project04:P2
P2
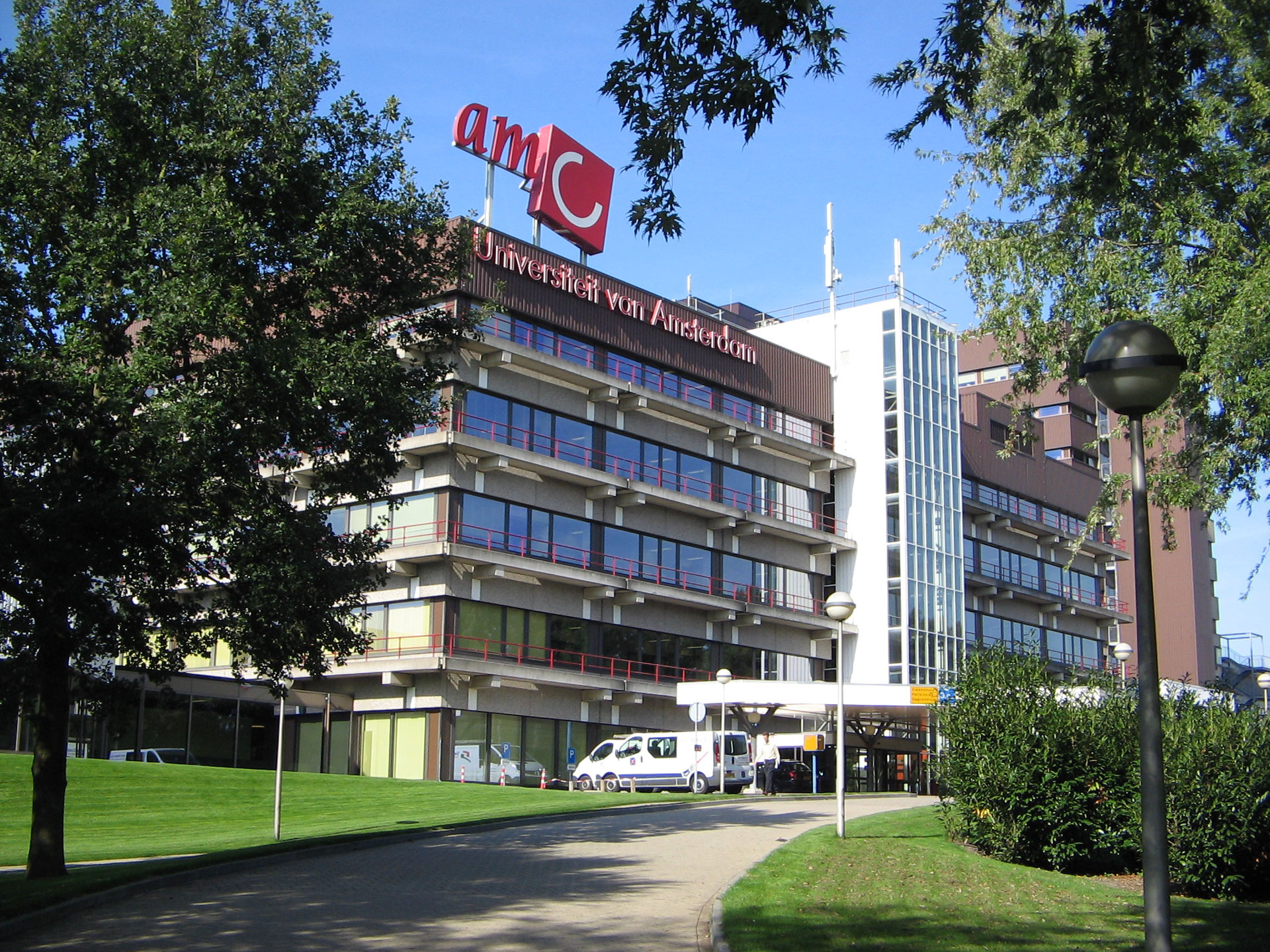
The Academic Medical Center(AMC) is one of the largest hospitals in the Netherlands. The AMC is among the top medical centers in the world. The building dates back to the eighties of the last century. Up until now various architectural interventions have been made but the currently the quality of the building is right on the acceptable level. To maintain an acceptable quality of the building renovation and transformation is required. Therefor the AMC building has to be renewed to face the future. Designing new state of the art medical facilities as for creating a sustainble hospital with a neutral carbon footprint. Within the Architectural Enigineering graduation track this challenge is explored. This is the second presentation in the graduation track presenting my proposal for the new AMC based on Robotic Building principles.
The Academic Medical Center
Key figures
Completed:
Floorspace:
Clinical admissions:
Day care admissions:
Outpatient visits:
Beds:
Employees:
Medical students:
Medical informatics students:
1983.
500.000m2
25.000 per year.
30.000 per year.
356.000 per year.
1.002.
7.000.
2.200.
100.
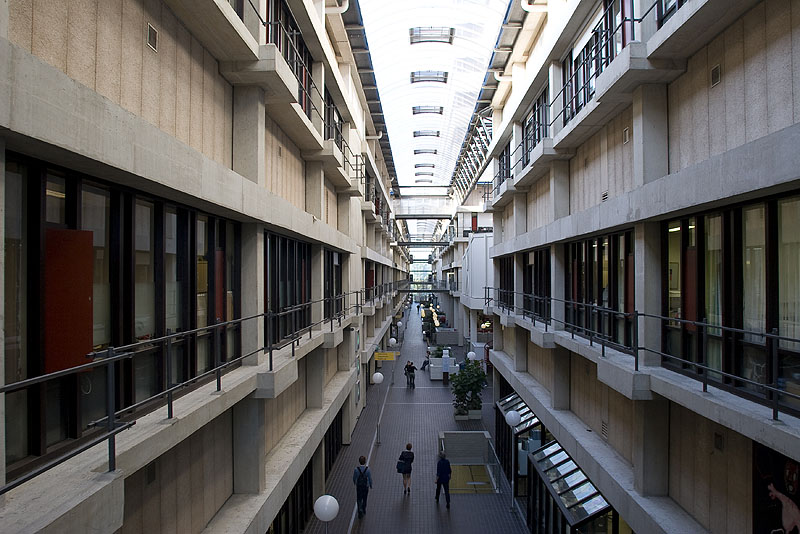
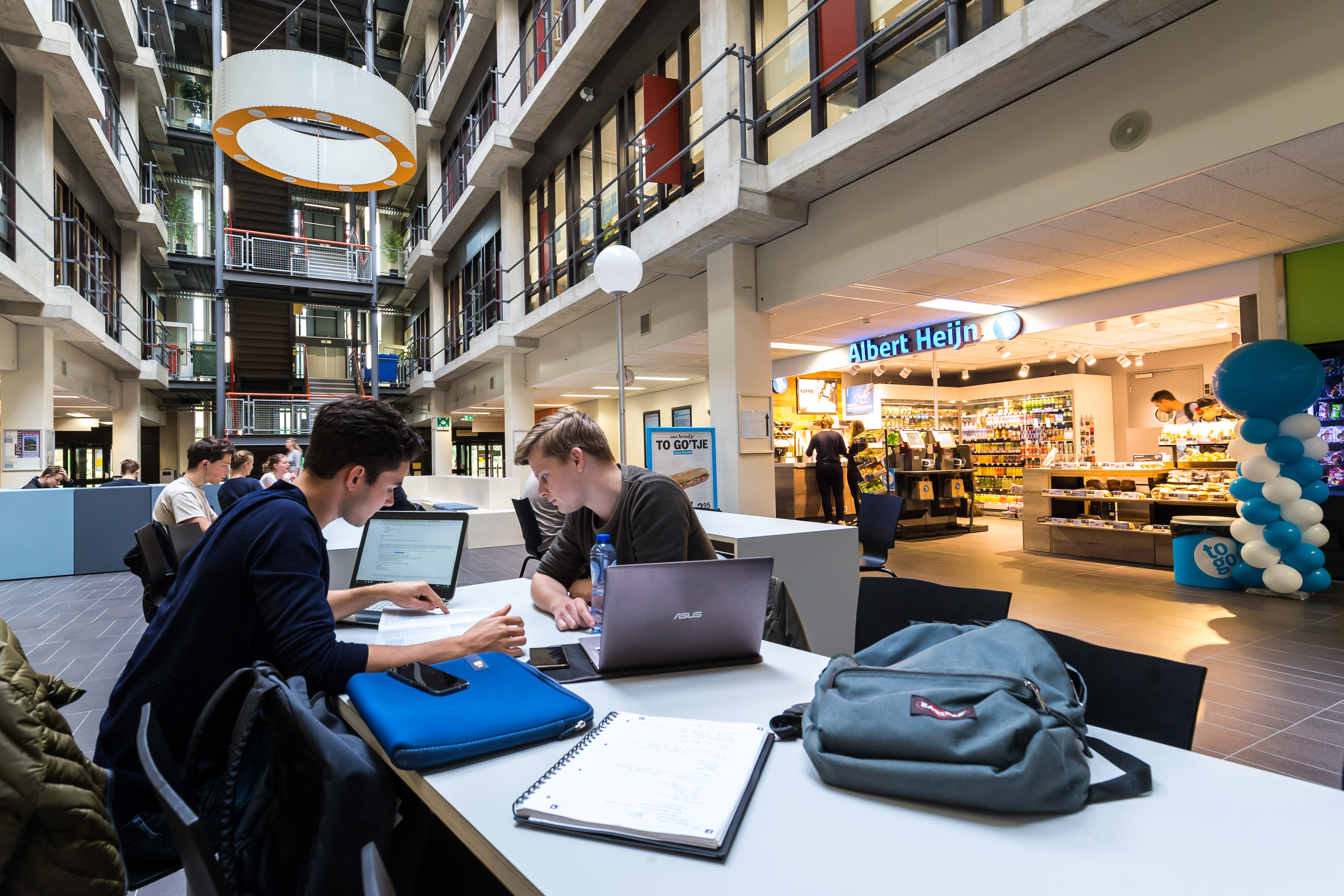
Impression
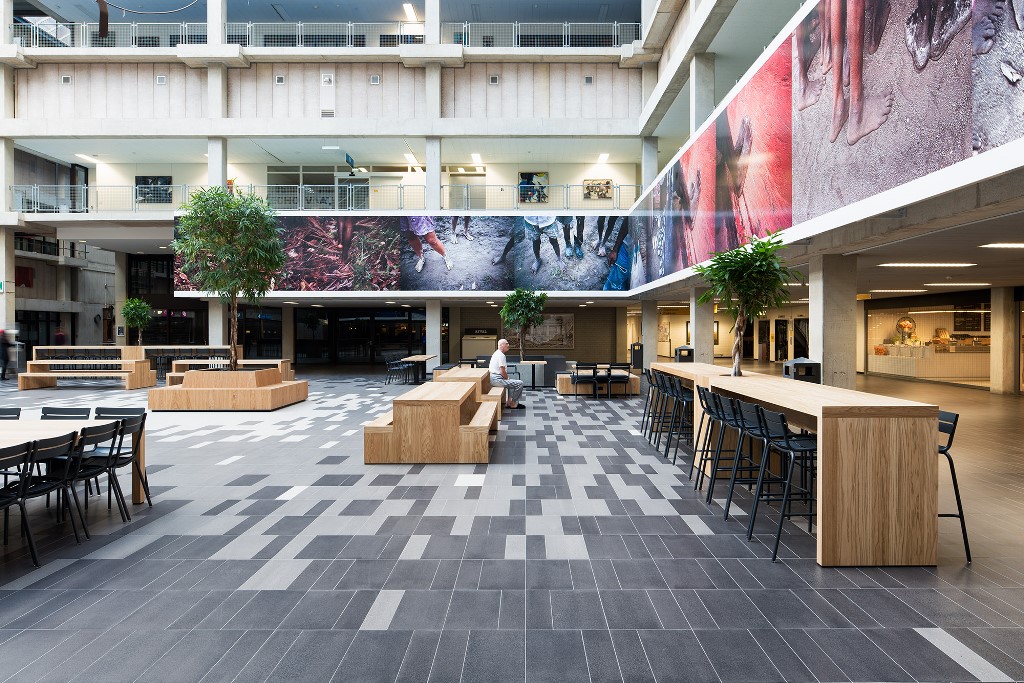
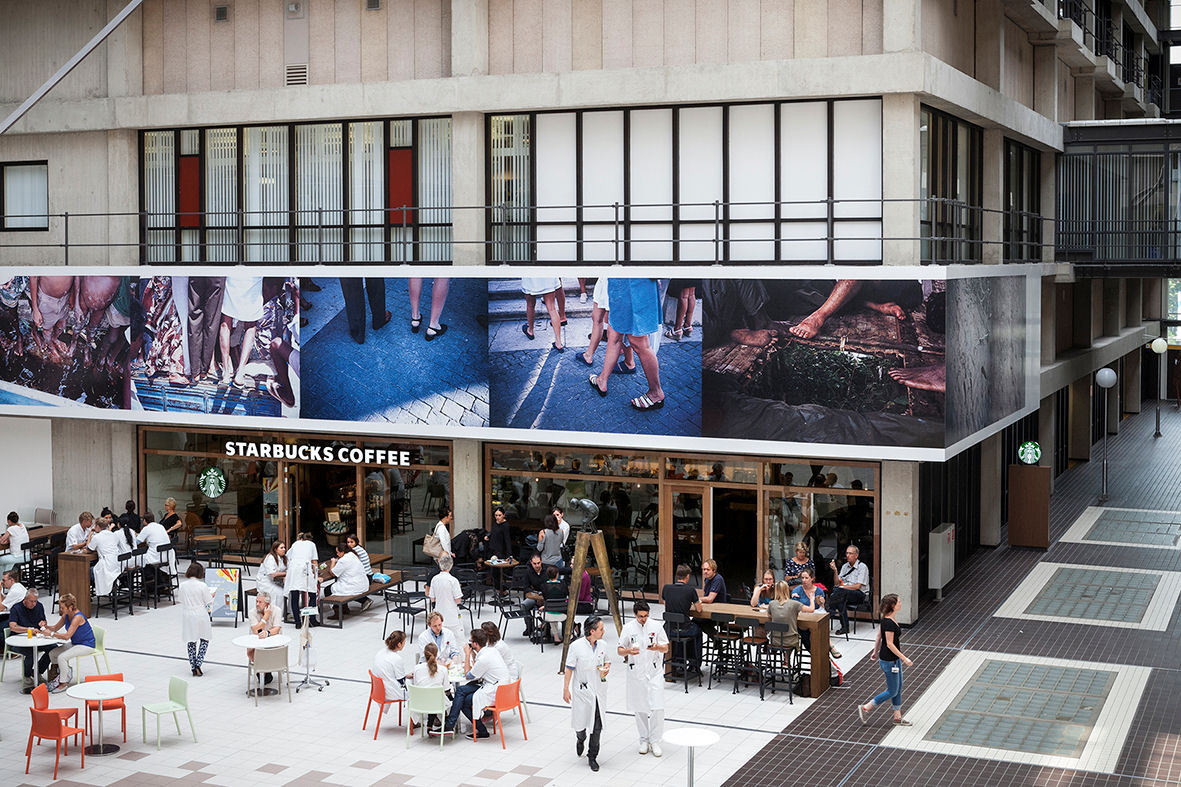
This slideshow presents images of the AMC. These images show the internal street of the AMC, the building as a whole which is often described as the monolith. Within these images the brutalist architecture is clearly visible as the bare concrete structure.
Various images of the AMC
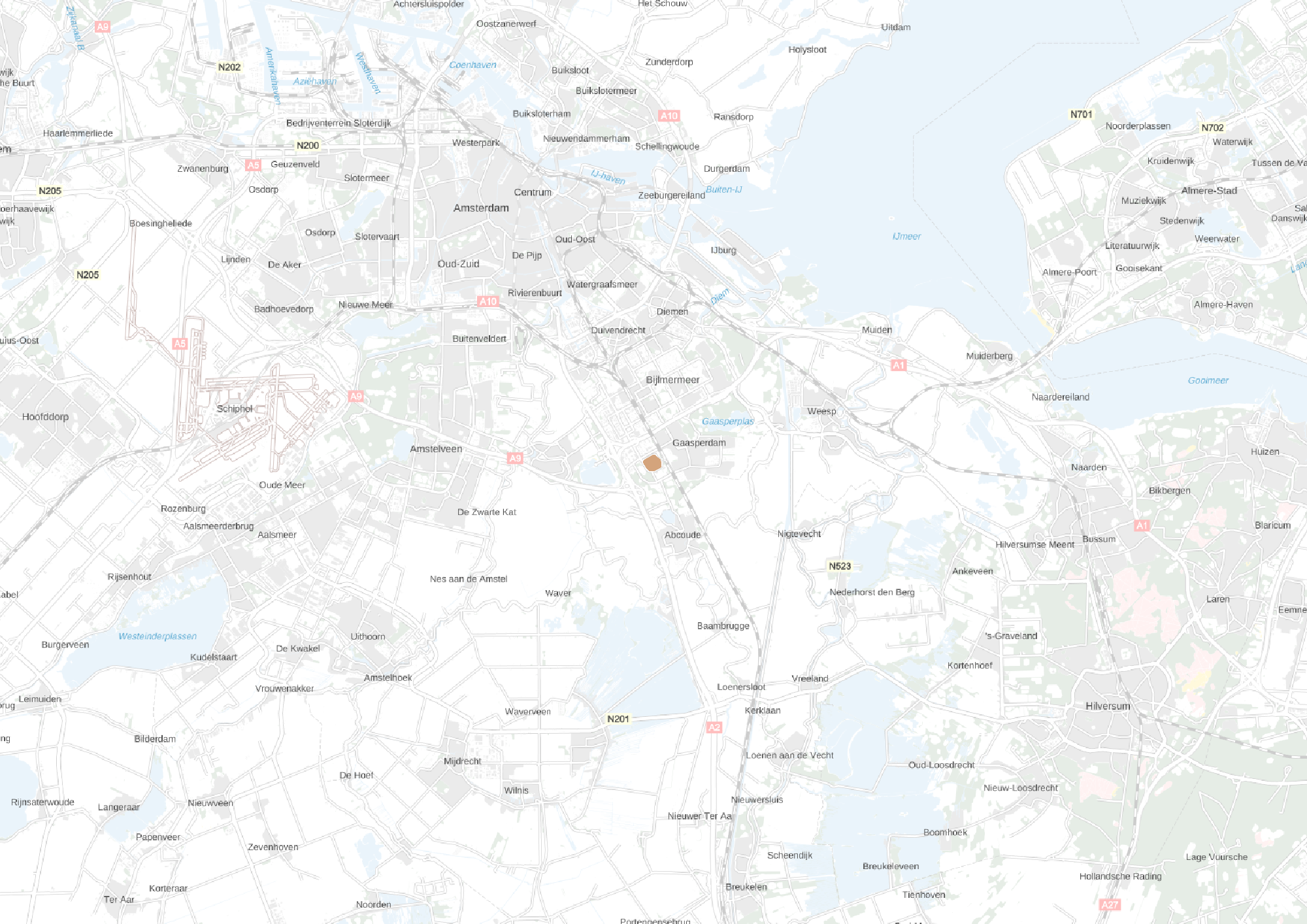
Location
This slideshow presents the location of the AMC. As previously mentioned the AMC is located in the southeast of Amsterdam. There it can be accessed by car from the A2 and A9 highway network and by train, metro and busses via Amsterdam Holendrecht station.
Own images showing the location of the AMC and the access to the building by car and public transport
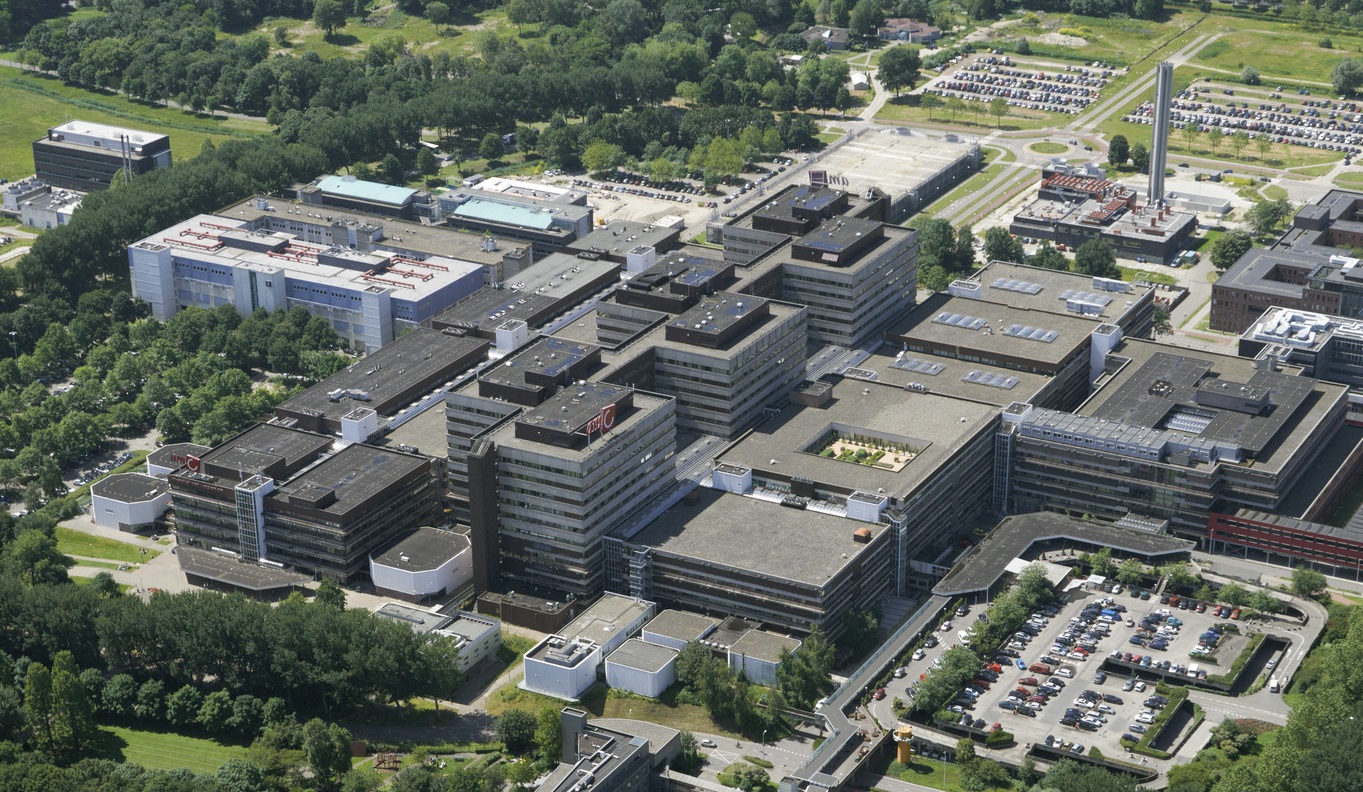
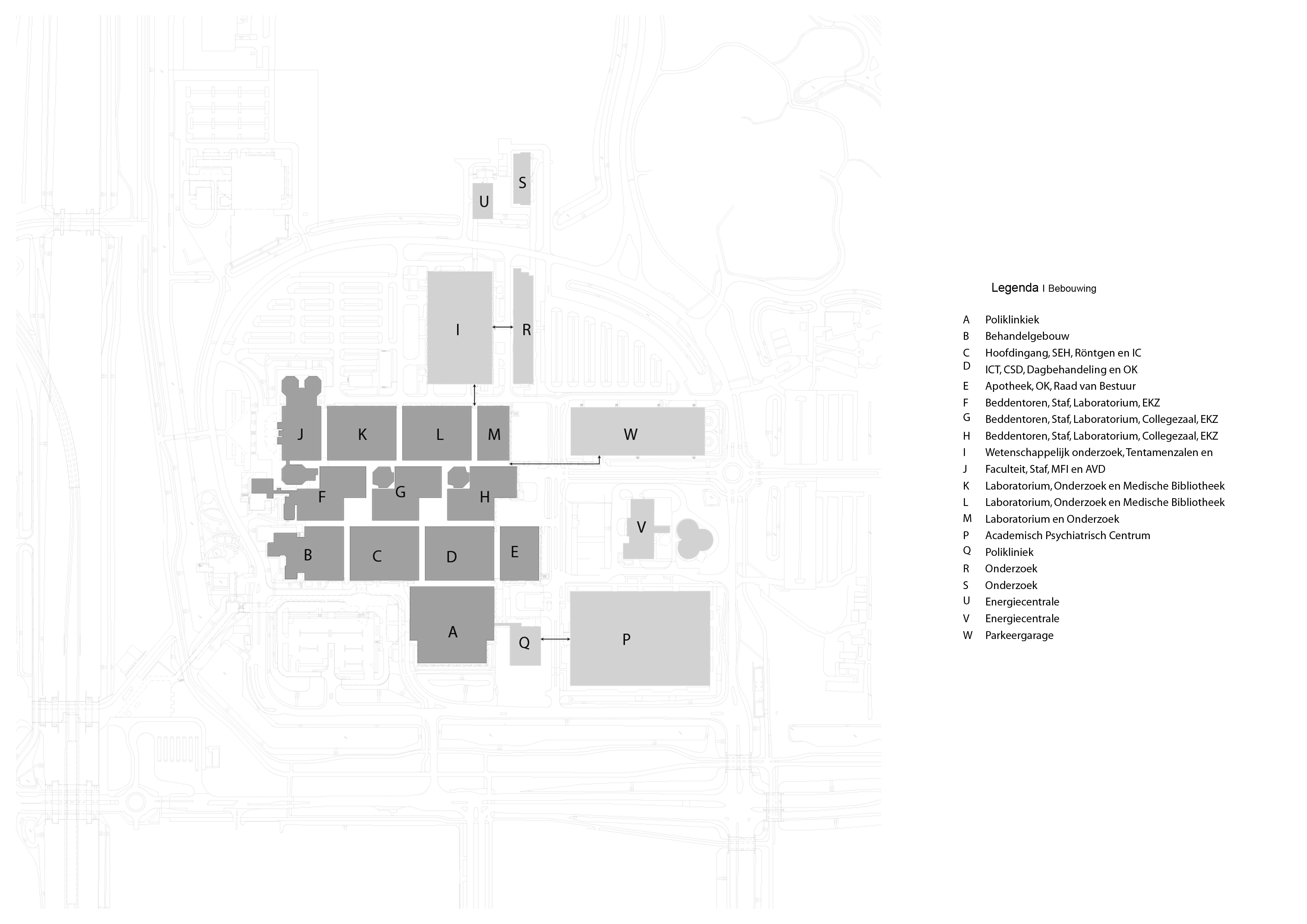
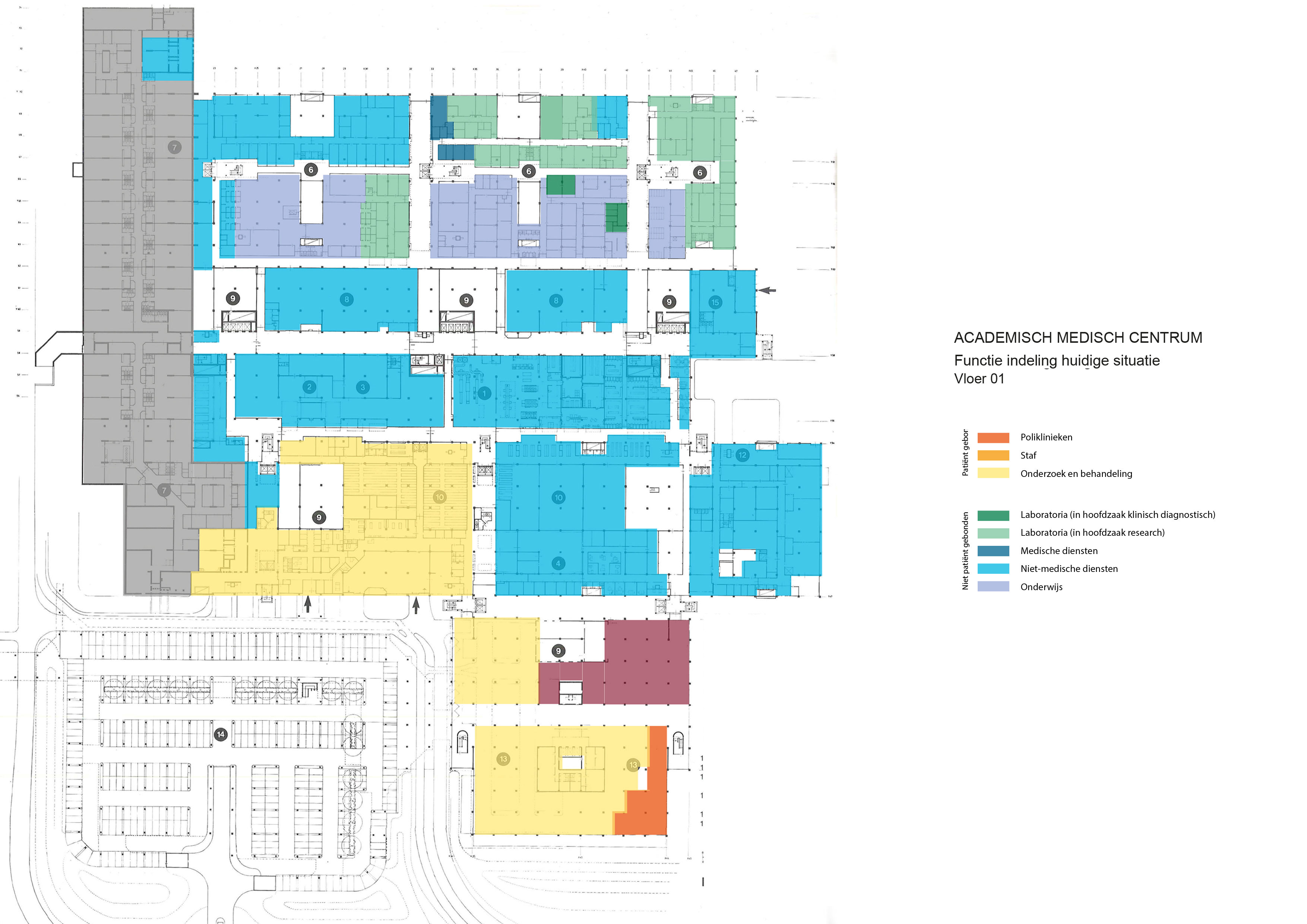
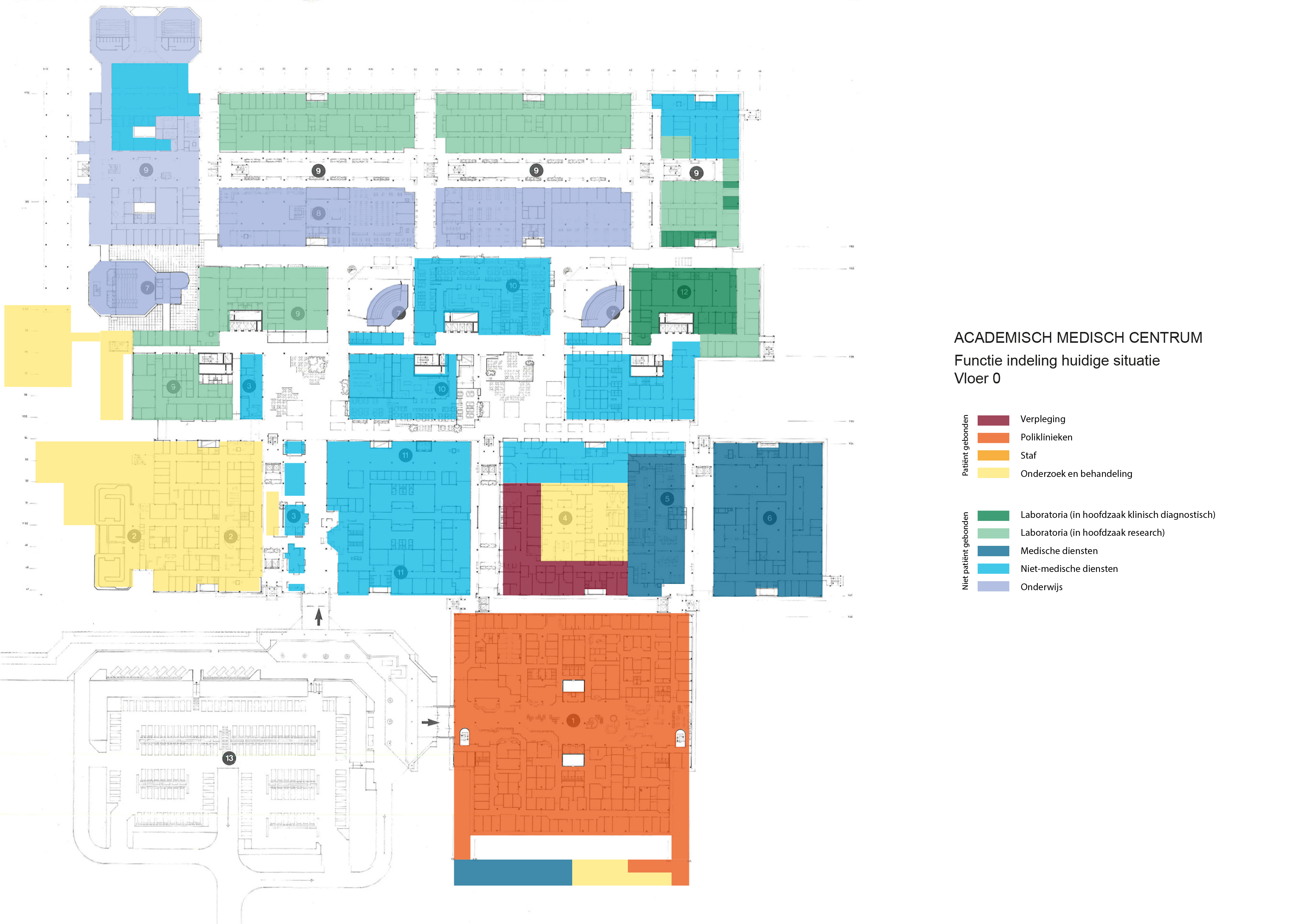
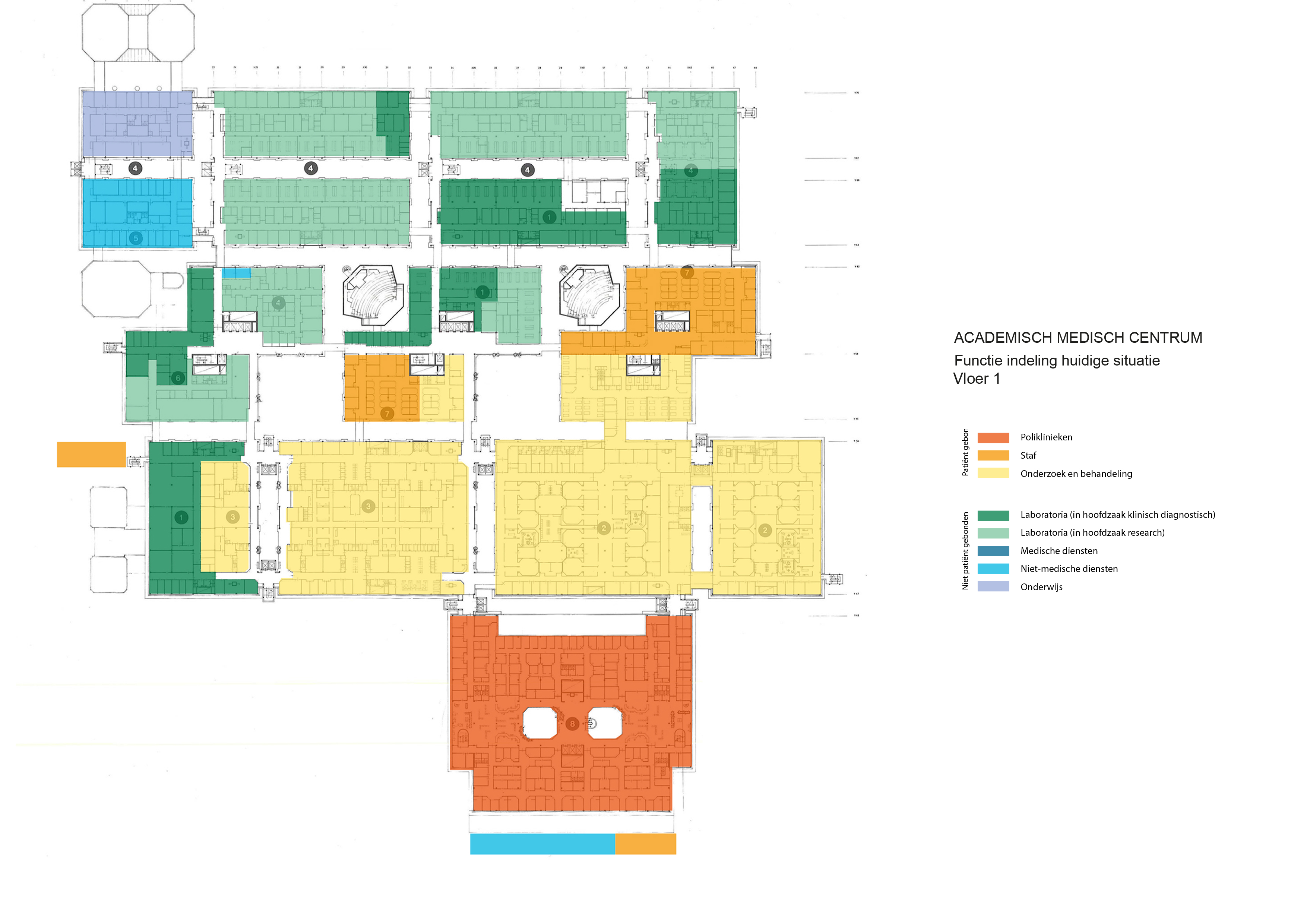
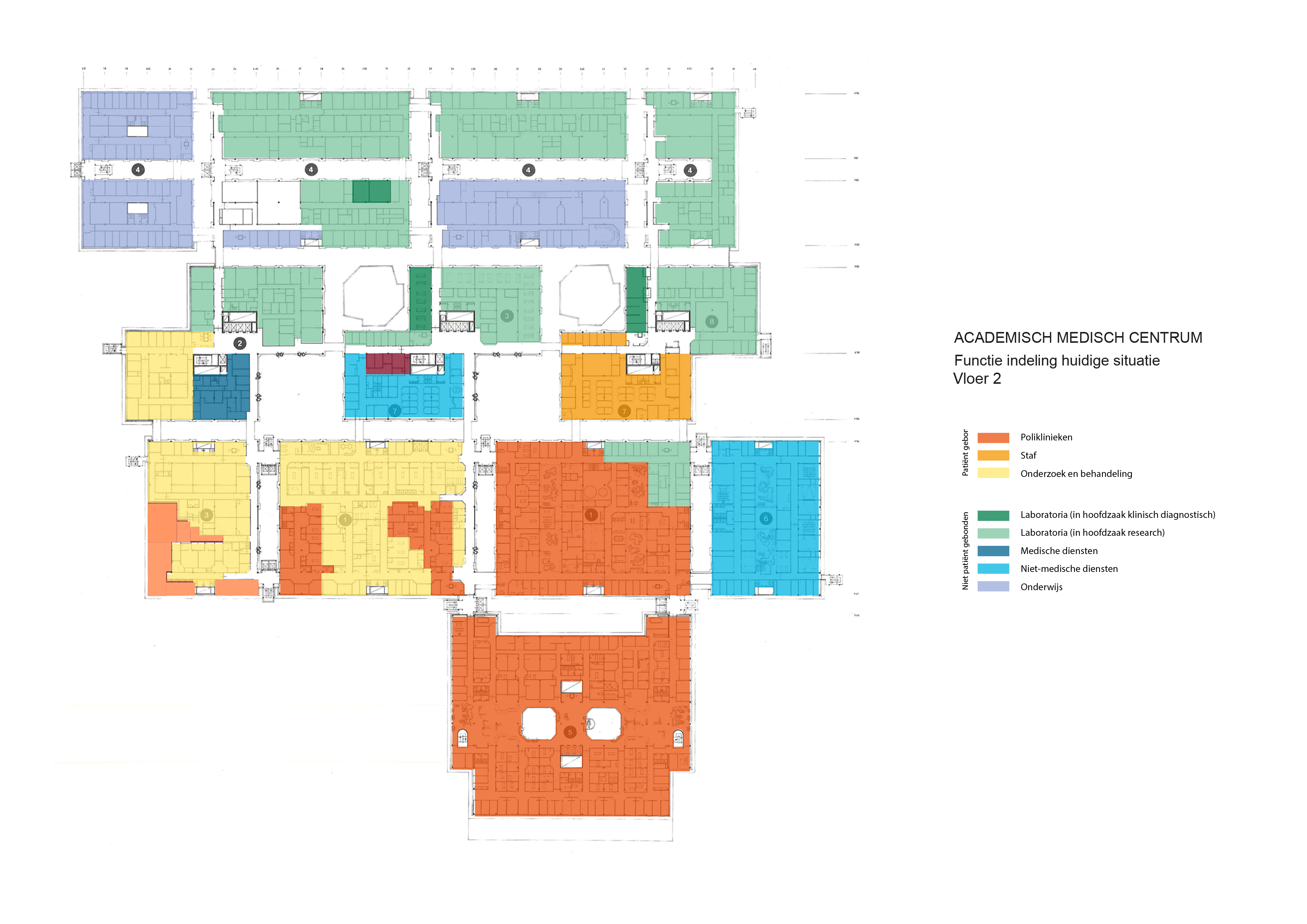
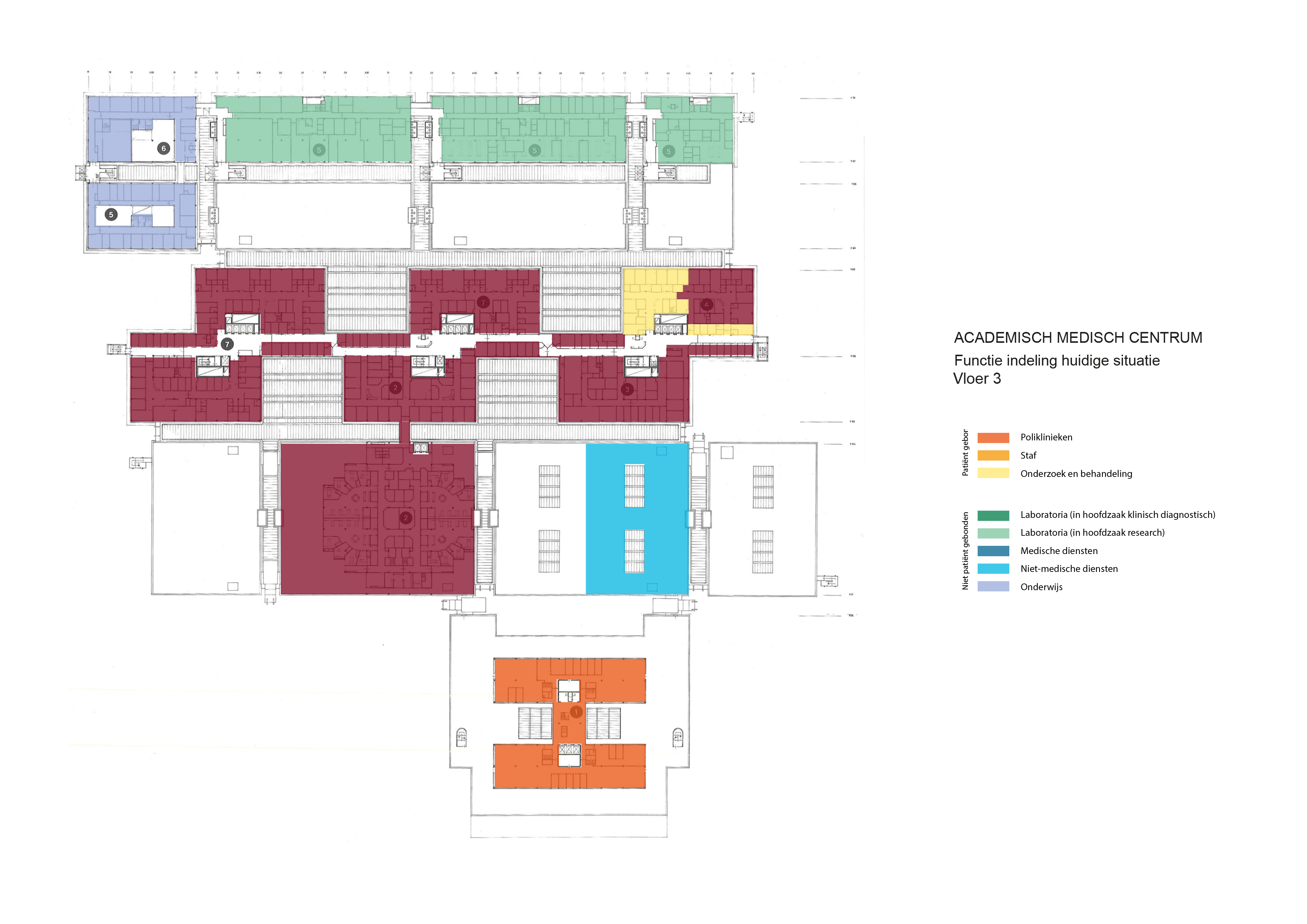
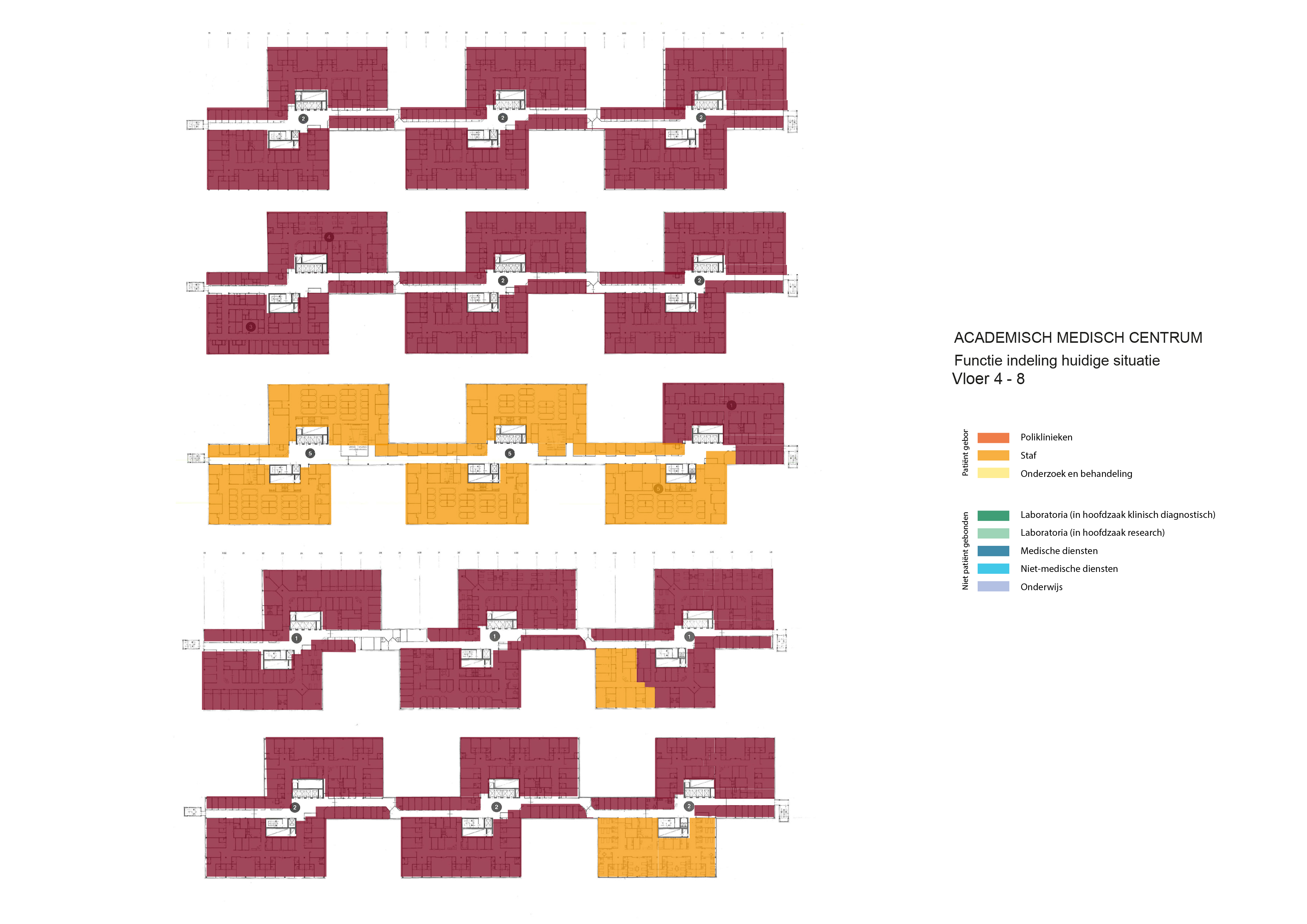
Floorplans
The floorplans of the AMC show that all the different floorplans within the AMC. Besides showing the floorplans it provides an analysis of the plans. It becomes clear that there is a clear division between the northern part and the southern part. The northern part is meant for non patient functions like education and laboratories while the southern part of the floorplans is meant for patient care.
The floorplans of the AMC with function analysis.(AMC, 2016)
Specialism
The AMC has various top-referral specialties. These include cardiovascular diseases, immunology and infectious diseases, diseases of the digestive system (surgery and internal medicine), metabolic diseases, gynecological oncology, specialized care in early pregnancy, prenatal diagnostics, pediatric oncology, pediatric immunology/ hematology, vascular disorders of the brain, severe hearing disorders, schizophrenia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and deep brain stimulation for severe obsessive-compulsive disorders. Besides these specialties the AMC has also been allocated various top clinical functions by the Dutch government. These are functions that provide medical treatments and services in limited number of hospitals, this due to high costs and required expertise. The AMC’s allocated top-clinical functions include kidney dialysis and kidney transplantation, open heart surgery, radiotherapy, neurosurgery, neonatology and nuclear medicine.
The AMC tries to distinguish itself from other hospitals through seven core areas of medical research. These are: cardiovascular diseases, immunity and infections, gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders, neurological and psychiatric disorders, oncology and epidemiology & public health. All of these core areas covers the whole spectrum of medical research: from fundamental biomedical, translational and clinical research to the evaluation of new medical methods and techniques.
Infectious diseases and immunity
In a Dutch and international context, AMC researchers are working on the development of drugs and the evaluation of combination therapies for HIV/AIDS. Another line of research focuses on the development of vaccines, and bacterial research concentrates on pneumonia, meningitis and septicemia. Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are also being studied, with researchers concentrating mainly on the inhibition of proinflammatory proteins by means of an inactivated virus. Phagocytes, dendritic cells and T-cells are the central focus of fundamental immunological research.
Oncology
Most of the research in the core area of oncology concerns the molecular and biochemical backgrounds of cancer. There are four lines of research: gastrointestinal oncology, hematological oncology, pediatric oncology and neuro-oncology. The focus of the research is the hypothesis that only cells of one certain type – called cancer stem cells – cause tumors to grow and spread. The pediatric oncology research covers everything from fundamental research (genetic profiling) to clinical research. Much attention is focused on new drugs, and the later effects of oncology therapy.(AMC, 2009)
cardiovascular diseases
immunity and infections
gastrointestinal diseases
metabolic disorders
neurological and psychiatric disorders
oncology
epidemiology & public health
The seven core areas of medical research, own image.
AMC's development vision and aims
In the spirit of the original principles of the core principles for redevelopment of the AMC are flexibility and standardisation. Within these principles safety and patient-centrality. The different phases of care will be more separated and then accordingly relocated within the hospital network. These phases include diagnostics, treatment, screening, after care, nursing and caring.
Another important aspect of the AMC is the increase in scientific research, in quantity (promotions and publications) as well as quality (research funds and impact scores). It is important for the AMC to remain as one of the top UMC research institutes. Through international cooperation it remains a key player within its core areas as previously mentioned. To increase its international presence valorisation is promoted from start-up companies.
The functional state of the bedroom towers has decreased under an acceptable level for modern medicine. Therefor these towers need to be redeveloped to once again live up to the modern standards. Another problem is that there is hidden vacancy within the towers. Theoretical one full tower could be removed or repurposed.
The research and treatment centre forms the core of the AMC, these function feature high investment costs, complex housing and growth. The functions feature policlinics, research centres e.g. but in the future the policlinic functions need to grow. In order to achieve this sub functions have to be segregated, that would mean that research functions are supposed to be clustered as for the other functions.
AMC functions remarkable well for its age when it comes down on patient care. But the wayfinding, approach and entering of the area and the complex are out dated. The current main entrance and the policlinic entrance are out dated, not representative and don't contribute to the welcome feelings patients and visitor should have.
Flexibility plays a role within the strategy to make more efficient use of the current facilities. This means that employees will have to share their office facilities with employees from other facilities. Therefore reducing 70 offices spots per 100 employees. Another aim is the redevelopment of internal spaces so that they can be used for one main purpose like offices, waiting, research, consultant rooms e.g. and not just for one specific department.(AMC, 2016)
Redevelopment constraints
Since the board of the AMC does not want to demolish the current building it means that the current building has to be transformed. The diffeculty with that is that a running hospital cannot simply be shut down. Appointments, surgercies and threatments are planned far ahead and what to think for the sterile research facilities that have to transported without any external influences on what is being researched. Therefor the AMC has to remain in function and with that come constrains in order to keep the atmosphere of the building as it is. The constraint that are set by the AMC are:
1. During transformation the hospital should remain in function. That would imply that a phased devellopment plan should be develloped.
2. The redevellopment should remain within the current boundries of the building. Excluding the entrences of the building and the renewed landscape plan.
3. The concrete structure should remain in place and should remain visible.
1. Remain active while construction
2. Building boundries
3. Concrete structure
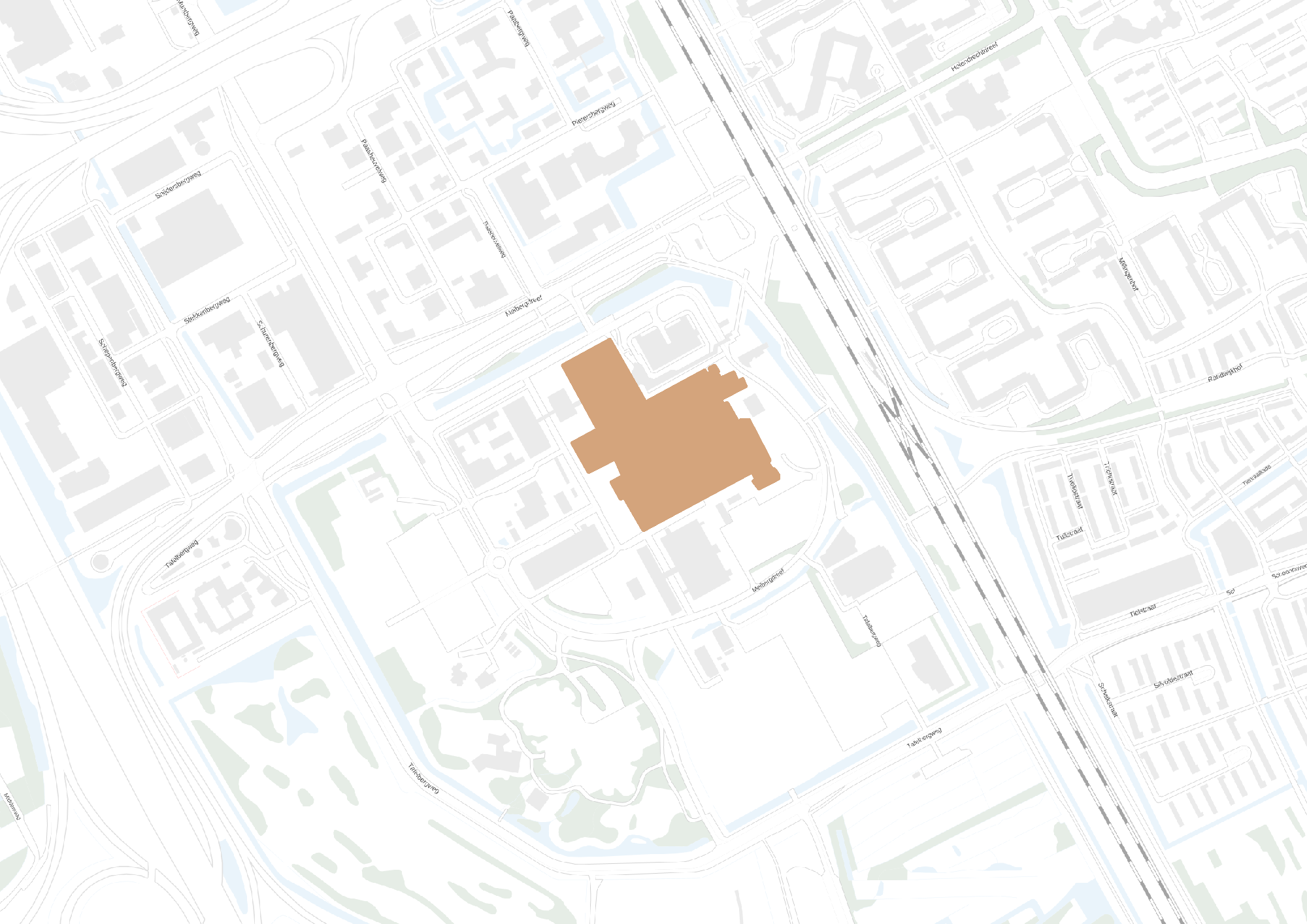
The Design Void
Medical centers are complicated buildings to design, often these buildings house a wide range of different functions with each of them having different requirements. In order to house these functions hospitals tend to be very large. Therefor a (re)design of a hospital building is very time consuming. Time that is not available within the graduation course. Therefor the design will be focused on a specific fragment.

The design fragment of the academic medical center.
The functions
The reduction in design space also implies a reduction in the amount of functions. The fragment will therefor house the functions below.
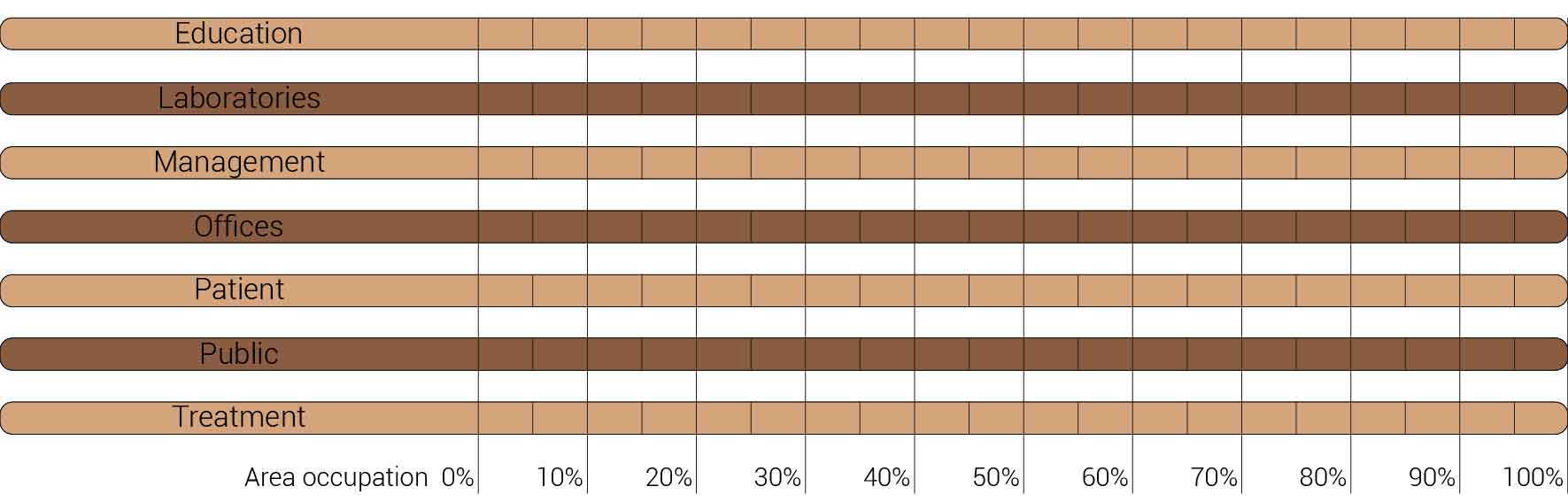
Overview functions and their occupation.
The image above is based on the current occupation of functions but as a mentioned this occupation can already be reduced for the functions of patient housing and offices. There for the image below will form the starting point for the further functional distribution.
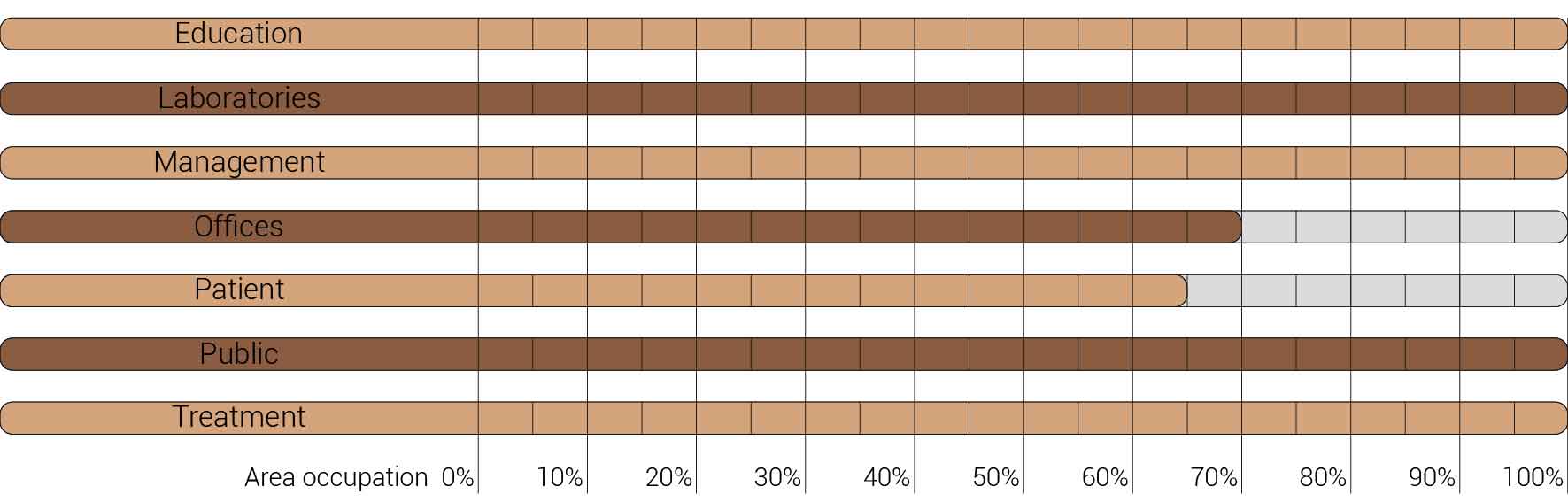
Overview functions and their occupation, renewed.
The future of healthcare and the hospital
The patient, health and healthcare
Survivability is at the core of every human being. Everything we do we do to survive. In order to live longer and survive diseases we have developed a large and complex healthcare system. One of element of this system is the hospital. This place is designed as a last resort, a last chance for the ill to get better. Since the hospital is a place for healing and becoming well, it would imply that being within a hospital would be experienced as a pleasant experience. But on the contrary people often experience anxiety and discomfort.
This is due to that same survivability, it is when we become ill we become uncertain. We lose the control of the situation of health. As a consequence of this uncertainty it becomes difficult to predict what will happen next. Which then can result in feelings like isolation, alienation and depression. These feelings do not improve the potential for regeneration. Patients can suffer from increased blood pressure, stress, reduced sleep.
But this is not what a hospital should cause any patients. It is here where architecture could play a role, a role to prevent these negative emotions from ever occuring and put patients at ease. Research done to find out which design factors matter to patients to create a healing environment. It proposes six themes with associated design characteristics to improve the healing environment; Spatial comfort, Privacy, Autonomy, Sensory comfort, Safety and security, and Social comfort.
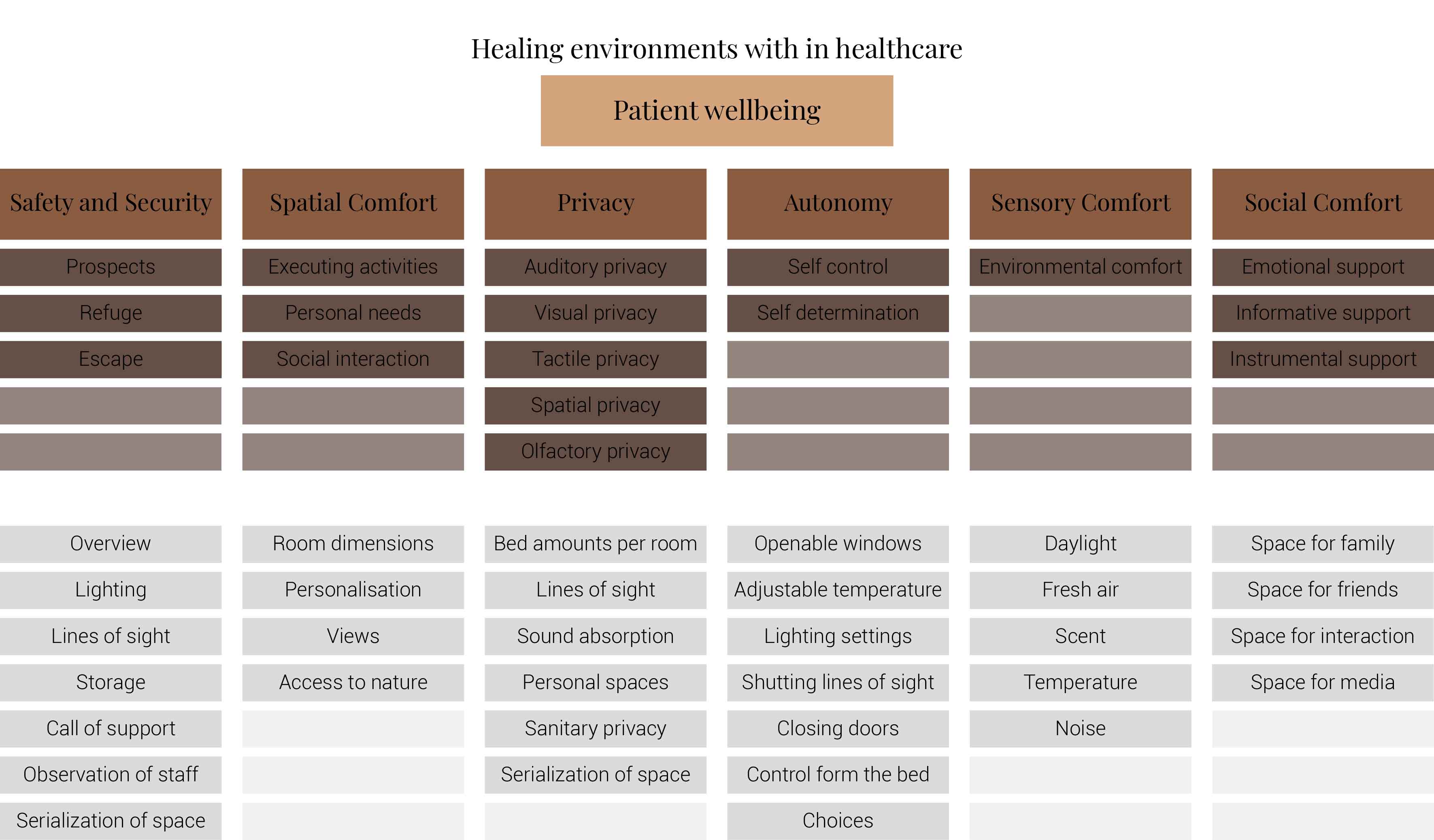
A summary of design characteristics based on the six themes
This image is based on (Schreuder, Lebesque, & Bottenheft, 2016)
The purpose of the research was to find out which design characteristics are more important to the patients than others. Concluding with an advice on which factors should be paid with more attention. It has founded that if hospitals would be transformed into healing environments they should focus on the spatial comfort, safety and security, autonomy and their associated design characteristics.
For spatial comfort it would mean that rooms should be large. It should provide views with sky and green, appealing materials, personal storage space, and space for private conversations.
When it comes to safety and security within the hospital patients appreciate a clear transition form public to private, where unauthorized persons will have restricted access to certain areas. Within the rooms focus should be on lighting, safe personal storage and the ability to call personnel from the rooms.
Many of these characteristics already show some form of autonomy. Another important factor is for patients to have their own influence on what food and drinks the patients consume.But also the possibility to determine resting periods, indoor climate settings and inclusion with decision for treatment.(Schreuder, Lebesque, & Bottenheft, 2016)
While designing all the six themes matter and all their corresponding design characteristics but these previously mentioned characteristics should be integrated with larger importance.
The future of healthcare and the hospital
Our hospitals in the way we know them are rapidly changing. With on going advances in the fields of technology and clinical informatics these changes are set in motion. While the exact impact of these advancements will remain guess work, certain trends are already visible. Based on these trends I'll sketch the impact of the future hospital.
Hospitals will be smaller
Hospitals will be more user-friendly
Telemedicine will be everywhere
Electronic medical records in connected health, primary care, demografic, diagnosis, lab, medicarion, medical history, digital health data, big data, Surgery through machinery.
Personal health records (PHRs)
Patient portals
Mobile health and medical apps
Communication tools and social networks
Wearable technologies and sensors
Robots will be more present and visible
New technologies and research fields
molucalar, nano, genome, personalised medicine, Virtual and augmented reality, 3d printed organs.
The Design
The functional distribution
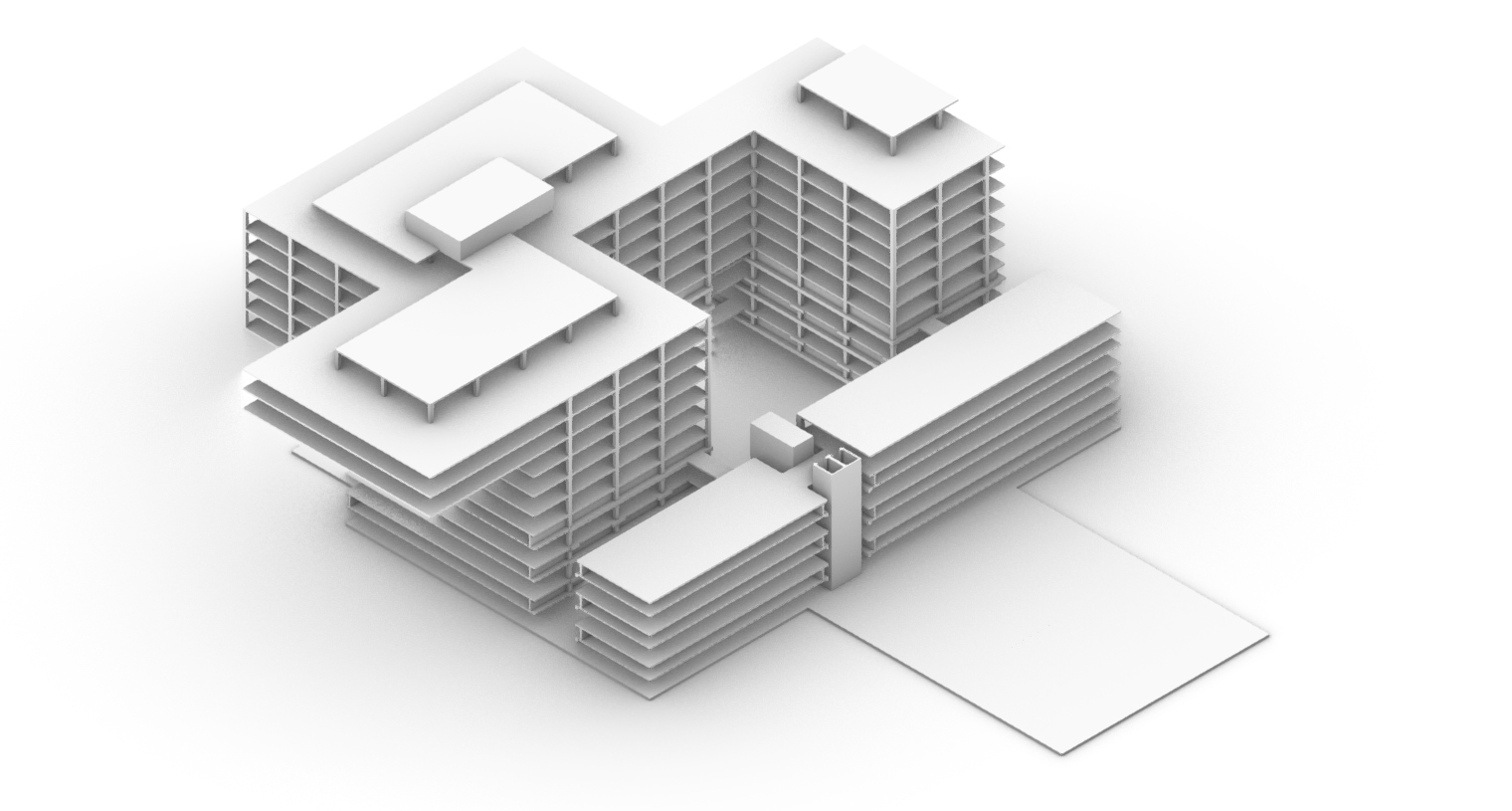
The design fragment for the functional distribution.
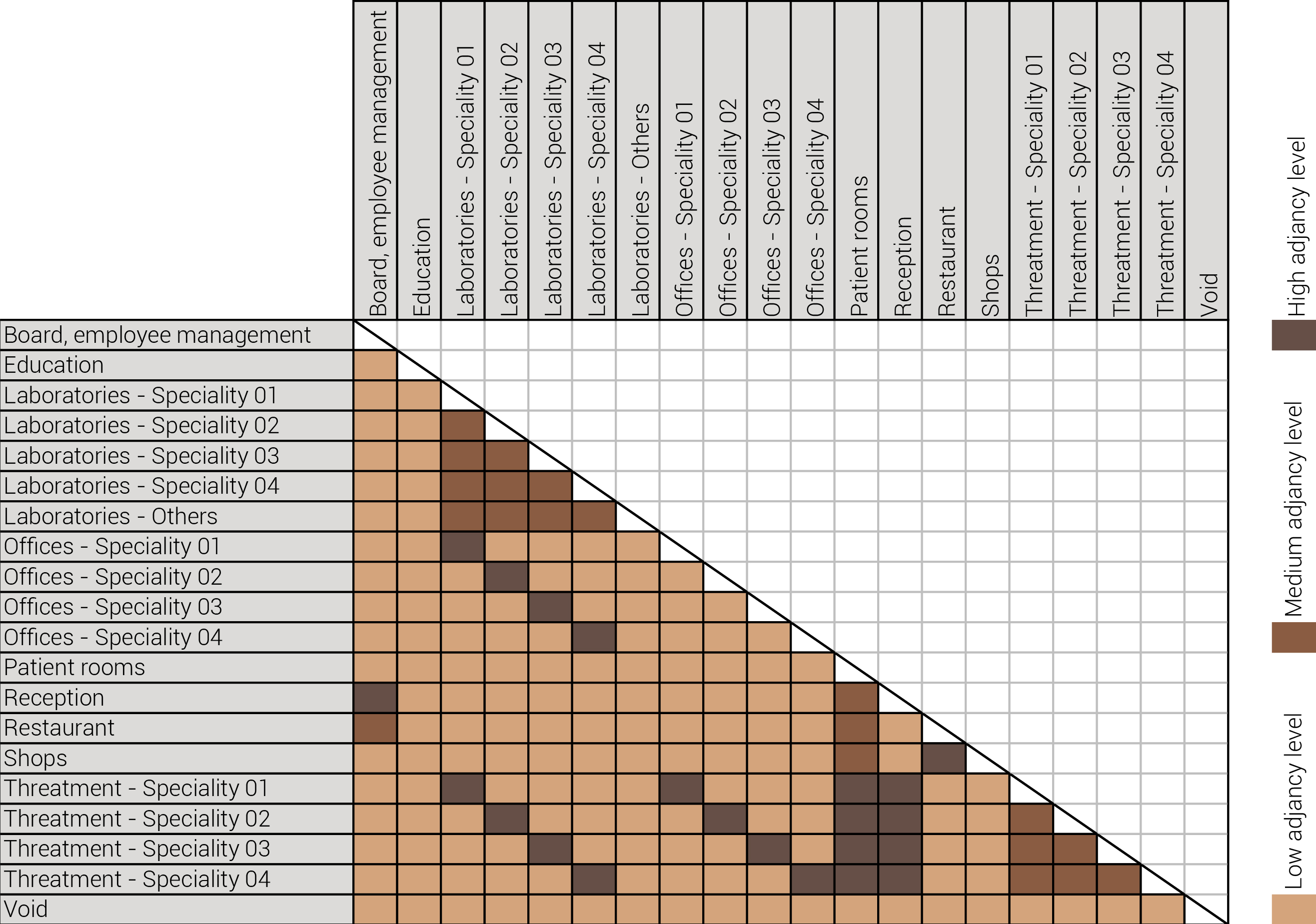
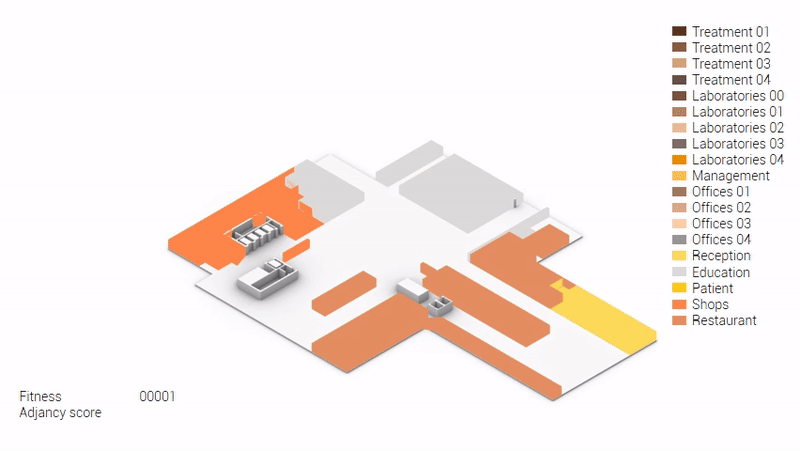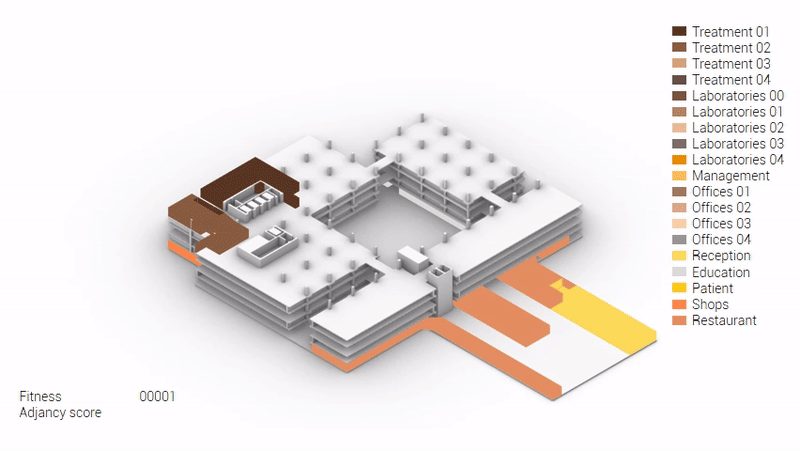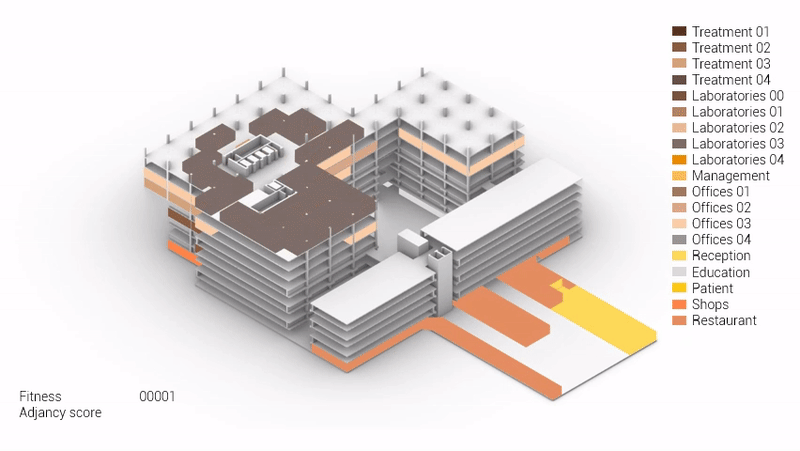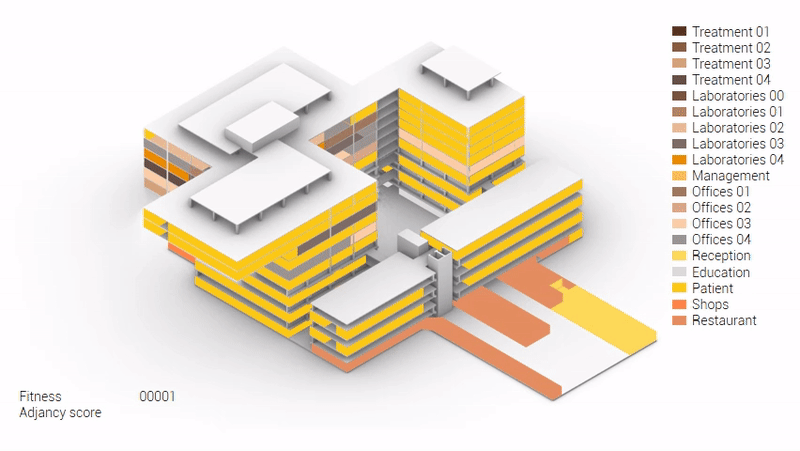
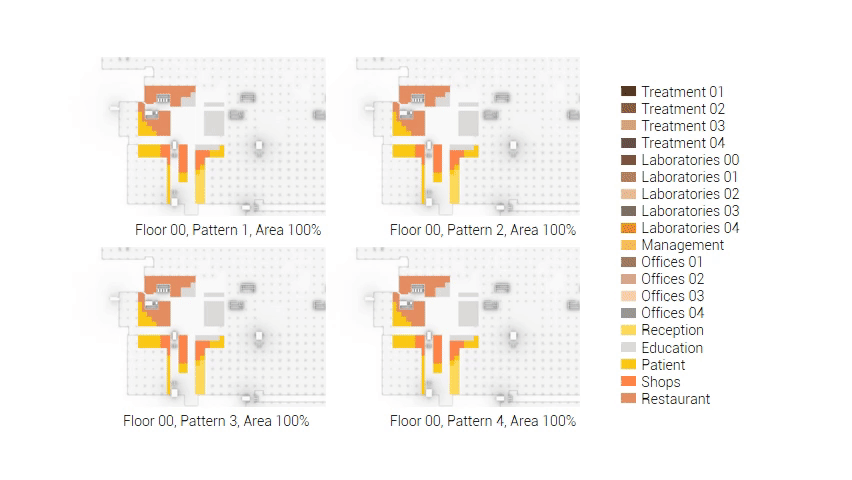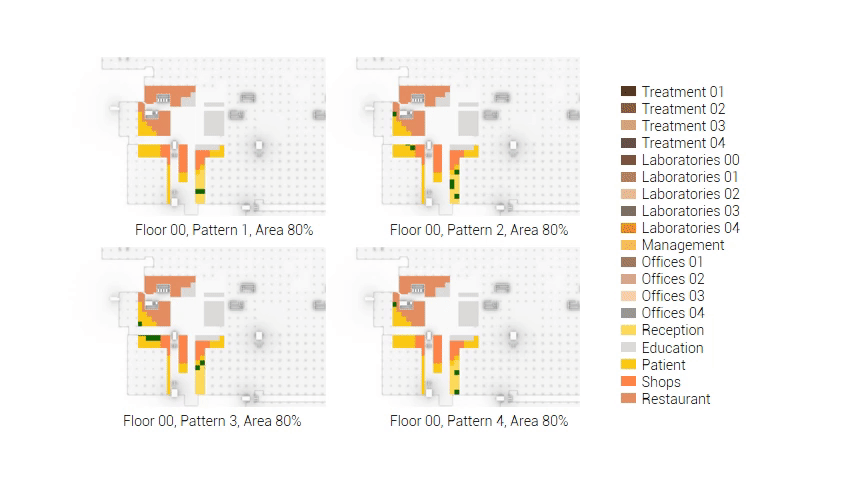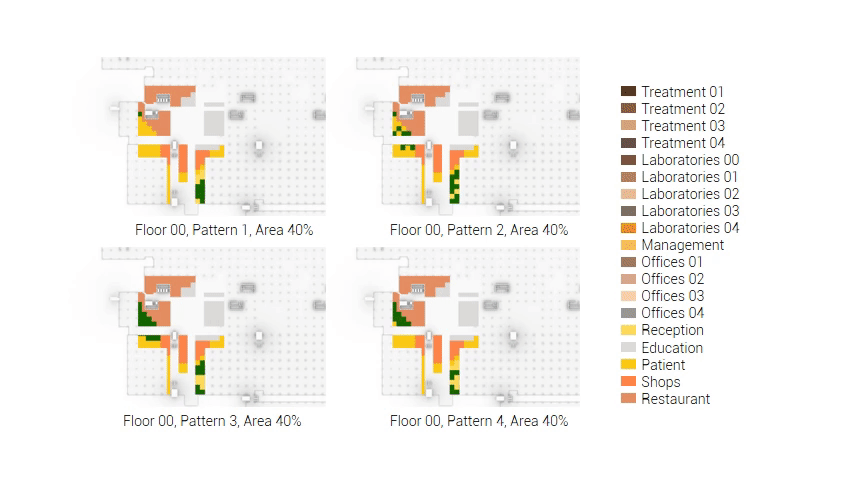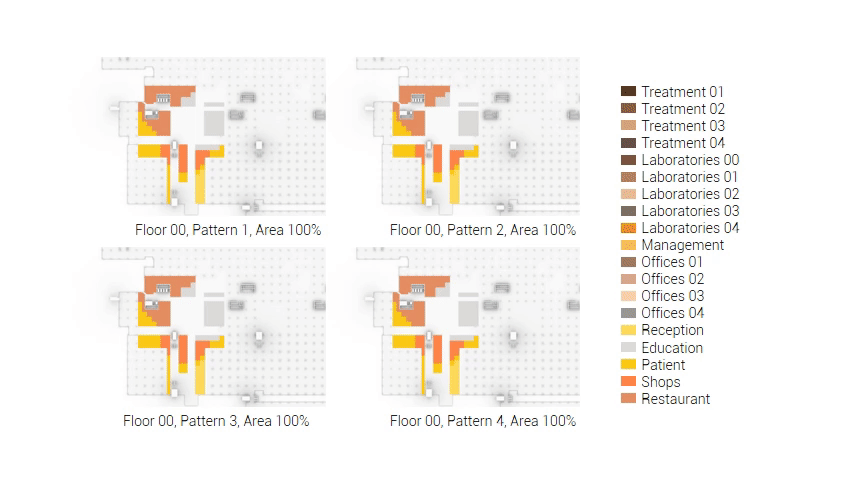
The adjacency matrix portraying the spatial relationship between the functions .
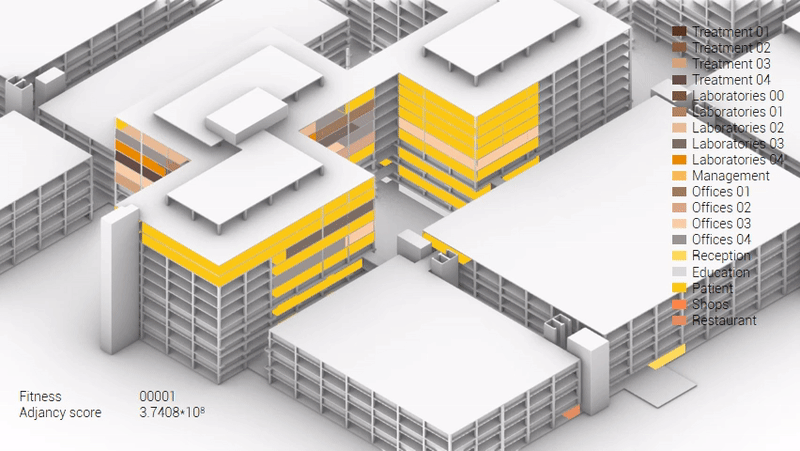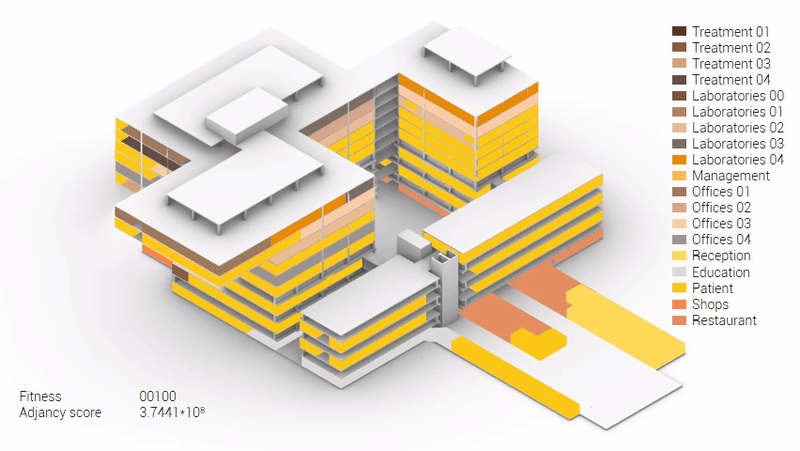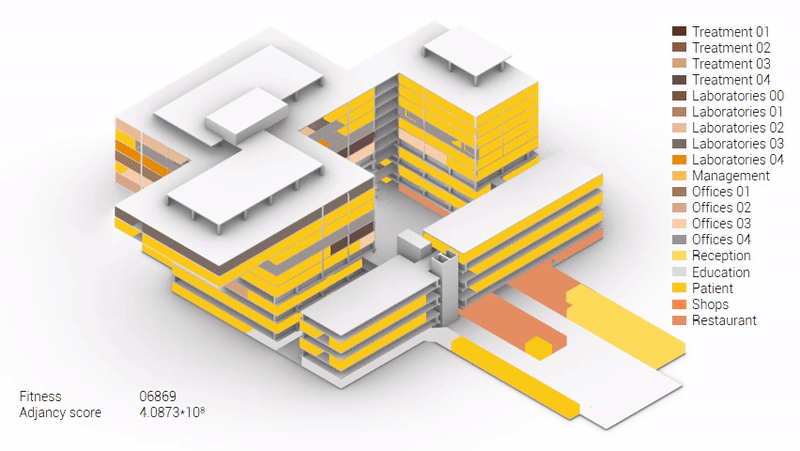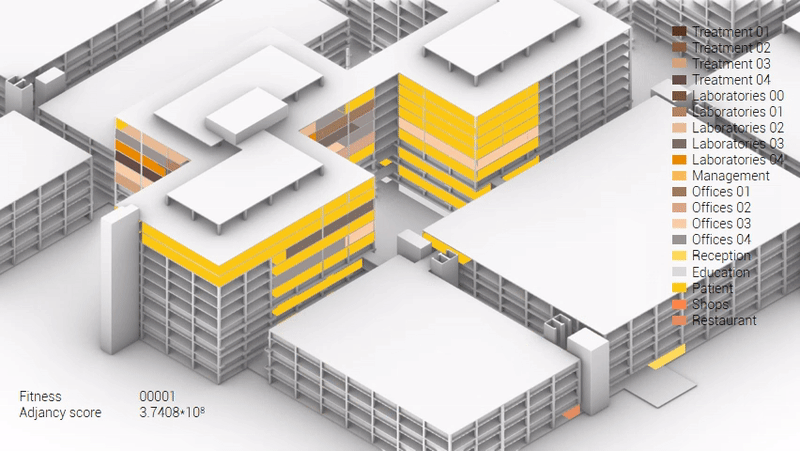
Various design solutions based on the adjacency matrix.
Build up of the various variations.
Build up of the various variations.