibers. These fibers are called hypha and are approximately 1 lm in diameter. Hypha grow by elogation of the apical tip. Which means that the fibers grow faster in the tips than in its branches. On occasion these fibers branch out and merge with other hyphae. As a consequence a random fibernetwork structure is formed; The mycelium (Lull et al., 2005).
The hyphae network
Mycelium can be grown in multiple forms, (pure) mycelium, synthetic mycelium and composite mycelium. The last one will be the main focus of this material study since this is the form that is most used within the product development and the built environment. The composite is a mixture of mycelium mixed with a organic substrate most preferably a lignocellulosic biomass. Mycelium than forms it's network of hyphae on and through the substrate by (partly) consuming the substrate. It then transforms the substrates biomass into chitine (up to 45%), Protein and polysacharides. As a result of this process mycelium and the substrate are bonded into the mycelium composite (Tazelaar, 2017).
Mycelium composite
Pure mycelium
Synthetic mycelium
Structural properties
The usage of mycelium as a building component is relatively new. Therefor there is not much research available involving this subject. Besides that mycelium is a biocomposite with many different possibilities for substrate, that fact makes it even more harder to determine average structural properties. In the table below structural properties are shown of mycelium in comparrision to EPS and concrete. EPS is shown since the characteristics of mycelium and EPS are very similiar as are their usages within product development. While concrete is shown as it is a widely used within the build environment.
As seen the structural properties are very similair when it comes down to their compressive strengths. While the young's modulus shows that mycelium is more flexible than EPS. With the mycelium flexibility it is also able to better deal with flexural forces than EPS. But the best the reason why mycelium is better for usages than EPS is its low energy consumption for production and it's biodegradable properties.
| Mycelium Composite | EPS | Concrete (C53/65) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density [Kg/m3] | 122 | 20 | 2500 |
| Compressive strength 10% [MPa] | 0,12 | 0,10 | 65 |
| Tensile strength [MPa] | - | 0,15 | 2,13 |
| Flexural strength [MPa] | 0,23 | 0,15 | 4,30 |
| Young's modulus [MPa] | 1,14 | 6,00 | 37300 |
This table is based on information from (Cement&BetonCentrum, n.d.;Tazelaar, 2017)
Acoustics
Fungi based composites show great potential in the usages as sound absorption. As seen below its absorption properties are depending on the composite material used.
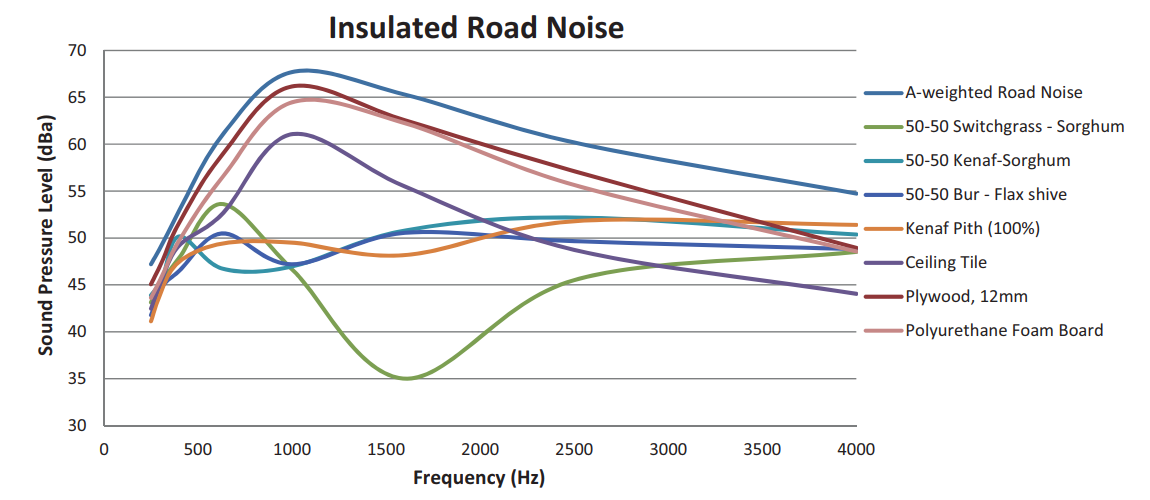
Acoustic absorption of different mycelium based acoustic panels.
Pelletier, M., Holt, G., Wanjura, J., Bayer, E., & McIntyre, G. (2013). An evaluation study of mycelium based acoustic absorbers grown on agricultural by-product substrates. Industrial Crops and Products, 51, 480–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.008
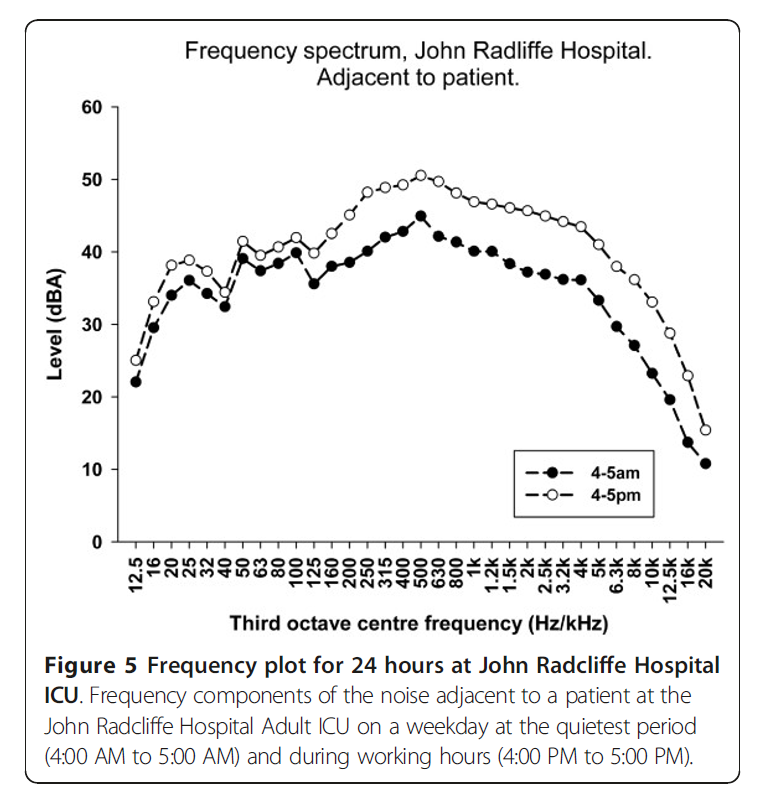
Frequency in patient care units.
Darbyshire, J. L., & Young, J. D. (2013). An investigation of sound levels on intensive care units with reference to the WHO guidelines. Critical Care, 17(5). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc12870
Material cycle
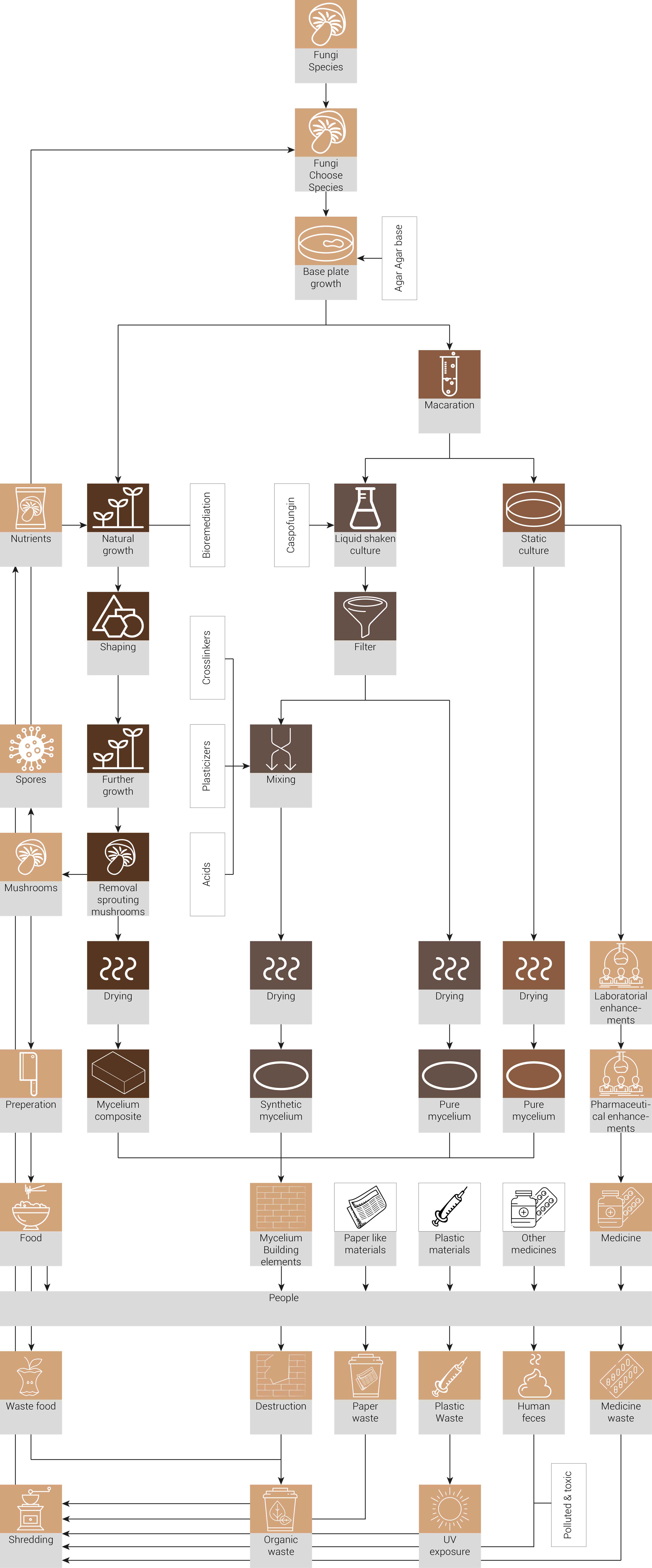
The material cycle proposed for within the AMC
Own image based on Blauwhoff, D. (2016). Mycelium based materials, a case on material driven design and forecasting acceptance. Retrieved from http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:6851aae6-9a46-410f-9f75-91a547770c50
Materialization references.
Various material references
Towards the P3
Things to work on.
At the moment there are still some things I am not yet fully convinced about. These are are largely due to the parametric dependency as an whole. During the development of the atrium script I noticed that to truly so the potential of these connected atria over the different buildings the design fragment should be a little more enlarged. But as a consequence this would change the functional distribution as well. Due lack of time creating images where these changes where integrated become impossible while still portaying an clean imagery. There are also few function reductions am not yet satisfied with. Currently there is an missed opportunity that makes use of the original grid within the building. Perhaps it is worth investigating if the original grid can be used aswell.
The next step when the new semester starts is to zoom in to a meso scale since this presentation has largely focused upon the macro scale of the design.