project04:P1
P1
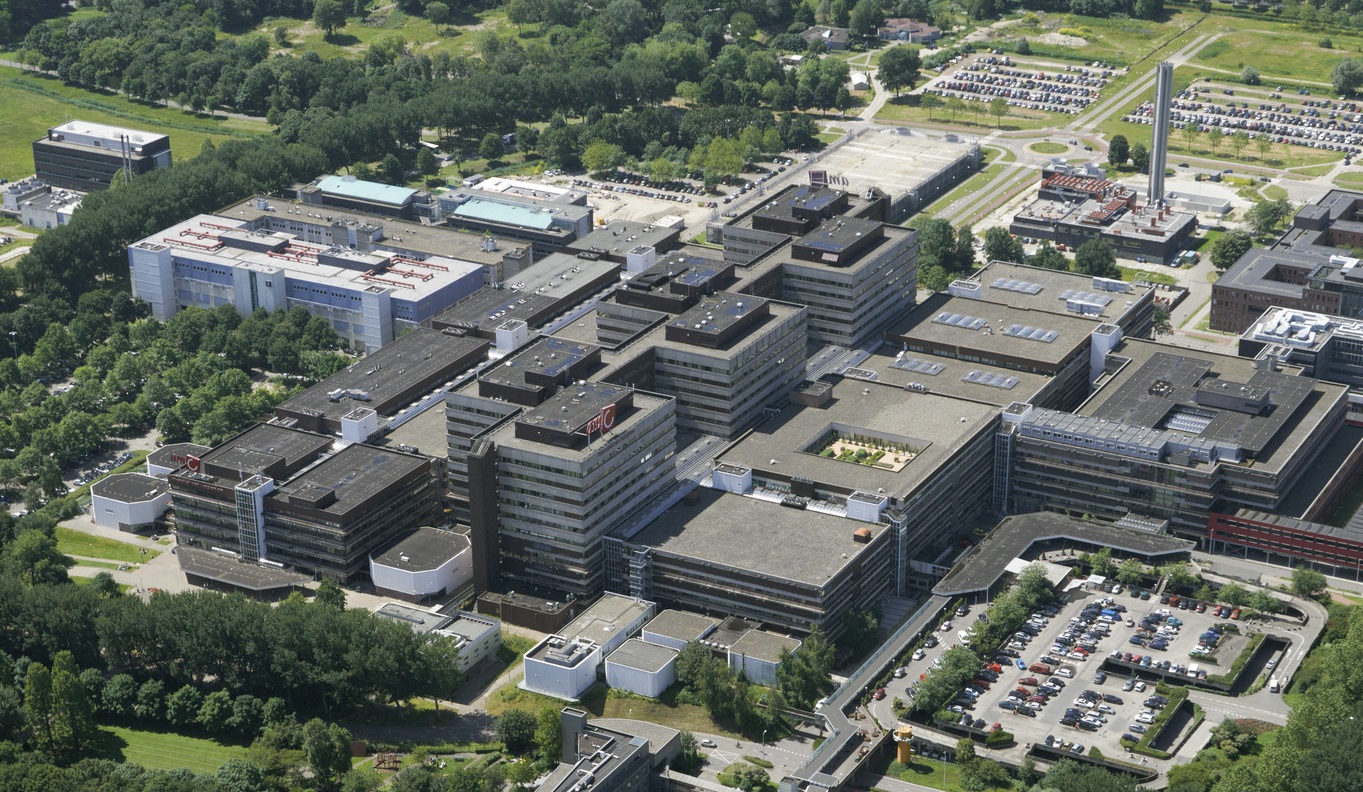
The Academic Medical Center(AMC) is one of the largest hospitals in the Netherlands. The AMC is among the top medical centers in the world. The building dates back to the eighties of the last century. Up until now various architectural interventions have been made but the currently the quality of the building is right on the acceptable level. To maintain an acceptable quality of the building renovation and transformation is required. Therefor the AMC building has to be renewed to face the future. Designing new state of the art medical facilities as for creating a sustainble hospital with a neutral carbon footprint. Within the Architectural Enigineering graduation track this challenge is explored. This is the first presentation in the graduation track presenting my proposal for the new AMC.
The Academic Medical Center
Key figures
Completed:
Floorspace:
Clinical admissions:
Day care admissions:
Outpatient visits:
Beds:
Employees:
Medical students:
Medical informatics students:
1983.
500.000m2
25.000 per year.
30.000 per year.
356.000 per year.
1.002.
7.000.
2.200.
100.
Impression
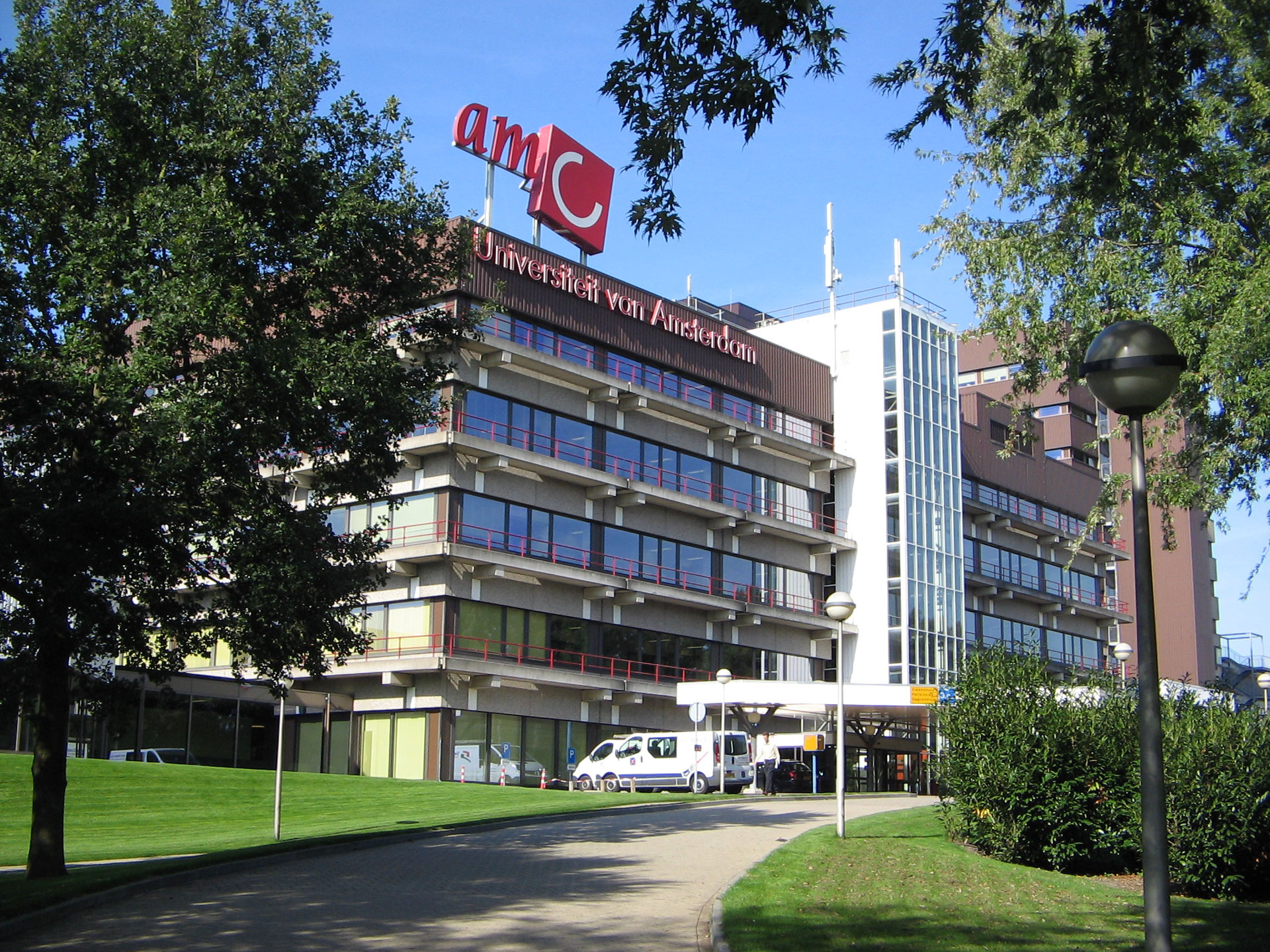
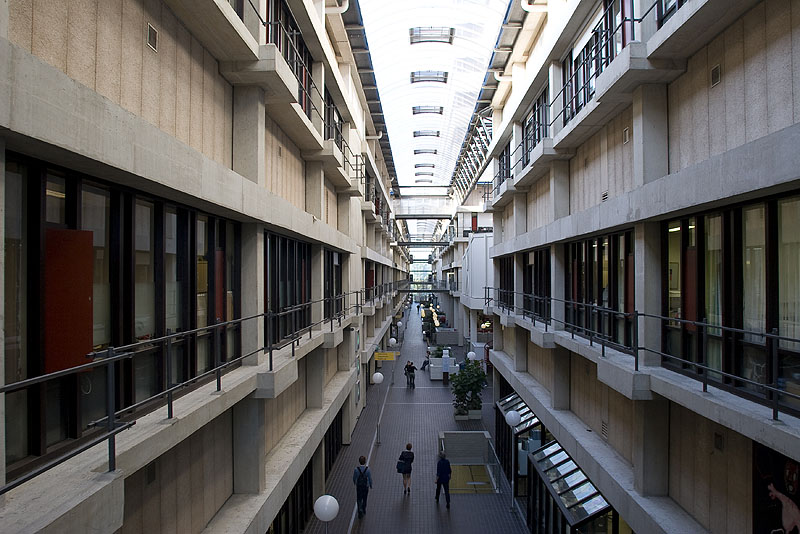
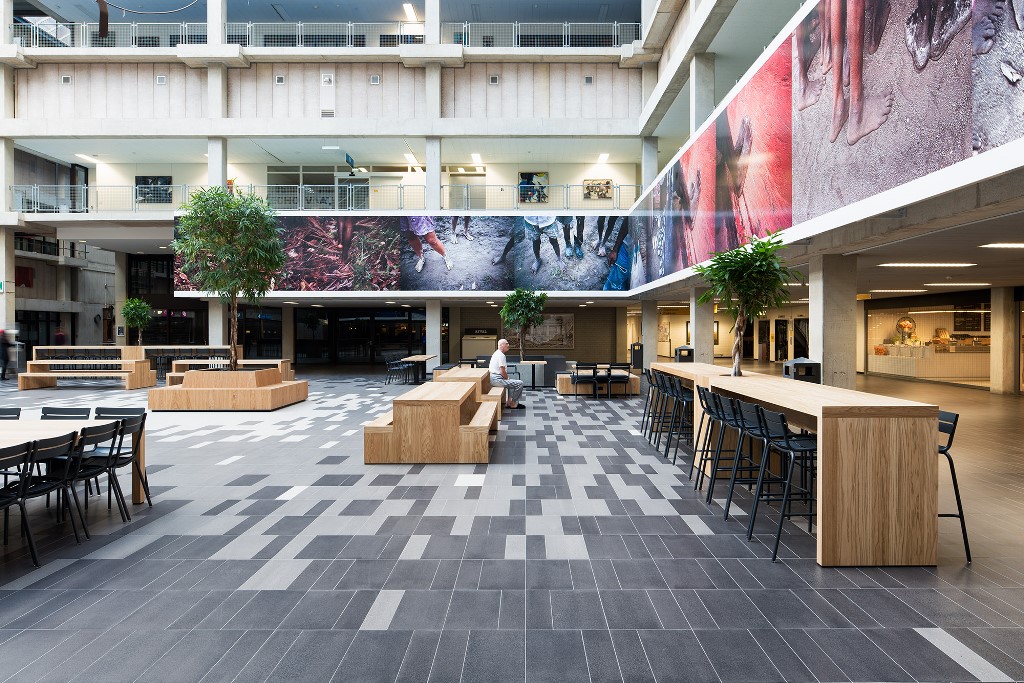
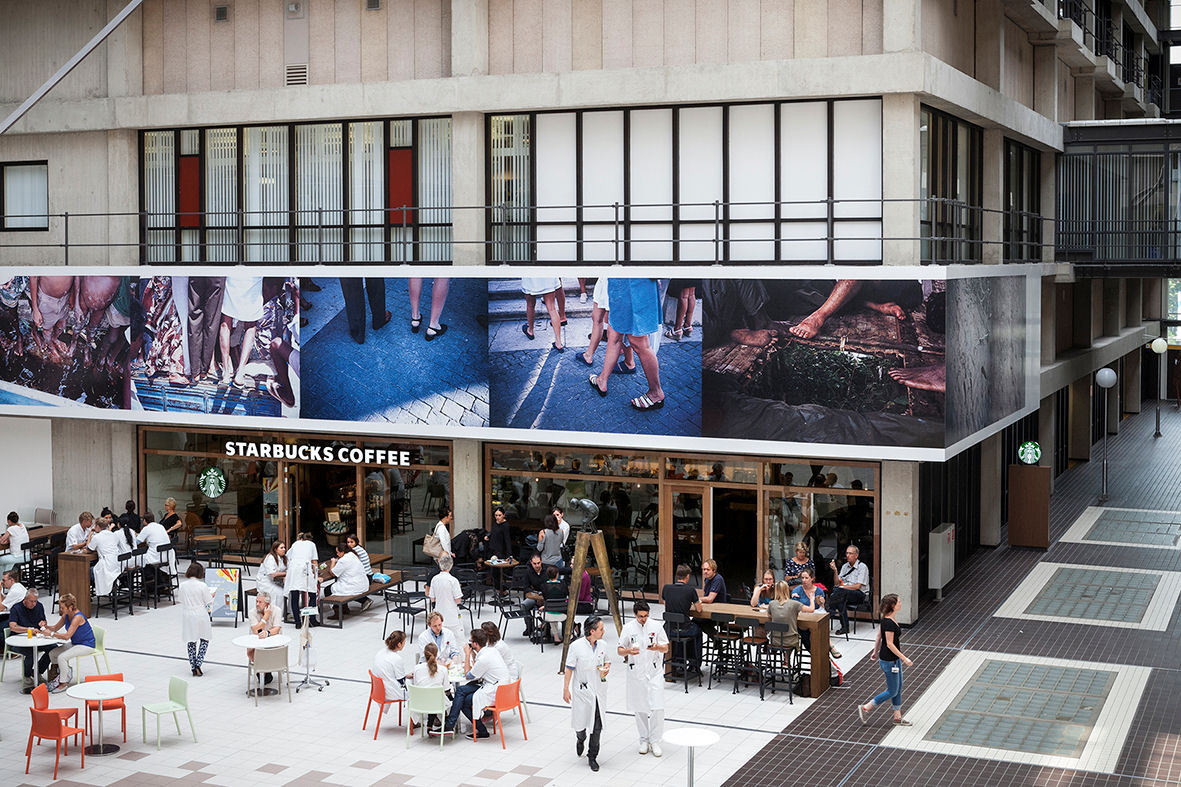
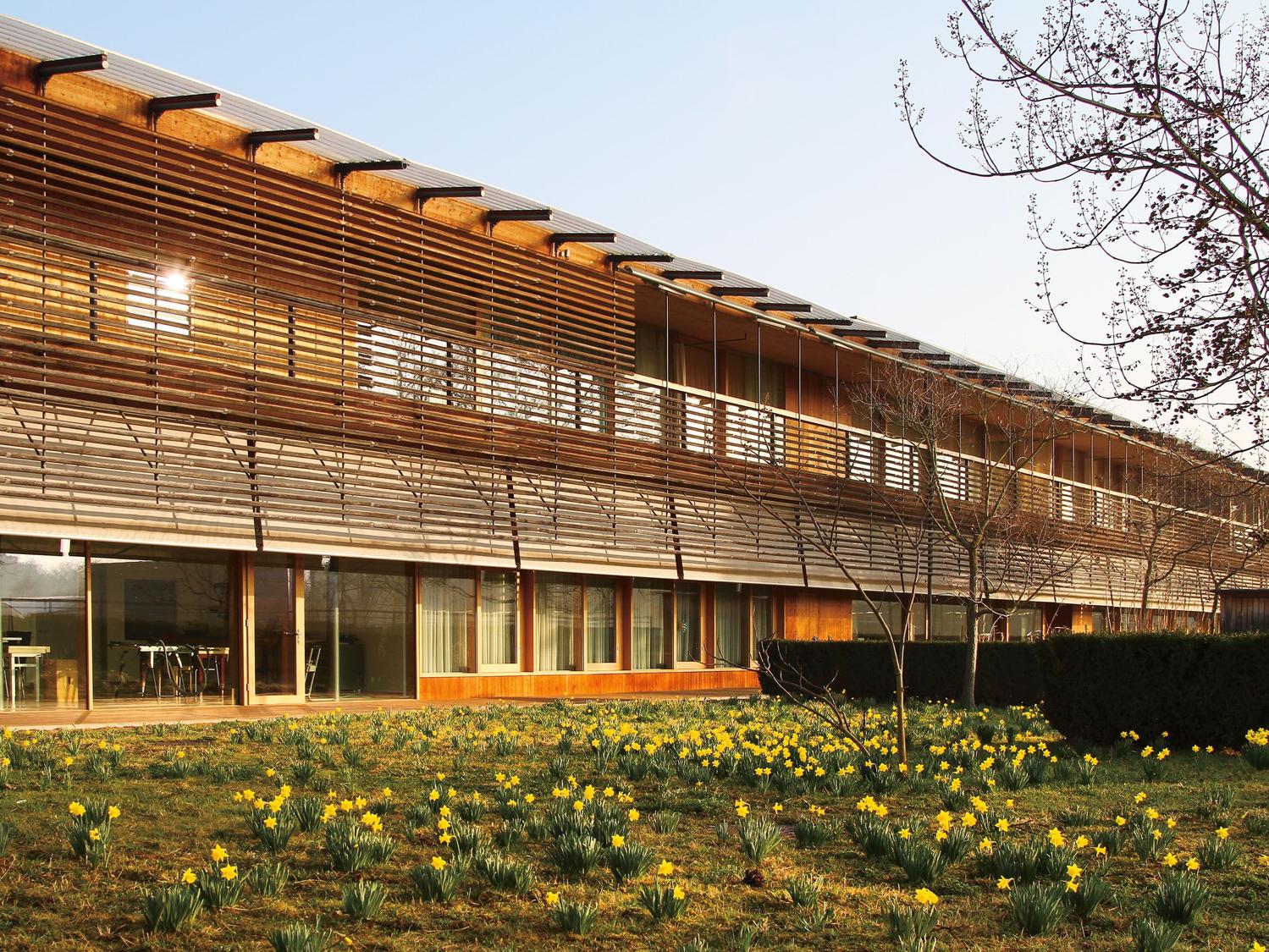
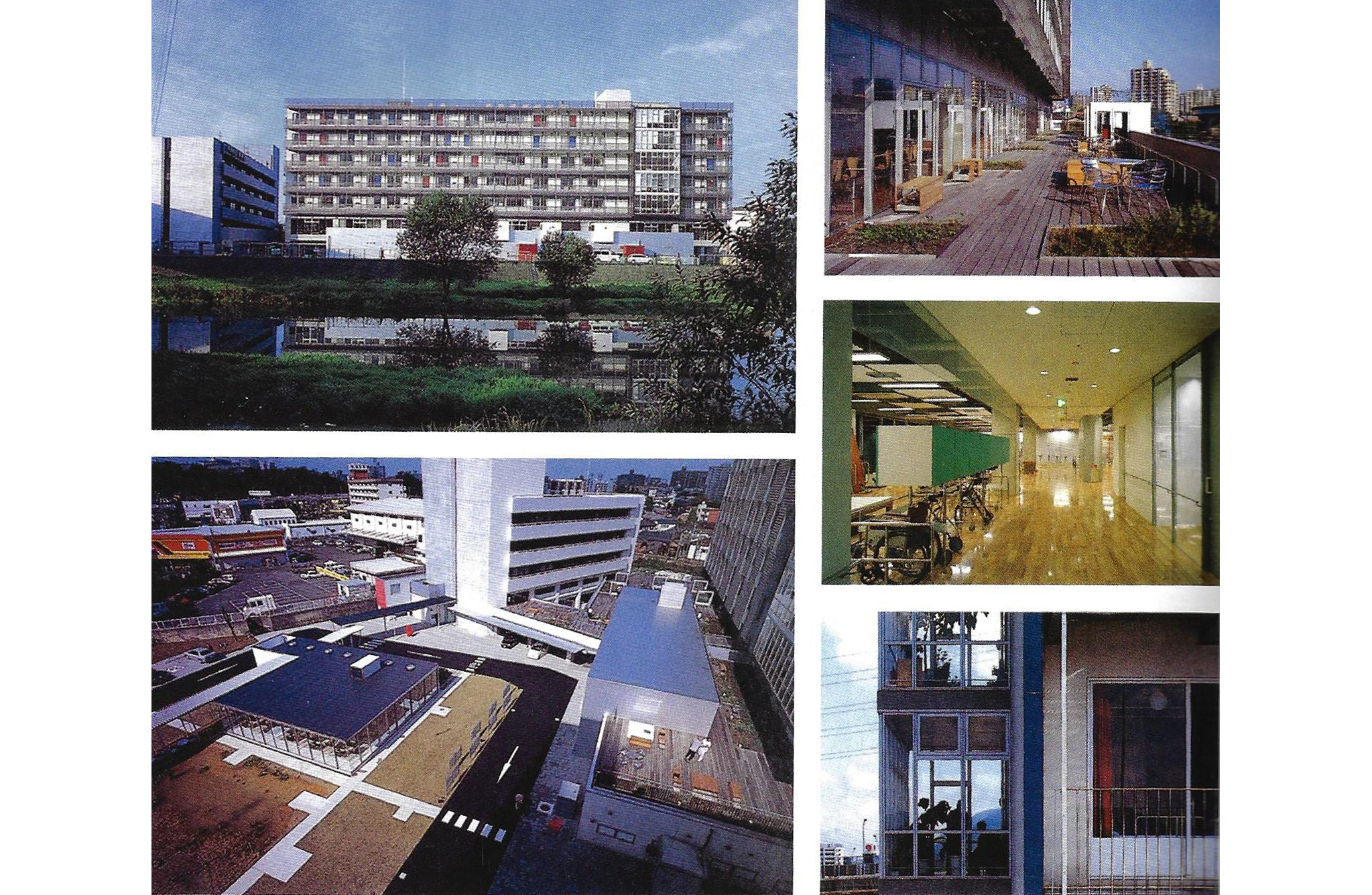
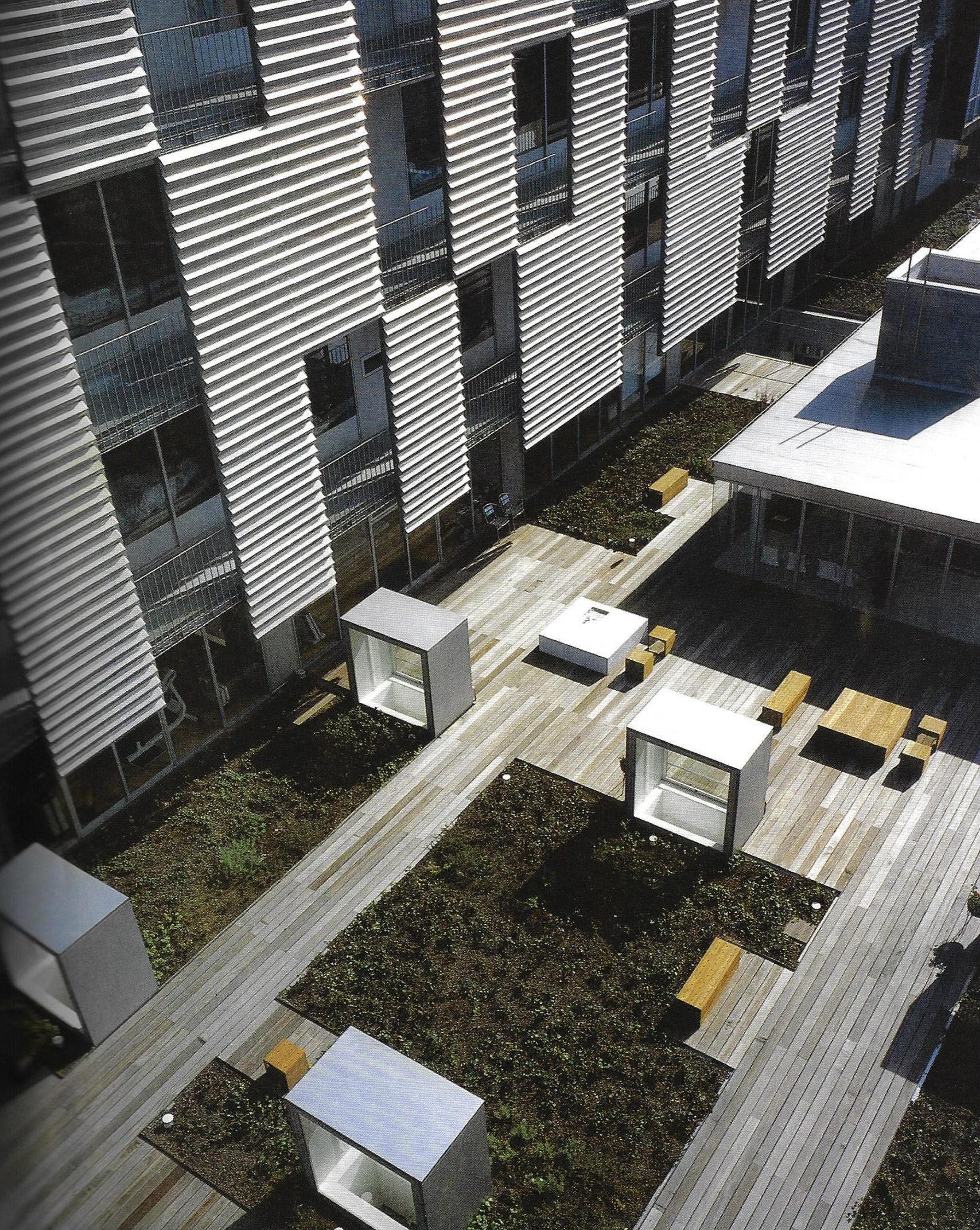
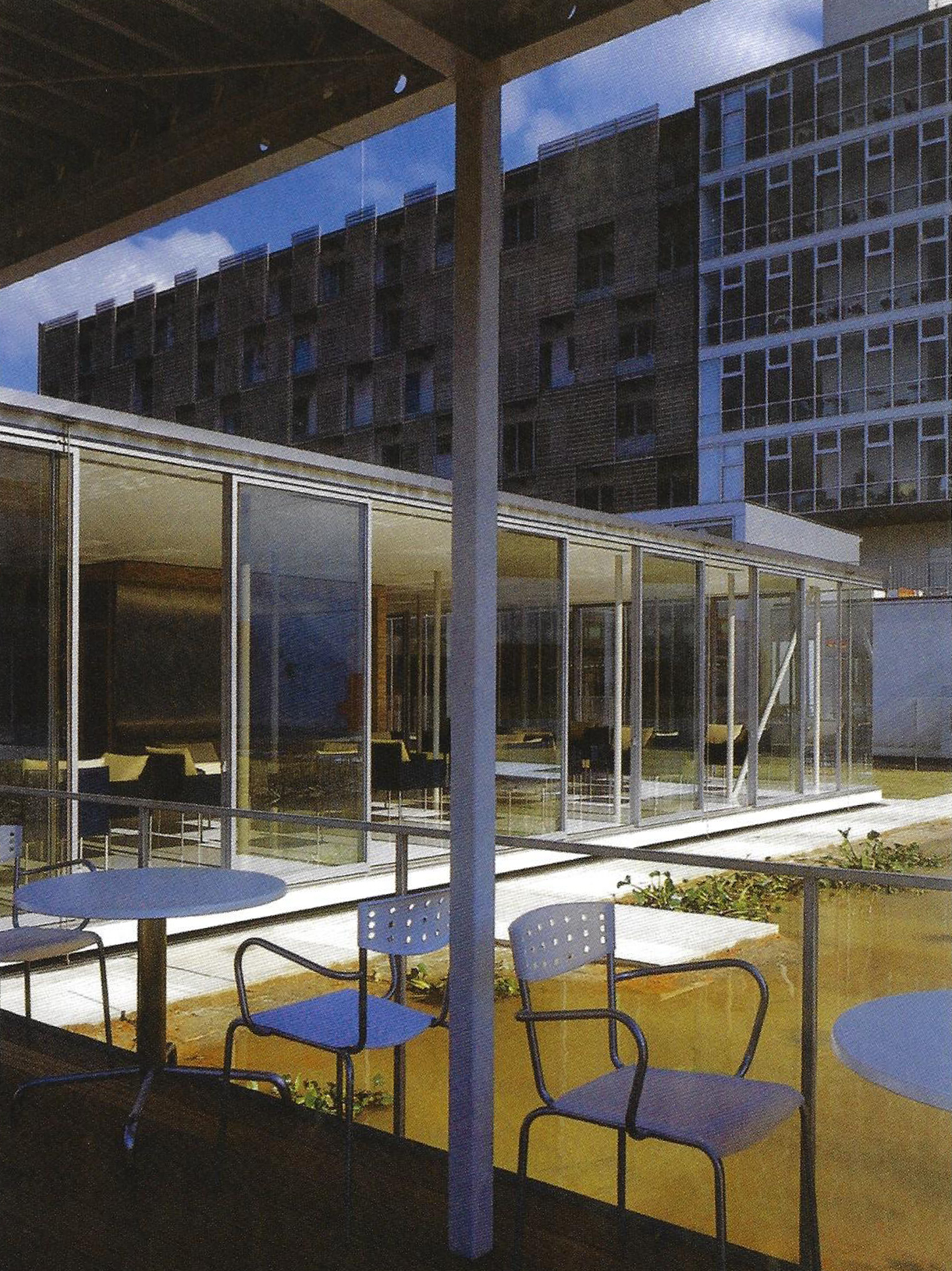
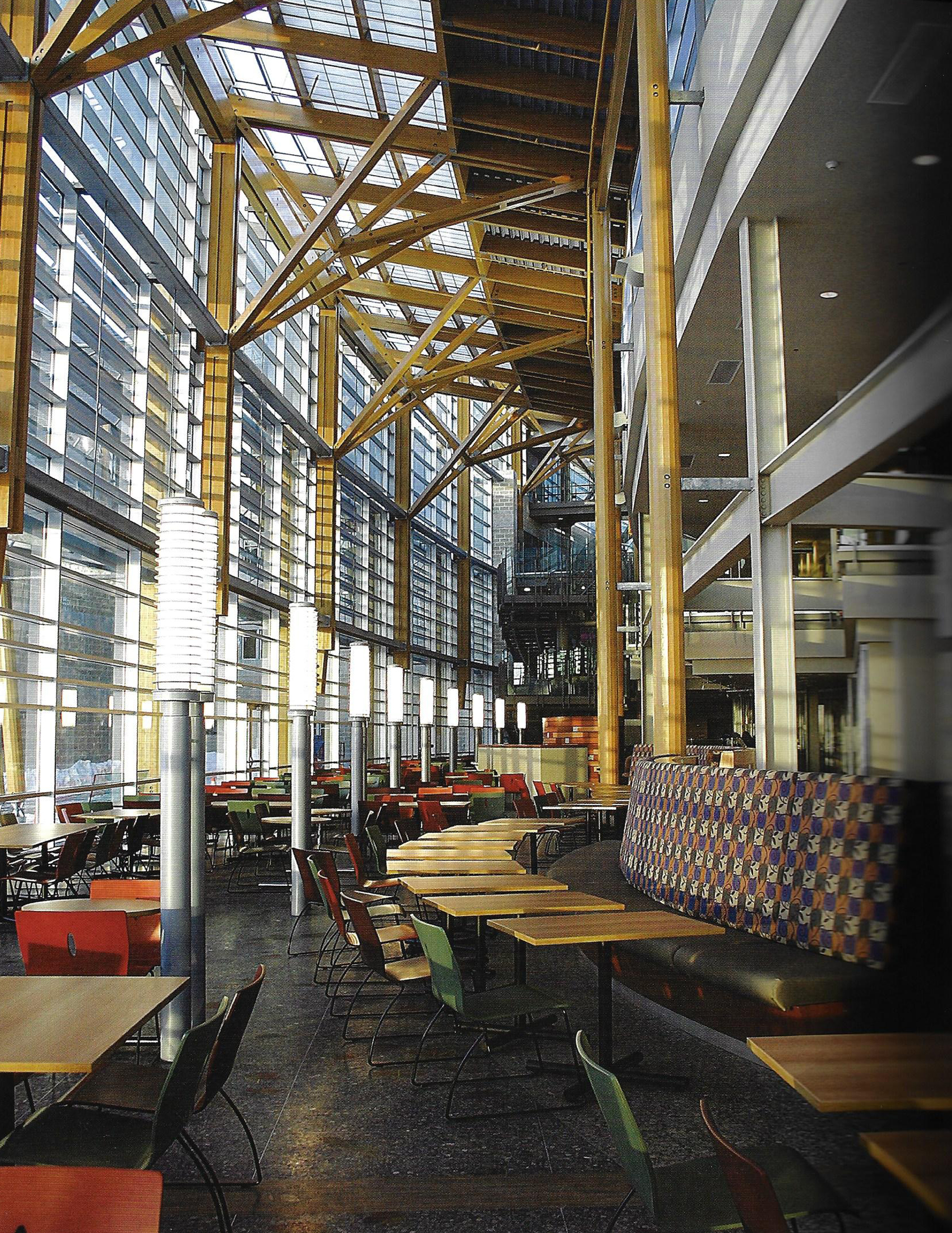
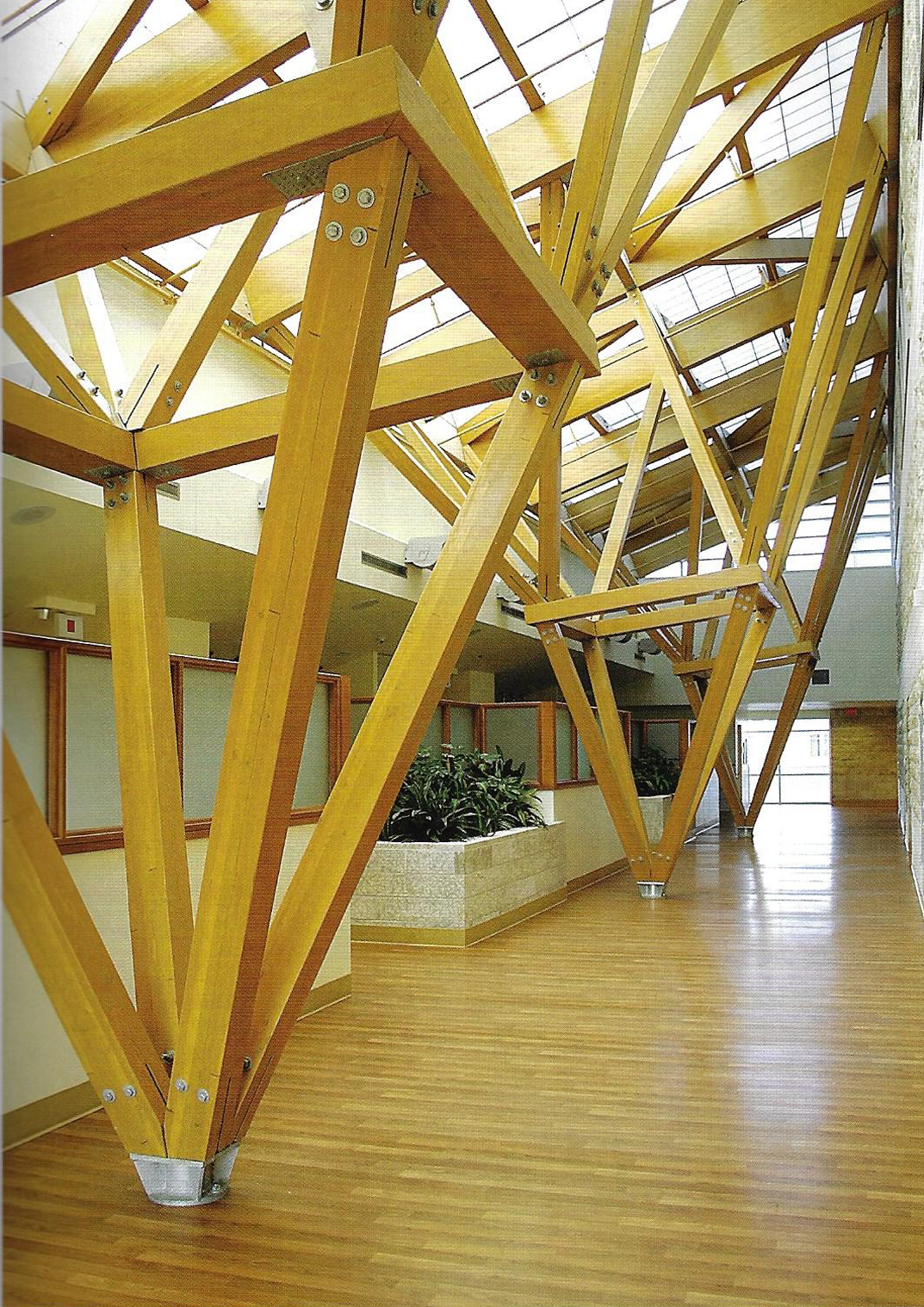
This slideshow presents images of the AMC. These images show the internal street of the AMC, the building as a whole which is often described as the monolith. Within these images the brutalist architecture is clearly visible as the bare concrete structure.
Various images of the AMC
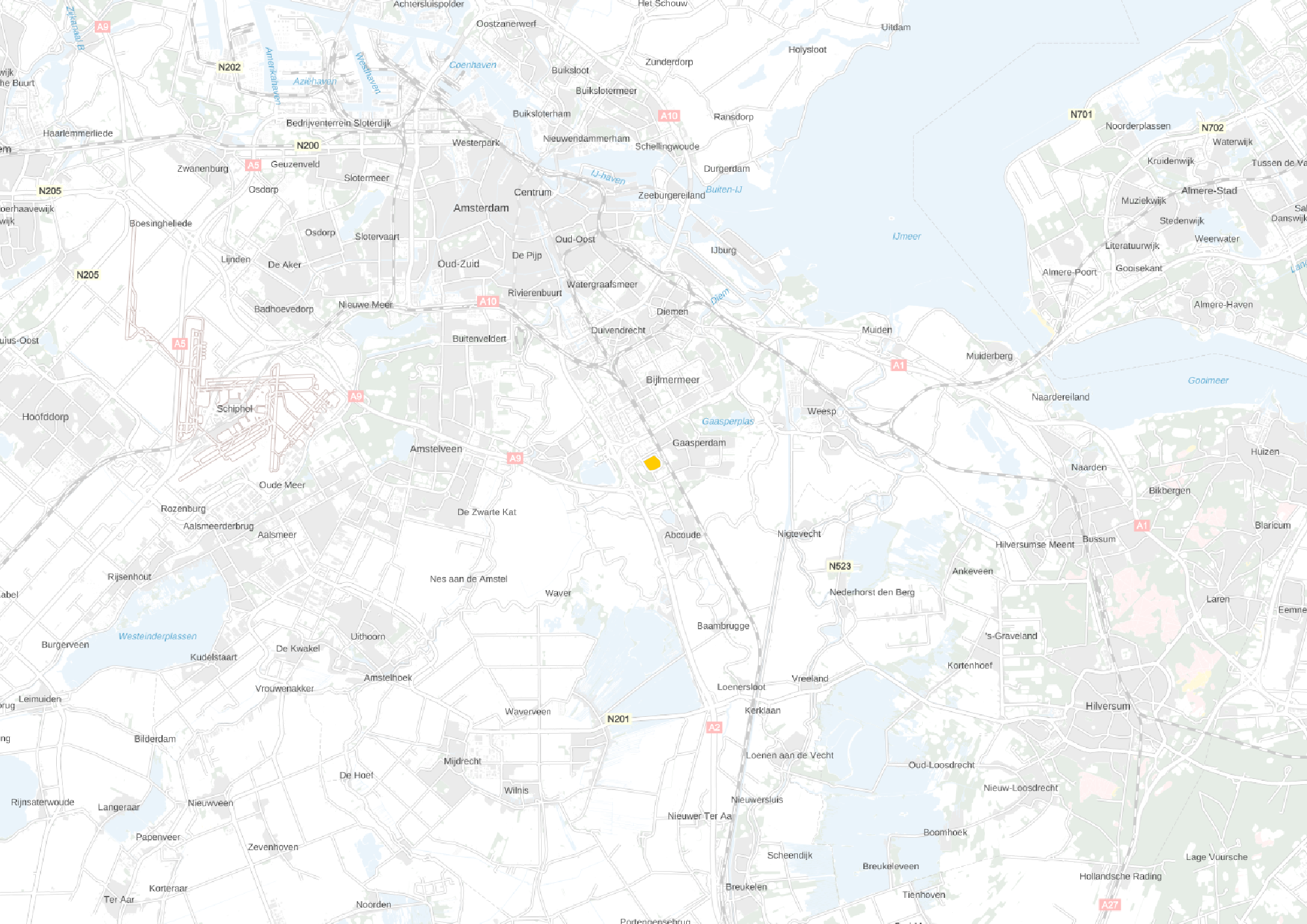
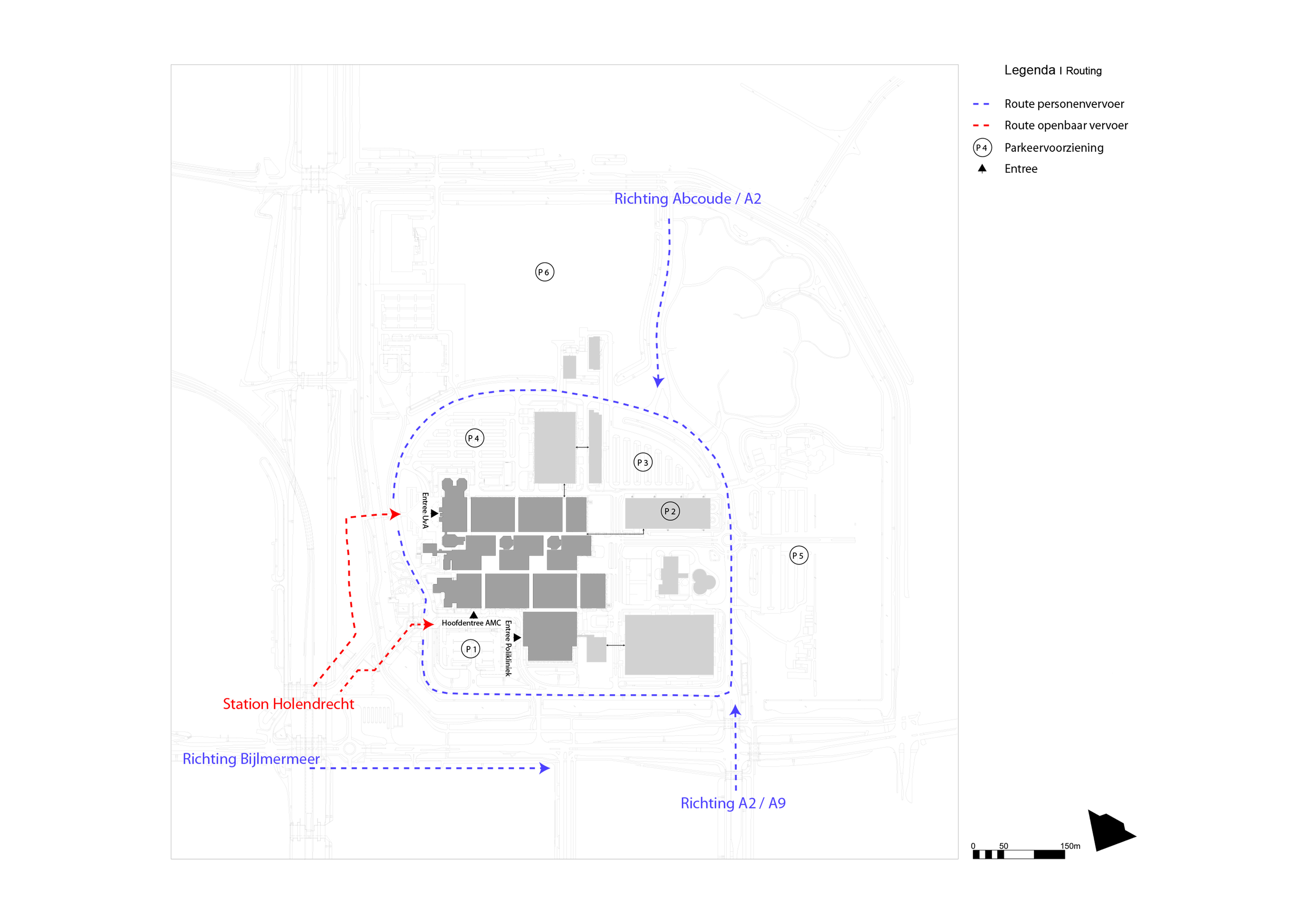
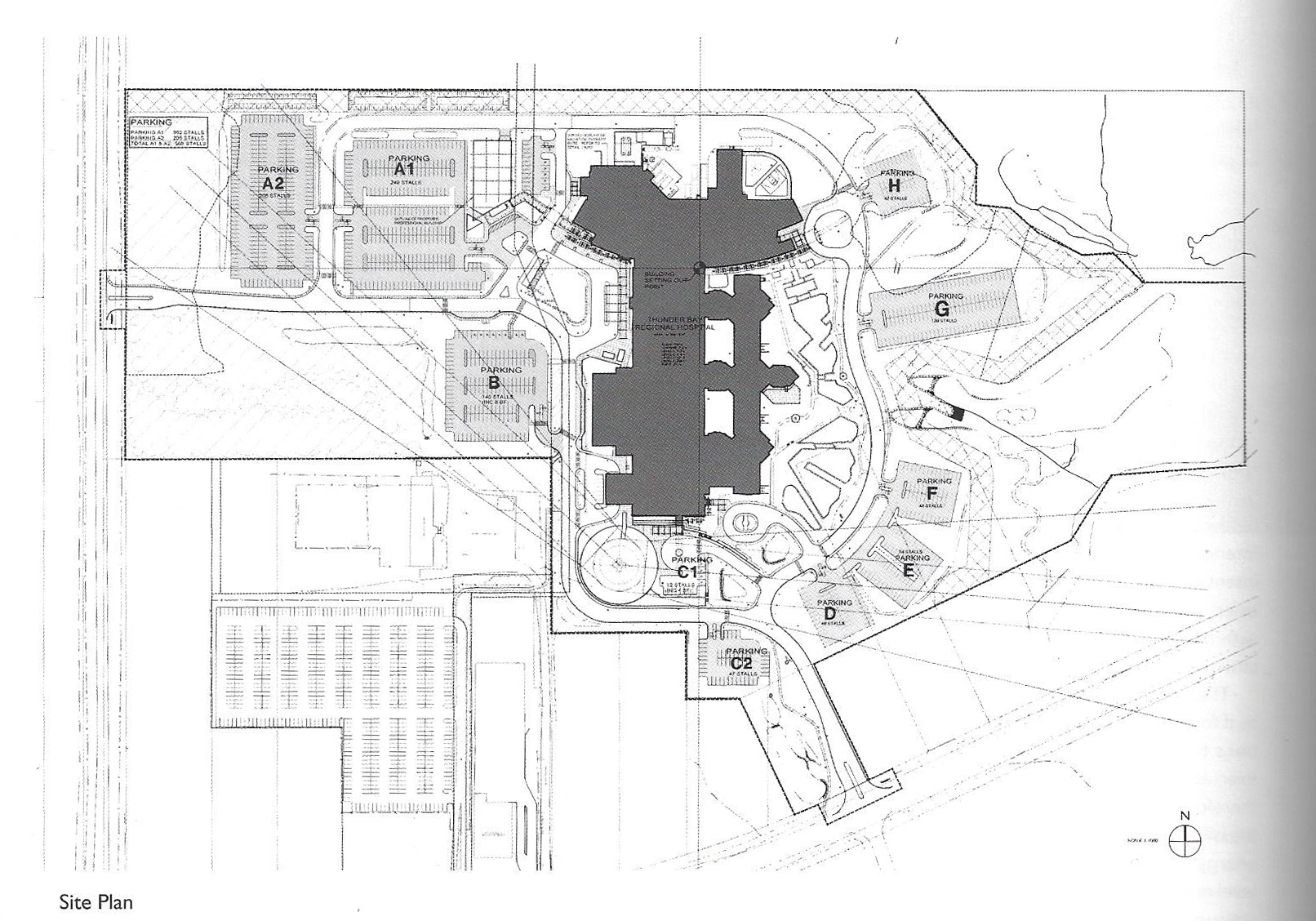
Location
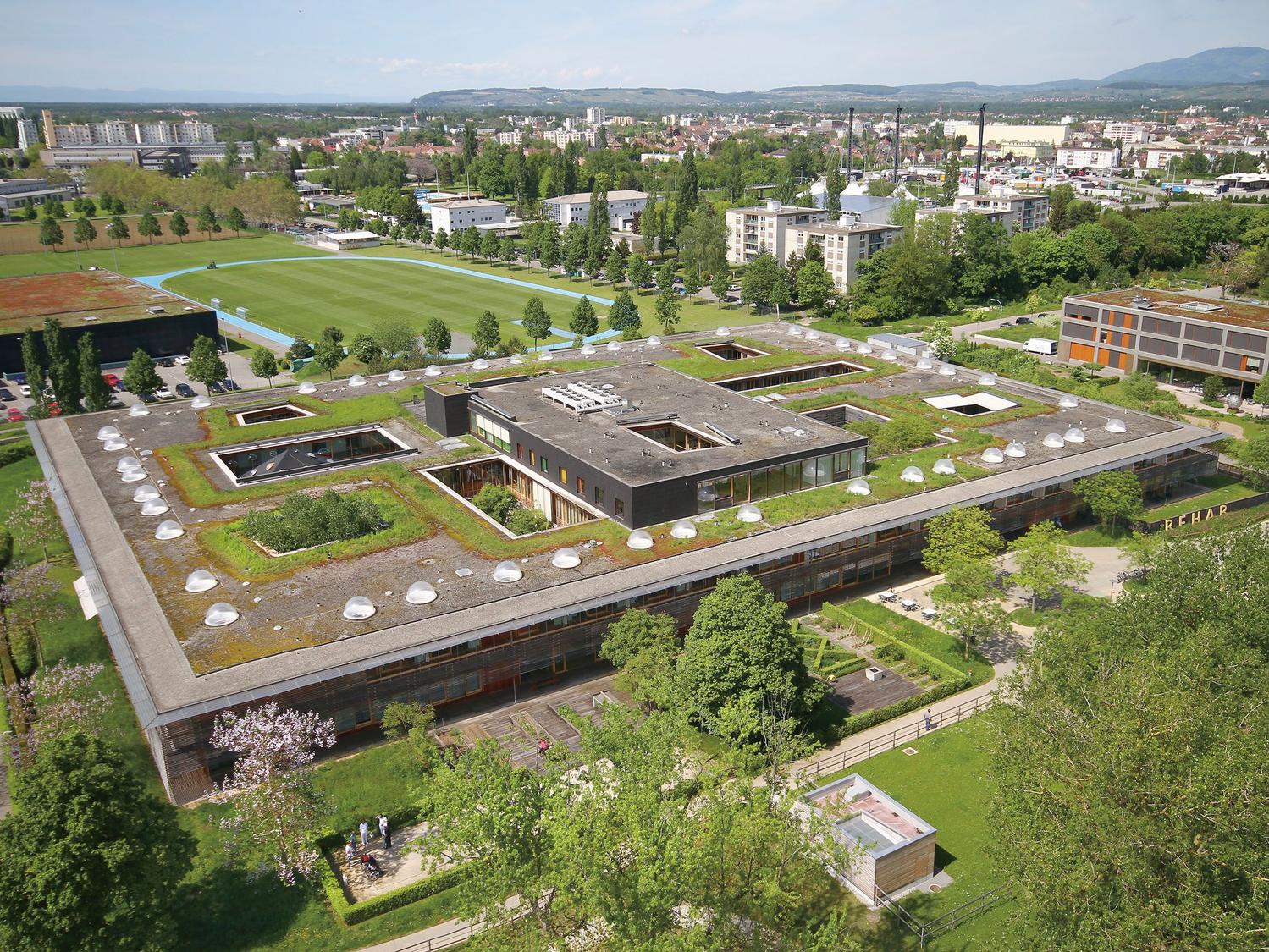
This slideshow presents the location of the AMC. As previously mentioned the AMC is located in the southeast of Amsterdam. There it can be accessed by car from the A2 and A9 highway network and by train, metro and busses via Amsterdam Holendrecht station.
Own images showing the location of the AMC and the access to the building by car and public transport
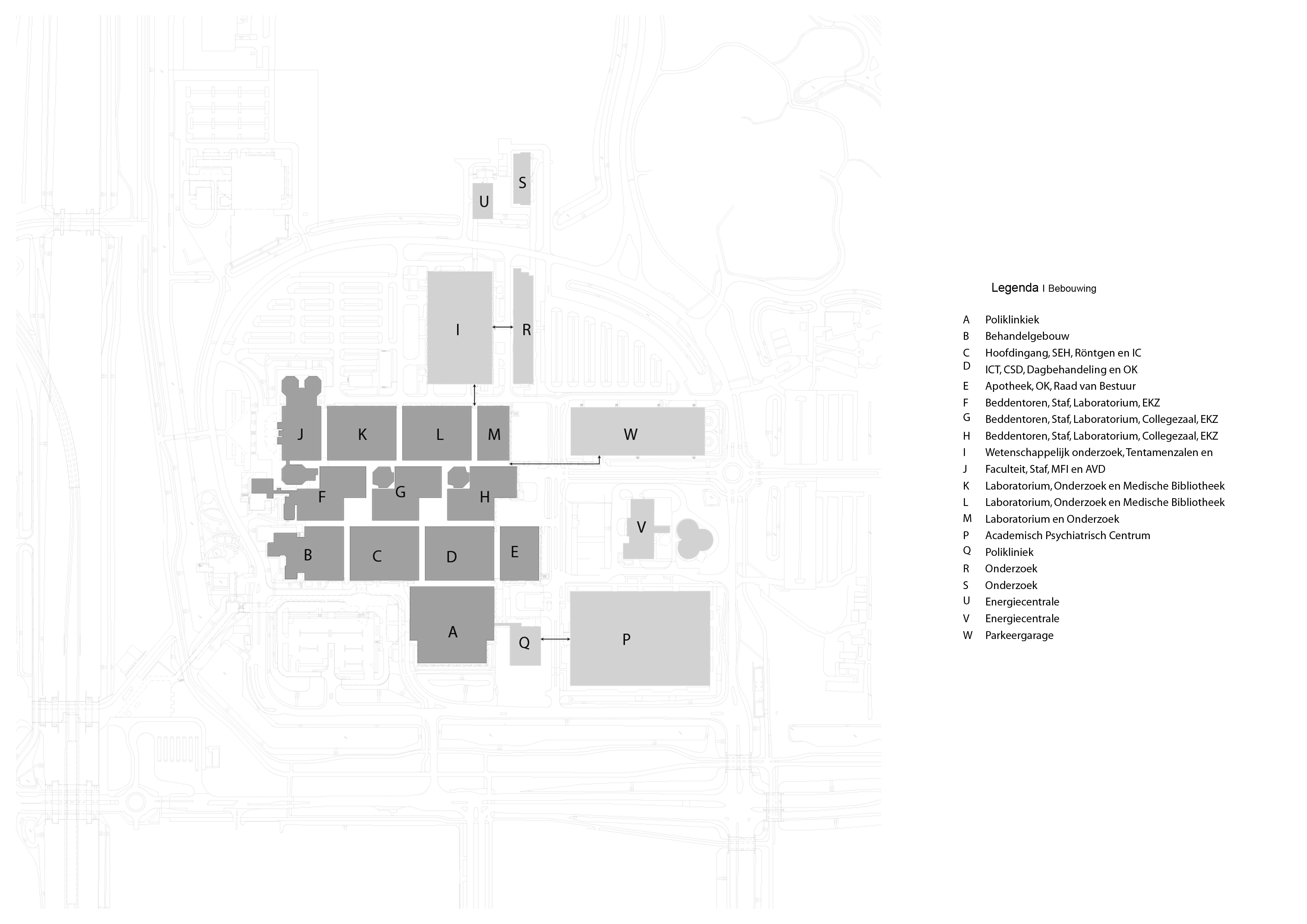
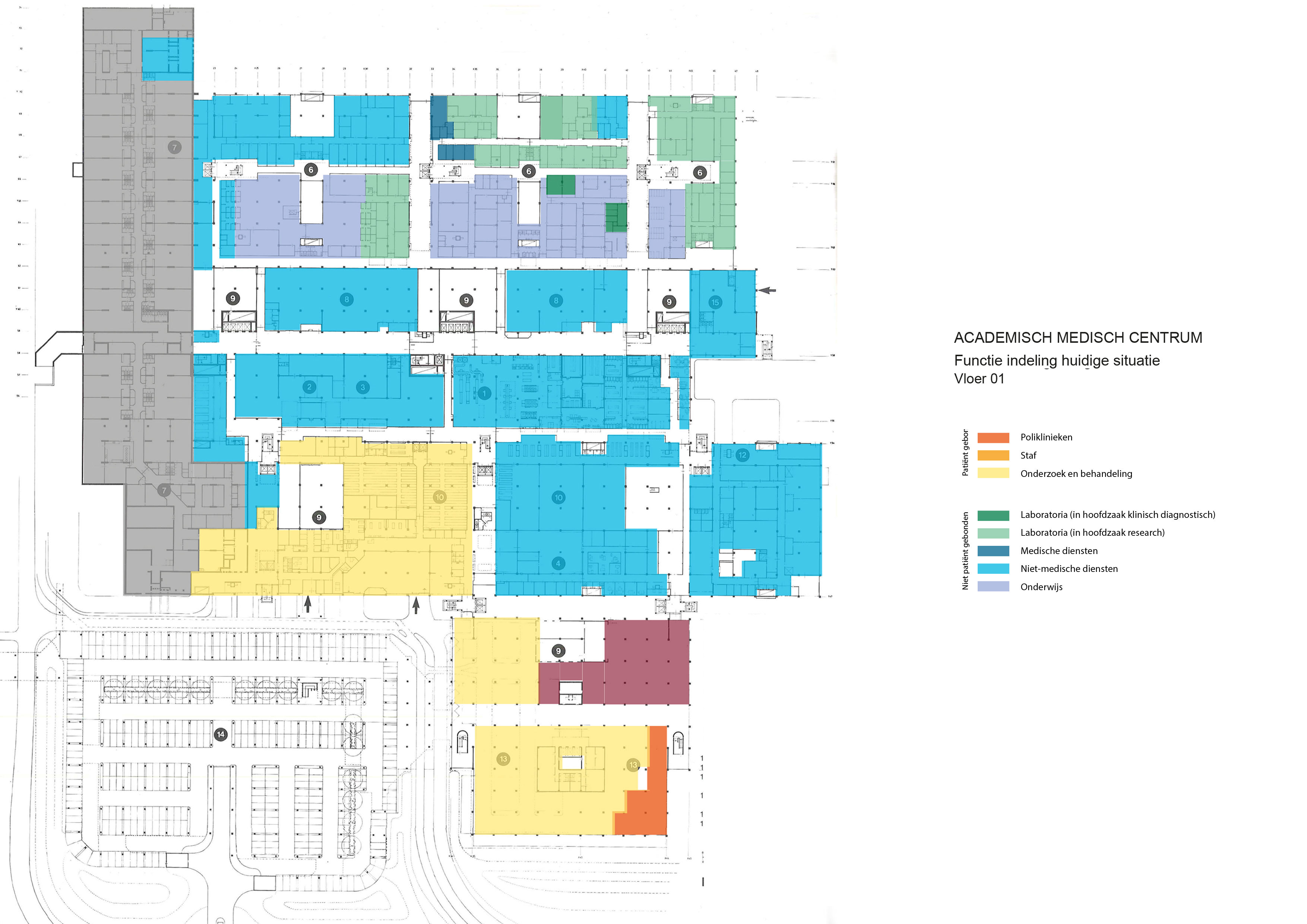
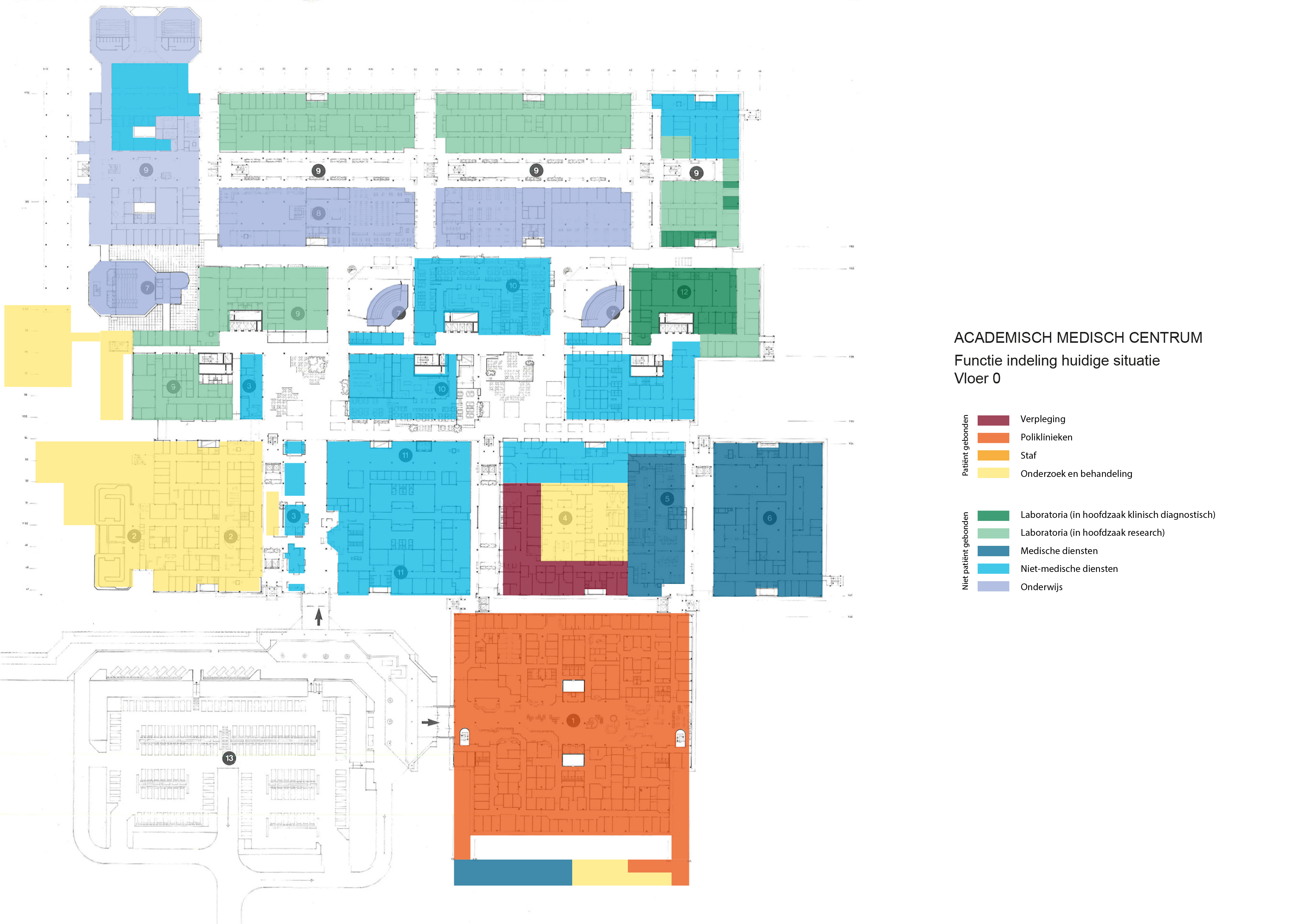
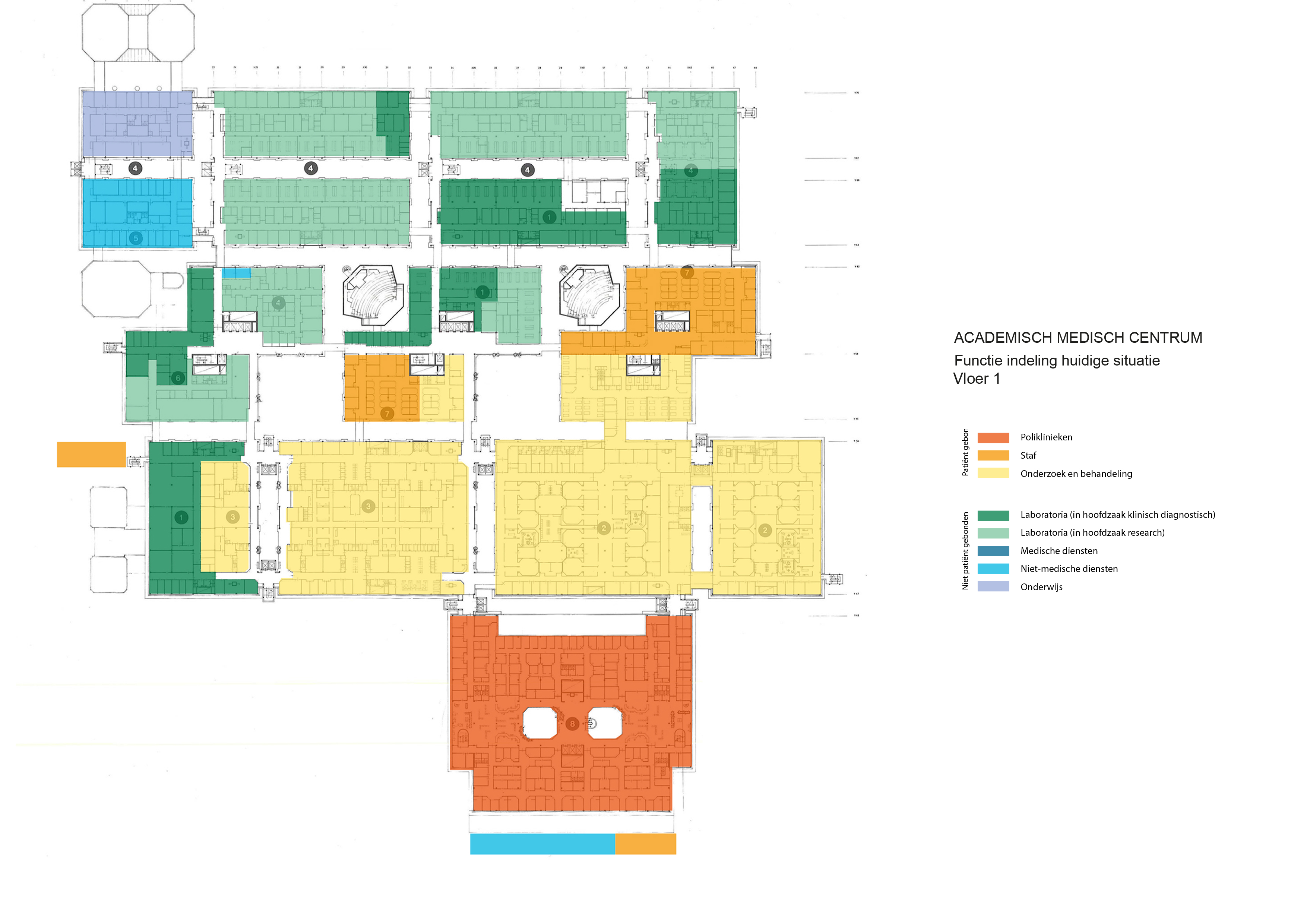
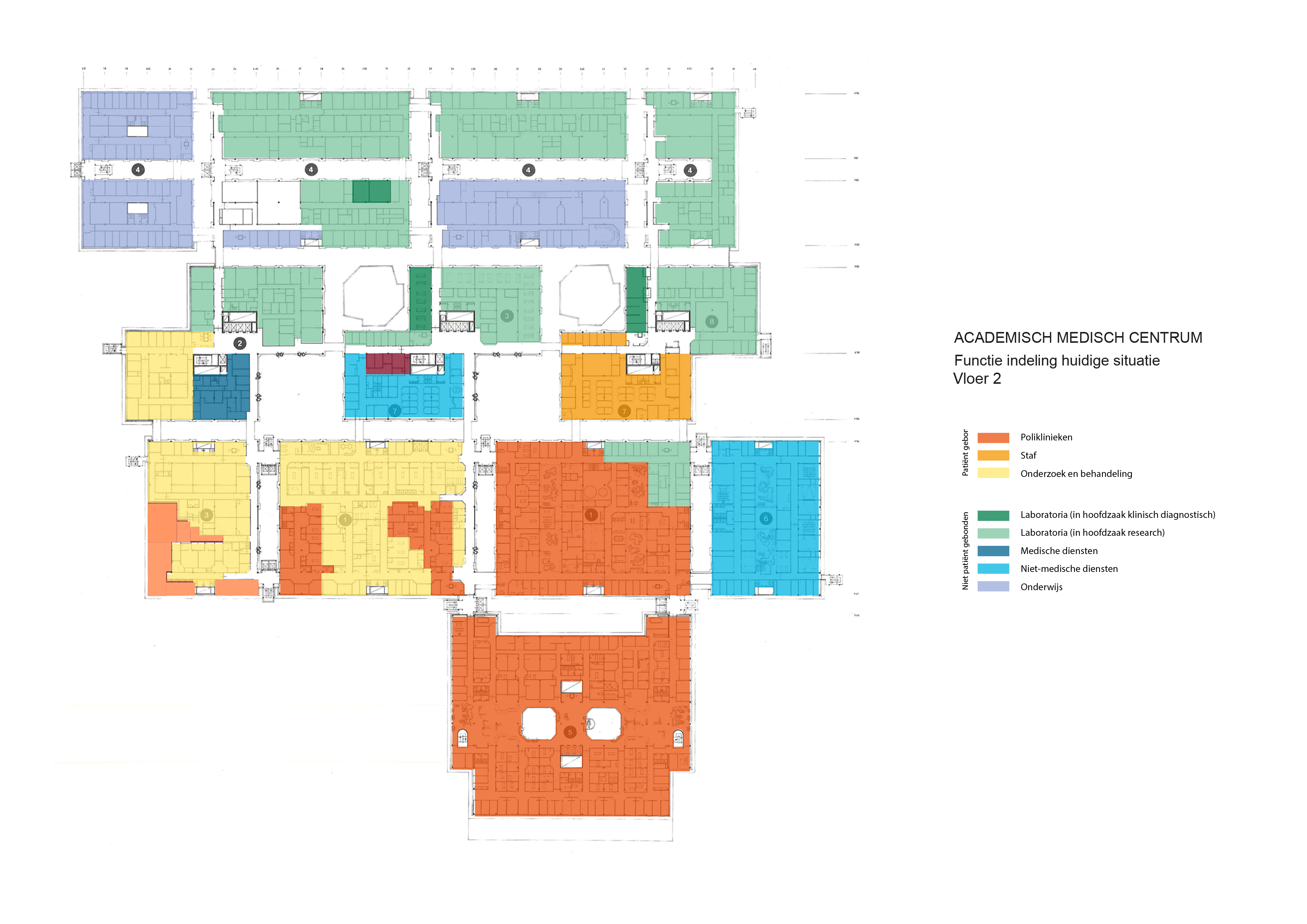
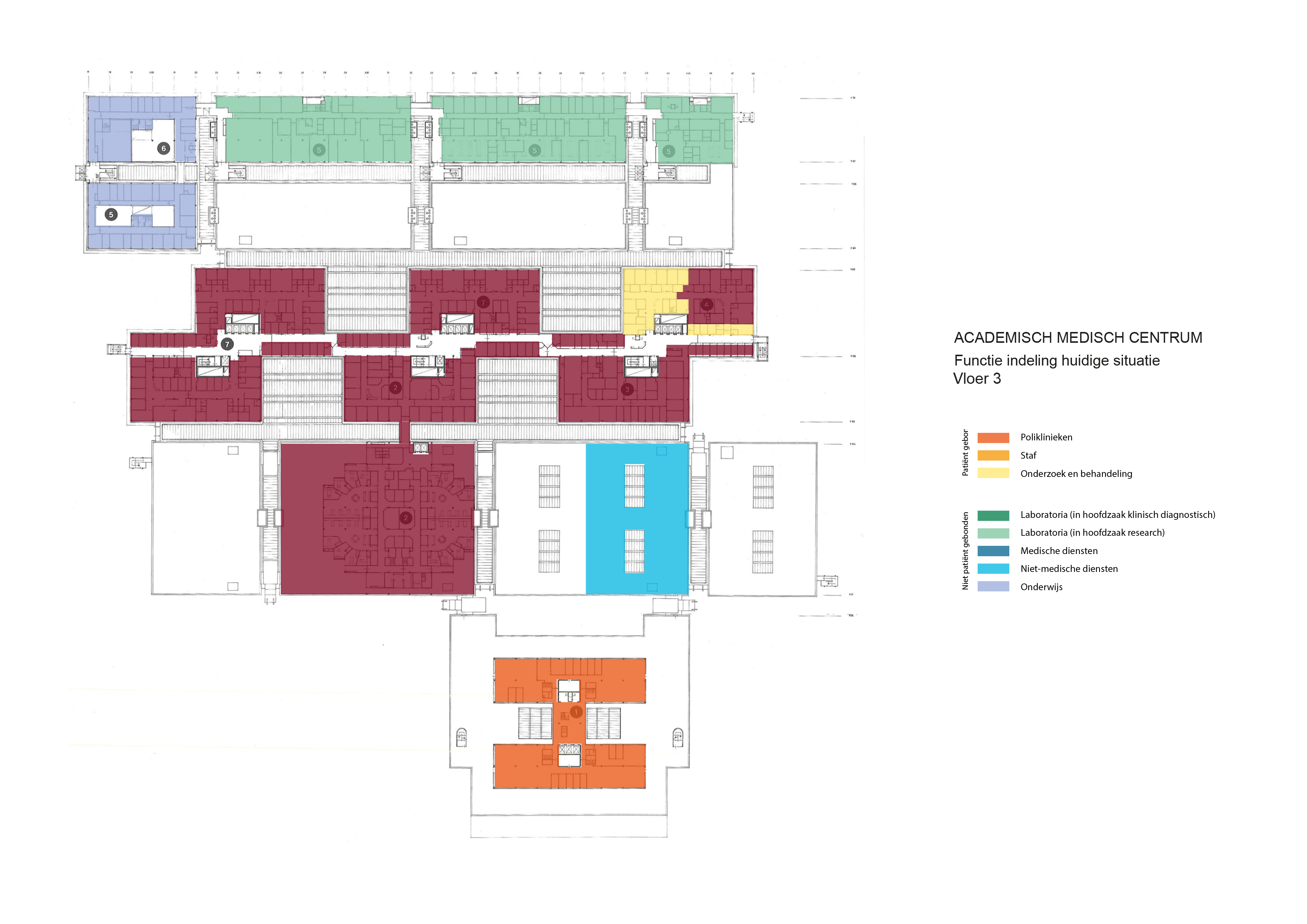
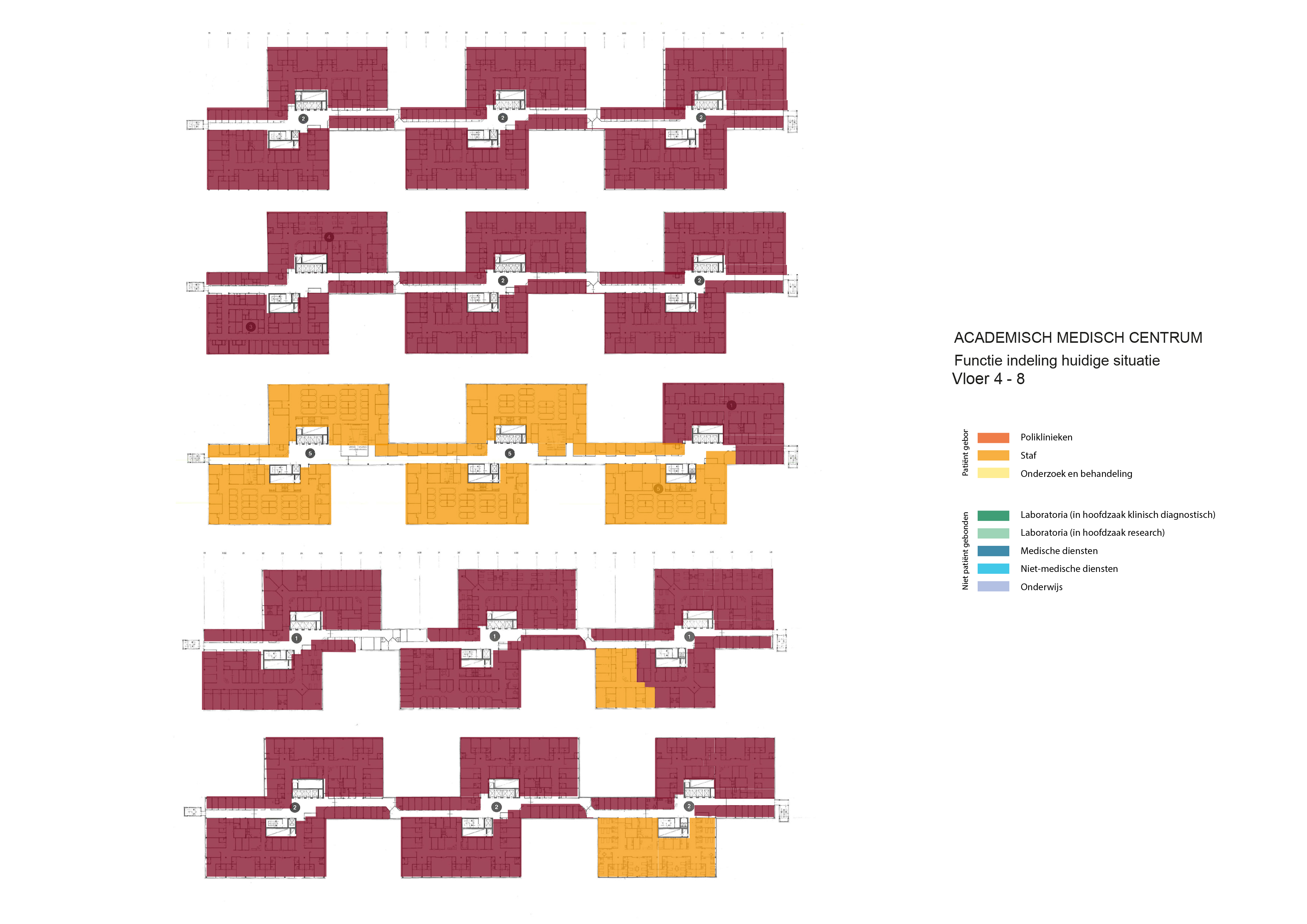
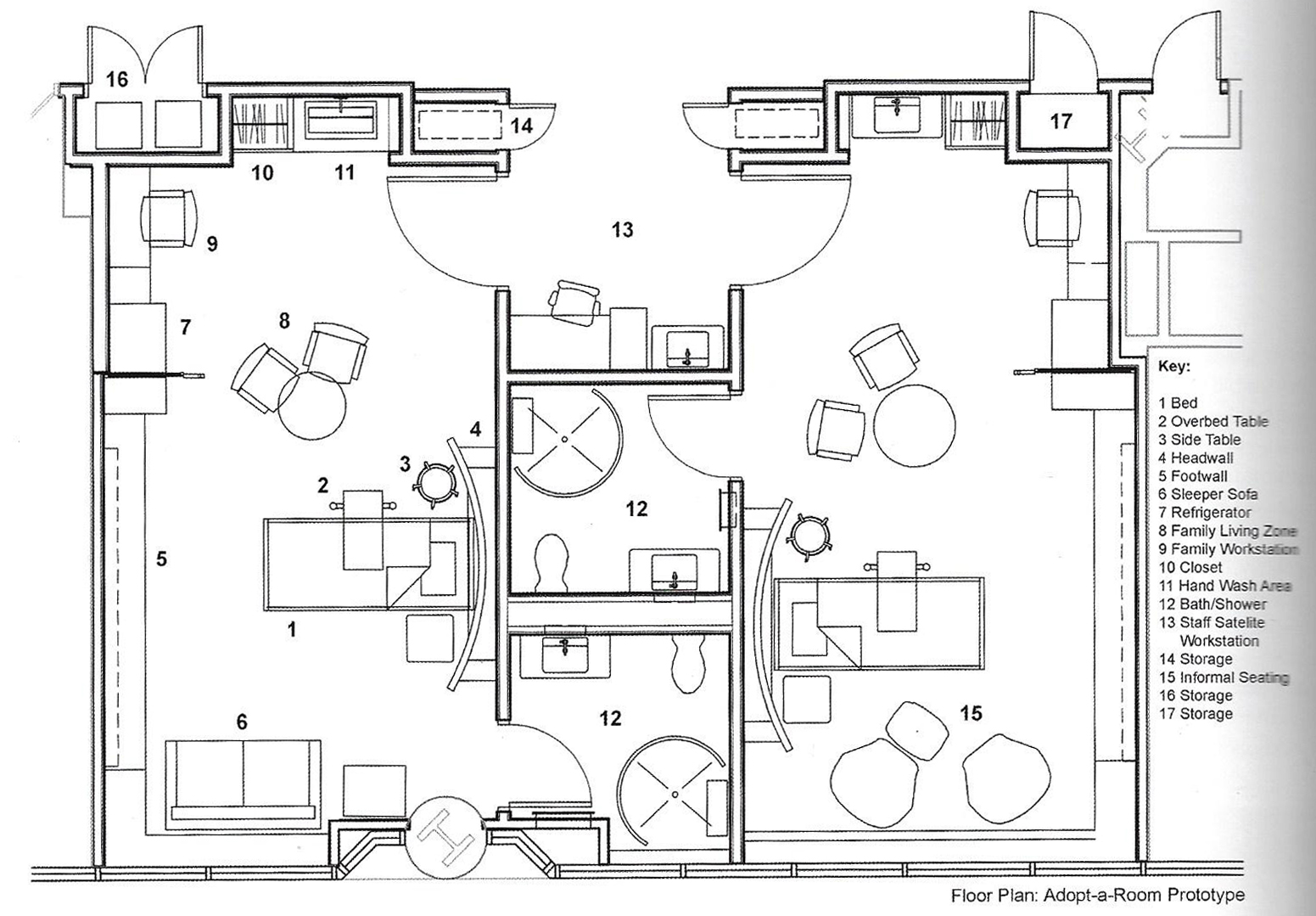
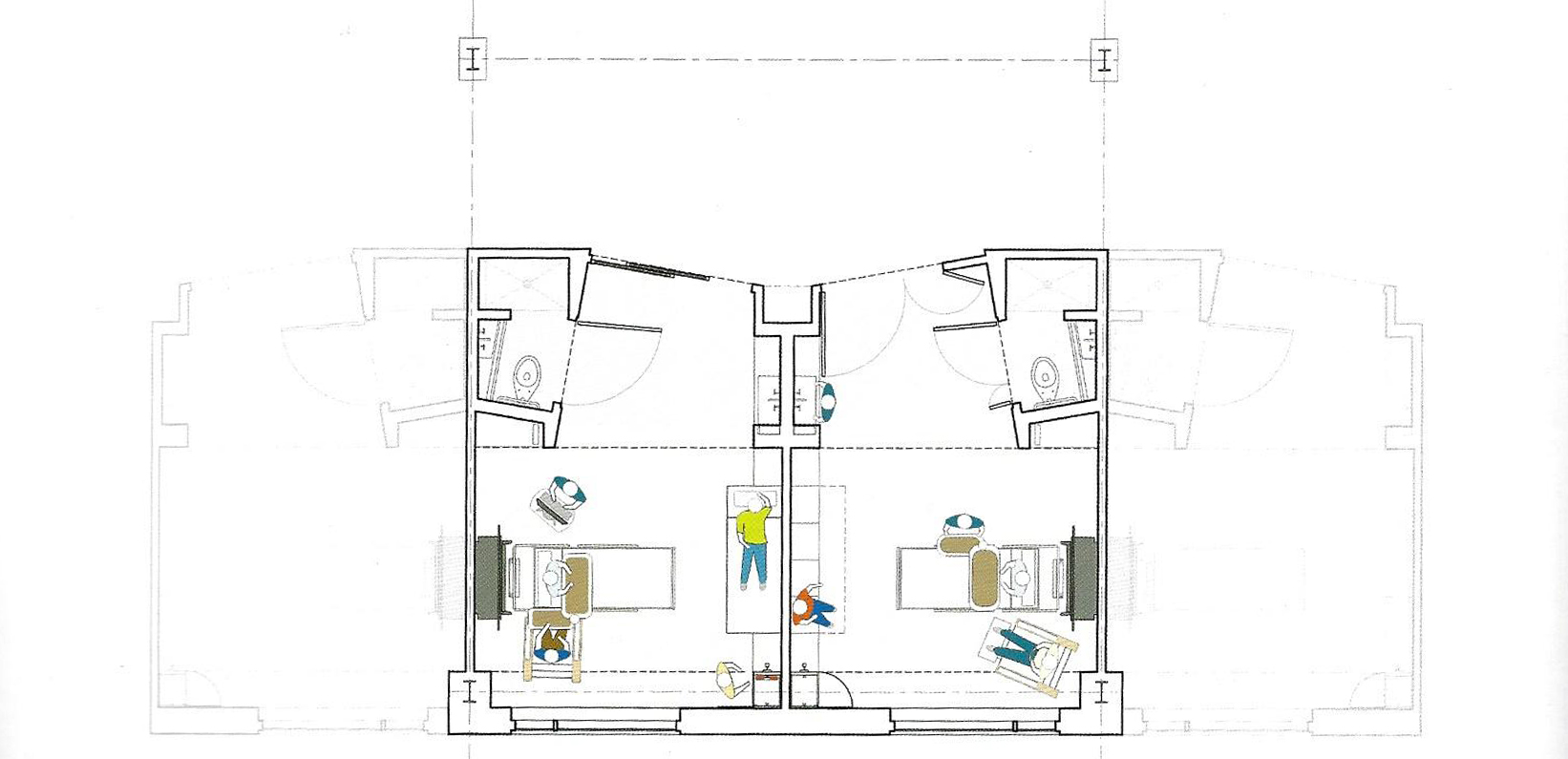
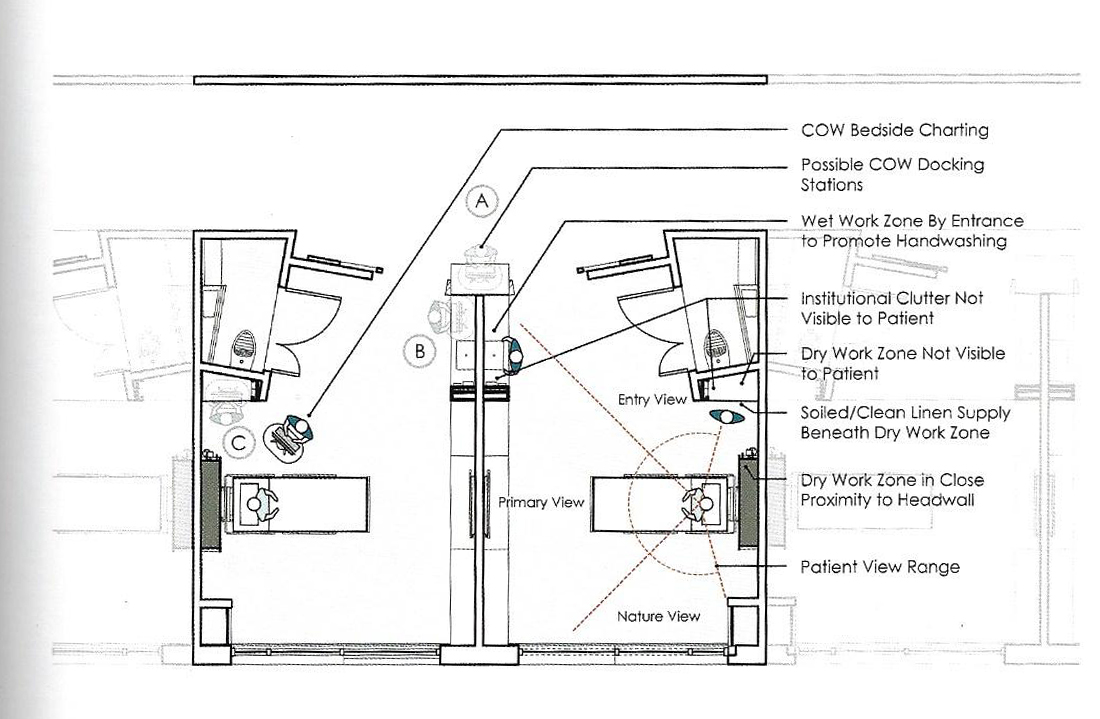
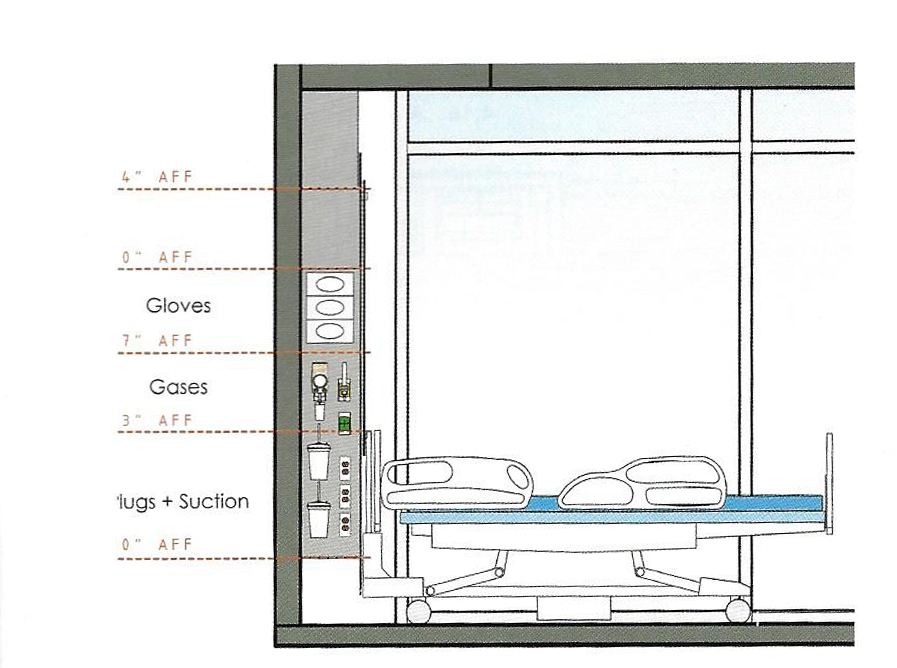
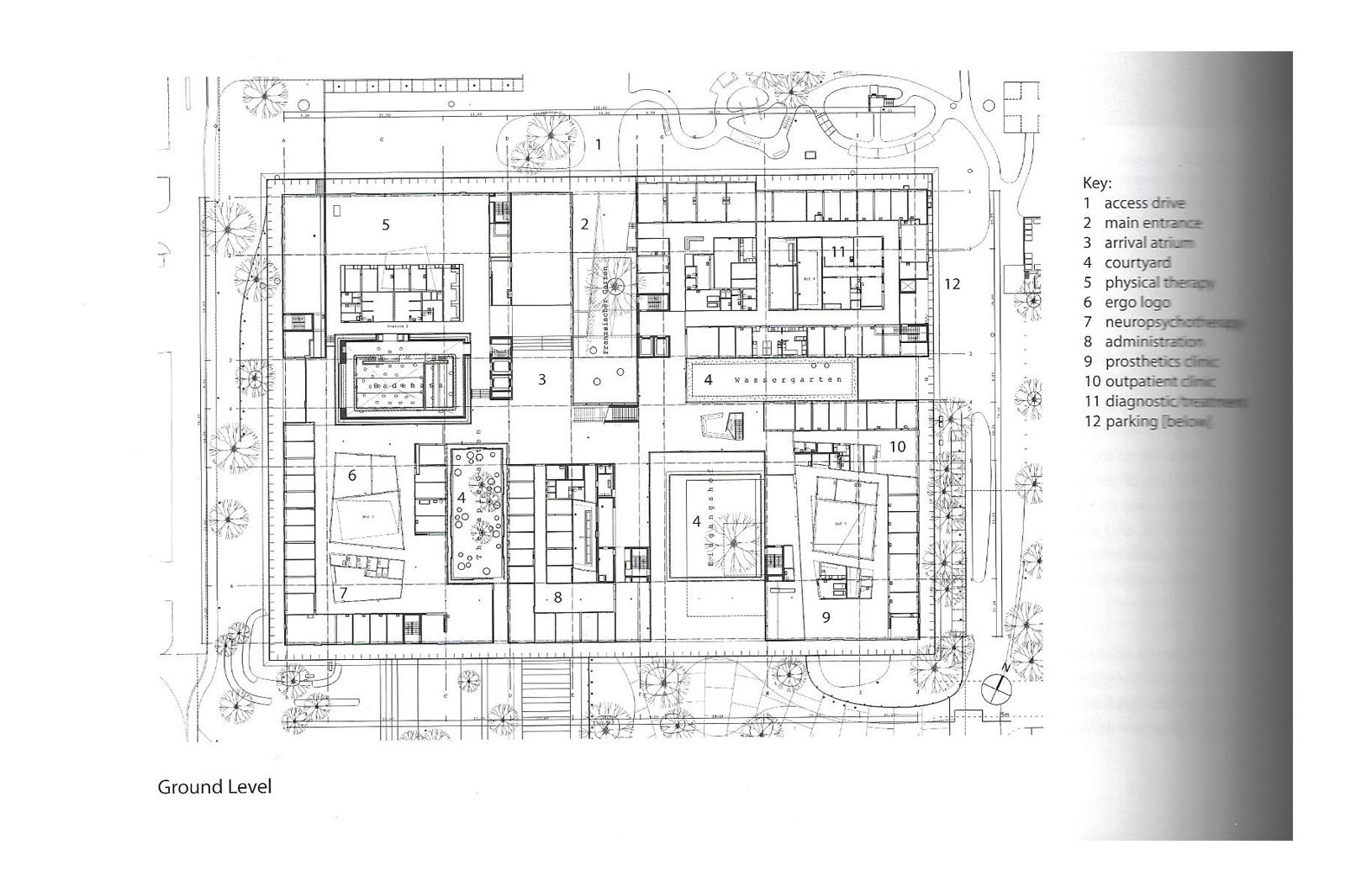
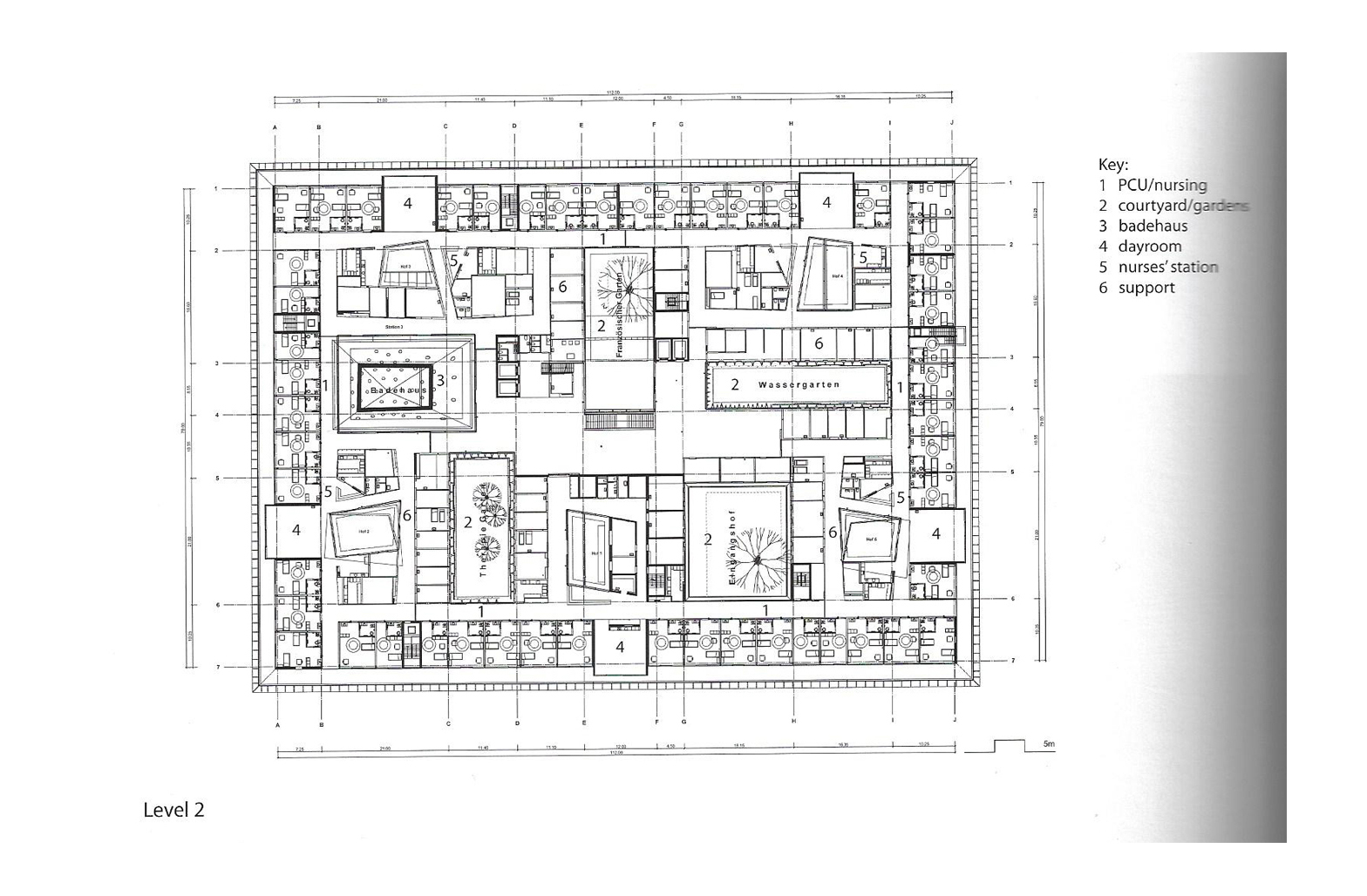
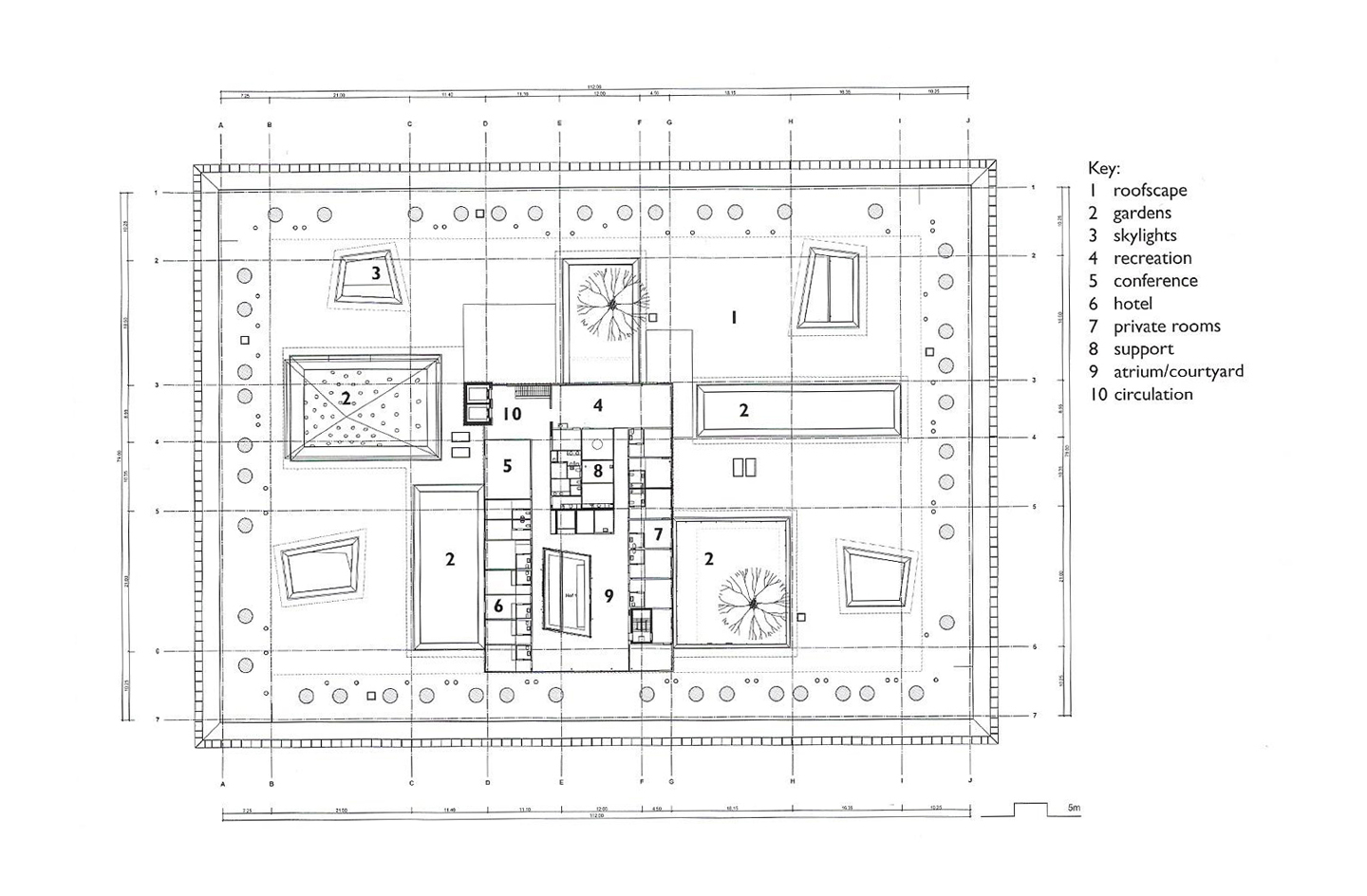
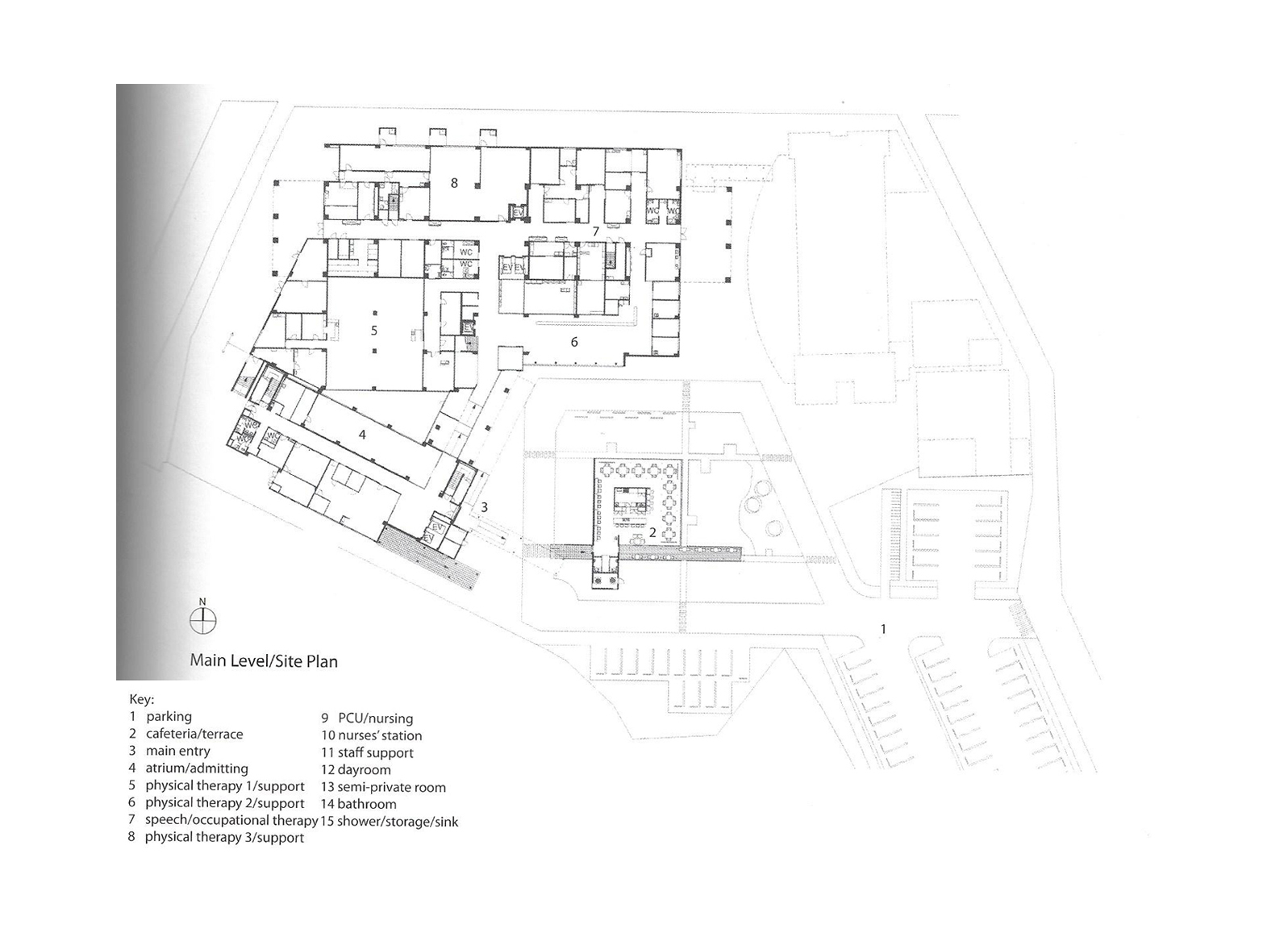
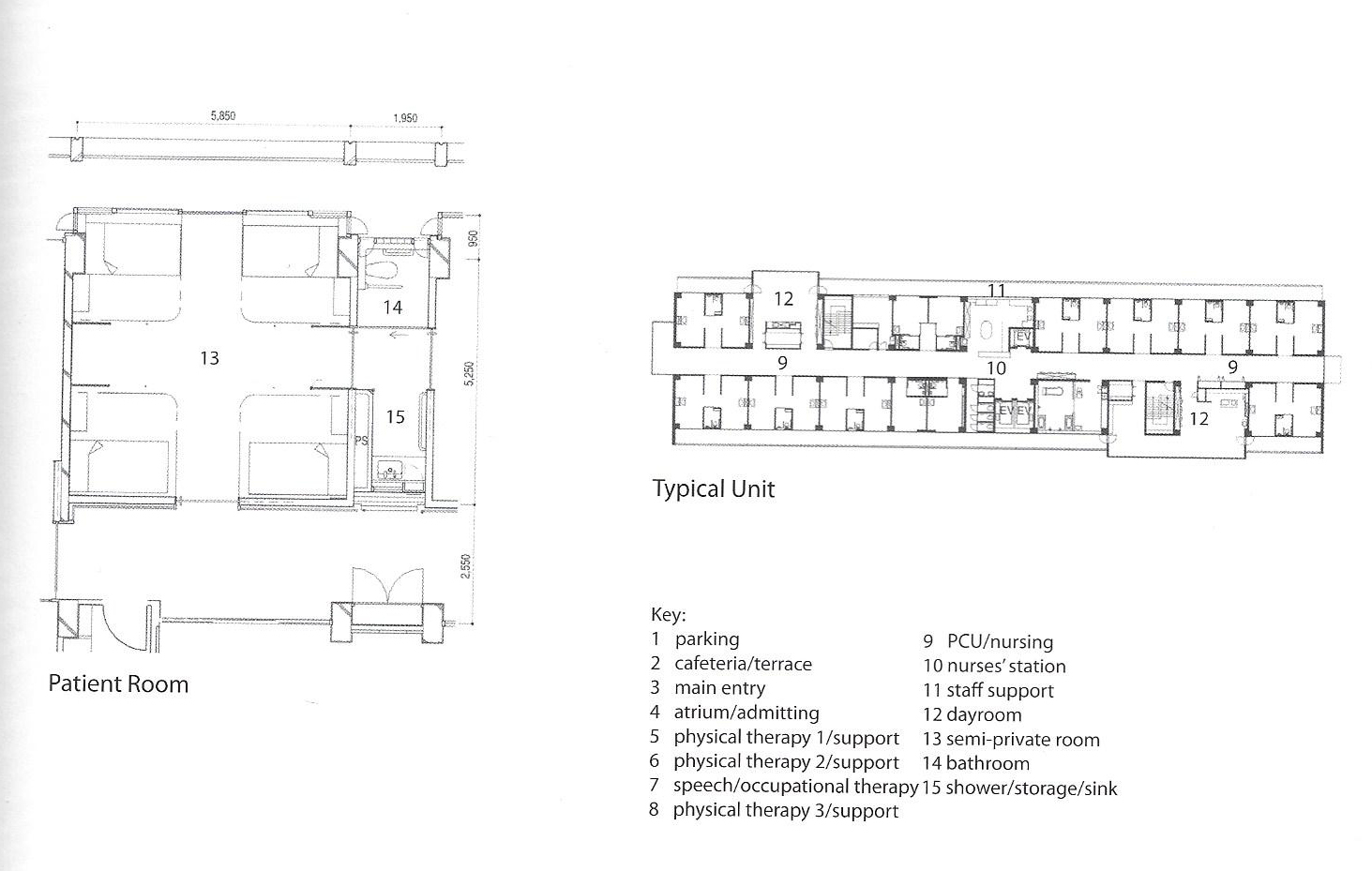
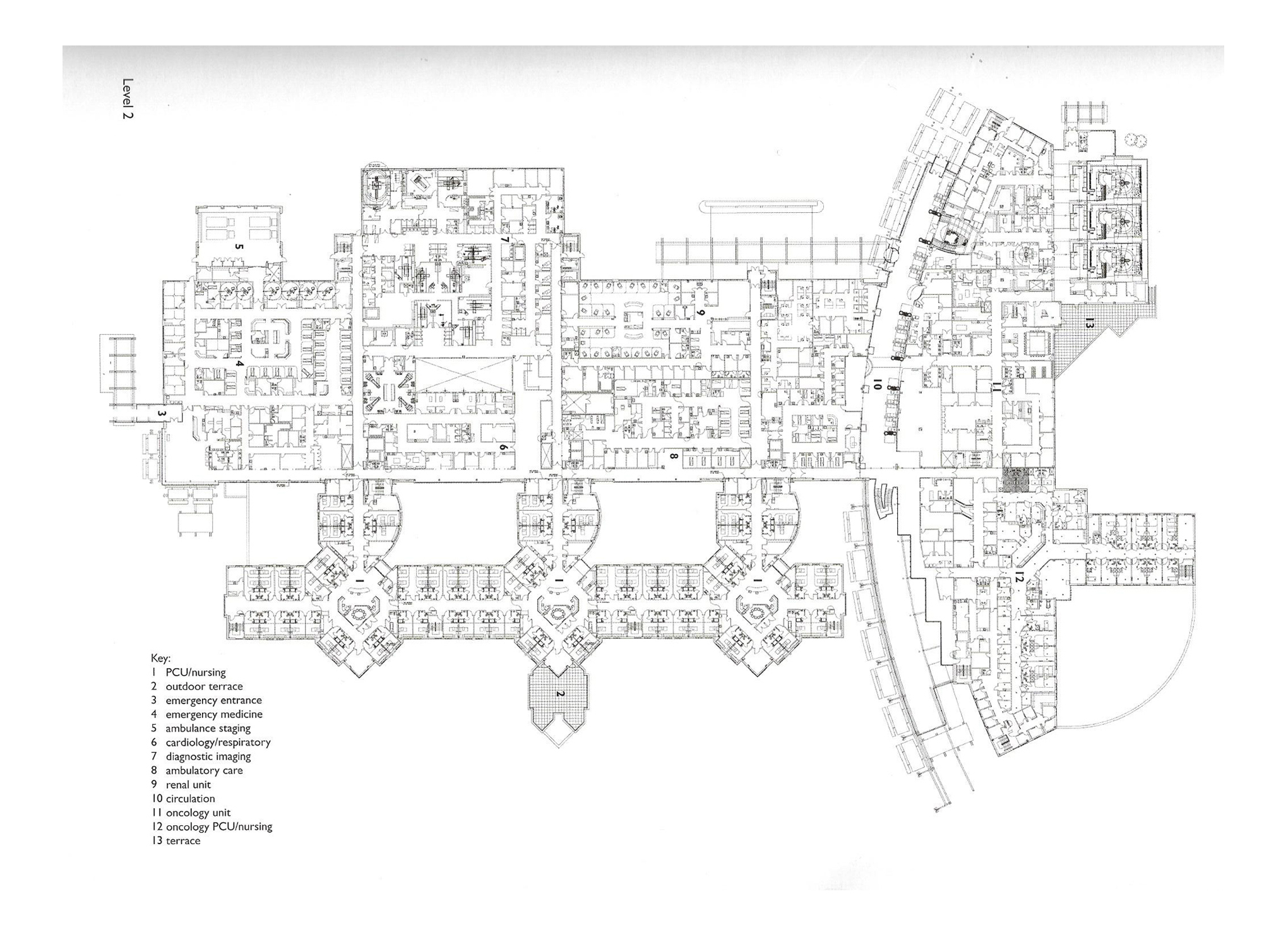
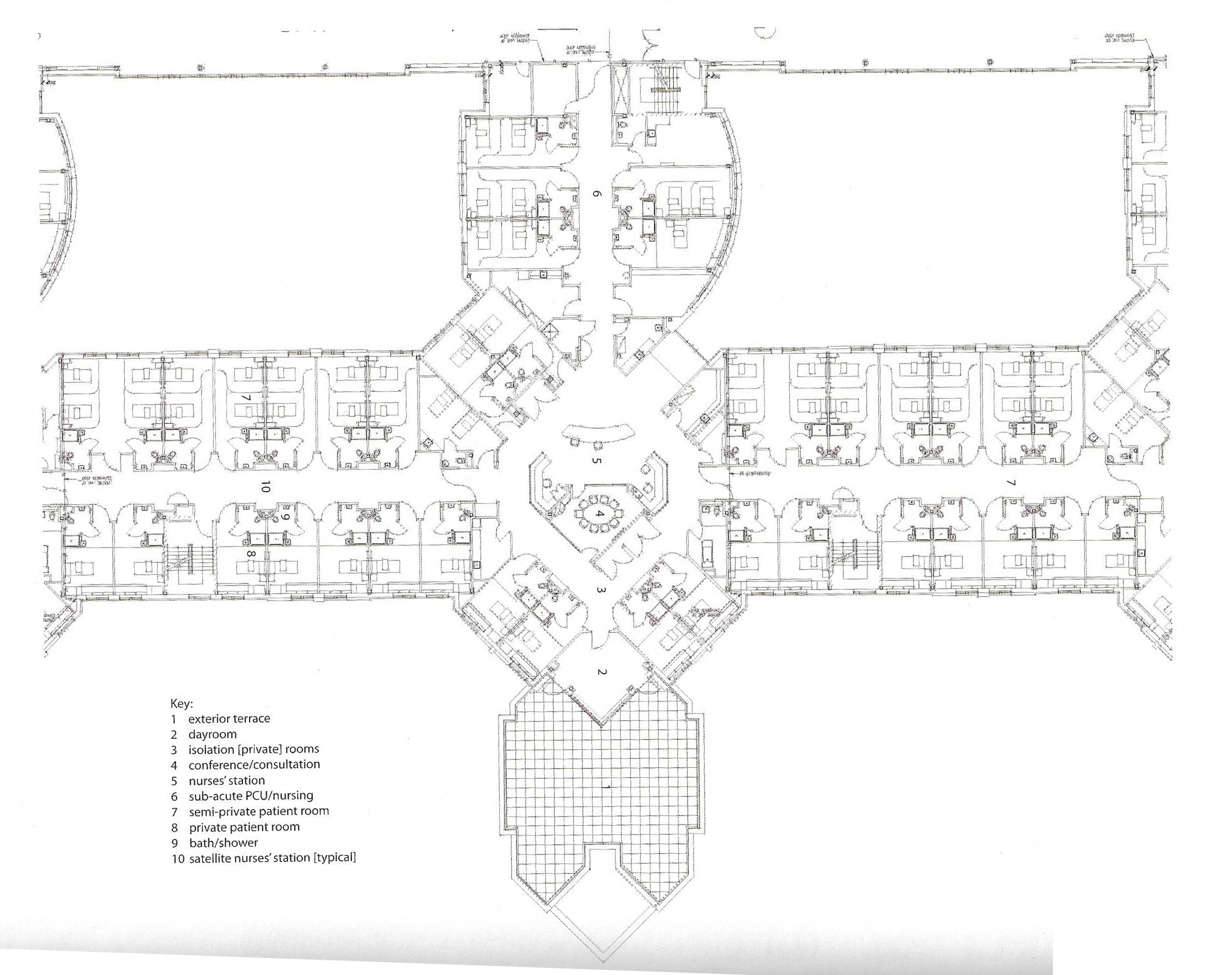
Floorplans
The floorplans of the AMC show that all the different floorplans within the AMC. Besides showing the floorplans it provides an analysis of the plans. It becomes clear that there is a clear division between the northern part and the southern part. The northern part is meant for non patient functions like education and laboratories while the southern part of the floorplans is meant for patient care.
The floorplans of the AMC with function analysis.(AMC, 2016)
Specialism
The AMC has various top-referral specialties. These include cardiovascular diseases, immunology and infectious diseases, diseases of the digestive system (surgery and internal medicine), metabolic diseases, gynecological oncology, specialized care in early pregnancy, prenatal diagnostics, pediatric oncology, pediatric immunology/ hematology, vascular disorders of the brain, severe hearing disorders, schizophrenia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and deep brain stimulation for severe obsessive-compulsive disorders. Besides these specialties the AMC has also been allocated various top clinical functions by the Dutch government. These are functions that provide medical treatments and services in limited number of hospitals, this due to high costs and required expertise. The AMC’s allocated top-clinical functions include kidney dialysis and kidney transplantation, open heart surgery, radiotherapy, neurosurgery, neonatology and nuclear medicine.
The AMC tries to distinguish itself from other hospitals through seven core areas of medical research. These are: cardiovascular diseases, immunity and infections, gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders, neurological and psychiatric disorders, oncology and epidemiology & public health. All of these core areas covers the whole spectrum of medical research: from fundamental biomedical, translational and clinical research to the evaluation of new medical methods and techniques.
Infectious diseases and immunity
In a Dutch and international context, AMC researchers are working on the development of drugs and the evaluation of combination therapies for HIV/AIDS. Another line of research focuses on the development of vaccines, and bacterial research concentrates on pneumonia, meningitis and septicemia. Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are also being studied, with researchers concentrating mainly on the inhibition of proinflammatory proteins by means of an inactivated virus. Phagocytes, dendritic cells and T-cells are the central focus of fundamental immunological research.
Oncology
Most of the research in the core area of oncology concerns the molecular and biochemical backgrounds of cancer. There are four lines of research: gastrointestinal oncology, hematological oncology, pediatric oncology and neuro-oncology. The focus of the research is the hypothesis that only cells of one certain type – called cancer stem cells – cause tumors to grow and spread. The pediatric oncology research covers everything from fundamental research (genetic profiling) to clinical research. Much attention is focused on new drugs, and the later effects of oncology therapy.(AMC, 2009)
cardiovascular diseases
immunity and infections
gastrointestinal diseases
metabolic disorders
neurological and psychiatric disorders
oncology
epidemiology & public health
The seven core areas of medical research, own image.
AMC's development vision and aims
In the spirit of the original principles of the core principles for redevelopment of the AMC are flexibility and standardisation. Within these principles safety and patient-centrality. The different phases of care will be more separated and then accordingly relocated within the hospital network. These phases include diagnostics, treatment, screening, after care, nursing and caring.
Another important aspect of the AMC is the increase in scientific research, in quantity (promotions and publications) as well as quality (research funds and impact scores). It is important for the AMC to remain as one of the top UMC research institutes. Through international cooperation it remains a key player within its core areas as previously mentioned. To increase its international presence valorisation is promoted from start-up companies.
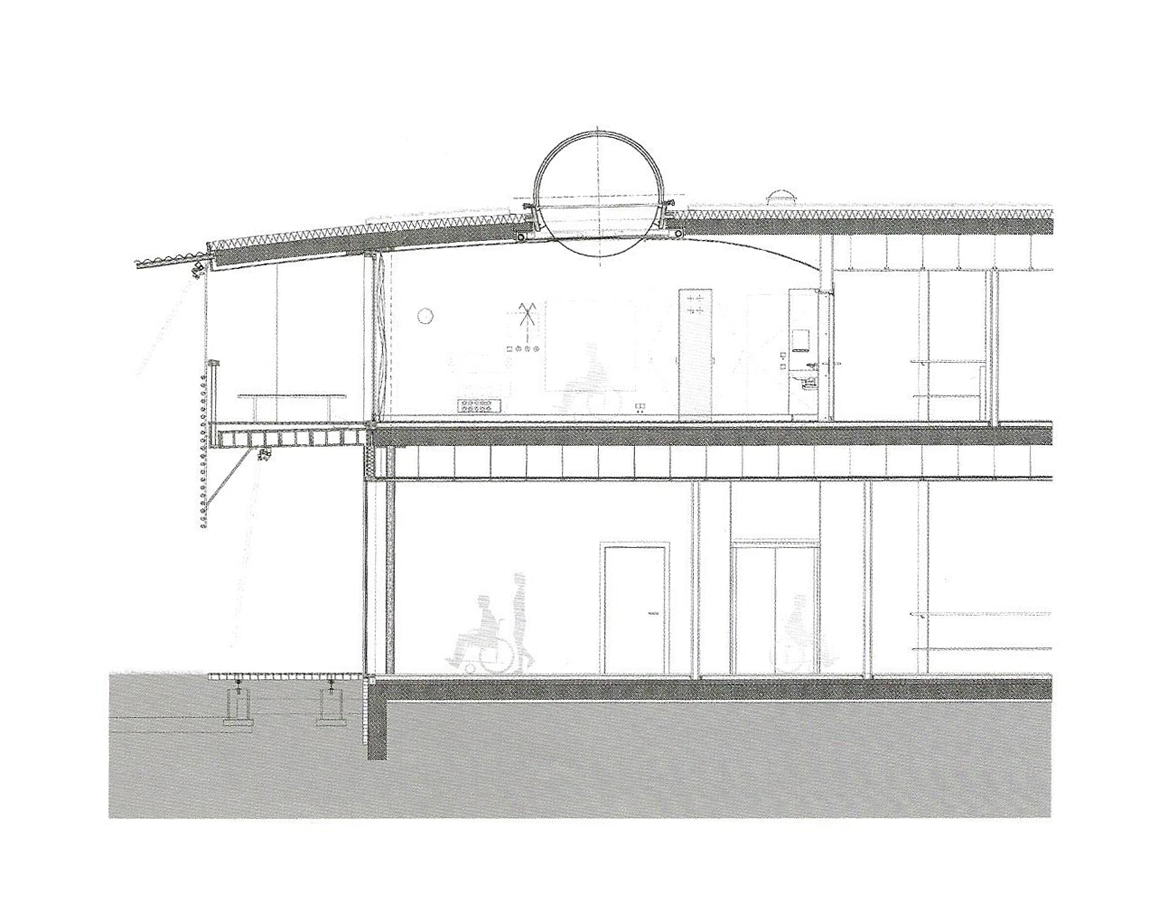
The functional state of the bedroom towers has decreased under an acceptable level for modern medicine. Therefor these towers need to be redeveloped to once again live up to the modern standards. Another problem is that there is hidden vacancy within the towers. Theoretical one full tower could be removed or repurposed.
The research and treatment centre forms the core of the AMC, these function feature high investment costs, complex housing and growth. The functions feature policlinics, research centres e.g. but in the future the policlinic functions need to grow. In order to achieve this sub functions have to be segregated, that would mean that research functions are supposed to be clustered as for the other functions.
AMC functions remarkable well for its age when it comes down on patient care. But the wayfinding, approach and entering of the area and the complex are out dated. The current main entrance and the policlinic entrance are out dated, not representative and don't contribute to the welcome feelings patients and visitor should have.
Flexibility plays a role within the strategy to make more efficient use of the current facilities. This means that employees will have to share their office facilities with employees from other facilities. Therefore reducing 70 offices spots per 100 employees. Another aim is the redevelopment of internal spaces so that they can be used for one main purpose like offices, waiting, research, consultant rooms e.g. and not just for one specific department.(AMC, 2016)
Redevelopment constraints
Since the board of the AMC does not want to demolish the current building it means that the current building has to be transformed. The diffeculty with that is that a running hospital cannot simply be shut down. Appointments, surgercies and threatments are planned far ahead and what to think for the sterile research facilities that have to transported without any external influences on what is being researched. Therefor the AMC has to remain in function and with that come constrains in order to keep the atmosphere of the building as it is. The constraint that are set by the AMC are:
1. During transformation the hospital should remain in function. That would imply that a phased devellopment plan should be develloped.
2. The redevellopment should remain within the current boundries of the building. Excluding the entrences of the building and the renewed landscape plan.
3. The concrete structure should remain in place and should remain visible.
1. Remain active while construction
2. Building boundries
3. Concrete structure
Future developments in healthcare
There is a lot of research and innovation being done in the field of medicine and healthcare. As a species we try to survive as long as possible on this planet. Globally many breakthroughs are being made to improve human health. With innovation not slowing down any time soon it is worth the investigation of what the future developments in healthcare and medicine will be. Below is a video visualising research done by the Economist showing what the future of healthcare and medicine will look like. In my opinion there are seven elements which are very important for healthcare and medicine, these are:
1. Data collection and exchange.
2. Virtual and augmented reality.
3. AI solutions for medication.
4. Nanomachinery.
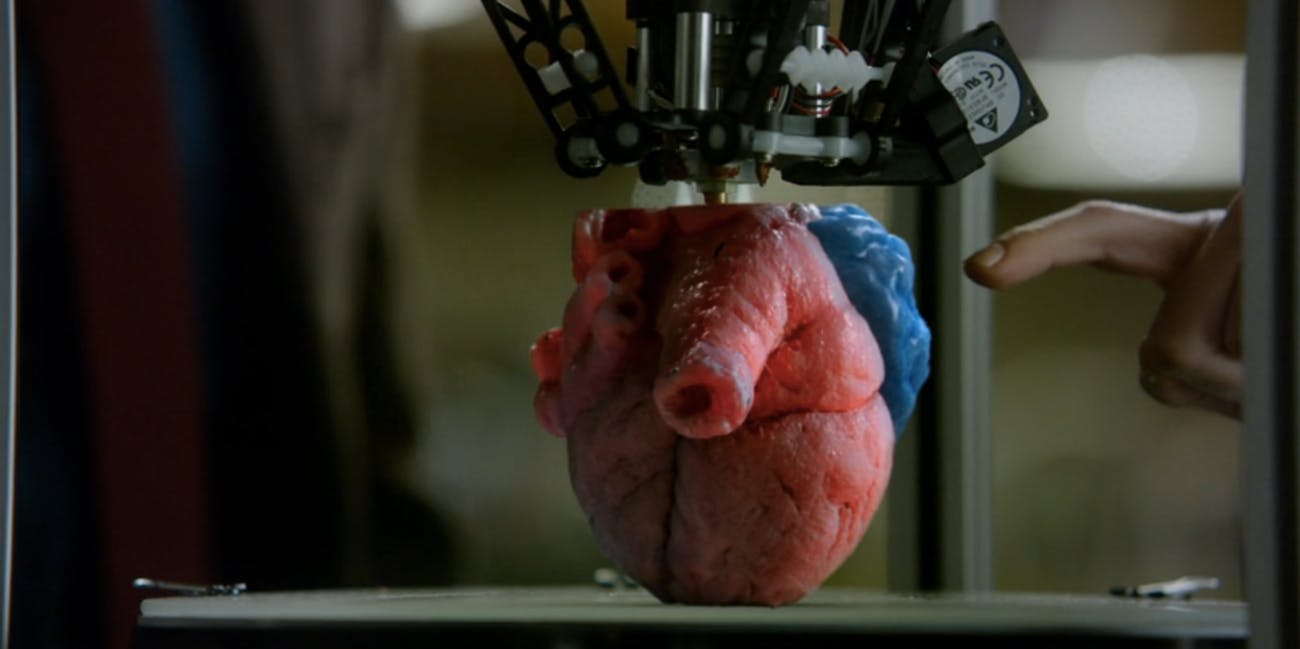
5. 3d printed organs.
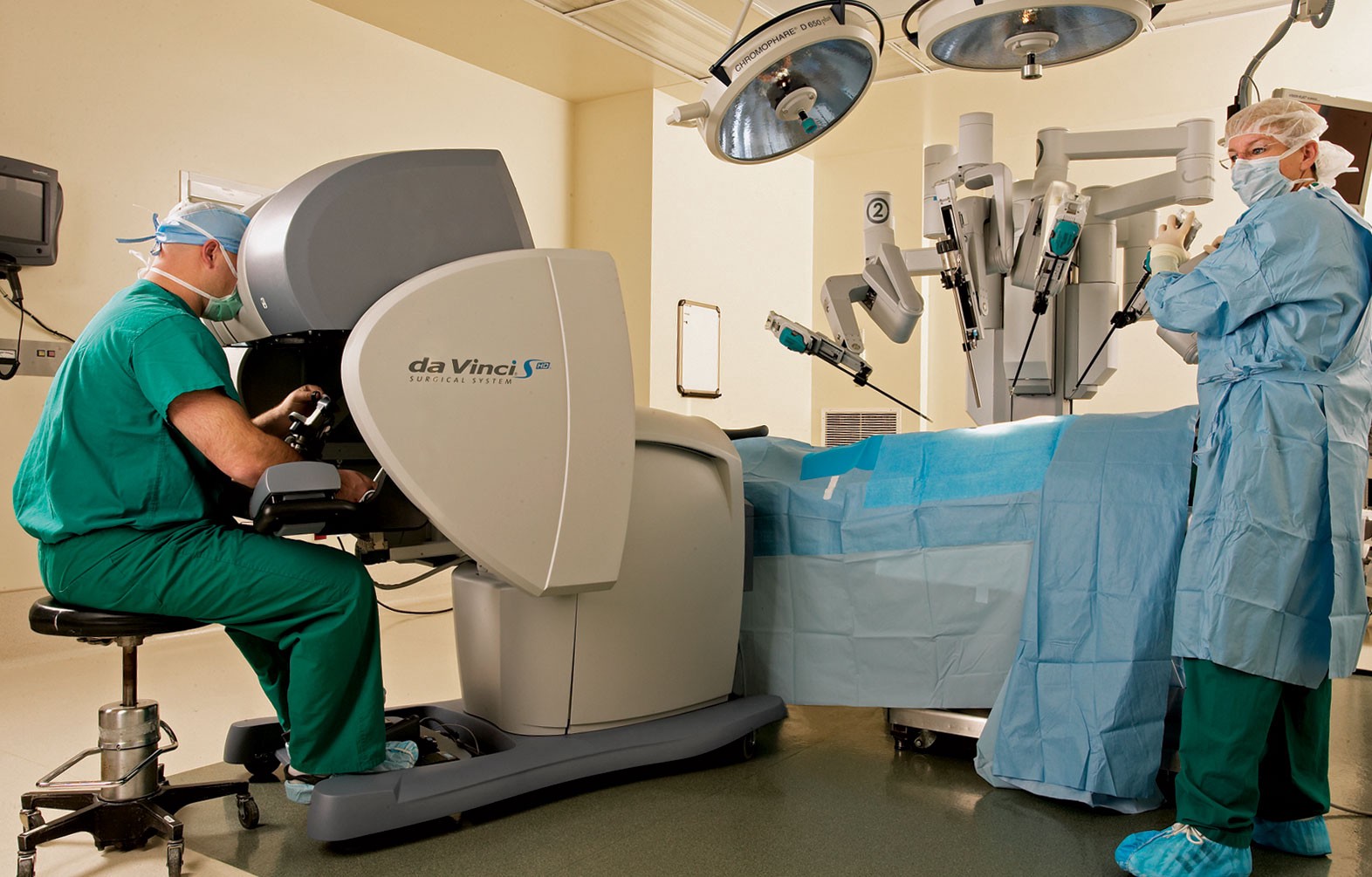
6. Surgery through machinery.
7. Genetical adeption of babies.
A video from the economist portaying the future of healthcare.
A slideshow portaying seven key elements of the future of healthcare.
Design Proposal
Currently we are faceing various environmental problems. The way we have been exploiting our planet in order to gain has lead to problems like mineral depletion and climate change. Every day we experience the consequences of our planetal exploitation. More and more people are trying to change the way we explote our planet. One of these things is changing the way we produce products. Not just using green energy for production but also changing the product flows from linear flows to circulair flows. As well as developping bio based alteratives for materials with large negative impacts for our planet.
Currently the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam is due for renovation and transformation. The AMC is a massive hospital building in Amsterdam often describe as a city due to it's large size. This hospital houses three key function, a working environment for doctors and nurses, a recovery area for patients and a working environment for education and research from the university of Amsterdam. Within these functions the AMC holds many more specialalities, research centers, drugstores and shops.
With the AMC containing so many functions it shows a lot of potential for transformation with many possiblities. It is there where I want to offer a solution. I believe the future to be bio-based and circulair. Therefor I would like to redesign a part of the AMC into a coherent state of the art hospital. In my opinion that would mean the hospital is has circulair waste streams and procoduces as much as it consumes. That would mean the hospital should produce it's own food, it's own antibiotics, it's own building materials. These three aspects have one thing in common which is that they can all be produced out of fungi.
It is the potential of this material I will push to boundries in order to create the hospital section. The proposed section will include, patient rooms, silent areas, family meeting rooms, antibiotic laboratories, restaurants, fungi farms and threatment rooms. Combining all these will result in an project proposol which I would like to call the blueAMC.
Fungi
Introduction
This project revolves around the growing of architecture by application of mycelium. Mycelium is the vegetative part of fungi. This biological tissue/ material is composed from tube-like fibers. These fibers are called hypha and are approximately 1 lm in diameter. Hypha grow by elogation of the apical tip. Which means that the fibers grow faster in the tips than in its branches. On occasion these fibers branch out and merge with other hyphae. As a consequence a random fibernetwork structure is formed; The mycelium (Lull et al., 2005).
Mycelium can be grown in multiple forms, (pure) mycelium, synthetic mycelium and composite mycelium. The last one will be the main focus of this material study since this is the form that is most used within the product development and the built environment. The composite is a mixture of mycelium mixed with a organic substrate most preferably a lignocellulosic biomass. Mycelium than forms it's network of hyphae on and through the substrate by (partly) consuming the substrate. It then transforms the substrates biomass into chitine (up to 45%), Protein and polysacharides. As a result of this process mycelium and the substrate are bonded into the mycelium composite (Tazelaar, 2017).
Lifecycle of fungi
Since fungi is a living organism the species goes through the cycle of life. In order to produce and reproduce mycelium knowledge of it's cycle is required. The image below portaits the lifecycle of the fungi.
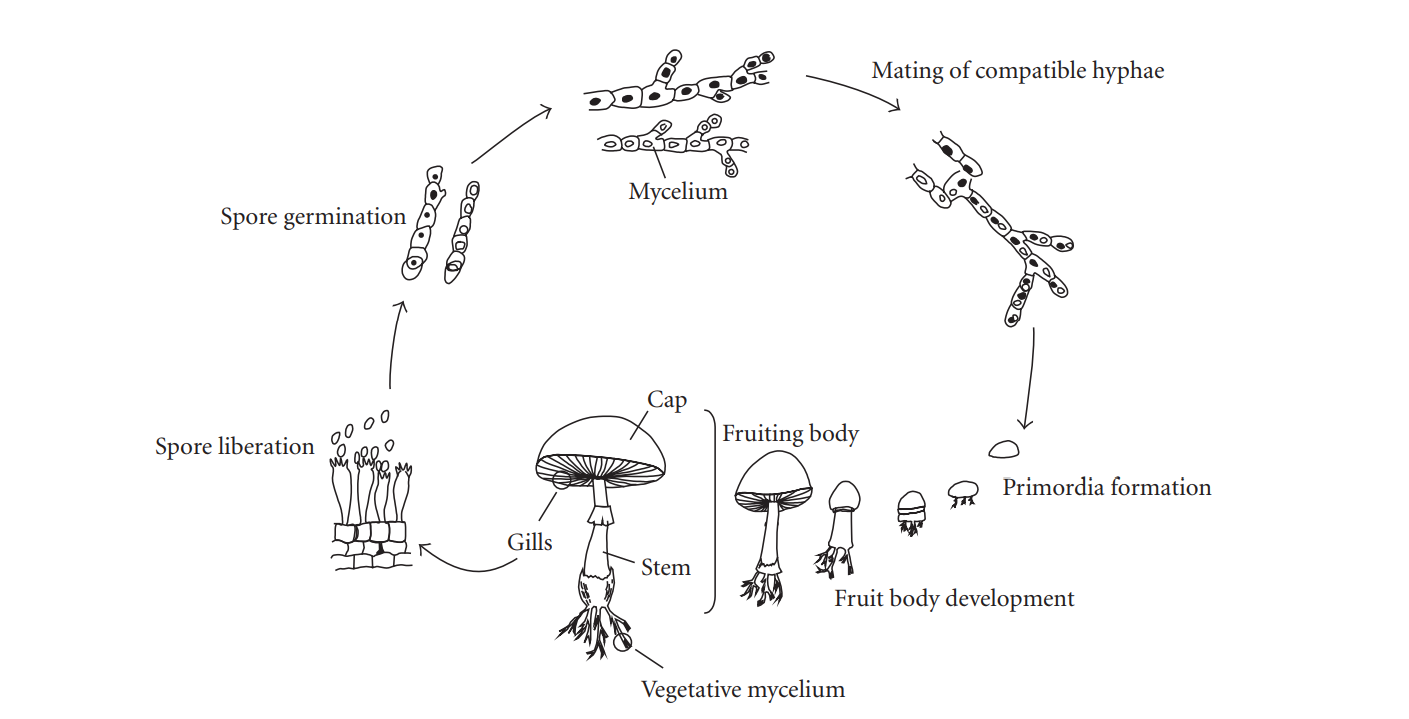
This image is based on a image from (Lull et al., 2005)
Bakker, L. (2019). Fungi Lifecycle. Own Image
Species
The taxonomical kingdom of fungi is vast. Within the this kingdom you can find species that act as food, produce medicine or in case of this research as building material. Form all the different taxonomical divisions on division is particularly intressting, this is the basidiomycota division. The reason why this division is so intressting is because of its ability to break down long and complex organic moleculs. The species that are most often used within this field are the Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus, "Oesterzwam" (NL)), the Split Gill (Schizophyllum commune, "Waaiertje" (NL)), Lingzhi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, "Gesteelde lakzwam"(NL)) and the Turkey tail (Trametes versicolor, "Gewoon elfenbankje" (NL)). The choices for these fungi are chosen due to their benifitial properties towards growth, strenght and ability to consume specific nutritions for example (Tazelaar, 2017).
Pleurotus Ostreatus
Schizophyllum Commune
Ganoderma Lucidum
Trametes Versicolor
Users Narratives
The taxonomical kingdom of fungi is vast. Within the this kingdom you can find species that act as food, produce medicine or in case of this research as building material. Form all the different taxonomical divisions on division is particularly intressting, this is the basidiomycota division. The reason why this division is so intressting is because of its ability to break down long and complex organic moleculs. The species that are most often used within this field are the Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus, "Oesterzwam" (NL)), the Split Gill (Schizophyllum commune, "Waaiertje" (NL)), Lingzhi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, "Gesteelde lakzwam"(NL)) and the Turkey tail (Trametes versicolor, "Gewoon elfenbankje" (NL)). The choices for these fungi are chosen due to their benifitial properties towards growth, strenght and ability to consume specific nutritions for example (Tazelaar, 2017).
The doctor
The doctor.
The patient and his family
The patient and his family.
The intern
The intern.
The doctor
The patient and the family
The intern
Material cycle
Material cycle.
Planning
Planning.
References
References.
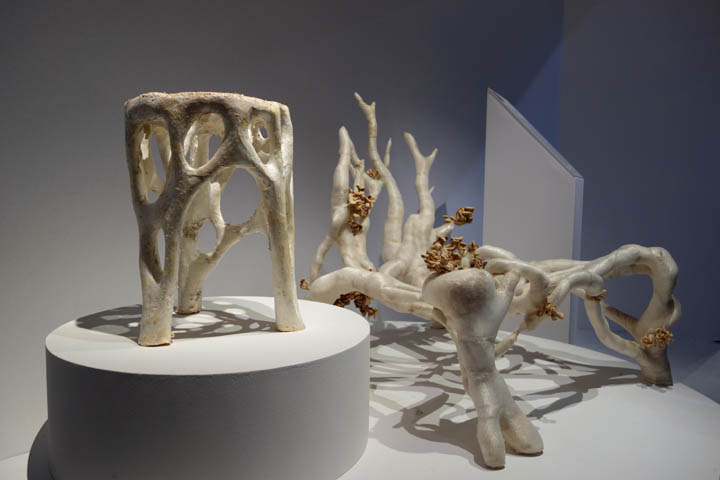
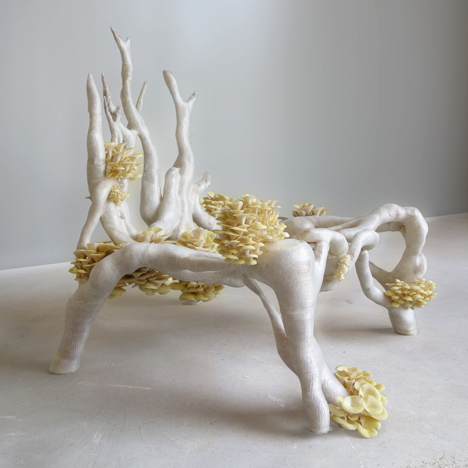
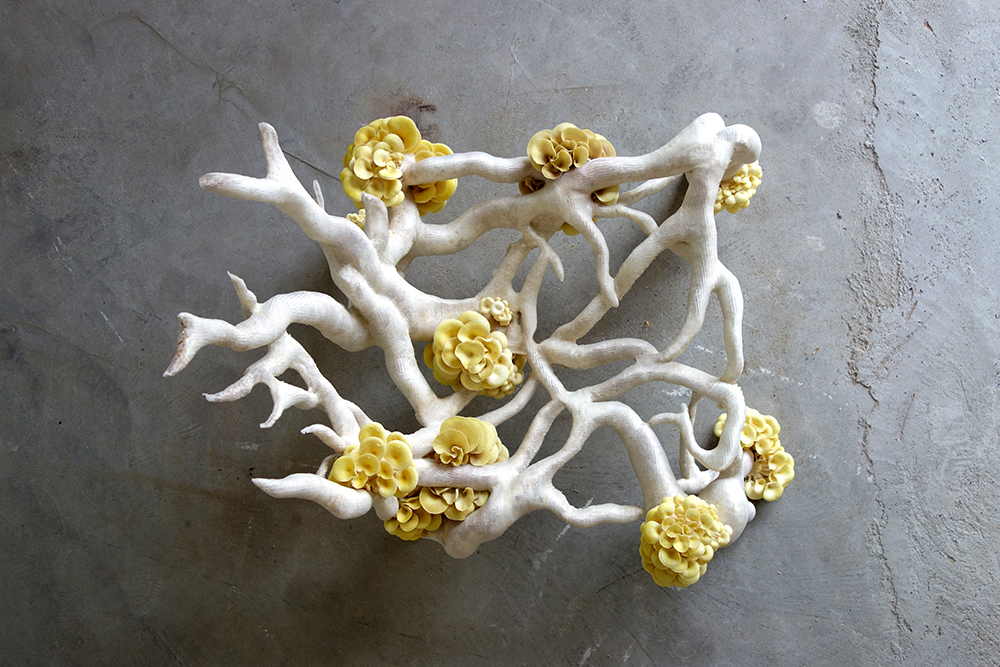
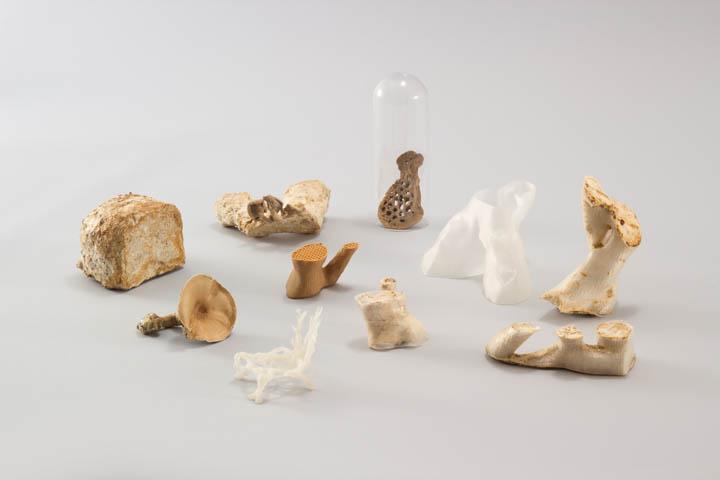
Studio Eric Klarenbeek - Veiled Lady 2.0
What is the Veiled Lady 2.0?
The Veiled Lady 2.0 is a project that focuses on 3D printing with mycelium. With this project the designer aims to solve the problematic chain of waste production both in the fabriction as well as the impact on our environment caused by the products.
Who designed the Veiled Lady 2.0?
The Veiled Lady 2.0 has been designed by Eric Klarenbeek. Mister Klarenbeek has a background in design at the Design Academy Eindhoven.
What properties does the fungi have?
The properties of this fungus is not perticulairly special, it does not differ form the regular properties of this species. But what makes this project different is the way in which the fungi is grown.
What techniques have been applied?
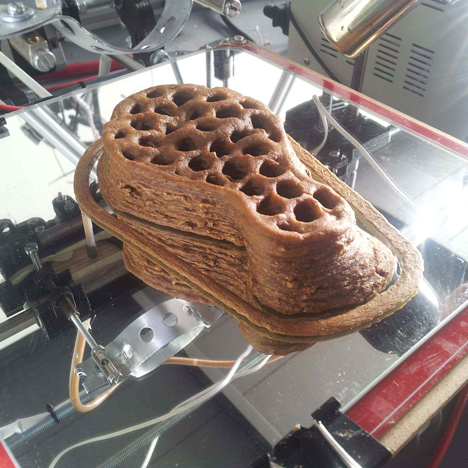
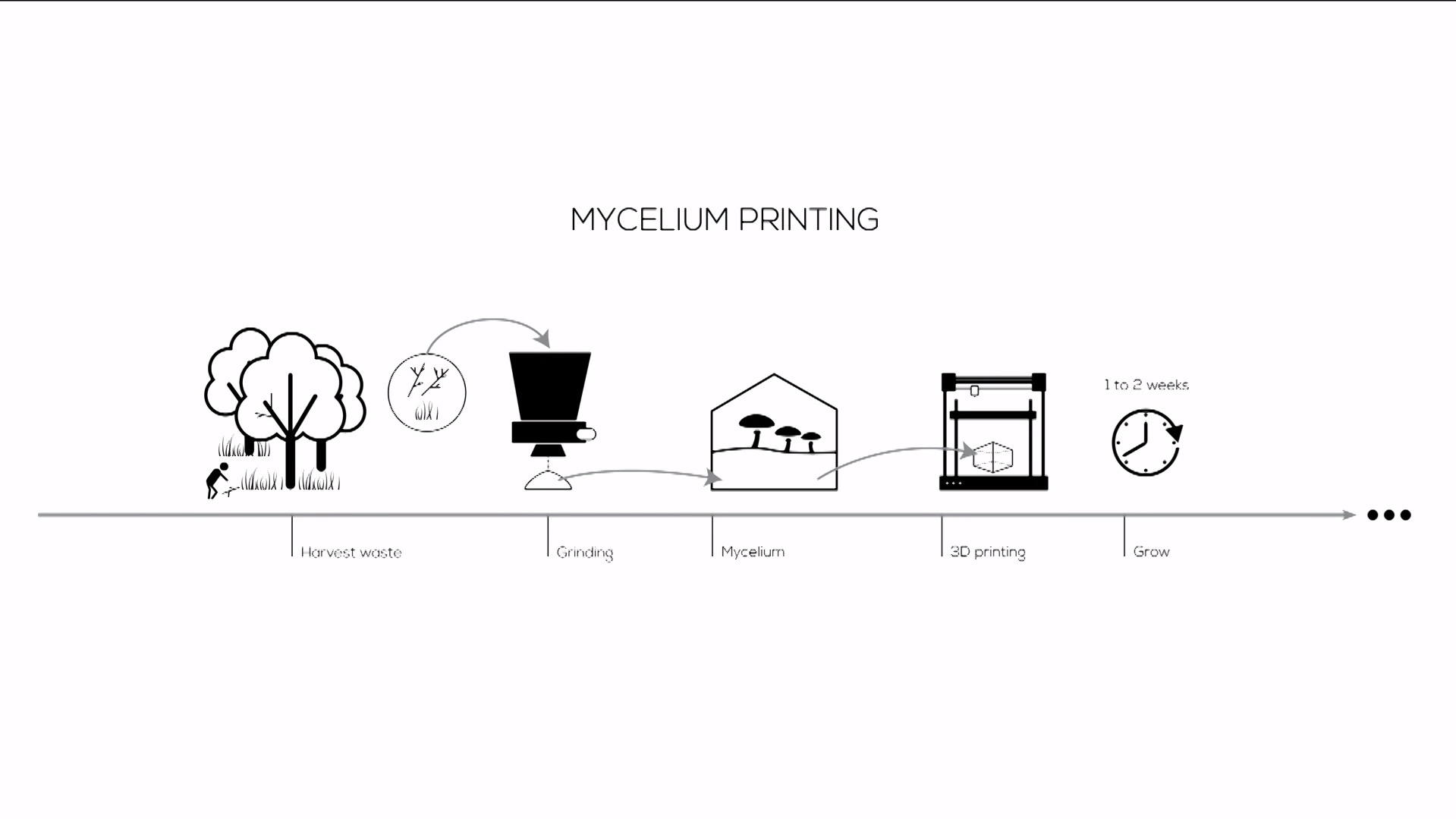
As mentioned in the brief describtion of the project, this project makes use of 3D printing. First Studio Eric Klarenbeek gathers local agricultural waste. This waste is than grinded into very small particles. With these particles are then cultivated with mycelium for a short period of time. After this the mixture is transformed into a printable paste, propably with water. The next step in this process is the printing of the outer layer which behaves like the mould of the project. This outer layer is printed by using a bio based filement like PLA created from local potato waste. When the outer shell is printed it can be filled up with the mycelium-agriculture paste. Or the outer shell and the paste can be printed some what simultanious. Whenever the model is printed the product is stored in a dark, sealed moist space. So the mycelium can consume and grow all over the agricultural paste. When the mycelium has fully grown it can be dried or baked in order to stop the fungi from further growth.
What fungi has been used?
For this project the following species of fungi has been used: "Schizophyllum commune".
What qualities can be of value for my own project?
3D printing of mycelium shows a lot of potential. The potential can be traced back to the fact that the mould is 3D printed instead of the regular vacuum formed moulds. With 3D printable moulds the range of free form and complex shapes becomes more realiseable which implies I can use complicated geometry to design my buildings with.
More information.
For more information about the Veiled Lady 2.0 please visit the website Ericklarenbeek.com.
The photos are property of the original designers and can be found on their own respective websites
Dietz, J. Mycotex. Retrieved from https://neffa.nl/